Airborne Downward Looking Sparse Linear Array 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. DLSLA 3-D SAR Imaging Geometry, Echo Signal Model and Heterogeneous Parallel Technique
2.1. DLSLA 3-D SAR Imaging Geometry
2.2. DLSLA 3-D SAR Echo Signal Model
2.3. Heterogeneous Parallel Technique
3. DLSLA 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Echo Generation Simulation
3.1. Heterogeneous Parallel Echo Generation Simulation with Time Domain Correlation Method
3.2. Heterogeneous Parallel Echo Generation Simulation with Frequency Domain Correlation Method
3.3. Heterogeneous Parallel Echo Generation Simulation Applicability
4. DLSLA 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Image Reconstruction Simulation
4.1. DLSLA 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Image Reconstruction Simulation with 3-D Polar Format Algorithm
4.2. DLSLA 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Image Reconstruction Simulation with Polar Formatting and L1 Regularization Algorithm
5. Simulation Results
5.1. Point Targets Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation
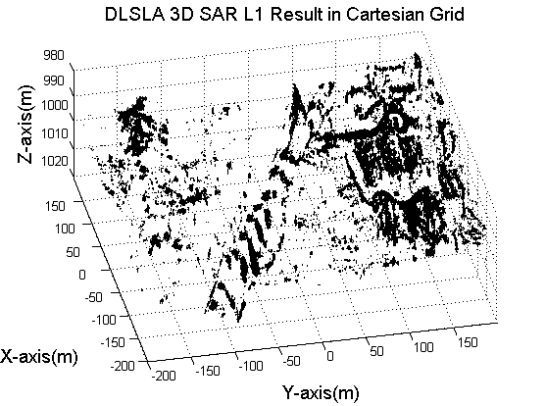
5.2. 3-D Distributed Scene Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest
References
- Carrara, W.G.; Goodman, R.S.; Majewski, R.M. Spotlight Processing Applications. In Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar: Signal Processing Algorithms; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 1995; pp. 361–367. [Google Scholar]
- Soumketh, M. Spotlight Synthetic Aperture Radar. In Synthetic Aperture Radar Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 262–372. [Google Scholar]
- Jakowatz, C.V.; Wahl, D.E.; Eichel, P.H.; Ghihlia, D.C.; Thompson, P.A. A. Tomographic Foundation for Spotlight-mode SAR Imaging. In Spotlight-Mode Synthetic Aperture Radar: A Signal Processing Approach; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1999; pp. 33–102. [Google Scholar]
- Weib, M.; Ender, J.H.G. A 3D Imaging Radar for Small Unmanned Airplanes-ARTINO. Proceedings of European Radar Conference 2005, EURAD 2005, Paris, France; 2005; pp. 209–212. [Google Scholar]
- Nouvel, J.F.; Jeuland, H.; Bonin, G.; Roques, S.; Plessis, D.; Peyret, J. A Ka Band Imaging Radar: DRIVE on Board ONERA Motorglider. Proceedings of 2006 International IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Denver, CO, USA, 31 July–4 August 2006; pp. 134–136.
- Akbarimehr, M.; Motagh, M.; Haghshenas-Haghighi, M. Slope stability assessment of the sarcheshmeh landslide, Northeast Iran, investigated using inSAR and GPS observations. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 3681–3700. [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig, M.E.; Paradella, W.R.; Mura, J.C. Detection and monitoring of surface motions in active open pit Iron mine in the Amazon region, using persistent scatterer interferometry with TerraSAR-X satellite data. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 4719–4734. [Google Scholar]
- Crosetto, M.; Monserrat, O.; Cuevas, M.; Crippa, B. Spaceborne differential SAR interferometry: Data analysis tools for deformation measurement. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 305–318. [Google Scholar]
- Tofani, V.; Raspini, F.; Catani, F.; Casagli, N. Persistent scatterer interferometry (PSI) technique for landslide characterization and monitoring. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 1045–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Aijazi, A.K.; Checchin, P.; Trassoudaine, L. Segmentation based classification of 3D urban point clouds: A super-voxel based approach with evaluation. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 1624–1650. [Google Scholar]
- Mura, J.C.; Pinheiro, M.; Rosa, R.; Moreira, J.R. A phase-offset estimation method for inSAR DEM generation based on phase-offset functions. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 745–761. [Google Scholar]
- Pivot, F.C. C-band SAR imagery for snow-cover monitoring at Treeline, Churchill, Manitoba, Canada. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 2133–2155. [Google Scholar]
- Gierull, C.H. On a concept for an airborne downward-looking imaging radar. Int. J. Electron Commun 1999, 53, 259–304. [Google Scholar]
- Nouvel, J.F.; Roques, S.; Plessis, O.R. A Low-cost Imaging Radar: DRIVE on Board ONERA Motorglider. Proceedings of 2007 International IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Barcelona, Spain; 2007; pp. 5306–5309. [Google Scholar]
- Nouvel, J.F.; Angelliaume, S.; Du Plessis, O.R. The ONERA Compact Ka-SAR. EURAD, In Proceedings of 2008 European Radar Conference, EuRAD 2008, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 30–31 August 2008; pp. 475–478.
