Using Ridge Regression Models to Estimate Grain Yield from Field Spectral Data in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Grown under Three Water Regimes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Plant Material and Experimental Sites
2.2. Measurements
2.3. Ridge Regression Model
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Relationship between Spectral Signature and Grain Yield
| Variable | N | Mean Kg∙ha−1 | Min Kg∙ha−1 | Max Kg∙ha−1 | SD Kg∙ha−1 | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe Stress | 391 | 1655 | 130 | 4394 | 696.1 | 42.1 |
| Medium Stress | 399 | 4739 | 607 | 10144 | 1425.8 | 30.1 |
| Full Irrigation | 397 | 7967 | 2240 | 12992 | 1788.4 | 22.5 |


3.2. Prediction with the Ridge Regression Model
| Model | n | Lambda | R2 (%) | RMSE (kg∙ha−1) | rRMSE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthesis | |||||
| FI | 397 | 56.7 | 80 | 809 | 10.2 |
| MWS | 399 | 3.8 | 88 | 498 | 10.5 |
| FI-MWS | 796 | 4.1 | 90 | 711 | 11.2 |
| Grain Filling | |||||
| FI | 301 | 3.8 | 83 | 725 | 9.2 |
| MWS | 399 | 20.7 | 77 | 684 | 14.4 |
| SWS | 391 | 2.1 | 91 | 210 | 12.7 |
| FI-MWS-SWS | 1091 | 1.1 | 92 | 760 | 16.8 |


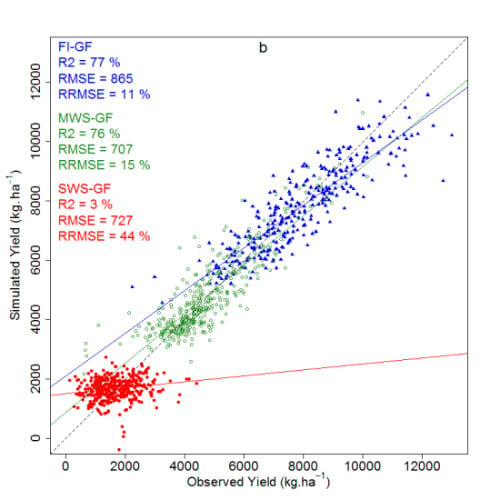
| Model | FI-AN | MWS-AN | FI-GF | MWS-GF | SWS-GF | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R | rRMSE (%) | R | rRMSE (%) | R | rRMSE (%) | R | rRMSE (%) | R | rRMSE (%) | |
| FI-AN * | 0.77 *** | 53 | 0.56 *** | 19 | 0.69 *** | 54 | 0.43 *** | 132 | ||
| MWS-AN * | 0.66 *** | 55 | 0.56 *** | 54 | 0.76 *** | 19 | 0.68 *** | 99 | ||
| FI-GF * | 0.67 *** | 22 | 0.46 *** | 54 | 0.65 *** | 54 | 0.71 *** | 136 | ||
| MWS-GF * | 0.02 ns | 65 | 0.18 ** | 43 | 0.31 *** | 62 | 0.67 *** | 104 | ||
| SWS-GF * | 0.46 *** | 137 | 0.43 *** | 107 | 0.25 ** | 136 | 0.78 *** | 102 | ||
3.3. Prediction with Spectral Vegetation Indices
3.4. Discussion
3.4.1. Canopy Reflectance in Genotypes of Contrasting Grain Yield
| Model | NDVI | PRI | WI | SR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 (%) | R2 (%) | R2 (%) | R2 (%) | |
| Anthesis | ||||
| FI | 23.3 *** | 25.2 *** | 55.8 *** | 23.8 *** |
| MWS | 34.1 *** | 42.6 *** | 55.9 *** | 40.2 *** |
| FI-MWS | 37.9 *** | 50.8 *** | 69.0 *** | 45.3 *** |
| Grain filling | ||||
| FI | 28.8 *** | 0.0 NS | 51.3 *** | 14.9 *** |
| MWS | 47.9 *** | 0.0 NS | 62.7 *** | 38.8 *** |
| SWS | 35.7 *** | 22.1 ** | 54.1 *** | 30.1 *** |
| FI-MWS-SWS | 79.8 *** | 0.0 NS | 79.8 *** | 53.0 *** |
3.4.2. Regression Coefficients for Different Spectral Zones
3.4.3. Grain Yield Prediction Using Multivariate Models
3.4.4. Comparison between the Spectral Vegetation Indices and Ridge Regression Predictions
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Araus, J.L.; Slafer, G.A.; Royo, C.; Serret, M.D. Breeding for yield potential and stress adaptation in cereals. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2008, 27, 377–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, D.; Jefferies, S.; Kuchel, H.; Langridge, P. Genetic and genomic tools to improve drought tolerance in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3211–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, M.; Pask, A.; Mullan, D. Physiological Breeding I: Interdisciplinary Approaches to Improve Crop Adaptation; International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT): Texcoco, Mexico, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cattivelli, L.; Rizza, F.; Badeck, F.-W.; Mazzucotelli, E.; Mastrangelo, A.M.; Francia, E.; Mare, C.; Tondelli, A.; Stanca, A.M. Drought tolerance improvement in crop plants: An integrated view from breeding to genomics. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araus, J.L.; Slafer, G.A.; Reynolds, M.P.; Royo, C. Plant breeding and drought in c3 cereals: What should we breed for? Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 925–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araus, J.L.; Serret, M.D.; Edmeades, G.O. Phenotyping maize for adaptation to drought. Front. Physiol. 