Quality Assessment of Roof Planes Extracted from Height Data for Solar Energy Systems by the EAGLE Platform
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Related Work
1.2.1. Roof Plane Extraction
Model-Driven Approaches
Data-Driven Approaches
Approaches Using Additional Information
1.2.2. Suitability of Roof Planes for RES
1.2.3. Quality Evaluation
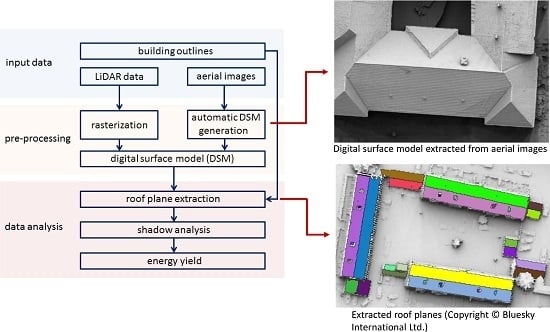
2. Methods
2.1. Extraction Approach

2.1.1. Data Pre-Processing
2.1.2. Roof Plane Extraction
2.1.3. Geometric Roof Plane Parameters
2.1.4. Further Processing

2.2. Evaluation Strategy

2.3. Data Sources and Software Environment
| Country | Location | Data Type | Resolution |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | Leicester |  | 0.25 m 0.14 m |
| Bristol | LiDAR | 0.50 m | |
| The Village | Aerial Images | 0.12 m | |
| Slough (London) | LiDAR | 0.50 m | |
| Germany | Karlsruhe |  | 0.50 m 0.06 m/0.20 m |
| UAV Images | 0.02 m/0.04 m | ||
| Sweden | Stockholm | LiDAR | 0.50 m |
| The Netherlands | The Hague | Aerial Images | 0.04 m |
| Spain | Madrid | LiDAR | 1.00 m |
3. Results
3.1. Geometric Coincidence of Building Outlines and Building Borders in Height Data (DSM)
| Test Site | Mean Distance | Max. Distance | Min. Distance | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leicester (UK) | 0.92 m | 1.91 m | 0.06 m | 0.40 m |
| Karlsruhe (GER) | 0.73 m | 1.57 m | 0.03 m | 0.37 m |

3.2. Roof Plane Extraction
3.2.1. Detection Rates
| Test Site | Data Type | # Planes | Tp | Fn | Completeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leicester (UK) | LiDAR Aerial Images | 522 | 485 | 37 | 92.9% |
| 522 | 456 | 66 | 87.4% | ||
| Karlsruhe (GER) | LiDAR Aerial Images | 502 | 483 | 19 | 96.2% |
| 502 | 484 | 18 | 96.4% |

| Test Site | Data Type | # Planes | Tp | Fp | Correctness | Quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leicester (UK) | LiDAR Aerial Img. | 522 | 514 | 8 | 98.5% | 91.9% |
| 522 | 515 | 7 | 98.7% | 87.6% | ||
| Karlsruhe (GER) | LiDAR Aerial Img. | 502 | 453 | 49 | 90.2% | 86.9% |
| 502 | 418 | 84 | 83.3% | 80.4% |
3.2.2. Quality of Roof Plane Parameters
| Test Site | Inclination Angle (Degree) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiDAR | Aerial Image | |||||||
| Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | |
| LEIC | 1.5 | 3.9 | 0.02 | 1.0 | 1.7 | 5.6 | 0.08 | 1.1 |
| KA | 1.6 | 4.8 | 0.06 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 4.2 | 0.06 | 1.1 |
| Test Site | Aspect Angle (Degree) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiDAR | Aerial Image | |||||||
| Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | |
| LEIC | 1.1 | 5.3 | 0.10 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 6.3 | 0.05 | 1.4 |
| KA | 0.8 | 1.9 | 0.02 | 0.6 | 0.6 | 2.0 | 0.01 | 0.6 |
| Test Site | Size (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiDAR | Aerial Image | |||||||
| Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | Mean | Max | Min | Std. Dev. | |
| LEIC | 11.6 | 34.7 | 0.3 | 10.3 | 12.3 | 29.9 | 0.7 | 9.1 |
| KA | 18.4 | 34.9 | 0.4 | 11.2 | 13.3 | 30.4 | 0.4 | 8.5 |
3.2.3. Additional Influences on the Quality of the Extracted Roof Planes


4. Discussion
4.1. Geometric Coincidence of Building Outlines and Building Borders in Height Data (DSM)
4.2. Roof Plane Extraction


