Seasonal Habitat Patterns of Japanese Common Squid (Todarodes Pacificus) Inferred from Satellite-Based Species Distribution Models
Abstract
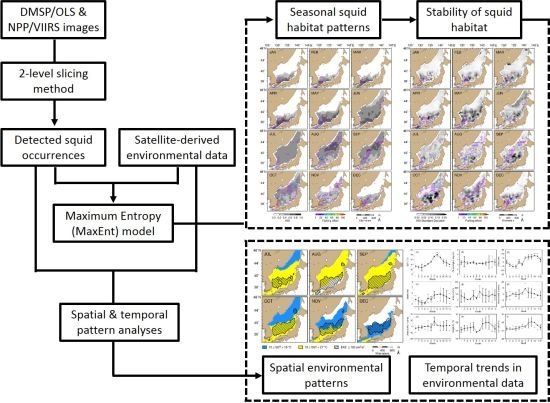
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Satellite-Derived Squid Occurrences
2.3. Satellite-Based Topographic and Environmental Variables
2.4. MaxEnt Model Construction and Evaluation
2.5. Spatio-Temporal Mapping of Potential Squid Habitat
3. Results
3.1. Distributional Patterns of Oceanographic and Geographic Factors in Squid Fishing Sites
3.2. Relative Importance of Environmental Factors to Squid Habitat
3.3. Model-Inferred Seasonal and Spatial Squid Habitat Patterns
3.4. Stability of Potential Squid Habitat and Patterns of Key Oceanographic Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sakurai, Y.; Kiyofuji, H.; Saitoh, S.; Goto, T.; Hiyama, Y. Changes in inferred spawning areas of Todarodes pacificus (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) due to changing environmental conditions. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2000, 57, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyofuji, H.; Saitoh, S.-I. Use of nighttime visible images to detect Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus fishing areas and potential migration routes in the sea of Japan. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2004, 276, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Lee, C.I.; Hwang, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Park, J.-H.; Gong, Y. Distribution and migration of Japanese common squid, Todarodes pacificus, in the southwestern part of the east (Japan) sea. Fish. Res. 2008, 91, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, B.; Chen, Y. A review of the development of Chinese distant-water squid jigging fisheries. Fish. Res. 2008, 89, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Myopsid and oegopsid squids. In Cephalopods of the World: An Annotated and Illustrated Catalogue of Cephalopod Species Known to Date; Jereb, P., Roper, C.F.E., Eds.; FAO United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2010; Volume 2, pp. 1–605. [Google Scholar]
- Food and Agriculture Organization. Fishery and aquaculture statistics 2012. In FAO Yearbook; FAO United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, T.; Fujise, Y. Geographical and seasonal changes of the prey species of minke whale in the northwestern Pacific. ICES J. Mar. Sci. 2002, 59, 516–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okutani, T. Todarodes pacificus. In Cephalopod Life Cycles; Boyle, P.R., Ed.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1983; pp. 201–214. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, H.G.; Park, J.H. Long-term changes in zooplankton and its relationship with squid, Todarodes pacificus, catch in Japan/East Sea. Fish. Oceanogr. 2002, 11, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Dudik, M.; Schapire, R.E. A maximum entropy approach to species distribution modeling. In Proceedings of the Twenty-First International Conference on Machine Learning, Banff, AB, Canada, 4–8 July 2004; p. 83.
- Lefkaditou, E.; Politou, C.-Y.; Palialexis, A.; Dokos, J.; Cosmopoulos, P.; Valavanis, V. Influences of environmental variability on the population structure and distribution patterns of the short-fin squid Illex coindetii (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) in the Eastern Ionian Sea. Hydrobiologia 2008, 612, 71–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alabia, I.D.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Mugo, R.; Igarashi, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Usui, N.; Kamachi, M.; Awaji, T.; Seito, M. Seasonal potential fishing ground prediction of neon flying squid (Ommastrephes bartramii) in the western and central North Pacific. Fish. Oceanogr. 2015, 24, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.-I.; Ito, S.-I.; Mooers, C.N.K.; Yoon, J.-H. Observation and modeling of the ocean circulation and marine ecosystem for creams/pices. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, C.O.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Park, K.-A.; Park, J.J.; Park, M.-K.; Li, S.; Kim, J.-Y.; Park, J.-E.; Kim, J.-Y.; et al. Spatial distribution of seasonality of seaWiFS chlorophyll-a concentrations in the East/Japan Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2014, 139, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashjian, C.; Arnone, R.; Davis, C.; Jones, B.; Kahru, M.; Lee, C.; Mitchell, B.G. Biological structure and seasonality in the Japan/east sea. Oceanography 2006, 19, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Zhang, C.-I. Fish and fisheries. In Oceanography of the East Sea (Japan Sa); Chang, K.-I., Zhang, C.-I., Park, C., Kang, D.-J., Ju, S.-J., Lee, S.-H., Wimbush, M., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2016; pp. 327–345. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa, Y.; Awaji, T.; Akitomo, K. Formation and circulation processes of intermediate water in the Japan sea. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 1999, 29, 1701–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Oceanic and Atomspheric Administration. Comprehensive Large Array-data Stewardship System (CLASS) Data Description. Available online: http://www.nsof.class.noaa.gov/saa/products/search?datatype_family=VIIRS_SDR (accessed on 9 November 2015).
