Season Spotter: Using Citizen Science to Validate and Scale Plant Phenology from Near-Surface Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
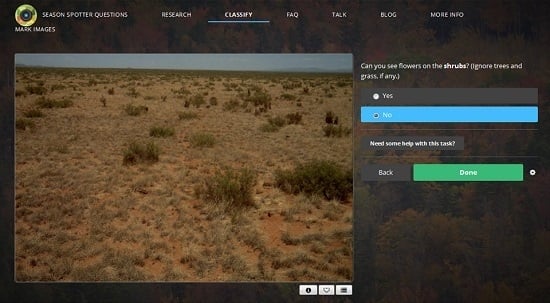
2.1. Citizen Science: Season Spotter
2.2. PhenoCam Images
2.3. Analyses
2.3.1. Classification Accuracy of Image Quality, Vegetation State, and Reproductive Phenophases
2.3.2. Identification of Individual Trees
2.3.3. Determination of Spring and Autumn Phenophase Transition Dates
2.3.4. Determination of Autumn Peak Color
2.3.5. Comparison of Season Spotter Spring and Autumn Transition Dates with Those Derived from Automated GCC Measures
2.3.6. Analysis of Left-Right Bias in Classification of Image Pairs
3. Results
3.1. Reproductive and Vegetative Phenophases, Snow, and Image Quality
3.2. Identification of Individual Trees
3.3. Spring and Autumn Phenophase Transitions
4. Discussion
4.1. Applications for Season Spotter Data
4.1.1. Direct Use for Biological Research
4.1.2. Connecting Between Ground Phenology Data and Satellite Sensed Phenology Data
4.1.3. Validating Vegetation Indices
4.1.4. Improving Automated Processing of Remote Sensing Data
4.2. Recommendations for Citizen Science Data Processing of Remote Sensing Imagery
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NDVI | normalized difference vegetation index |
| EVI | enhanced vegetation index |
| MODIS | moderate-resolution imaging spectroradiometer |
| GCC | green chromatic coordinate |
| RCC | red chromatic coordinate |
| DBSCAN | density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise |
| GF | goodness of fit |
| RMSD | root-mean-square deviation |
References
- Richardson, A.D.; Keenan, T.F.; Migliavacca, M.; Ryu, Y.; Sonnentag, O.; Toomey, M. Climate change, phenology, and phenological control of vegetation feedbacks to the climate system. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2013, 169, 156–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibáñez, I.; Primack, R.B.; Miller-Rushing, A.J.; Ellwood, E.; Higuchi, H.; Lee, S.D.; Kobori, H.; Silander, J.A. Forecasting phenology under global warming. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 3247–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menzel, A.; Sparks, T.H.; Estrella, N.; Koch, E.; Aasa, A.; Ahas, R.; Alm-Kübler, K.; Bissolli, P.; Braslavská, O.; Briede, A.; et al. European phenological response to climate change matches the warming pattern. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2006, 12, 1969–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garonna, I.; de Jong, R.; de Wit, A.J.W.; Mücher, C.A.; Schmid, B.; Schaepman, M.E. Strong contribution of autumn phenology to changes in satellite-derived growing season length estimates across Europe (1982–2011). Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 3457–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, T.F.; Richardson, A.D. The timing of autumn senescence is affected by the timing of spring phenology: implications for predictive models. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2015, 21, 2634–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, E.E.; Chuine, I.; Menzel, A.; Mooney, H.A.; Schwartz, M.D. Shifting plant phenology in response to global change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2007, 22, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettorelli, N.; Vik, J.O.; Mysterud, A.; Gaillard, J.-M.; Tucker, C.J.; Stenseth, N.C. Using the satellite-derived NDVI to assess ecological responses to environmental change. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2005, 20, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.B.; Hultine, K.R.; Steltzer, H.; Denny, E.G.; Denslow, M.W.; Granados, J.; Henderson, S.; Moore, D.; Nagai, S.; SanClements, M.; et al. Using phenocams to monitor our changing Earth: Toward a global phenocam network. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 14, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morisette, J.T.; Richardson, A.D.; Knapp, A.K.; Fisher, J.I.; Graham, E.A.; Abatzoglou, J.; Wilson, B.E.; Breshears, D.D.; Henebry, G.M.; Hanes, J.M.; et al. Tracking the rhythm of the seasons in the face of global change: Phenological research in the 21st century. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badeck, F.-W.; Bondeau, A.; Bottcher, K.; Doktor, D.; Lucht, W.; Schaber, J.; Sitch, S. Responses of spring phenology to climate change. New Phytol. 2004, 162, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crimmins, M.A.; Crimmins, T.M. Monitoring plant phenology using digital repeat photography. Environ. Manag. 2008, 41, 949–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, A.; Crowston, K. From conservation to crowdsourcing: A typology of citizen science. In Proceedings of 44th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences (HICSS), Kauai, HI, USA, 4–7 January 2011; pp. 1–10.