- Plessis, O.R.; Nouvel, J.F.; Baque, R.; Bonin, G.; Dreuillet, P.; Coulombeix, C.; Oriot, H. ONERA SAR Facilities. Proceedings of 2010 IEEE Radar Conference, Washington, DC, USA; 2010; pp. 667–672. [Google Scholar]
- Klare, J.M.; Weib, M.; Peters, O.; Brenner, R.; Ender, J.H.G. ARTINO: A New High Resolution 3D Imaging Radar System on an Autonomous Airborne Platform. Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGRASS 2006, Denver, CO, USA; 2006; pp. 3842–3845. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Peters, O.; Ender, J. A Three Dimensional SAR System on an UAV. Proceedings of 2007 IEEE International Conference Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, IGRASS 2007, Barcelona, Spain; 2007; pp. 5315–5318. [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, M.; Peters, O.; Ender, J. First Flight Trials with ARTINO. EUSAR, In Proceedings of 2008 7th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Friedrichshafen, Germany, 2–5 June 2008; pp. 1–4.
- Weiss, M.; Gilles, M. Initial ARTINO Radar Experiments. Proceedings of 2010 8th European Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar (EUSAR), Aachen, Germany, 7–10 June 2010; pp. 857–860.
- Peng, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, W.X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.R. Airborne downward-looking MIMO 3D-SAR imaging algorithm based on cross-track thinned array. J. Electron. Inf. Technol 2012, 34, 943–949. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, W.X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.R. Fast wavenumber domain imaging algorithm for airborne downward-looking array 3D-SAR based on region of interest pick. J. Electron. Inf. Technol 2013, 35, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.G.; Zhang, X.L. Downward-looking 3-D Linear Array SAR Imaging Based on Chirp Scaling Algorithm. Proceedings of 2nd Asian-Pacific Conference on Synthetic Aperture Radar, 2009, APSAR 2009, Xi’an, China, 26–30 October 2009; pp. 1043–1046.
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Xiang, G.; Jianyu, Y. Signal processing for microwave array imaging: TDC and sparse recovery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2012, 50, 4584–4598. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Very high resolution spaceborne SAR tomography in urban environment. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2010, 48, 4296–4308. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.X.; Bamler, R. Tomographic SAR Inversion by L1-norm regularization, The Compressive Sensing Approach. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2010, 48, 3839–3846. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, J.L.; Fortuny, G.J. 3-D radar imaging using range migration techniques. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag 2000, 48, 728–737. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, K.F.; Zhang, X.L.; Shi, J. Fast 3-D microwave imaging method based on subpaerture approximation. Prog. Electromagn. Res 2012, 126, 333–353. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, W.X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.R. Convolution back-projection imaging algorithm for downward-looking sparse linear array three dimensional synthetic aperture radar. Prog. Electromagn. Res 2012, 129, 287–313. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.B. Surface tracing based LASAR 3-D imaging method via multiresolution approximation. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2008, 46, 3719–3730. [Google Scholar]
- Heterogeneous computation. Available online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heterogeneouscomputing (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- Franceschetti, G.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D.; Schirinzi, G. SARAS: A synthetic aperture radar (SAR) raw signal simulator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 1992, 30, 110–123. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschetti, G.; Iodice, A.; Migliaccio, M.; Riccio, D. A novel across-track SAR interferometry simulator. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 1998, 36, 950–962. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, W.X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.R. Polar Format Imaging Algorithm with wave front curvature phase error Compensation for Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR. In IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens.; 2013; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Tan, W.X.; Hong, W.; Wu, Y.R. Airborne DLSLA 3-D SAR Image Reconstruction by Combination of Polar Formatting and L1 Regularization. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, in press.. [Google Scholar]
- CPU. Available online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CPU (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- GPU. Available online: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GPU (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- CUDA C Programming Guide. Available online: http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-programming-guide/index.html (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- CUDA C Best Practices Guide. Available online: http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-c-best-practices-guide/index.html (accessed on 20 August 2013).
- Doerry, A.W. Wavefront Curvature Limitations and Compensation to Polar Format Processing for Synthetic Aperture Radar Images; Tech. Rep, Tech. Rep. AND2007–0046; Sandia Nat. Labs: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, X.H.; Zhu, D.Y.; Zhu, Z.D. Polar format algorithm wavefront curvature compensation under arbitrary radar flight path. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett 2012, 9, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.; Hong, W.; Tan, W.X.; Wang, Y.P.; Xiang, M.S. Airborne Circular Sar Imaging: Results at P-band. Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 5594–5597.