4.3. Qualitative Comparison of Results Derived from LiDAR and Aerial Imagery
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- EAGLE Development and Demonstration of a Dynamic, Web-Based, Renewable Energy Rating Platform. Available online: http://www.eagle-fp7.eu (accessed on 28 November 2014).
- Dorninger, P.; Pfeifer, N. A comprehensive automated 3D approach for building extraction, reconstruction, and regularization from airborne laser scanning point clouds. Sensors 2008, 8, 7323–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, S.; Nevatia, R. Detection and modeling of buildings from multiple aerial images. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 501–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oude Elberink, S.J. Problems in automated building reconstruction based on dense airborne laser scanning data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Vosselman, G.; Maas, H.-G. (Eds.) Airborne and Terrestrial Laser Scanning; Whittles: Dunbeath, UK, 2010.
- Tarsha-Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. Joint combination of point cloud and DSM for 3D building reconstruction using airborne laser scanner data. In Proceedings of the Urban Remote Sensing Joint Event, Paris, France, 11–13 April 2007.
- Tarsha-Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P.; Koehl, M. Model-driven and data-driven approaches using LiDAR data: Analysis and comparison. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2007, 36, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Weidner, U.; Foerstner, W. Towards automatic building extraction from high resolution digital elevation models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1995, 59, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maas, H.-G.; Vosselman, G. Two algorithms for extracting building models from raw laser altimetry data. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochem, A.; Hoefle, B.; Hollaus, M.; Rutzinger, M. Object detection in airborne LiDAR data for improved solar radiation modeling in urban areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2009, 38, W8. [Google Scholar]
- Schwalbe, E.; Maas, H.-G.; Seidel, F. 3D building model generation from airborne laser scanner data using 2D GIS data and orthogonal point cloud projections. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Workshop Laser Scanning 2005 WG III/3–III/4, Enschede, The Netherlands, 12–14 September 2005.
- Tarsha-Kurdi, F.; Landes, T.; Grussenmeyer, P. Hough-transform and extended RANSAC algorithms for automatic detection of 3D building roof planes from LiDAR data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Workshop on Laser Scanning 2007 and SilviLaser 2007, Espoo, Finland, 12–14 September 2007; pp. 407–412.
- Rottensteiner, F.; Trinder, J.; Clode, S.; Kubik, K. Automated delineation of roof planes from LiDAR data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2005, 36, 221–226. [Google Scholar]
- Jochem, A.; Hoefle, B.; Rutzinger, M.; Pfeifer, N. Automatic roof plane detection and analysis in airborne LiDAR point clouds for solar potential assessment. Sensors 2009, 9, 5241–5262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oude Elberink, S.; Vosselman, G. Building reconstruction by target based graph matching on incomplete laser data: analysis and limitations. Sensors 2009, 9, 6101–6118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, B.; Jancosek, M.; Oude Elberink, S.; Vosselman, G. Flexible building primitives for 3D building modeling. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 101, 275–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, S.N.; Nalani, H.A.; Maas, H.-G. An automated method for 3D roof outline generation and regularization in airborne laser scanner data. In Proceedings of the ISPRS Annals of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Melbourne, Australia, 25 August–1 September 2012; pp. 281–286.
- Awrangjeb, M.; Zhang, C.; Fraser, C.S. Automatic extraction of building roofs using LiDAR data and multispectral imagery. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 83, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Brise, C. Automatic generation of building models from LiDAR data and the integration of aerial images. In Proceedings of the International Archives of Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, Dresden, Germany, 8–10 October 2003; Volume XXXIV-3/W13.
- Rottensteiner, F.; Trinder, J.; Clode, S.; Kubik, K. Fusing airborne laser scanner data and aerial imagery for the automatic extraction of buildings in densely built-up areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2004, 35, 512–517. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, C. Building reconstruction from images and laser scanning. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinform. 2005, 6, 187–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novacheva, A. Building roof reconstruction from LiDAR data and aerial images through plane extraction and colour edge detection. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 53–57. [Google Scholar]
- Brenner, C.; Haala, N. Fast production of virtual reality city models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 1998, 32, 77–84. [Google Scholar]
- Vosselman, G.; Dijkman, S. 3D building model reconstruction from point clouds and ground plans. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2001, 34, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kaartinen, H.; Hyyppä, J.; Gülch, E.; Vosselman, G.; Hyyppä, H.; Matikainen, L.; Hofmann, A.; Mäder, U.; Persson, A.; Söderman, U.; et al. Accuracy of 3D city models: EuroSDR comparison. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2005, 36, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- ISPRS Test Project on Urban Classification and 3D Building Reconstruction: Results. 2013. Available online: http://www2.isprs.org/commissions/comm3/wg4/results.html (accessed on 22 October 2014).