- Lintott, C.J.; Schawinski, K.; Slosar, A.; Land, K.; Bamford, S.; Thomas, D.; Raddick, M.J.; Nichol, R.C.; Szalay, A.; Andreescu, D.; et al. Galaxy Zoo: Morphologies derived from visual inspection of galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey. Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 2008, 389, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Westphal, A.J.; Stroud, R.M.; Bechtel, H.A.; Brenker, F.E.; Butterworth, A.L.; Flynn, G.J.; Frank, D.R.; Gainsforth, Z.; Hillier, J.K.; Postberg, F.; et al. Evidence for interstellar origin of seven dust particles collected by the Stardust spacecraft. Science 2014, 345, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanson, A.; Kosmala, M.; Lintott, C.; Packer, C. A generalized approach for producing, quantifying, and validating citizen science data from wildlife images. Conserv. Biol. 2016, 30, 520–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richardson, A.D.; Braswell, B.H.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Jenkins, J.P.; Ollinger, S.V. Near-surface remote sensing of spatial and temporal variation in canopy phenology. Ecol. Appl. 2009, 19, 1417–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnentag, O.; Hufkens, K.; Teshera-Sterne, C.; Young, A.M.; Friedl, M.; Braswell, B.H.; Milliman, T.; O’Keefe, J.; Richardson, A.D. Digital repeat photography for phenological research in forest ecosystems. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2012, 152, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klosterman, S.T.; Hufkens, K.; Gray, J.M.; Melaas, E.; Sonnentag, O.; Lavine, I.; Mitchell, L.; Norman, R.; Friedl, M.A.; Richardson, A.D. Evaluating remote sensing of deciduous forest phenology at multiple spatial scales using PhenoCam imagery. Biogeosciences 2014, 11, 4305–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toomey, M.; Friedl, M.A.; Frolking, S.; Hufkens, K.; Klosterman, S.; Sonnentag, O.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Bernacchi, C.J.; Biraud, S.C.; Bohrer, G.; et al. Greenness indices from digital cameras predict the timing and seasonal dynamics of canopy-scale photosynthesis. Ecol. Appl. 2015, 25, 99–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowyer, A.; Lintott, C.; Hines, G.; Allen, C.; Paget, E. Panoptes, a project building tool for citizen science. 2015; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Crall, A.W.; Kosmala, M.; Cheng, R.; Brier, J.; Cavalier, D.; Henderson, S.; Richardson, A.D. Marketing online citizen science projects to support volunteer recruitment and retention: Lessons from season spotter. PLOS ONE 2016. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Keenan, T.F.; Darby, B.; Felts, E.; Sonnentag, O.; Friedl, M.A.; Hufkens, K.; O’Keefe, J.; Klosterman, S.; Munger, J.W.; Toomey, M.; et al. Tracking forest phenology and seasonal physiology using digital repeat photography: A critical assessment. Ecol. Appl. 2014, 24, 1478–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; Jenkins, J.P.; Braswell, B.H.; Hollinger, D.Y.; Ollinger, S.V.; Smith, M.-L. Use of digital webcam images to track spring green-up in a deciduous broadleaf forest. Oecologia 2007, 152, 323–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V.; et al. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland, W.S.; Grosse, E.; Shyu, W.M. Local regression models. In Statistical Models in S; Chambers, J.M., Hastie, T.J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; Volume 2, pp. 309–376. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, M.D.; Betancourt, J.L.; Weltzin, J.F. From Caprio’s lilacs to the USA National Phenology Network. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 10, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.; Ward, D.L.; Meymaris, K.K.; Alaback, P.; Havens, K. Project Budburst: Citizen science for all seasons. In Citizen Science: Public Participation in Environmental Research; Dickinson, J.L., Bonney, R., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 50–57. [Google Scholar]
