Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
- What caused the fissures in the Quetta Valley? Is the appearance of the fissures related to the earthquakes, or mainly caused by groundwater decline?
- (2)
- Can InSAR data be used to separate contributions of anthropogenic and tectonic processes to subsidence?
- (3)
- Are there significant changes in the slip rate along the Harnai and Karahi Faults before and after the 2008 earthquake swarms?
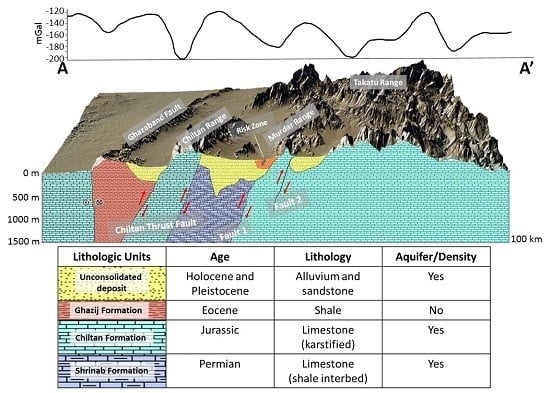
1.1. Aquifers of the Study Area
1.2. Quetta-Ziarat Earthquake Sequence
2. Datasets and Methods
2.1. Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar (InSAR)
2.2. Gravity
2.3. Two-Dimensional Seismic Profile
2.4. GPS
2.5. One-Dimensional Differential Compaction Theory
3. Results
3.1. SBAS Surface Displacement in the Quetta Valley
3.2. Structural Styles from Seismic Interpretation
3.3. SBAS Co-Seismic Displacement at the 2008 Earthquake Epicenter
3.4. Gravity
4. Discussion
4.1. Anthropogenic- versus Tectonic-Induced Subsidence
4.2. Earthquake Displacement Interpretation
4.3. Ground Fissures Interpretation and Zone of Potential Failure
5. Conclusions
- InSAR results from 2003–2010 show a rate of 5.5 mm/year for subsidence in the Quetta Valley and a rate of 1.8 mm/year for uplift in the mountain ranges surrounding the valley. A median filter was applied to the InSAR velocity curve to separate the subsidence caused by tectonic processes from subsidence caused by anthropogenic processes. The results indicate subsidence in the Quetta Valley is mainly caused by anthropogenic processes followed by movement along thrust faults.
- Multi-temporal InSAR analysis shows a sinusoidal displacement pattern for the swarm of earthquakes that occurred in 2008 along the Harnai and Karahi strike-slip faults.
- This study identified a high risk for potential fissures.
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kazmi, A.H.; Jan, M.Q. Geology and Tectonics of Pakistan; Graphic publishers: Brisbane, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Water and Power Development Authority. Individual Basinal Reports of Balochistan, Hydrogelogy Project, Quetta, 1982–2000, Pakistan; Water and Power Development Authority: Lahore, Pakistan, 2001.
- Khan, A.S.; Khan, S.D.; Kakar, D.M. Land subsidence and declining water resources in Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 70, 2719–2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohadjer, S.; Bendick, R.; Ischuk, A.; Kuzikov, S.; Kostuk, A.; Saydullaev, U.; Lodi, S.; Kakar, D.; Wasy, A.; Khan, M. Partitioning of India-Eurasia convergence in the Pamir-Hindu Kush from GPS measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, M.; Satyabala, S. Slow earthquake in Afghanistan detected by InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannert, D.; Cheema, A.; Ahmed, A.; Schäffer, U. The structural development of the western fold thrust belt, Pakistan. Geol. Jahrbuch Reihe 1992, 80, 1–60. [Google Scholar]
- Engelkemeir, R.; Khan, S.D.; Burke, K. Surface deformation in Houston, Texas using GPS. Tectonophysics 2010, 490, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Bawden, G.W.; Kim, J.-W.; Zhao, C.; Qu, W. Mapping ground deformation over Houston-Galveston, Texas using multi-temporal InSAR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 169, 290–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzovic, M.; Ghulam, A. Evaluation of land subsidence from underground coal mining using TimeSAR (SBAS and PSI) in Springfield, Illinois, USA. Nat. Hazards 2015, 79, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, X. Urbanization and land subsidence in China. China Geol. Surv. 2006, 31, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, D.; Jones, D.R.; Ingebritsen, S.E. Land Subsidence in the United States; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1999.
