Anatomy of Subsidence in Tianjin from Time Series InSAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Geological Background
2.1. Tectonic Divisions
2.2. Sediments
2.3. Hydrogeological Conditions
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Methods
4. Results
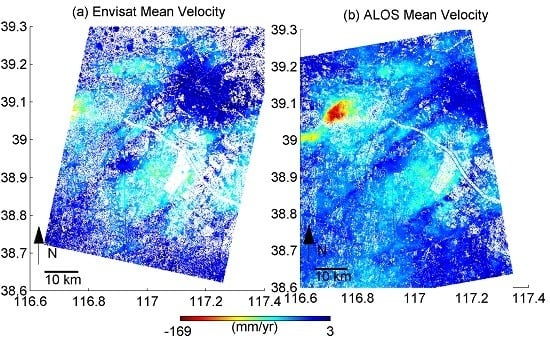
4.1. Mean Velocities from ALOS and Envisat
4.2. InSAR and Leveling Comparison
4.3. Model of West Subsidence
5. Discussion
5.1. Impact of Reservoir Grid Size
5.2. Tectonic Division and Its Effect on Subsidence
5.3. Water Level and Subsidence
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| InSAR | Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| ASAR | Advanced Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| ALOS | Advanced Land Observing Satellite |
| PALSAR | The Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar |
| NCP | North China Plain |
| ROI_PAC | Repeat Orbit Interferometry PACkage |
| DORIS | The Delft Object-oriented Radar Interferometric software |
| StaMPS | Stanford Method for Persistent Scatterers |
| SRTM | Shuttle Radar Topography Mission |
| PS | Persistent Scatter |
| SDFP | Slowly-Decorrelating Filtered Phase |
| APS | Atmospheric Phase Screen |
| GWS | Ground Water Storage |
Appendix


References
- Chaussard, E.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Amelung, F. Land subsidence in central Mexico detected by ALOS InSAR time-series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 94–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmanoglu, B.; Dixon, T.H.; Wdowinski, S.; Cabral-Cano, E.; Jiang, Y. Mexico city subsidence observed with persistent scatterer InSAR. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform. 2011, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Wang, H.-S.; Sun, Y.-L.; Hou, J.-G.; Liang, J. Long-term land subsidence monitoring of Beijing (China) using the small baseline subset (SBAS) technique. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 3648–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of the People’s Republic of China. Population of Tianjin in 2010 from Sixth Nationwide Population Census. Available online: http://www.Stats.Gov.Cn/tjsj/tjgb/rkpcgb/dfrkpcgb/201202/t20120228_30405.Html (accessed on 11 Novermber 2015). (In Chinese)
- Yi, L.; Zhang, F.; Xu, H.; Chen, S.; Wang, W.; Yu, Q. Land subsidence in Tianjin, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2010, 62, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.L.; Yue, Z.Q.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, S.J. Review on current status and challenging issues of land subsidence in China. Eng. Geol. 2004, 76, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.L.; Wang, S.J.; Lee, C.F.; Li, M.L. Characteristics and trends of land subsidence in Tanggu, Tianjin, China. Bull. Eng. Geol. Environ. 2002, 61, 213–225. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Q.; Perissin, D.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, Y. L- and X-band multi-temporal InSAR analysis of Tianjin subsidence. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 7933–7951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ge, L.; Li, X.; Ng, A.-M. Monitoring ground surface deformation over the North China Plain using coherent ALOS PALSAR differential interferograms. J. Geod. 2013, 87, 253–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jia, H.; Nie, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B.; Li, Z. Detecting subsidence in coastal areas by ultrashort-baseline TCPInSAR on the time series of high-resolution TerraSAR-X images. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 1911–1923. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zou, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B. Deformation trend extraction based on multi-temporal InSAR in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erban, L.E.; Gorelick, S.M.; Zebker, H.A. Groundwater extraction, land subsidence, and sea-level rise in the Mekong Delta, Vietnam. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, S.A.; Overeem, I.; Steckler, M.S.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Seeber, L.; Akhter, S.H. InSAR measurements of compaction and subsidence in the Ganges-Brahmaputra Delta, Bangladesh. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2014, 119, 1768–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani, M.; Valadan Zoej, M.J.; Hooper, A.; Hanssen, R.F.; Entezam, I.; Saatchi, S. Hybrid conventional and persistent scatterer SAR interferometry for land subsidence monitoring in the Tehran Basin, Iran. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 79, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Walter, T.R.; Sharifi, M.A.; Fielding, E.; Schenk, A.; Anderssohn, J.; Zschau, J. Land subsidence in Iran caused by widespread water reservoir overexploitation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 428–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderssohn, J.; Wetzel, H.