- Gallinat, A.S.; Primack, R.B.; Wagner, D.L. Autumn, the neglected season in climate change research. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2015, 30, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Schwartz, M.D.; Fei, S. Validating satellite phenology through intensive ground observation and landscape scaling in a mixed seasonal forest. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmore, A.; Stylinski, C.; Pradhan, K. Synergistic use of citizen science and remote sensing for continental-scale measurements of forest tree phenology. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.D.; O’Keefe, J. Phenological differences between understory and overstory. In Phenology of Ecosystem Processes; Noormets, A., Ed.; Springer New York: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 87–117. [Google Scholar]
- Hufkens, K.; Friedl, M.; Sonnentag, O.; Braswell, B.H.; Milliman, T.; Richardson, A.D. Linking near-surface and satellite remote sensing measurements of deciduous broadleaf forest phenology. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 117, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melaas, E.K.; Sulla-Menashe, D.; Gray, J.M.; Black, T.A.; Morin, T.H.; Richardson, A.D.; Friedl, M.A. Multisite analysis of land surface phenology in North American temperate and boreal deciduous forests from Landsat. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Alpaydin, E. Introduction to Machine Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kosmala, M.; Wiggins, A.; Swanson, A.; Simmons, B. Assessing data quality in citizen science. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Crall, A.W.; Newman, G.J.; Jarnevich, C.S.; Stohlgren, T.J.; Waller, D.M.; Graham, J. Improving and integrating data on invasive species collected by citizen scientists. Biol. Invasions 2010, 12, 3419–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough MacKenzie, C.; Murray, G.; Primack, R.; Weihrauch, D. Lessons from citizen science: Assessing volunteer-collected plant phenology data with Mountain Watch. Biol. Conserv. 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michener, W.K.; Jones, M.B. Ecoinformatics: supporting ecology as a data-intensive science. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiggins, A.; Bonney, R.; Graham, E.; Henderson, S.; Kelling, S.; LeBuhn, G.; Litauer, R.; Lotts, K.; Michener, W.; Newman, G.; et al. Data Management Guide for Public Participation in Scientific Research; DataOne Working Group: Albuquerque, NM, USA, 2013; pp. 1–41. [Google Scholar]
- Zooniverse Best Practices. Available online: https://www.zooniverse.org/lab-best-practices/great-project (accessed on 12 July 2016).
- Cox, J.; Oh, E.Y.; Simmons, B.; Lintott, C.; Masters, K.; Greenhill, A.; Graham, G.; Holmes, K. Defining and measuring success in online citizen science: A case study of Zooniverse projects. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2015, 17, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, R.C.; Ehrenfeld, J.G.; Gray, S.A.; Brooks, W.R.; Howe, D.V.; Hmelo-Silver, C.E. Cognitive considerations in the development of citizen science projects. In Citizen Science: Public Participation in Environmental Research; Dickinson, J.L., Bonney, R., Eds.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 167–178. [Google Scholar]
- Floating Forests. Available online: https://www.floatingforests.org/#/classify (accessed on 12 July 2016).












