Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Culicoides imicola: Climatic versus Remote Sensing Data †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Culicoides Life Cycle
2.2. C. imicola in situ Data
2.3. Climatic and Remote Sensing Datasets
2.4. Modelling Techniques
2.5. Model Validation
3. Results and Discussion
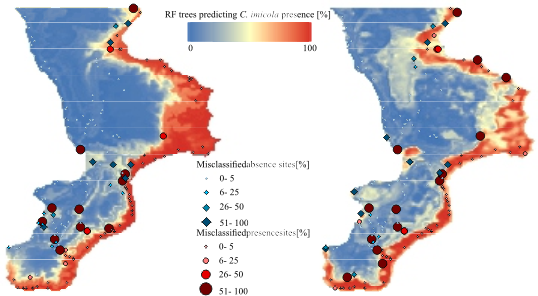
3.1. Modelling Accuracies
3.2. Variable Importance
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, A.J.; Mellor, P.S. Bluetongue in Europe: Past, present and future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2009, 364, 2669–2681. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, P.S.; Boorman, J.; Baylis, M. Culicoides biting midges: Their role as arbovirus vectors. Annu. Rev. Entomol 2000, 45, 307–340. [Google Scholar]
- Saegerman, C.; Berkvens, D.; Mellor, P.S. Bluetongue epidemiology in the European Union. Emerg. Infect. Dis 2008, 14, 539–544. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, M.; Bouayoune, H.; Touti, J.; El Hasnaoui, H. Use of climate data and satellite imagery to model the abundance of Culicoides imicola, the vector of African horse sickness virus, in Morocco. Med. Vet. Entomol 1998, 12, 255–266. [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann, E.J.; Mellor, P.S.; Baylis, M. Using climate data to map the potential distribution of Culicoides imicola (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Europe. Rev. Sci. Tech. Off. Int. Epiz 2001, 20, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Calistri, P.; Goffredo, M.; Caporale, V.; Meiswinkel, R. The distribution of Culicoides imicola in Italy: Application and evaluation of current Mediterranean models based on climate. J. Vet. Med 2003, B50, 132–138. [Google Scholar]
- Baylis, M.; Mellor, P.S.; Wittmann, E.J.; Rogers, D.J. Prediction of areas around the Mediterranean at risk of bluetongue by modelling the distribution of its vector using satellite imaging. Vet. Rec 2001, 149, 639–643. [Google Scholar]
- Tatem, A.J.; Baylis, M.; Mellor, P.S.; Purse, B.V.; Capela, R.; Pena, I.; Rogers, D.J. Prediction of bluetongue vector distribution in Europe and North Africa using satellite imagery. Vet. Microbiol 2003, 97, 13–29. [Google Scholar]
- Purse, B.V.; Tatem, A.J.; Caracappa, S.; Rogers, D.J.; Mellor, P.S.; Baylis, M.; Torina, A. Modelling the distribution of Culicoides bluetongue virus vectors in Sicily in relation to satellite-derived climate variables. Med. Vet. Entomol 2004, 18, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Guis, H.; Tran, A.; de La Rocque, S.; Baldet, T.; Gerbier, G.; Barragué, B.; Biteau-Coroller, F.; Roger, F.; Viel, J.F.; Mauny, F. Use of high spatial resolution satellite imagery to characterize landscapes at risk for bluetongue. Vet. Res 2007, 38, 669–683. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, A.; Giovannini, A.; Savini, L.; Goffredo, M.; Calistri, P.; Meiswinkel, R. The effect of climate on the presence of Culicoides imicola in Italy. J. Vet. Med 2003, B50, 139–147. [Google Scholar]
- Acevedo, P.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Estrada, R.; Márques, A.L.; Miranda, M.A.; Gortázar, C.; Lucientes, J. A broad assessment of factors determining Culicoides imicola abundance: Modelling the present and forecasting its future in climate change scenarios. PLoS One 2010, 5, e14236. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; De Baets, B.; Van doninck, J.; Calvete, C.; Lucientes, J.; De Clercq, E.M.; Ducheyne, E.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Absence reduction in entomological surveillance data to improve niche-based distribution models for Culicoides imicola. Prev. Vet. Med 2011, 100, 15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Cameron, S.E.; Parra, J.L.; Jones, P.G.; Jarvis, A. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas. Int. J. Climatol 2005, 25, 1965–1978. [Google Scholar]
- Calvete, C.; Estrada, R.; Miranda, M.A.; Borrás, D.; Calvo, J.H.; Lucientes, J. Modelling the distributions and spatial coincidence of bluetongue vectors Culicoides imicola and the Culicoides obsoletus group throughout the Iberian Peninsula. Med. Vet. Entomol 2008, 22, 124–134. [Google Scholar]
