A Quantitative Inspection on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Land Surface Evapotranspiration in South Asia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Data Sources
3. Method
3.1. Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) Model

3.2. Evapotranspiration (ET) Estimation
3.2.1. Daily Net Radiation
3.2.2. Gap Filling and Daily, Monthly and Yearly ET Estimation
3.3. Validation Scheme
4. Results and Validation
4.1. Daily and Monthly ET Estimation Result



4.2. Validation and Analysis


5. Spatio-Temporal Variation Analysis
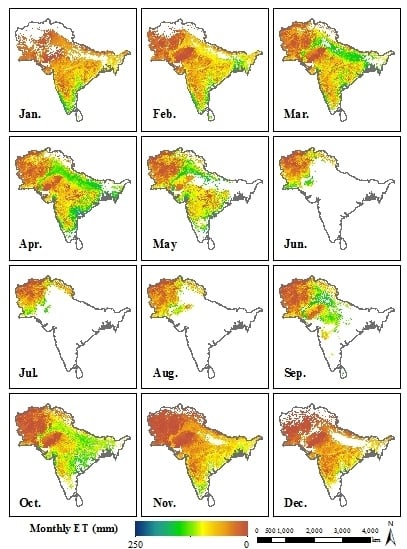
5.1. Monthly Variation

5.2. Typical Sites Analysis

| ID | Latitude | Longitude | Land Cover Type | Country | Climate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 30.3426 | 64.8752 | Barren or sparsely vegetated | Pakistan | Warm desert |
| B | 26.0326 | 71.6239 | Open shrublands | India | Warm desert |
| C | 30.9279 | 72.7146 | Croplands | India | Warm semi-arid |
| D | 23.7535 | 75.313 | Croplands | India | Temperate continent |
| E | 25.8287 | 83.2057 | Croplands | India | Humid subtropical |
| F | 20.6408 | 82.2657 | Woody savannas | India | Temperate continent |
| G | 12.6062 | 75.5879 | Evergreen Broadleaf forest | India | Tropical savanna |
| H | 34.5195 | 65.966 | Grasslands | Afghanistan | Cold desert |
| I | 17.5547 | 76.3772 | Croplands | India | Warm semi-arid |
| J | 13.0674 | 79.1973 | Cropland/Natural vegetation mosaic | India | Temperate continent |


