Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sets and Preprocessing
2.2.1. Soil Samples and Preprocessing
2.2.2. Soil Spectra and Preprocessing
2.2.3. Soil Physico-Chemical Measurement
2.2.4. Satellite Imagery and Preprocessing
2.3. Methodological Approach
3. Results
3.1. Salinity and Alkalinity Properties of Soil Samples
3.2. Spectral Properties of Sample Soils
3.3. Sensitivity of Broad Band Reflectance
3.4. Stepwise Regression for Estimating Soil pH and EC
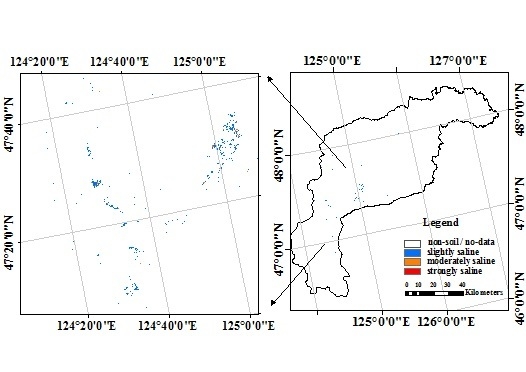
3.5. Soil EC and pH Distributions in the Study Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Characteristics of the Study Area
4.2. Potential Use of Soil Spectra for Soil Alkalinity and Salinity Retrieval
4.3. Potential Use of OLI Image for Soil Alkalinity and Salinity Retrieval
4.4. Geographic and Land Use Consideration of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, L.; Seki, K.; Miyazaki, T.; Ishihama, Y. The causes of soil alkalinization in the Songnen Plain of Northeast China. Paddy Water Environ. 2009, 7, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G. Assessing temporal and spatial changes of salinity using fuzzy logic, remote sensing and GIS: Foundations of expert system. Ecol. Model. 2001, 144, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.Z.; Li, J.D. Dynamic population models of the ecological dominance during the deterioration of Leymuschinensis grassland. ActaPhytoecol Sin. 1995, 19, 170–174. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.J. The alkili-saline land and agricultural sustainable development of the Western Songnen Plain in China. SciGeogr Sin. 2000, 20, 51–55. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, N.F.; Bounlom, V.; Tang, J.; Bian, J.M. Study on the relation between the formation of saline-alkali soil and the neotectonic movement. Global Geol. 2005, 24, 282–288. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.Z.; Li, Q.S. Research of mechanism of saline desertification in Western Songnen Plain. Soil Water Conserv. 2003, 17, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, R.Z.; Gao, Q.; Chen, Q. Effects of climatic change on biomass and biomass allocation in Leymuschinensis (Poaceae) along the North-east China Transect (NECT). J. Arid Environ. 2003, 54, 653–665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.S.; Tian, Z.C. The groundwater effect in the process of soil salinization of the Songnen Plain, Jilin province. Jilin Geol. 2002, 21, 79–87. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.F.; Wang, S.J. Mechanism of freeze-thaw action in the process of soil salinization in northeast China. Environ. Geol. 2001, 41, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.W.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.C. Analyses on current situation, causes of formation, and way of management of desertification in western Northeast Plain of China. Quat. Sci. 2005, 25, 63–73. [Google Scholar]
- Fauck, R. Influences of agriculture practices on soil degradation. FAO Soil Bulletion. UN. 1977, 34, 83–84. [Google Scholar]
- Schipper, L.A.; Sparling, G.P. Performance of soil condition indicators aross taxonomic groups and land uses. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csillag, F.; Pásztor, L.; Biehl, L.L. Spectral band selection for the characterization of salinity status of soils. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 43, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckman, H.O.; Brady, N.C.; Weil, R.R. The Nature and Properties of Soils; Prentice Hall: Englewod Cliffs, NJ, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, L.A. Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils. Soil Sci. 1954, 78, 154–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y. Detection in Near-Infrared Spectroscopy of Soils; Chemistry Industry Press: Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Corwin, D.L.; Lesch, S.M. Application of soil electrical conductivity to precision ag-riculture: Theory, principles, and guidelines. Agron. J. 2003, 95, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhoades, J.D. Soluble Salts; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Dwivedi, R.S. Monitoring of salt-affected soils of the Indo-Gangetic alluvial plains using principal component analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah Shamsi, S.R.; Zare, S.; Abtahi, S.A. Soil salinity characteristics using moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) images and statistical analysis. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2013, 59, 471–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobell, D.B.; Lesch, S.M.; Corwin, D.L.; Ulmer, M.G.; Anderson, K.A.; Potts, D.J.; Doolittle, J.A.; Matos, M. Regional-scale assessment of soil salinity in the Red River Valley using multi-year MODIS EVI and NDVI. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.R.M.; Dwivedi, R.S.; Venkataratnam, L.; Ravishankar, T.; Thammappa, S.S.; Bhargawa, G.P.; Singh, A.N. Mapping the magnitude of sodicity in part of the Indo-Gangetic Plains of Uttar Pradesh, Northern India using Landsat-TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.S.; Liu, Z.L. Remote sensing and mapping of saline sodic land based on spectral characteristics for Da’an city. Syst. Sci. Compr. Stud. Agric. 2007, 23, 178–182. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.; Zinck, J.A. Spatial discrimination of salt- and sodium-affected soil surfaces. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.I. Categorical fuzziness: A comparison between crisp and fuzzy class boundary modelling for mapping salt-affected soils using Landsat TM data and a classification based on anion ratios. Ecol. Model. 2003, 168, 371–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, R.S.; Sreenivas, K. Image transforms as a tool for the study of soil salinity and alkalinity dynamics. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 605–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, N.K.; Joshi, D.C. Potentiality of Landsat, SPOT and IRS satellite imagery, for recognition of salt affected soils in Indian Arid Zone. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 3001–3014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrjardi, R.T.; Mahmoodi, S.; Taze, M.; Sahebjalal, E. Accuracy assessment of soil salinity map in Yazd-Ardakan Plain, central Iran, based on Landsat ETM+ imagery. Am.-Eurasian J. Agric. Environ. Sci. 2008, 3, 708–712. [Google Scholar]