- Ivins, E.R.; Dokka, R.K.; Blom, R.G. Post-glacial sediment load and subsidence in coastal Louisiana. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Royden, L.; Keen, C. Rifting process and thermal evolution of the continental margin of eastern Canada determined from subsidence curves. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 1980, 51, 343–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.D.; Huang, Z.; Karacay, A. Study of ground subsidence in northwest Harris county using GPS, LiDAR, and InSAR techniques. Nat. Hazards 2014, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coplin, L.S.; Galloway, D. Houston-Galveston, Texasas—Managing coastal subsidence. In Land Subsidence in the United States; Galloway, D.L., Jones, D.R., Ingebritsen, S.E., Eds.; US Geological Survey Circular: Reston, VA, USA, 1999; pp. 35–48. [Google Scholar]
- O’Neill, M.; Van Siclen, D. Activation of Gulf Coast faults by depressuring of aquifers and an engineering approach to siting structures along their traces. Bull. Assoc. Eng. Geol. 1984, 21, 73–87. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.; Manistre, B.; Oliver, R.; Willson, G.; Scott, H. Reconnaissance Geology of Part of West Pakistan (Colombo Plan Co-Operative Project Conducted and Compiled by Hunting Survey Corporation); Government of Canada: Toronto, ON, Canada, 1960.
- GeoMapApp. Available online: http://www.geomapapp.org (accessed on 1 June 2016).
- Ryan, W.B.; Carbotte, S.M.; Coplan, J.O.; O’Hara, S.; Melkonian, A.; Arko, R.; Weissel, R.A.; Ferrini, V.; Goodwillie, A.; Nitsche, F. Global multi-resolution topography synthesis. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagintayev, Z.; Sultan, M.; Khan, S.D.; Khan, S.A.; Mahmood, K.; Yan, E.; Milewski, A.; Marsala, P. A remote sensing contribution to hydrologic modelling in arid and inaccessible watersheds, Pishin Lora basin, Pakistan. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcrow and Cameos Consultant Companies. Groundwater Management Plan for Quetta Sub-Basin; Balochistan Irrigation and Power Department: Quetta, Pakistan, 2010.
- Khan, M.A.; Bendick, R.; Bhat, M.I.; Bilham, R.; Kakar, D.M.; Khan, S.F.; Lodi, S.H.; Qazi, M.S.; Singh, B.; Szeliga, W. Preliminary geodetic constraints on plate boundary deformation on the western edge of the Indian plate from TriGGnet (Tri-University GPS Geodesy Network). J. Himal. Geosci. 2008, 41, 71–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kazmi, A.H. Active fault systems in Pakistan. Geodyn. Pak. 1979, 1979, 285–294. [Google Scholar]
- Zebker, H.A.; Rosen, P.A.; Goldstein, R.M.; Gabriel, A.; Werner, C.L. On the derivation of coseismic displacement fields using differential radar interferometry: The Landers earthquake. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth (1978–2012) 1994, 99, 19617–19634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2002, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanari, R.; Mora, O.; Manunta, M.; Mallorquí, J.J.; Berardino, P.; Sansosti, E. A small-baseline approach for investigating deformations on full-resolution differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulam, A.; Amer, R.; Ripperdan, R. A filtering approach to improve deformation accuracy using large baseline, low coherence DInSAR phase images. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Honolulu, HI, USA, 25–30 July 2010; pp. 3494–3497.
- Abir, I.A.; Khan, S.D.; Ghulam, A.; Tariq, S.; Shah, M.T. Active tectonics of western Potwar Plateau—Salt Range, northern Pakistan from InSAR observations and seismic imaging. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 168, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauknes, T.; Shanker, A.P.; Dehls, J.; Zebker, H.; Henderson, I.; Larsen, Y. Detailed rockslide mapping in northern Norway with small baseline and persistent scatterer interferometric SAR time series methods. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 2097–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandwell, D.T.; Müller, R.D.; Smith, W.H.; Garcia, E.; Francis, R. New global marine gravity model from CryoSat-2 and Jason-1 reveals buried tectonic structure. Science 2014, 346, 65–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quetta Water Supply and Environmental Improvement Project. Available online: https://www.adb.org/projects/documents/quetta-water-supply-and-environmental-improvement-project (accessed on 16 November 2016).