5.3. Annual Analysis


6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bastiaanssen, W.; Noordman, E.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.; Allen, R. SEBAL model with remotely sensed data to improve water-resources management under actual field conditions. J. Irrigat. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.C.; Allen, R.G.; Morse, A.; Kustas, W.P. Use of Landsat thermal imagery in monitoring evapotranspiration and managing water resources. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 122, 50–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biemans, H.; Speelman, L.H.; Ludwig, F.; Moors, E.J.; Wiltshire, A.J.; Kumar, P.; Gerten, D.; Kabat, P. Future water resources for food production in five South Asian river basins and potential for adaptation—A modeling study. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 468–469, S117–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Tsiang, M.; Rajaratnam, B.; Diffenbaugh, N.S. Observed changes in extreme wet and dry spells during the South Asian summer monsoon season. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.M.Q. Climate change, flooding in South Asia and implications. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2011, 11, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffhammer, M.; Ramanathan, V.; Vincent, J. Climate change, the monsoon, and rice yield in India. Clim. Chang. 2012, 111, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Bhadra, A.; Raghuwanshi, N.; Singh, R. Temporal trends in estimates of reference evapotranspiration over India. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhajharia, D.; Dinpashoh, Y.; Kahya, E.; Singh, V.P.; Fakheri-Fard, A. Trends in reference evapotranspiration in the humid region of northeast India. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, K.; Bhattacharya, B.K.; Chaurasia, S.; Dutta, S.; Nigam, R.; Mukherjee, J.; Banerjee, S.; Kar, G.; Rao, V.U.M.; Gadgil, A.S.; Parihar, J.S. Evapotranspiration using MODIS data and limited ground observations over selected agroecosystems in India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 2091–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.A.; Jarmain, C.; Su, Z.; Eckardt, F.E. Estimating evapotranspiration using remote sensing and the Surface Energy Balance System—A South African perspective. Water SA 2013, 39, 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Ju, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; He, H.; Wang, H.; Guan, D.; Zhao, F.; Li, Y.; Hao, Y. Changes of evapotranspiration and water yield in China’s terrestrial ecosystems during the period from 2000 to 2010. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2013, 10, 5397–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.-L.; Tang, B. An application of the Ts-VI triangle method with enhanced edges determination for evapotranspiration estimation from MODIS data in arid and semi-arid regions: Implementation and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.-L.; Jia, Y.; Li, C.; Sun, X.; Kustas, W.P.; Anderson, M.C. An intercomparison of three remote sensing-based energy balance models using Large Aperture Scintillometer measurements over a wheat-corn production region. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3187–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL). 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roerink, G.J.; Su, Z.; Menenti, M. S-SEBI: A simple remote sensing algorithm to estimate the surface energy balance. Phys. Chem. Earth PT. B 2000, 25, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z. The Surface Energy Balance System (SEBS) for estimation of turbulent heat fluxes. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2002, 6, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A.; Trezza, R.; Wright, J.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kramber, W.; Lorite, I.; Robison, C. Satellite-based energy balance for Mapping Evapotranspiration with Internalized Calibration (METRIC)—Applications. J. Irrigat. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowda, P.H.; Howell, T.A.; Paul, G.; Colaizzi, P.D.; Marek, T.H.; Su, B.; Copeland, K.S. Deriving hourly evapotranspiration rates with SEBS: A lysimetric evaluation. Vadose Zone J. 2013, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hafeez, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Y. Evaluation of SEBS for estimation of actual evapotranspiration using ASTER satellite data for irrigation areas of Australia. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 112, 609–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmermans, J.; Su, Z.; van der Tol, C.; Verhoef, A.; Verhoef, W. Quantifying the uncertainty in estimates of surface-atmosphere fluxes through joint evaluation of the SEBS and SCOPE models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1561–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Li, Z.-L.; Tang, R.; Tang, B.-H.; Wu, H.; Yang, F.; Labed, J.; Zhou, G. Evaluating the SEBS-estimated evaporative fraction from MODIS data for a complex underlying surface. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; McCabe, M.F.; Wood, E.F.; Su, Z.; Prueger, J.H. Modeling evapotranspiration during SMACEX: Comparing two approaches for local- and regional-scale prediction. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 910–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Ma, Y.; Hu, Z.; Su, Z.; Wang, J.; Ishikawa, H. Estimating surface fluxes over middle and upper streams of the Heihe River Basin with ASTER imagery. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinukollu, R.K.; Wood, E.F.; Ferguson, C.R.; Fisher, J.B. Global estimates of evapotranspiration for climate studies using multi-sensor remote sensing data: Evaluation of three process-based approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, L.A.; Münch, Z.; Engelbrecht, J. Particular uncertainties encountered in using a pre-packaged SEBS model to derive evapotranspiration in a heterogeneous study area in South Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 295–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, W.; Li, A.; Deng, W. Surface energy fluxes estimation over the South Asia subcontinent through assimilating MODIS/TERRA satellite data with in situ observations and GLDAS product by SEBS model. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3704–3712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.V.; Peters-Lidard, C.D.; Tian, Y.; Houser, P.R.; Geiger, J.; Olden, S.; Lighty, L.; Eastman, J.L.; Doty, B.; Dirmeyer, P.; Adams, J.; Mitchell, K.; Wood, E.F.; Sheffield, J. Land information system: An interoperable framework for high resolution land surface modeling. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2006, 21, 1402–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Houser, P.; Jambor, U.E.A.; Gottschalck, J.; Mitchell, K.; Meng, C.; Arsenault, K.; Cosgrove, B.; Radakovich, J.; Bosilovich, M. The global land data assimilation system. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2004, 85, 381–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, Z.