- Lillesand, T.M.; Kiefer, R.W. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, K.L.; Xiong, H.G.; Zang, F. Optimal model of soil pH and influencing factors by using hyperspectral data. Soils 2014, 46, 544–549. [Google Scholar]
- Ong, C.C.H.; Cudahy, T.J. Mapping contaminated soils: Using remotely-sensed hyperspectral data to predict pH. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2014, 65, 897–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.L.; Gong, P.; Zhu, Z.L. A spectral index for estimating soil salinity in the Yellow River Delta Region of China using EO-1 Hyperion data. Pedosphere 2010, 20, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, Z.M.; Song, K.S.; Hu, M.G.; Duan, H.T. Soil saline-alkalization evaluation basing on spectral reflectance characteristics. J. Infrared Millim. Waves. 2008, 27, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Guedon, A.M.; El-Harti, A.; Cherkaoui, F.; El-Ghmari, A. Characterization of slightly and moderately saline and sodic soils in irrigated agriculture land using simulated data of advanced land imaging (EO-1) sensor. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant. Anal. 2008, 39, 2795–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.W.; Liu, Y.B.; Tao, J.M.; Weng, Y.L. Soil salinity retrieval from advanced multi-spectral sensor with partial least square regression. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 488–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, E.R.; Baumgardner, M.F. Physiochemical, Site and Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Characteristics of Uniformly Moist Soils; LARS, Purdue University: West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Metternicht, G.I.; Zinck, J.A. Remote sensing of soil salinity: Potentials and constraints. Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 85, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLean, E.O. Soil pH and Lime Requirement. Methods of Soil Analysis. Part. 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; ASA and SSSA: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.; Gao, X.Z. Technical Specifications of Soil Analysis, 2nd ed.; Chinese Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Morfitt, R.; Barsi, J.; Levy, R.; Markham, B.; Micijevic, E.; Ong, L.; Scaramuzza, P.; Vanderwerff, K. Landsat-8 Operational Land Imager (OLI) radiometric performance on-orbit. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 2208–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The United States Geological Survey (USGS). Available online: http://glovis.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 4 May 2015).
- Adler-Golden, S.M.; Matthew, M.W.; Bernstein, L.S.; Levine, R.Y.; Berk, A.; Richtsmeier, S.C.; Acharya, P.K.; Anderson, G.P.; Felde, G.; Gardner, J.; et al. Atmospheric correction for shortwave spectral imagery based on MODTRAN4. Proc. SPIE 1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, A.F. Comparison of ATREM, ACORN, and FLAASH atmospheric corrections using low-altitude AVIRIS data of Boulder, Co. In Proceedings of the Summaries of 13th JPL Airborne Geoscience Workshop, Pasadena, CA, USA, 31 March 2004.
- Yu, L.Y.; Cai, H.J.; Yao, F.Q.; Zheng, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.J. Applicability of vegetation indices to estimate fractional vegetation coverage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 231–239. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.H. Mathematical Methods in Contemporary Geography; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kutner, M.H.; Nachtsheim, C.J.; Neter, J. Applied Linear Statistical Models; Irwin: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Belsley, D.A.; Kuh, E.; Welsch, R.E. Regression Diagnostics: Identifying Influential Data and Sources of Collinearity; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Chorom, M.; Rengasamy, P. Carbonate chemistry, pH, and physical properties of an alkaline sodic soil as affected by various amendments. Aust. J. Soil Res. 1997, 35, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chorom, M.; Rengasamy, P.; Murray, R.S. Clay dispersion as infuenced by pH and net particle charge of sodic soils. Soil Res. 1994, 32, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Granados, F.; Jurado-Expósito, M.; Peña-Barragán, J.M.; García-Torres, L. Using geoestatistical and remote sensing approaches for mapping soil properties. Eur. J. Agron. 2005, 23, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, F.R. Physicochemical, Site, and Bidirectional Reflectance Factor Characteristics of Uniformly Moist Soils. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Bear, F.E. Chemistry of the Soil, 2nd ed.; Reinhold Publication Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Panda, B.C. Remote Sensing: Principle and Application; Viva Books Pvt Ltd.: New Delhi, India, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Farifteh, J.; Farshad, A. Remote sensing and modeling of topsoil properties: A clue for assessing land degradation. In Proceedings of the 17th World Congress of Soil Science CD-ROM Conference, Bangkok, Thailand, 14–21 August 2002.