- Remondino, F. Heritage Recording and 3D modeling with photogrammetry and 3D scanning. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 1104–1138. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, A.; Heck, R.J.; Brenning, A.; Brown, R.; Miller, S. Remote sensing of soil moisture in vineyards using airborne and ground-based thermal inertia Data. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 3729–3748. [Google Scholar]
- Perko, R.; Raggam, H.; Deutscher, J.; Gutjahr, K.; Schardt, M. Forest assessment using high resolution SAR data in X-band. Remote Sens 2011, 3, 792–815. [Google Scholar]
- Arefi, H.; Reinartz, P. Building reconstruction using DSM and orthorectified images. Remote Sens 2013, 5, 1681–1703. [Google Scholar]
- Skoglar, P.; Orguner, U.; Törnqvist, D.; Gustafsson, F. Road target search and tracking with gimballed vision sensor on an unmanned aerial vehicle. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 2076–2111. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Canosa, G.R.; Thomas, S.; del Cerro, J.; Barrientos, A.; MacDonald, B. A real-time method to detect and track moving objects (DATMO) from unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) using a single camera. Remote Sens 2012, 4, 1090–1111. [Google Scholar]




















| Coordinates | Value (m) |
|---|---|
| Transmitted Array | Ti = −1.34 + i × 0.02, i = 1, 2,…,4. |
| Transmitted Array | Ti = −1.14 + i × 0.02, i = 5, 6,…,8. |
| Receiving Array | Ri = −1.32 + i × 0.08, i = 1, 2,…,32. |
| Equivalent Array | TRi = −1.28 + (i − 1) × 0.01, i = 1, 2,…,256. |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Center Frequency | 37.5 GHz |
| Transmitting Signal Bandwidth | 300 MHz |
| A/D Sampling Frequency | 360 MHz |
| Platform Fly Height | 1,000 m |
| Platform Fly Velocity | 50 m/s |
| Transmitting Signal Pulse Width | 1.0 us |
| A/D Sampling Range Gate | [750.0, 1026.7 m] |
| Range Sample Number | 1024 |
| PRF (Pulse Repetition Frequency) | 5,000 Hz |
| Along-track Dimension Sampling Interval | 0.01 m |
| Along-track Dimension Sampling Number | 256 |
| Transmitting Array Elements | 8 |
| Receiving Array Elements | 32 |
| Beam width of T/R Array | 14 × 14 |
| Equivalent Phase Center Number | 256 |
| Cross-track Dimension Sampling Interval | 0.01 m |
| Measured Parameter | Along-Track | Cross-Track | Wave-Propagation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSLR (dB) | −9.3 | −9.4 | −16.7 |
| ISLR (dB) | −10.5 | −10.3 | −12.7 |
| Measured Parameter | Along-Track | Cross-Track | Wave-Propagation |
|---|---|---|---|
| PSLR (dB) | −13.3 | −13.3 | −13.4 |
| ISLR (dB) | −14.9 | −14.3 | −12.7 |
| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Center Frequency | 37.5 GHz |
| Transmitting Signal Bandwidth | 300 MHz |
| A/D Sampling Frequency | 360 MHz |
| Platform Fly Height | 1,000 m |
| Platform Fly Velocity | 50 m/s |
| Transmitting Signal Pulse Width | 3.85 us |
| A/D Sampling Range Gate | [974.0, 1026.5 m] |
| Range Sample Number | 1024 |
| PRF (Pulse Repetition Frequency) | 5,000 Hz |
| Along-track Dimension Sampling Interval | 0.01 m |
| Along-track Dimension Sampling Number | 256 |
| Transmitting Array Elements | 8 |
| Receiving Array Elements | 32 |
| Beam width of T/R Array | 14 × 14 |
| Equivalent Phase Center Number | 256 |
| Cross-track Dimension Sampling Interval | 0.01 m |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Peng, X.; Wang, Y.; Hong, W.; Tan, W.; Wu, Y. Airborne Downward Looking Sparse Linear Array 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5304-5329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5105304
Peng X, Wang Y, Hong W, Tan W, Wu Y. Airborne Downward Looking Sparse Linear Array 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation. Remote Sensing. 2013; 5(10):5304-5329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5105304
Chicago/Turabian StylePeng, Xueming, Yanping Wang, Wen Hong, Weixian Tan, and Yirong Wu. 2013. "Airborne Downward Looking Sparse Linear Array 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation" Remote Sensing 5, no. 10: 5304-5329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5105304
APA StylePeng, X., Wang, Y., Hong, W., Tan, W., & Wu, Y. (2013). Airborne Downward Looking Sparse Linear Array 3-D SAR Heterogeneous Parallel Simulation. Remote Sensing, 5(10), 5304-5329. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs5105304