- Šúri, M.; Hofierka, J. A new GIS-based solar radiation model and its application to photovoltaic assessments. Trans. GIS 2004, 8, 175–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittman, H.; Bajons, P.; Doneus, M.; Friesinger, H. Identification of roof areas suited for solar energy conversion systems. Renew. Energy 1997, 11, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegtle, T.; Steinle, E.; Tovari, D. Airborne laser scanning data for determination of suitable areas for photovoltaics. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2005, 36, 215–220. [Google Scholar]
- Kassner, R.; Koppe, W.; Schüttenberg, T.; Bareth, G. Analysis of the solar potential of roofs by using official LiDAR data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2008, 37, 399–403. [Google Scholar]
- Edelsbrunner, H.; Kirkpatrick, D.; Seidel, R. On the shape of a set of points in the plane. IEEE Trans. Inform. Theory 1983, 29, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludwig, D.; Lanig, S.; Klärle, M. Location analysis for solar panels by LiDAR-data with geoprocessing—SUN-AREA. In Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Informatics for Environmental Protection, Berlin, Germany, 9–11 September 2009; pp. 83–89.
- Agugiaro, G.; Remondino, F.; Stevanato, G.; de Filippi, R.; Furlanello, C. Estimation of solar radiation on building roofs in mountainous areas. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2011, 38, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agugiaro, G.; Nex, F.; Remondino, F.; de Filippi, R.; Droghetti, S.; Furlanello, C. Solar radiation estimation on building roofs and web-based solar cadaster. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2012, 1, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gooding, J.; Crook, R.; Tomlin, A.S. Modelling of roof geometries from low-resolution LiDAR data for city-scale solar energy applications using a neighbouring buildings method. Appl. Energy 2015, 148, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foody, G. Status of land cover classification accuracy assessment. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 80, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.; Wang, J.; Lehrbass, B. An evaluation system for building footprint extraction from remotely sensed data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2013, 6, 1640–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutzinger, M.; Rottensteiner, F.; Pfeifer, N. A comparison of evaluation techniques for building extraction from airborne laser scanning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Observ. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong-Hong, L.; Laefer, D.F. Quantitative evaluation strategies for urban 3D model generation from remote sensing data. Comput. Graphics 2015, 49, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Haithcoat, T.L. Development of comprehensive accuracy assessment indexes for building footprint extraction. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 402–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, P.F.; Tate, N.J. Causes and consequences of error in digital elevation models. Prog. Phys. Geog. 2006, 30, 467–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuffert, S. An automatic data driven approach to derive photovoltaic-suitable roof surfaces from ALS data. In Proceedings of the Joint Urban Remote Sensing Event (JURSE), Sao Paulo, Brazil, 21–23 April 2013; pp. 267–270.
- Douglas, D.H.; Peucker, T.K. Algorithms for the reduction of the number of points required to represent a digitized line or its caricature. Can. Cartogr. 1973, 10, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeus, J. Astronomische Algorithmen, 2nd ed.; Johann Ambrosius Barth: Leipzig, Germany, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- MicMac, IGN. Available online: http://logiciels.ign.fr/?Micmac (accessed on 13 November 2014).
- Awrangjeb, M.; Fraser, C. Automatic and threshold-free evaluation of 3D building roof reconstruction techniques. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Melbourne, Australia, 21–26 July 2013; pp. 3970–3973.
- Slota, M. Full-waveform data for building roof step edge localization. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 106, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.Y.; Shaker, A.; El-Ashmawy, N. Urban land cover classification using airborne LiDAR data: A review. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 158, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schuffert, S.; Voegtle, T.; Tate, N.; Ramirez, A. Quality Assessment of Roof Planes Extracted from Height Data for Solar Energy Systems by the EAGLE Platform. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 17016-17034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215866
Schuffert S, Voegtle T, Tate N, Ramirez A. Quality Assessment of Roof Planes Extracted from Height Data for Solar Energy Systems by the EAGLE Platform. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(12):17016-17034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215866
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchuffert, Simon, Thomas Voegtle, Nicholas Tate, and Alberto Ramirez. 2015. "Quality Assessment of Roof Planes Extracted from Height Data for Solar Energy Systems by the EAGLE Platform" Remote Sensing 7, no. 12: 17016-17034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215866
APA StyleSchuffert, S., Voegtle, T., Tate, N., & Ramirez, A. (2015). Quality Assessment of Roof Planes Extracted from Height Data for Solar Energy Systems by the EAGLE Platform. Remote Sensing, 7(12), 17016-17034. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs71215866