- Alam, K.; Ahmad, N. Determination of aquifer geometry through geophysical methods: A case study from Quetta Valley, Pakistan. Acta Geophys. 2014, 62, 142–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambolat, G.; Freeze, R. Mathmatical Simulation of Subsidence of Venice; Transactions-American Geophysical Union, 1973; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 1973; p. 214. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, R.; Yeats, R.; Khan, S.; Subhani, A.; Bonelli, D. Crystalline rocks of the Spinatizha area, Pakistan. J. Struct. Geol. 1981, 3, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.R. Median filtering: Review and a new F/K analogue design. J. Can. Soci. Explor. Geophys. 1985, 21, 54–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.S.; Wessel, P. Directional median filtering for regional-residual separation of bathymetry. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, T.L. Faulting caused by groundwater level declines, San Joaquin Valley, California. Water Resour. Res. 1980, 16, 1065–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Van Nieuwenhuise, D.; Khan, S.D. Integrated fault and hazard analysis in Downtown Houston, Texas. GCAGS J. 2015, 4, 147–154. [Google Scholar]
- Holzer, T.L.; Davis, S.N.; Lofgren, B.E. Faulting caused by groundwater extraction in southcentral Arizona. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth (1978–2012) 1979, 84, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattahi, H.; Amelung, F. InSAR observations of strain accumulation and fault creep along the Chaman Fault system, Pakistan and Afghanistan. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.; Gahalaut, V.; Chopra, S.; Shan, B. Tectonic implications and seismicity triggering during the 2008 Baluchistan, Pakistan earthquake sequence. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 45, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monalisa, Q.J. Geoseismological study of the Ziarat (Balochistan) Earthquake (Doublet?) of October 28, 2008. Curr. Sci. 2010, 98, 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Pinel-Puysségur, B.; Grandin, R.; Bollinger, L.; Baudry, C. Multifaulting in a tectonic syntaxis revealed by InSAR: The case of the Ziarat earthquake sequence (Pakistan). J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119, 5838–5854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzo, G.; Boncori, J.P.M.; Atzori, S.; Antonioli, A.; Salvi, S. Deformation of the western Indian Plate boundary: Insights from differential and multi-aperture InSAR data inversion for the 2008 Baluchistan (Western Pakistan) seismic sequence. Geophys. J. Int. 2014, 198, 25–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.D.; Yeats, R.S. Geological reconnaissance of the Chaman Fault in Pakistan. Geodyn. Pak. 1979, 9, 351–357. [Google Scholar]
- Leeman, J.; Saffer, D.; Scuderi, M.; Marone, C. Laboratory observations of slow earthquakes and the spectrum of tectonic fault slip modes. Nat. Commun. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fialko, Y. Interseismic strain accumulation and the earthquake potential on the southern San Andreas fault system. Nature 2006, 441, 968–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.P.; Williams, G.A. Sedimentary basin inversion and intra-plate shortening. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2004, 65, 277–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.; Pytharouli, S.; Stiros, S. Ground subsidence, Quaternary faults and vulnerability of utilities and transportation networks in Thessaly, Greece. Environ. Geol. 2007, 52, 1085–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| ENVISAT ASAR Descending 40 Images | ALOS PALSAR Ascending 15 Images | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 April 2003 | 18 November 2004 | 1 June 2006 | 24 December 2006 |
| 8 May 2003 | 23 December 2004 | 28 December 2006 | 8 February 2007 |
| 12 June 2003 | 27 January 2005 | 21 June 2007 | 26 June 2007 |
| 30 October 2003 (2 images) | 3 March 2005 | 8 November 2007 | 11 August 2007 |
| 8 January 2004 | 7 April 2005 | 1 May 2008 | 27 December 2007 |
| 12 February 2004 | 12 May 2005 (2 images) | 27 November 2008 | 11 February 2008 |
| 18 March 2004 | 16 June 2005 | 11 January 2009 | 28 March 2008 |
| 22 April 2004 | 21 July 2005 | 21 May 2009 | 13 November 2008 |
| 27 May 2004 | 25 August 2005 | 3 September 2009 | 29 December 2008 |
| 5 August 2004 | 29 September 2005 | 12 November 2009 | 13 February 2009 |
| 9 September 2004 | 3 November 2005 | 21 January 2010 | 1 October 2009 |
| 14 October 2004 | 8 December 2005 | 6 May 2010 | 16 February 2010 |
| 12 January 2006 | 23 September 2010 | 4 July 2010 | |
| 19 August 2010 | |||
| 19 February 2011 | |||
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, J.; Khan, S.D.; Ghulam, A.; Crupa, W.; Abir, I.A.; Khan, A.S.; Kakar, D.M.; Kasi, A.; Kakar, N. Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110956
Huang J, Khan SD, Ghulam A, Crupa W, Abir IA, Khan AS, Kakar DM, Kasi A, Kakar N. Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(11):956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110956
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Jingqiu, Shuhab D. Khan, Abduwasit Ghulam, Wanda Crupa, Ismail A. Abir, Abdul S. Khan, Din M. Kakar, Aimal Kasi, and Najeebullah Kakar. 2016. "Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan" Remote Sensing 8, no. 11: 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110956
APA StyleHuang, J., Khan, S. D., Ghulam, A., Crupa, W., Abir, I. A., Khan, A. S., Kakar, D. M., Kasi, A., & Kakar, N. (2016). Study of Subsidence and Earthquake Swarms in the Western Pakistan. Remote Sensing, 8(11), 956. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8110956