2012, 3, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynolds, M.; Mujeeb-Kazi, A.; Sawkins, M. Prospects for utilising plant-adaptive mechanisms to improve wheat and other crops in drought-and salinity-prone environments. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2005, 146, 239–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E. Field high-throughput phenotyping: The new crop breeding frontier. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.W.; Andrade-Sanchez, P.; Gore, M.A.; Bronson, K.F.; Coffelt, T.A.; Conley, M.M.; Feldmann, K.A.; French, A.N.; Heun, J.T.; Hunsaker, D.J. Field-based phenomics for plant genetics research. Field Crops Res. 2012, 133, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatfield, J.; Gitelson, A.A.; Schepers, J.S.; Walthall, C. Application of spectral remote sensing for agronomic decisions. Agron. J. 2008, 100, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, G.A. Hyperspectral remote sensing of plant pigments. J. Exp. Bot. 2007, 58, 855–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, C.; Villegas, D. Field measurements of canopy spectra for biomass assessment of small-grain cereals. In Biomass-Detection, Production and Usage; Matovic, D., Ed.; INTECH: Rijeka, Croatia, 2011; pp. 27–52. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Relationships between leaf pigment content and spectral reflectance across a wide range of species, leaf structures and developmental stages. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 337–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garriga, M.; Retamales, J.B.; Romero, S.; Caligari, P.D.S.; Lobos, G.A. Chlorophyll, anthocyanin and gas exchangechanges assessed by spectroradiometry in fragaria chiloensis under salt stress. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pattey, E.; Miller, J.R.; McNairn, H.; Smith, A.; Hu, B. Estimating crop stresses, aboveground dry biomass and yield of corn using multi-temporal optical data combined with a radiation use efficiency model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1167–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seelig, H.D.; Hoehn, A.; Stodieck, L.S.; Klaus, D.M.; Adams Iii, W.W.; Emery, W.J. The assessment of leaf water content using leaf reflectance ratios in the visible, near-, and short-wave-infrared. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2008, 29, 3701–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, N.; Villegas, D.; Casadesus, J.; Araus, J.L.; Royo, C. Spectral vegetation indices as nondestructive tools for determining durum wheat yield. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobos, G.A.; Matus, I.; Rodriguez, A.; Romero-Bravo, S.; Araus, J.L.; del Pozo, A. Wheat genotypic variability in grain yield and carbon isotope discrimination under mediterranean conditions assessed by spectral reflectance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2014, 56, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araus, J.L. Integrative physiological criteria associated with yield potential. In Increasing Yield Potential in Wheat: Breaking the Barriers; Reynolds, M.P., Rajaram, S., McNab, A., Eds.; International Maize and Wheat Improvement Center (CIMMYT): Texcoco, Mexico, 1996; pp. 150–167. [Google Scholar]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I. Visible and near-infrared reflectance techniques for diagnosing plant physiological status. Trends Plant Sci. 1998, 3, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royo, C.; Aparicio, N.; Villegas, D.; Casadesus, J.; Monneveux, P.; Araus, J.L. Usefulness of spectral reflectance indices as durum wheat yield predictors under contrasting mediterranean conditions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 4403–4419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graeff, S.; Claupein, W. Quantifying nitrogen status of corn (Zea mays L.) in the field by reflectance measurements. Eur. J. Agron. 