-U.; Walter, T.R.; Motagh, M.; Djamour, Y.; Kaufmann, H. Land subsidence pattern controlled by old alpine basement faults in the Kashmar Valley, Northeast Iran: Results from InSAR and levelling. Geophys. J. Int. 2008, 174, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motagh, M.; Djamour, Y.; Walter, T.R.; Wetzel, H.-U.; Zschau, J.; Arabi, S. Land subsidence in Mashhad Valley, Northeast Iran: Results from InSAR, levelling and GPS. Geophys. J. Int. 2007, 168, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiding, M.; Árnadóttir, T.; Jónsson, S.; Decriem, J.; Hooper, A. Plate boundary deformation and man-made subsidence around geothermal fields on the Reykjanes Peninsula, Iceland. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 2010, 194, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Wu, L.; Ran, Y.; Ye, Y. The concealed active tectonics and their characteristics as revealed by drainage density in the North China Plain (NCP). J. Asian Earth Sci. 2003, 21, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Pang, Z.; Lin, L.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, F.; Duan, Z.; Zong, Z. Hydrogeochemical and isotopic evidence for trans-formational flow in a sedimentary basin: Implications for CO2 storage. Appl. Geochem. 2013, 30, 4–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Xiao, G.; Wang, Q.; Shi, X.; Wang, X. Sedimentary history of the western bohai coastal plain since the late pliocene: Implications on tectonic, climatic and sea-level changes. J. Asian Earth Sci. 2012, 54–55, 192–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minissale, A.; Borrini, D.; Montegrossi, G.; Orlando, A.; Tassi, F.; Vaselli, O.; Huertas, A.D.; Yang, J.; Cheng, W.; Tedesco, D.; et al. The Tianjin geothermal field (North-Eastern China): Water chemistry and possible reservoir permeability reduction phenomena. Geothermics 2008, 37, 400–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Stratigraphy and sedimentary features of paleogene sediments of Bohai bay basin. Mar. Geol. Res. 1981, 1, 11–27. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jia, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, J.; Fang, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J. Crustal structure of the rift-depression basin and Yanshan uplift in the northeast part of North China. Chin. J. Geophys. 2009, 52, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, P.; Teng, J. Crustal structure and its tectonic responses during mesozoic and cenozoic in Beijing-Tianjin-Tangshan and its adjacent region. Chin. J. Geophys. 2008, 51, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Su, C.; Shao, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X. Development and application of a regional land subsidence model for the plain of Tianjin. J. Earth Sci. 2014, 25, 550–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Li, C.; Liu, Z. Characteristics of the groundwater level regime and effect factors in the plain region of Tianjin city. Geol. Surv. Res. 2011, 34, 313–320. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rosen, P.A.; Hensley, S.; Joughin, I.R.; Li, F.K.; Madsen, S.N.; Rodriguez, E.; Goldstein, R.M. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry, Persistent Scatterer Technique; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; Volume 12. [Google Scholar]
- Farr, T.G. The shuttle radar topography mission. Rev. Geophys. 2007, 45, 37–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Segall, P.; Zebker, H.A. Persistent scatterer interferometric synthetic aperture radar for crustal deformation analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.; Zebker, H.; Segall, P.; Kampes, B. A new method for measuring deformation on volcanoes and other natural terrains using InSAR persistent scatterers. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colesanti, C.; Wasowski, J. Investigating landslides with space-borne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) interferometry. Eng. Geol. 2006, 88, 173–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Kincal, C.; Zhang, J.; Zeng, Q.; Muller, J.-P. Using advanced InSAR time series techniques to monitor landslide movements in badong of the three gorges region, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinform. 2013, 21, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Zebker, H.A. Two-dimensional phase unwrapping with use of statistical models for cost functions in nonlinear optimization. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2001, 18, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirzaei, M.; Bürgmann, R. Topography correlated atmospheric delay correction in radar interferometry using wavelet transforms. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolivet, R.; Grandin, R.; Lasserre, C.; Doin, M.P.; Peltzer, G. Systematic InSAR tropospheric phase delay corrections from global meteorological reanalysis data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Fielding, E.J.; Cross, P.; Muller, J.-P. Interferometric synthetic aperture radar atmospheric correction: GPS topography-dependent turbulence model. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 1059–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Ji, J.; Han, Y.; Chen, J. Research on vertical stability of Liqizhuang bedrock point. J. Geod. Geodyn. 2013, 33, 49–52. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Leighton, J.M.; Sowter, A.; Tragheim, D.; Bingley, R.M.; Teferle, F.N. Land motion in the urban area of nottingham observed by ENVISAT-1. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 982–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.M.; Shirzaei, M. Spatiotemporal characterization of land subsidence and uplift in phoenix using insar time series and wavelet transforms. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 5822–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokker, P.; Orlic, B. Semi-analytic modelling of subsidence. Math. Geol. 2006, 38, 565–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTigue, D.F. Elastic stress and deformation near a finite spherical magma body: Resolution of the point source paradox. J. Geophys. Res. 1987, 92, 12931–12940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.C. Analysis of discrete ill-posed problems by means of the L-curve. SIAM Rev. 1992, 34, 561–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Pan, Y.; Gong, H.; Yeh, P.J.F.; Li, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhao, W. Subregional-scale groundwater depletion detected by grace for both shallow and deep aquifers in North China Plain. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Leblanc, M.; Tweed, S.; Liu, W. Groundwater depletion in the Hai River Basin, China, from in situ and grace observations. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 60, 671–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Zhong, M.; Lemoine, J.-M.; Biancale, R.; Hsu, H.-T.; Xia, J. Evaluation of groundwater depletion in north China using the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) data and ground-based measurements. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 2110–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, G.; Zheng, C.; Scanlon, B.R.; Liu, J.; Li, W. Use of flow modeling to assess sustainability of groundwater resources in the North China Plain. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisowski, M. Analytical volcano deformation source models. In Volcano Deformation; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 279–304. [Google Scholar]
- Burbey, T.J.; Warner, S.M.; Blewitt, G.; Bell, J.W.; Hill, E. Three-dimensional deformation and strain induced by municipal pumping, part 1: Analysis of field data. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 123–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-S.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, C.-Y.; Wang, Q.-L.; Ji, L.-Y. Monitoring land subsidence and fault deformation using the small baseline subset insar technique: A case study in the Datong Basin, China. J. Geodyn. 2014, 75, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhao, C.; Yang, C.; Qu, W. Recent ground deformation of Taiyuan basin (China) investigated with C-, L-, and X-bands SAR images. J. Geodyn. 2013, 70, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, F.; Galloway, D.L.; Bell, J.W.; Zebker, H.A.; Laczniak, R.J. Sensing the ups and downs of Las Vegas: InSAR reveals structural control of land subsidence and aquifer-system deformation. Geology 1999, 27, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaussard, E.; Bürgmann, R.; Shirzaei, M.; Fielding, E.J.; Baker, B. Predictability of hydraulic head changes and characterization of aquifer-system and fault properties from insar-derived ground deformation. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2014, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G. The Research on the Main Factors of Controlling the Development of Ordovician Geothermal Reservoirs in Tianjin; China University of Geoscience: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L. Sustainable Development and Utilization of Thermal Groundwater Resources in the Geothermal Reservoir of the Wumishan Group in Tianjin; China University of Geosciences: Beijing, China, 2006. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y. Tectonic Activity Features and Segmentation of Seismic risk of the Buried Haihe Fault in Tianjin; China Earthquake Administration: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Shao, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Ren, F.; Yao, Z. A study on the quaternary activity of the Tianjin fault. Earthq. Res. China 2010, 24, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. The Geochemical Character of Geothermal Liquid in Tianjin Area; China University of Geoscience: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, S.; Gao, B.; Li, X.; Li, H.; Hu, Y. Character and water temperature conductivity of the Cangdong fault Tianjin segment. Geol. Surv. Res. 2007, 30, 121–127. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, E.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F.; Yin, H. Increased yield potential of wheat-maize cropping system in the North China Plain by climate change adaptation. Clim. Chang. 2012, 113, 825–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Jin, M.; van Genuchten, M.T.; Wang, B. Groundwater recharge at five representative sites in the Hebei plain, China. Groundwater 2011, 49, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Meteorological Administration. Available online: http://data.Cma.Gov.Cn/ (accessed on 20 September 2015). (In Chinese)
- Wang, S.; Song, X.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, G.; Liu, C.; Liu, J. Shallow groundwater dynamics in North China Plain. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Qinghai, X.; Xiuqing, Z.; Yonghong, M. Palaeochannels on the North China Plain: Types and distributions. Geomorphology 1996, 18, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, J.; Zebker, H.A.; Galloway, D.L.; Amelung, F. Seasonal subsidence and rebound in Las Vegas valley, Nevada, observed by synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A practical guide to wavelet analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Application of the cross wavelet transform and wavelet coherence to geophysical time series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomás, R.; Li, Z.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.M.; Liu, P.; Singleton, A. Using wavelet tools to analyse seasonal variations from InSAR time-series data: A case study of the Huangtupo landslide. Landslides 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Location | Tanggu District of Tianjin | Plain to the South of Baodi Fault | Plain of Tianjin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Literature | [6] (unit: m) | [27] (unit: m) | [26] (unit: m) |
| Aquifer I | 60–70 | <70 | 40–123 |
| Aquifer II | 170–190 | 160–220 | 191–202 |
| Aquifer III | 270–310 | 260–340 | 309–326 |
| Aquifer IV | 370–400 | 360–430 | 390–405 |
| Aquifer V | ~550 | 500–550 | 505–544 |
| Aquifer VI | N/A | N/A | 608–613 |
| SAR Image | Acquisition Time | Baseline Perpendicular |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4 January 2008 | −401 m |
| 2 | 8 February 2008 | 289 m |
| 3 | 14 March 2008 | −75 m |
| 4 | 18 April 2008 | 270 m |
| 5 | 23 May 2008 | 32 m |
| 6 | 1 August 2008 | 129 m |
| 7 | 5 September 2008 | 312 m |
| 8 | 10 October 2008 | 0 m |
| 9 | 23 January 2009 | 164 m |
| 10 | 27 February 2009 | 235 m |
| 11 | 3 April 2009 | 624 m |
| 12 | 8 May 2009 | −48 m |
| 13 | 12 June 2009 | 308 m |
| SAR Image | Acquisition Time | Baseline Perpendicular |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 17 January 2007 | 295 m |
| 2 | 4 March 2007 | 1963 m |
| 3 | 20 July 2007 | 2700 m |
| 4 | 20 October 2007 | 3154 m |
| 5 | 5 December 2007 | 3288 m |
| 6 | 20 January 2008 | 3764 m |
| 7 | 21 April 2008 | 4866 m |
| 8 | 6 June 2008 | 4829 m |
| 9 | 22 July 2008 | 1624 m |
| 10 | 6 September 2008 | −746 m |
| 11 | 7 December 2008 | 0 m |
| 12 | 22 January 2009 | 484 m |
| 13 | 9 March 2009 | 938 m |
| 14 | 24 April 2009 | 1490 m |
| 15 | 9 September 2009 | 1756 m |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, P.; Li, Q.; Li, Z.; Hoey, T.; Liu, G.; Wang, C.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Singleton, A. Anatomy of Subsidence in Tianjin from Time Series InSAR. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030266
Liu P, Li Q, Li Z, Hoey T, Liu G, Wang C, Hu Z, Zhou Z, Singleton A. Anatomy of Subsidence in Tianjin from Time Series InSAR. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(3):266. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030266
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Peng, Qingquan Li, Zhenhong Li, Trevor Hoey, Guoxiang Liu, Chisheng Wang, Zhongwen Hu, Zhiwei Zhou, and Andrew Singleton. 2016. "Anatomy of Subsidence in Tianjin from Time Series InSAR" Remote Sensing 8, no. 3: 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030266
APA StyleLiu, P., Li, Q., Li, Z., Hoey, T., Liu, G., Wang, C., Hu, Z., Zhou, Z., & Singleton, A. (2016). Anatomy of Subsidence in Tianjin from Time Series InSAR. Remote Sensing, 8(3), 266. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8030266