| Map | Site Name | Group 1 | Group 2 | Group 3 | Latitude | Longitude | Location |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | alligatorriver | X | 35.79 | −75.90 | Alligator River National Wildlife Refuge, NC, USA | ||
| B | arbutuslake | X | 43.98 | −74.23 | Arbutus Lake, Huntington Forest, NY, USA | ||
| C | arizonagrass | g | 31.59 | −110.51 | Sierra Vista, AZ, USA | ||
| D | asa | s, b | X | 2011–2013 | 57.16 | 14.78 | Asa, Sweden |
| E | bartlettir | b | X | 2008–2014 | 44.06 | −71.29 | Bartlett Forest, NH, USA |
| F | bostoncommon | X | 42.36 | −71.06 | Boston Common, Boston, MA, USA | ||
| G | canadaOA | b | X | 2012–2014 | 53.63 | −106.20 | Prince Albert National Park, SK, Canada |
| H | caryinstitute | X | 41.78 | −73.73 | Cary Institute of Ecosystem Studies, Millbrook, NY, USA | ||
| I | downerwoods | b | X | 2013–2014 | 43.08 | −87.88 | Downer Woods Natural Area, WI, USA |
| J | harvard | b | X | 2008–2014 | 42.54 | −72.17 | Harvard Forest, Petersham, MA, USA |
| J | harvardhemlock | n | X | 42.54 | −72.18 | Harvard Forest, Petersham, MA, USA | |
| K | howland1 | X | 45.20 | −68.74 | Howland, ME, USA | ||
| L | ibp | g, s | 32.59 | −106.85 | Jornada Experimental Range, NM, USA | ||
| M | imcrkridge1 | g | 68.61 | −149.30 | Imnavait Creek, AK, USA | ||
| L | jerbajada | s | 32.58 | −106.63 | Jornada Experimental Range, NM, USA | ||
| N | mountranier | n | X | 46.78 | −121.73 | Paradise, Mount Rainier National Park, WA, USA | |
| O | sedgwick | g, s | 34.70 | −120.05 | Sedgwick Ranch Reserve, CA, USA | ||
| P | snipelake | g | 60.61 | −154.32 | Snipe Lake, Lake Clark National Park and Preserve, AK, USA | ||
| Q | turkeypointdbf | b | X | 2012–2014 | 42.64 | −80.56 | Turkey Point Carbon Cycle Research Project, ON, Canada |
| R | uiefmaize | c | 40.06 | −88.20 | University of Illinois Energy Farm, IL, USA | ||
| S | underhill | g, b | X | 2009–2012 | 44.53 | −72.87 | Underhill Air Quality Center, VT, USA |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kosmala, M.; Crall, A.; Cheng, R.; Hufkens, K.; Henderson, S.; Richardson, A.D. Season Spotter: Using Citizen Science to Validate and Scale Plant Phenology from Near-Surface Remote Sensing. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090726
Kosmala M, Crall A, Cheng R, Hufkens K, Henderson S, Richardson AD. Season Spotter: Using Citizen Science to Validate and Scale Plant Phenology from Near-Surface Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing. 2016; 8(9):726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090726
Chicago/Turabian StyleKosmala, Margaret, Alycia Crall, Rebecca Cheng, Koen Hufkens, Sandra Henderson, and Andrew D. Richardson. 2016. "Season Spotter: Using Citizen Science to Validate and Scale Plant Phenology from Near-Surface Remote Sensing" Remote Sensing 8, no. 9: 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090726
APA StyleKosmala, M., Crall, A., Cheng, R., Hufkens, K., Henderson, S., & Richardson, A. D. (2016). Season Spotter: Using Citizen Science to Validate and Scale Plant Phenology from Near-Surface Remote Sensing. Remote Sensing, 8(9), 726. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8090726