2003, 19, 611–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.; Schjoerring, J. Reflectance measurement of canopy biomass and nitrogen status in wheat crops using normalized difference vegetation indices and partial least squares regression. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, V.S.; Araus, J.L.; Cairns, J.E.; Sanchez, C.; Melchinger, A.E.; Orsini, E. Prediction of grain yield using reflectance spectra of canopy and leaves in maize plants grown under different water regimes. Field Crops Res. 2012, 128, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrio, J.P.; Villegas, D.; Zarco, J.; Aparicio, N.; Araus, J.L.; Royo, C. Assessment of durum wheat yield using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectra of canopies. Field Crops Res. 2005, 94, 126–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R.; Friedman, J.; Franklin, J. The elements of statistical learning: Data mining, inference and prediction. Math. Intell. 2005, 27, 83–85. [Google Scholar]
- Lazaridis, D.C.; Verbesselt, J.; Robinson, A.P. Penalized regression techniques for prediction: A case study for predicting tree mortality using remotely sensed vegetation indices this article is one of a selection of papers from extending forest inventory and monitoring over space and time. Can. J. For. Res. 2010, 41, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, T.; Ju, C.; Yang, X. Comparison of ridge regression and partial least squares regression for estimating above-ground biomass with landsat images and terrain data in mu us sandy land, China. Arid Land Res. Manag. 2009, 23, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikhonov, A. On the stability of inverse problems. Proc. URSS Acad. Sci. 1943, 39, 195–198. [Google Scholar]
- Hoerl, A.E.; Kennard, R.W. Ridge regression: Applications to nonorthogonal problems. Technometrics 1970, 12, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolpe, N. Descripciones de los Principales Suelos de la Octava Región de Chile; Universidad de Concepción,Facultad de Agronomía: Chillán, Chile, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Del Pozo, A.; del Canto, P. Características del Valle Central: Áreas Agroclimáticas y Sistemas Productivos en las VII y VIII Regiones; Instituto de Investigaciones Agropecuarias,Centro Regional de Investigación Quilamapu: Chillan, Chile, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Zadoks, J.C.; Chang, T.T.; Konzak, C.F. A decimal code for the growth stages of cereals. Weed Res. 1974, 14, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randolph, T.W. Scale-based normalization of spectral data. Cancer Biomark. 2006, 2, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Serrano, L.; Ustin, S.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Gamon, J.A.; Peñuelas, J. Deriving water content of chaparral vegetation from AVIRIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 74, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venables, W.N.; Ripley, B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Serrano, L.; Filella, I.; Peñuelas, J. Remote sensing of biomass and yield of winter wheat under different nitrogen supplies. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Peñuelas, J.; Inoue, Y. Reflectance indices indicative of changes in water and pigment contents of peanut and wheat leaves. Photosynthetica 1999, 36, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Chivkunova, O.B.; Merzlyak, M.N. Nondestructive estimation of anthocyanins and chlorophylls in anthocyanic leaves. Am. J. Bot. 2009, 96, 1861–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penuelas, J.; Gamon, J.A.; Griffin, K.L.; Field, C.B. Assessing community type, plant biomass, pigment composition, and photosynthetic efficiency of aquatic vegetation from spectral reflectance. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Raja Reddy, K.; Kakani, V.G.; Read, J.J.; Carter, G.A. Corn (Zea mays L.) growth, leaf pigment concentration, photosynthesis and leaf hyperspectral reflectance properties as affected by nitrogen supply. Plant Soil 2003, 257, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, I.; Serrano, L.; Serra, J.; Peñuelas, J. Evaluating wheat nitrogen status with canopy reflectance indices and discriminant analysis. Crop Sci. 1995, 35, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Isla, R.; Filella, I.; Araus, J.L. Visible and near-infrared reflectance assessment of salinity effects on barley. Crop Sci. 1997, 37, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Serrano, L.; Savé, R. Cell wall elasticity and water index (r970 nm/r900 nm) in wheat under different nitrogen availabilities. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Filella, I.; Biel, C.; Serrano, L.; Savé, R. The reflectance at the 950–970 nm region as an indicator of plant water status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 1887–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peñuelas, J.; Pinol, J.; Ogaya, R.; Filella, I. Estimation of plant water concentration by the reflectance water index WI (r900/r970). Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2869–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, S.; Schepers, J.S.; Francis, D.; Schlemmer, M.R. Use of spectral radiance to estimate in-season biomass and grain yield in nitrogen-and water-stressed corn. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sims, D.A.; Gamon, J.A. Estimation of vegetation water content and photosynthetic tissue area from spectral reflectance: A comparison of indices based on liquid water and chlorophyll absorption features. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 84, 526–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, N.; Villegas, D.; Araus, J.L.; Casadesús, J.; Royo, C. Relationship between growth traits and spectral vegetation indices in durum wheat. Crop Sci. 2002, 42, 1547–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.; Reynolds, M.P.; Raun, W.R.; Stone, M.L.; Klatt, A.R. Spectral water indices for assessing yield in elite bread wheat genotypes under well-irrigated, water-stressed, and high-temperature conditions. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 197–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babar, M.; Reynolds, M.; van Ginkel, M.; Klatt, A.; Raun, W.; Stone, M. Spectral reflectance indices as a potential indirect selection criteria for wheat yield under irrigation. Crop Sci. 2006, 46, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hernandez, J.; Lobos, G.A.; Matus, I.; Del Pozo, A.; Silva, P.; Galleguillos, M. Using Ridge Regression Models to Estimate Grain Yield from Field Spectral Data in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Grown under Three Water Regimes. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2109-2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202109
Hernandez J, Lobos GA, Matus I, Del Pozo A, Silva P, Galleguillos M. Using Ridge Regression Models to Estimate Grain Yield from Field Spectral Data in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Grown under Three Water Regimes. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(2):2109-2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202109
Chicago/Turabian StyleHernandez, Javier, Gustavo A. Lobos, Iván Matus, Alejandro Del Pozo, Paola Silva, and Mauricio Galleguillos. 2015. "Using Ridge Regression Models to Estimate Grain Yield from Field Spectral Data in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Grown under Three Water Regimes" Remote Sensing 7, no. 2: 2109-2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202109
APA StyleHernandez, J., Lobos, G. A., Matus, I., Del Pozo, A., Silva, P., & Galleguillos, M. (2015). Using Ridge Regression Models to Estimate Grain Yield from Field Spectral Data in Bread Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Grown under Three Water Regimes. Remote Sensing, 7(2), 2109-2126. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70202109