-L.; Zhang, R. A direct method for estimating net surface shortwave radiation from MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, B.; Li, Z.-L. Estimation of instantaneous net surface longwave radiation from MODIS cloud-free data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3482–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, T.N.; Ripley, D.A. On the relation between NDVI, fractional vegetation cover, and leaf area index. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 62, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prihodko, L.; Goward, S.N. Estimation of air temperature from remotely sensed surface observations. Remote Sens. Environ. 1997, 60, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.-L.; Sun, X. Temporal upscaling of instantaneous evapotranspiration: An intercomparison of four methods using eddy covariance measurements and MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2013, 138, 102–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samani, Z.; Bawazir, A.S.; Bleiweiss, M.; Skaggs, R.; Tran, V.D. Estimating daily net radiation over vegetation canopy through remote sensing and climatic data. J. Irrigat. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 291–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, E.; Sobrino, J. Daily net radiation estimated from air temperature and NOAA-AVHRR data: A case study for the Iberian Peninsula. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1521–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyt, D.V. A model for the calculation of solar global insolation. Solar Energy 1978, 21, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konzelmann, T.; van de Wal, R.S.; Greuell, W.; Bintanja, R.; Henneken, E.A.; Abe-Ouchi, A. Parameterization of global and longwave incoming radiation for the Greenland Ice Sheet. Glob. Planet. Chang. 1994, 9, 143–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, N.S.; Vendrame, Í.F.; Da Rocha, H.R.; Chou, S.C.; Cabral, O. Downward longwave radiation estimates for clear and all-sky conditions in the Sertãozinho region of São Paulo, Brazil. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 99, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcrette, J.-J.; Deschamps, P.-Y. Downward longwave radiation at the surface in clear-sky atmospheres: Comparisons of measured, satellite-derived, and calculated fluxes. In Proceedings of the International Satellite Land-Surface Climatology Project (ISLSCP) Conference, Rome, Italy, 2–6 December 1985.
- Prata, A. A new long-wave formula for estimating downward clear-sky radiation at the surface. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 1996, 122, 1127–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASCE-EWRI. The ASCE Standardized Reference Evapotranspiration Equation: ASCE-EWRI Standardization of Reference Evapotranspiration Task Committe Report. Available online: http://www.irrisoft.net/downloads/literature/ASCE%20Standardized%20Equation%20Jan%202005%20Apendix%20A.pdf (accessed on 21 January 2015).
- Irmak, S.; Mutiibwa, D.; Payero, J.O. Net radiation dynamics: Performance of 20 daily net radiation models as related to model structure and intricacy in two climates. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 1059–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doorenbos, J.; Pruitt, W. Guidelines for predicting crop water requirements. In Irrigation and Drainage Paper; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Brunt, D. Physical and Dynamical Meteorology; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Brunt, D. Notes on radiation in the atmosphere. I. Q. J. R. Meteorolog. Soc. 1932, 58, 389–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Guo, R.; Xia, W. Distribution of actual evapotranspiration over qaidam basin, an arid area in China. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 6976–6996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y. Remote sensing parameterization of regional net radiation over heterogeneous land surface of Tibetan Plateau and arid area. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 3137–3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Hafeez, M.; Rabbani, U.; Ishikawa, H.; Ma, Y. Retrieved actual ET using SEBS model from Landsat-5 TM data for irrigation area of Australia. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawford, T.M.; Stensrud, D.J.; Carlson, T.N.; Capehart, W.J. Using a soil hydrology model to obtain regionally averaged soil moisture values. J. Hydrometeorol. 2000, 1, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecikalski, J.R.; Diak, G.R.; Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M. Estimating fluxes on continental scales using remotely sensed data in an atmospheric-land exchange model. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1999, 38, 1352–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanguy, M.; Baille, A.; Gonzalez-Real, M.M.; Lloyd, C.; Cappelaere, B.; Kergoat, L.; Cohard, J.M. A new parameterisation scheme of ground heat flux for land surface flux retrieval from remote sensing information. J. Hydrol. 2012, 454, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cammalleri, C.; Ciraolo, G.; La Loggia, G.; Maltese, A. Daily evapotranspiration assessment by means of residual surface energy balance modeling: A critical analysis under a wide range of water availability. J. Hydrol. 2012, 452–453, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodell, M.; Famiglietti, J.S.; Chen, J.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Viterbo, P.; Holl, S.; Wilson, C.R. Basin scale estimates of evapotranspiration using GRACE and other observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.-L.; Wang, L.; Li, X.; Yang, K.; Chen, D.; Sun, L. Evaluation of evapotranspiration estimates for two river basins on the Tibetan Plateau by a water balance method. J. Hydrol. 2013, 492, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, A.; Zhao, W.; Deng, W. A Quantitative Inspection on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Land Surface Evapotranspiration in South Asia. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 4726-4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70404726
Li A, Zhao W, Deng W. A Quantitative Inspection on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Land Surface Evapotranspiration in South Asia. Remote Sensing. 2015; 7(4):4726-4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70404726
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ainong, Wei Zhao, and Wei Deng. 2015. "A Quantitative Inspection on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Land Surface Evapotranspiration in South Asia" Remote Sensing 7, no. 4: 4726-4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70404726
APA StyleLi, A., Zhao, W., & Deng, W. (2015). A Quantitative Inspection on Spatio-Temporal Variation of Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Land Surface Evapotranspiration in South Asia. Remote Sensing, 7(4), 4726-4752. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70404726