- Veronesi, E.; Venter, G.J.; Labuschagne, K.; Mellor, P.S.; Carpenter, S. Life history of Culicoides (Avaritia) imicola Kieffer in the laboratory at different rearing temperatures. Vet. Parasitol 2009, 163, 370–373. [Google Scholar]
- Venter, G.J.; Nevil, E.M.; van der Linde, T.C.D. Seasonal abundance and parity of stock-associated Culicoides species (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in different climatic regions in southern Africa in relation to their viral vector potential. Onderstepoort J. Vet. Res 1997, 64, 25–271. [Google Scholar]
- Purse, B.V.; McCormick, B.J.J.; Mellor, P.S.; Baylis, M.; Boorman, J.P.T.; Borras, D.; Burgu, I.; Capela, R.; Caracappa, S.; Collantes, F.; et al. Incriminating bluetonge virus vectors with climate envelope models. J.Appl. Ecol 2007, 44, 1231–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Blackwell, A.; King, F.C. The vertical distribution of Culicoides impunctatus larvae. Med. Vet. Entomol 1997, 11, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Uslu, U.; Dik, B. Vertical distribution of Culicoides larvae and pupae. Med. Vet. Entomol 2006, 20, 350–352. [Google Scholar]
- Braverman, Y.; Galun, R.; Ziv, M. Breeding sites of some Culicoides spp. (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) in Israel. Mosq. News 1974, 34, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Mellor, P.S.; Pizolis, G. Observations on breeding sites and light-trap collections of Culicoides during an outbreak of bluetongue in Cyprus. Bull. Entomol. Res 1979, 69, 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Foxi, C.; Delrio, G. Larval habitats and seasonal abundance of Culicoides biting midges found in association with sheep in northern Sardinia, Italy. Med. Vet. Entomol 2010, 24, 199–209. [Google Scholar]
- Delrio, G.; Deliperi, S.; Foxi, S.; Pantaleoni, R.A.; Piras, S. Osservazioni in Sardegna sulla dinamica di popolazione di Culicoides imicola Kiefer vettore della bluetongue. Proceedings of the 2002 Atti XIX Congresso Nazionale Italiano di Entomologia, Catania, Italy, 10–15 June 2002; pp. 1089–1094.
- Nevill, E.M. Biological Studies on Some South African Culicoides Species (Diptera: Ceratopogonidae) and the Morphology of Their Immature Stages.
- Conte, A.; Goffredo, M.; Ippoliti, C.; Meiswinkel, R. Influence of biotic and abiotic factors on the distribution and abundance of Culicoides imicola and the Obsoletus Complex in Italy. Vet. Parasitol 2007, 150, 333–344. [Google Scholar]
- Kettle, D.S. Biology and bionomics of bloodsuckung Ceratopogonids. Annu. Rev. Entomol 1977, 22, 33–51. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, A.; Ippoliti, C.; Savini, L.; Goffredo, M.; Meiswinkel, R. Novel environmental factors influencing the distribution and abundance of Culicoides imicola and the Obsoletus Complex in Italy. Vet. Italiana 2007, 43, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; Conte, A.; Van doninck, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Clercq, E.M.; Goffredo, M.; De Baets, B.; Hendrickx, G.; Ducheyne, E. On the relation between soil moisture dynamics and the geographical distribution of Culicoides imicola. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 622–632. [Google Scholar]
- Goffredo, M.; Meiswinkel, R. Entomological surveillance of bluetongue in Italy: Methods of capture, catch analysis and identification of Culicoides biting midges. Vet. Italiana 2004, 40, 260–265. [Google Scholar]
- Conte, A.; Gilbert, M.; Goffredo, M. Eight years of entomological surveillance in Italy show no evidence of Culicoides imicola geographical range expansion. J. Appl. Ecol 2009, 46, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random forests. Mach. Learn 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A.; Wiener, M. Classification and regression by random forest. R News 2002, 2, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Loosvelt, L.; Peters, J.; Skriver, H.; Lievens, H.; Van Coillie, F.M.B.; De Baets, B.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Random Forests as a tool for estimating uncertainty at pixel-level in SAR image classification. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf 2012, 19, 173–184. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; De Baets, B.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; Samson, R.; Degroeve, S.; De Becker, P.; Huybrechts, W. Random forests as a tool for ecohydrological distribution modelling. Ecol. Model 2007, 207, 304–318. [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal, R.N.M.; Buermann, W.; Harrigan, R.J.; Bonneaud, C.; Loiseau, C.; Chasar, A.; Sepil, I.; Valkiũnas, G.; Iezhova, T.; Saatchi, S.; et al. Spatially explicit predictions of blood parasites in a widely distributed African rainforest bird. Proc. R. Soc. B 2011, 278, 1025–1033. [Google Scholar]
- Loosvelt, L.; Peters, J.; Skriver, H.; De Baets, B.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Impact of reducing polarimetric SAR input on the uncertainty of crop classifications based on the Random Forests algorithm. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens 2012, 50, 4185–4200. [Google Scholar]
- Vincenzi, S.; Zucchetta, M.; Franzoi, P.; Pellizzato, M.; Pranovi, F.; de Leo, G.A.; Rorricelli, P. Application of a Random Forest algorithm to predict spatial distribution of the potential yield of Ruditapes philippinarum in the Venice Lagoon, Italy. Ecol. Model 2011, 222, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S, 4th ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Fawcett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recognit. Lett 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar]
- Peters, J.; Waegeman, W.; Van doninck, J.; Ducheyne, E.; Calvete, C.; Lucientes, J.; Verhoest, N.E.C.; De Baets, B. Predicting spatio-temporal Culicoides imicola distribution in Spain based on environmental habitat characteristics and species dispersal. Ecol. Inform 2014, 22, 69–80. [Google Scholar]
- Genuer, R.; Poggi, J.; Tuleau-Malot, C. Variable selection using Random Forests. Pattern Recognit. Lett 2010, 31, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Abulafia, D. The Great Sea; Penguin Books: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Bakri, J.; Suleiman, A. NDVI response to rainfall in different ecological zones in Jordan. Int. J. Remote Sens 2004, 25, 3897–3912. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Hunt, E.; Wardlow, B.; Basara, J.B.; Brown, J.F.; Verdin, J.P. Evaluation of MODIS NDVI and NDWI for vegetation drought monitoring using Oklahoma Mesonet soil moisture data. Geophys. Res. Lett 2008, 35, L22401. [Google Scholar]




| Climatic Data | Remote Sensing Data | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCC (St. Dev.) (%) | AUC (St. Dev.) (%) | PCC (St. Dev.) (%) | AUC (St. Dev.) (%) | |
| RF | 87.7 (1.4) | 92.5 (1.2) | 85.9 (1.6) | 91.2 (1.4) |
| LDA | 84.3 (2.2) | 89.2 (1.8) | 86.3 (1.8) | 89.9 (1.3) |
| MLR | 76.7 (2.4) | 80.7 (2.7) | 75.7 (2.8) | 77.6 (2.9) |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Van Doninck, J.; De Baets, B.; Peters, J.; Hendrickx, G.; Ducheyne, E.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Culicoides imicola: Climatic versus Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6604-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076604
Van Doninck J, De Baets B, Peters J, Hendrickx G, Ducheyne E, Verhoest NEC. Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Culicoides imicola: Climatic versus Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing. 2014; 6(7):6604-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076604
Chicago/Turabian StyleVan Doninck, Jasper, Bernard De Baets, Jan Peters, Guy Hendrickx, Els Ducheyne, and Niko E.C. Verhoest. 2014. "Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Culicoides imicola: Climatic versus Remote Sensing Data" Remote Sensing 6, no. 7: 6604-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076604
APA StyleVan Doninck, J., De Baets, B., Peters, J., Hendrickx, G., Ducheyne, E., & Verhoest, N. E. C. (2014). Modelling the Spatial Distribution of Culicoides imicola: Climatic versus Remote Sensing Data. Remote Sensing, 6(7), 6604-6619. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs6076604