- ETOPO1 Global Relief Model. Available online: http://ngdc.noaa.gov/mgg/global/ (accessed on 27 April 2016).
- National Oceanic and Atomspheric Administration ERDDAP. Available online: http://coastwatch.pfeg.noaa.gov/erddap/index.html (accessed on 20 April 2016).
- AVISO Satellite Altimetry Data. Available online: http://www.aviso.altimetry.fr/en/home.html (accessed on 23 April 2016).
- Chavanne, C.P.; Klein, P. Can oceanic submesoscale processes be observed with satellite altimetry? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, L22602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.J.; Anderson, R.P.; Schapire, R.E. Maximum entropy modeling of species geographic distributions. Ecol. Model. 2006, 190, 231–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClellan, C.M.; Brereton, T.; Dell'Amico, F.; Johns, D.G.; Cucknell, A.-C.; Patrick, S.C.; Penrose, R.; Ridoux, V.; Solandt, J.-L.; Stephan, E.; et al. Understanding the distribution of marine megafauna in the english channel region: Identifying key habitats for conservation within the busiest seaway on earth. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e89720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alabia, I.D.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Mugo, R.; Igarashi, H.; Ishikawa, Y.; Usui, N.; Kamachi, M.; Awaji, T.; Seito, M. Identifying pelagic habitat hotspots of neon flying squid in the temperate waters of the central North Pacific. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maxent Software for Species Habitat Modeling. Available online: https://www.cs.princeton.edu/~schapire/maxent/ (accessed on 6 May 2016).
- Thuiller, W.; Georges, D.; Robin, E. Biomod2: Ensemble Platform for Species Distribution Modeling. Available online: http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=biomod2 (accessed on 31 August 2014).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Barbet-Massin, M.; Jiguet, F.; Albert, C.H.; Thuiller, W. Selecting pseudo-absences for species distribution models: How, where and how many? Methods Ecol. Evol. 2012, 3, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijmans, R.J.; Phillips, S.J.; Leathwick, J.R.; Elith, J. Dismo: Species distribution modeling. Available online: https://cran.R-project.Org/package=dismo (accessed on 31 August 2014).
- Hijmans, R.J. Cross-validation of species distribution models: Removing spatial sorting bias and calibration with a null model. Ecology 2012, 93, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swets, J.A. Measuring the accuracy of diagnostic systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouche, O.; Tsoar, A.; Kadmon, R. Assessing the accuracy of species distribution models: Prevalence, kappa and the true skill statistic (TSS). J. Appl. Ecol. 2006, 43, 1223–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J. A coefficient of agreement for nominal scales. Educ. Psychol. Meas. 1960, 20, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, P.; Smith, W.H.F.; Scharroo, R.; Luis, J.; Wobbe, F. Generic mapping tools: Improved version released. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2013, 94, 409–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dell, J.; Wilcox, C.; Hobday, A.J. Estimation of yellowfin tuna (Thunnus albacares) habitat in waters adjacent to Australia’s east coast: Making the most of commercial catch data. Fish. Oceanogr. 2011, 20, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, W.; Seaman, C.; Baugh, K.; Cole, K.; Stevens, E.; Miller, S. Utilization of the Suomi national polar-orbiting partnership (NPP) visible infrared imaging radiometer suite (VIIRS) day/night band for arctic ship tracking and fisheries management. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 971–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syah, A.F.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Alabia, I.D.; Hirawake, T. Predicting potential fishing zones for Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) with maximum entropy models and remotely sensed data. Fish. Bull. 2016, 114, 330–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elith, J.; Leathwick, J.R. Species distribution models: Ecological explanation and prediction across space and time. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2009, 40, 677–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugo, R.M.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Takahashi, F.; Nihira, A.; Kuroyama, T. Evaluating the role of fronts in habitat overlaps between cold and warm water species in the western North Pacific: A proof of concept. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2014, 107, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidokoro, H.; Sakurai, Y. Effect of water temperature on gonadal development and emaciation of Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus (Ommastrephidae). Fish. Sci. 2008, 74, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, J.; Miyanaga, S.; Fukui, S.; Sakurai, Y. Effect of temperature on swimming behavior of paralarvae of the Japanese common squid Todarodes pacificus. Bull. Japanese Soc. Fish. Oceanogr. 2012, 76, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Puneeta, P.; Vijai, D.; Yoo, H.-K.; Matsui, H.; Sakurai, Y. Observations on the spawning behavior, egg masses and paralarval development of the ommastrephid squid Todarodes pacificus in a laboratory mesocosm. J. Exp. Biol. 2015, 218, 3825–3835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigmatullin, C.M.; Nesis, K.N.; Arkhipkin, A.I. A review of the biology of the jumbo squid Dosidicus gigas (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae). Fish. Res. 2001, 54, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zainuddin, M.; Kiyofuji, H.; Saitoh, K.; Saitoh, S.-I. Using multi-sensor satellite remote sensing and catch data to detect ocean hot spots for albacore (Thunnus alalunga) in the northwestern North Pacific. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2006, 53, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morimoto, A.; Yanagi, T.; Kaneko, A. Eddy field in the Japan sea derived from satellite altimetric data. J. Oceanogr. 2000, 56, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-K.; Niiler, P. Eddies in the southwestern East/Japan Sea. Deep Sea Res. Part I Oceanogr. Res. Pap. 2010, 57, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaube, P.; Chelton, D.B.; Strutton, P.G.; Behrenfeld, M.J. Satellite observations of chlorophyll, phytoplankton biomass, and ekman pumping in nonlinear mesoscale eddies. J. Geophys. Res Oceans 2013, 118, 6349–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-A.; Chung, J.Y.; Kim, K. Sea surface temperature fronts in the East (Japan) sea and temporal variations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L07304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Year/Month | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 121 | 1003 | 634 | 2908 |
| February | 179 | 479 | 217 | 1133 |
| March | 0 | 413 | 131 (3198) | 171 (2861) |
| April | 159 | 41 | 56 (2539) | 0 (1541) |
| May | 179 | 29 | 14 (14) | 205 (2948) |
| June | 0 | 21 | 0 (714) | 8 (8) |
| July | 0 | 6 | 101 (382) | 40 (765) |
| August | 978 | 471 | 505 | 371 |
| September | 3682 | 1673 | 1956 | 2250 |
| October | 2881 | 3208 | 5387 | 3158 |
| November | 3300 | 2814 | 1522 | 4722 |
| December | 3127 | 3963 | 2374 | 1044 |
| Month | Bartlett K-Squared | p-Value | chi-Squared |
|---|---|---|---|
| January | 0.5731 | 0.9026 | 7.8147 |
| February | 0.4550 | 0.7965 | 7.8147 |
| March | 4.2120 | 0.2395 | 7.8147 |
| April | 4.5426 | 0.2085 | 7.8147 |
| May | 3.4146 | 0.3320 | 7.8147 |
| June | 0.5315 | 0.9119 | 7.8147 |
| July | 2.5550 | 0.4654 | 7.8147 |
| August | 0.7082 | 0.8713 | 7.8147 |
| September | 0.3433 | 0.9517 | 7.8147 |
| October | 0.5641 | 0.7542 | 7.8147 |
| November | 0.6513 | 0.8846 | 7.8147 |
| December | 0.4990 | 0.9191 | 7.8147 |
| Statistics | Environmental Variables | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST | Chl-a | SSHA | EKE | u | v | dep | |
| Mean | 0.808 | 0.004 | 0.141 | 0.099 | 0.040 | 0.023 | 0.186 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.023 | 0.007 | 0.012 | 0.048 | 0.023 | 0.013 | 0.015 |
| Statistics | Model Performance Metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| AUC | TSS | Kappa | |
| Mean | 0.695 | 0.306 | 0.132 |
| Standard Deviation | 0.010 | 0.010 | 0.010 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alabia, I.D.; Dehara, M.; Saitoh, S.-I.; Hirawake, T. Seasonal Habitat Patterns of Japanese Common Squid (Todarodes Pacificus) Inferred from Satellite-Based Species Distribution Models. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110921
Alabia ID, Dehara M, Saitoh S-I, Hirawake T. Seasonal Habitat Patterns of Japanese Common Squid (Todarodes Pacificus) Inferred from Satellite-Based Species Distribution Models. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(11):921. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110921
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlabia, Irene D., Mariko Dehara, Sei-Ichi Saitoh, and Toru Hirawake. 2016. "Seasonal Habitat Patterns of Japanese Common Squid (Todarodes Pacificus) Inferred from Satellite-Based Species Distribution Models" Remote Sensing 8, no. 11: 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110921
APA StyleAlabia, I. D., Dehara, M., Saitoh, S. -I., & Hirawake, T. (2016). Seasonal Habitat Patterns of Japanese Common Squid (Todarodes Pacificus) Inferred from Satellite-Based Species Distribution Models. Remote Sensing, 8(11), 921. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110921