| Data sets | Samples | Types | Time | Measurements |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spectral properties analysis and predictive model building | 113 | cultivated lands and grasslands | spring 2014, 2015 | pH, EC, spectra |
| Soil properties analysis | 108 | cultivated lands and grasslands | Autumn 2013 | pH, EC, contents of eight ions, ESP |
| Accuracy assessment of image inversion | 14 | cultivated lands and grasslands | spring 2014 | pH, EC |
| Data-Set | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | SD | Median | Confidence Interval * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.92 | 10.72 | 5.34 | 1.65 | 8.00 | 7.68–8.16 |
| EC (dS/m) | 0.76 | 17.80 | 0.05 | 1.76 | 0.28 | 0.51–1.00 |
| SO42− (mg/L) | 284.32 | 522.43 | 3.72 | 115.63 | 283.81 | 266.41–302.24 |
| HCO3− (mg/L) | 147.68 | 1507.00 | 55.57 | 120.26 | 127.86 | 129.05–166.32 |
| CO32− (mg/L) | 47.62 | 314.52 | 0 | 90.03 | 0 | 33.67–61.57 |
| Na+ (mg/L) | 154.94 | 808.50 | 7.28 | 132.34 | 129.23 | 134.43–175.44 |
| K+ (mg/L) | 7.41 | 28.89 | 3.06 | 3.55 | 6.45 | 6.87–7.96 |
| Ca2+ (mg/L) | 116.85 | 177.80 | 43.45 | 23.94 | 112.75 | 113.15–120.56 |
| Mg2+ (mg/L) | 16.90 | 59.85 | 4.78 | 7.37 | 15.64 | 15.76–18.04 |
| Data-set | EC | pH | SO42− | HCO3− | CO32− | Na+ | K+ | Ca2+ | Mg2+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EC | 1 | ||||||||
| pH | 0.77 * | 1 | |||||||
| SO42− | −0.17 | −0.26 | 1 | ||||||
| HCO3− | 0.25 | 0.18 | 0.0006 | 1 | |||||
| CO32− | 0.87 * | 0.88 * | −0.32 | 0.15 | 1 | ||||
| Na+ | 0.93 * | 0.81 * | −0.17 | 0.33* | 0.86 * | 1 | |||
| K+ | −0.12 | −0.23 | 0.17 | −0.09 | −0.05 | −0.15 | 1 | ||
| Ca2+ | −0.32 | −0.39 * | 0.41 * | −0.04 | −0.28 | −0.31 * | 0.48 * | 1 | |
| Mg2+ | 0.13 | 0.21 | 0.32 | −0.04 | 0.19 | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 1 |
| Data-Set | pH | EC | b1 | b2 | b3 | b4 | b5 | b6 | b7 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 1 | ||||||||
| EC | 0.51 * | 1 | |||||||
| b1 | 0.82 * | 0.78 * | 1 | ||||||
| b2 | 0.82 * | 0.77 * | 1 * | 1 | |||||
| b3 | 0.81 * | 0.75 * | 1 * | 1 * | 1 | ||||
| b4 | 0.79 * | 0.72 * | 0.98 * | 0.99 * | 1 * | 1 | |||
| b5 | 0.73 * | 0.66 * | 0.94 * | 0.95 * | 0.98 * | 0.97 * | 1 | ||
| b6 | 0.30 * | 0.41 * | 0.62 * | 0.62 * | 0.64 * | 0.66 * | 0.77 * | 1 | |
| b7 | 0.26 * | 0.35 * | 0.54 * | 0.54 * | 0.56 * | 0.58 * | 0.67 * | 0.96 * | 1 |
| Model | Calibration Set | Collinearity Diagnostics | Validation Set | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2Adj | Variance Inflation | Proportion of Variation | Condition Index | RMSE | R2 | Slope | |
| pH | 0.74 | 0.73 | 2.11 | 45.77% 99.26% | 18.94 | 0.98 | 0.75 | 0.61 |
| EC | 0.73 | 0.72 | - | - | - | 1.07 dS/m | 0.52 | 1.49 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bai, L.; Wang, C.; Zang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, Q.; Wu, Y. Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020163
Bai L, Wang C, Zang S, Zhang Y, Hao Q, Wu Y. Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(2):163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020163
Chicago/Turabian StyleBai, Lin, Cuizhen Wang, Shuying Zang, Yuhong Zhang, Qiannan Hao, and Yuexiang Wu. 2016. "Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China" Remote Sensing 8, no. 2: 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020163
APA StyleBai, L., Wang, C., Zang, S., Zhang, Y., Hao, Q., & Wu, Y. (2016). Remote Sensing of Soil Alkalinity and Salinity in the Wuyu’er-Shuangyang River Basin, Northeast China. Remote Sensing, 8(2), 163. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8020163