Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data
2.1.1. Satellite Data
2.1.2. Ground-Based Measurements
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. LibRadtran Model Description
2.2.2. ARE Calculations
2.2.3. Back Trajectories
3. Results
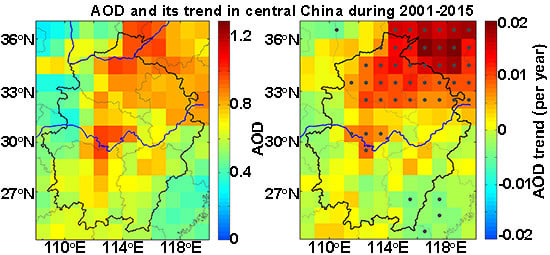
3.1. Spatial Patterns of Aerosol Loading over Central China
3.2. Inter-Annual Variations of AOD Over Central China
3.3. Comparison of Aerosol Optical and Radiative Properties at Urban and Rural Locations in Central China
3.4. Source Region Analysis during Haze Periods in Central China
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stocker, T. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis: Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, B.A. Aerosols, cloud microphysics, and fractional cloudiness. Science 1989, 245, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Wang, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, B. Toward characterization of the aerosol optical properties over loess plateau of NorthWestern China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. Transf. 2011, 112, 346–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, I.B.; Ramaswamy, V.; Ming, Y. Contrasting climate responses to the scattering and absorbing features of anthropogenic aerosol forcings. J. Clim. 2014, 27, 5329–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, S.; Hansen, J.; Nazarenko, L.; Luo, Y. Climate effects of black carbon aerosols in China and India. Science 2002, 297, 2250–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Niu, F.; Fan, J.; Liu, Y.; Rosenfeld, D.; Ding, Y. Long-term impacts of aerosols on the vertical development of clouds and precipitation. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Huang, J.; Bi, J.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; Fu, Q.; Li, Z.; Tsay, S.C.; Shi, J. Dust aerosol vertical structure measurements using three mpl lidars during 2008 China-Us joint dust field experiment. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, 1307–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X. Parameterization of clear-sky surface irradiance and its implications for estimation of aerosol direct radiative effect and aerosol optical depth. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penner, J.E.; Dong, X.; Chen, Y. Observational evidence of a change in radiative forcing due to the indirect aerosol effect. Nature 2004, 427, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, U.; Diehl, K. Sensitivity studies of the importance of dust ice nuclei for the indirect aerosol effect on stratiform mixed-phase clouds. J. Atmos. Sci. 2006, 63, 968–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, M.; Nakajima, T.; Suzuki, K.; Kawamoto, K.; Higurashi, A.; Rosenfeld, D.; Sano, I.; Mukai, S. A study of the direct and indirect effects of aerosols using global satellite data sets of aerosol and cloud parameters. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 2025–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, I.B.; Ramaswamy, V.; Ginoux, P.; Ming, Y.; Horowitz, L.W. Sensitivity of scattering and absorbing aerosol direct radiative forcing to physical climate factors. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, 20203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjánsson, J.E. Studies of the aerosol indirect effect from sulfate and black carbon aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramabhadran, T.E.; Peterson, T.W.; Seinfeld, J.H. Dynamics of aerosol coagulation and condensation. Aiche J. 2010, 22, 840–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.P.; Dey, S.; Tripathi, S.N.; Tare, V.; Holben, B. Variability of aerosol parameters over Kanpur, Northern India. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, 2543–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Aerosol optical and microphysical properties of four typical sites of sonet in China based on remote sensing measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9928–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Fu, Q.; Su, J.; Tang, Q.; Minnis, P.; Hu, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhao, Q. Taklimakan dust aerosol radiative heating derived from calipso observations using the fu-liou radiation model with ceres constraints. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 4011–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Singh, R.P.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhang, M.; Lin, H. Aerosol optical properties over mount song, a rural site in central China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2051–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.; Tanré, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.-R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.; Kleidman, R. The modis aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanré, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Vermote, E.; Reagan, J.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Nakajima, T. Aeronet—A federated instrument network and data archive for aerosol characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Chin, M.; Feingold, G. A review of measurement-based assessments of the aerosol direct radiative effect and forcing. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 613–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, S.; Ji, Y.; Lu, B.; Zhao, X.; Han, B.; Bai, Z. Similarities and differences in PM2.5, PM10 and tsp chemical profiles of fugitive dust sources in a coastal oilfield city in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 2017–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.; Holben, B.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Chatenet, B.; Gomes, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tsay, S.C. Columnar aerosol optical properties at aeronet sites in central Eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical Mid-Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2005, 110, 887–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocko, I.B.; Ginoux, P.A. Comparing multiple model-derived aerosol optical properties to collocated ground-based and satellite measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalashnikova, O.V.; Mills, F.P.; Eldering, A.; Anderson, D. Application of satellite and ground-based data to investigate the uv radiative effects of australian aerosols. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 107, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Li, Z.; Holben, B.; Wang, P.; Eck, T.; Chen, H.; Cribb, M.; Zhao, Y. Aerosol optical properties and radiative effects in the yangtze delta Region of China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2007, 112, 449–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, J.; Shi, G.; Takamura, T. Aerosol optical properties and radiative effect determined from sky-radiometer over loess plateau of Northwest China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 11455–11463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, G. Aerosol optical properties under the condition of heavy haze over an urban site of Beijing, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingmüller, K.; Pozzer, A.; Metzger, S.; Stenchikov, G.L.; Lelieveld, J. Aerosol optical depth trend over the Middle East. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 5063–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z. Long-term observations of aerosol optical properties at Wuhan, an urban site in central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 101, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A. The collection 6 modis aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledano, C.; Wiegner, M.; Groß, S.; Freudenthaler, V.; Gasteiger, J.; Müller, D.; Müller, T.; Schladitz, A.; Weinzierl, B.; Torres, B. Optical properties of aerosol mixtures derived from sun-sky radiometry during samum-2. Tellus Ser. B Chem. Phys. Meteorol. 2011, 63, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, H.; Damiri, B.; Goloub, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, H.; Dong, F. Instrument calibration and aerosol optical depth validation of the China aerosol remote sensing network. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114, D03206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; King, M.D. A flexible inversion algorithm for retrieval of aerosol optical properties from sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2000, 105, 20673–20696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Sinyuk, A.; Lapyonok, T.; Holben, B.N.; Mishchenko, M.; Yang, P.; Eck, T.F.; Volten, H.; Muñoz, O.; Veihelmann, B. Application of spheroid models to account for aerosol particle nonsphericity in remote sensing of desert dust. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, E.; Sheridan, P.J.; Fiebig, M.; Mccomiskey, A.; Ogren, J.A.; Arnott, P.; Covert, D.; Elleman, R.; Gasparini, R.; Collins, D. Comparison of methods for deriving aerosol asymmetry parameter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D05S04. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.; Kylling, A. Technical note: The libradtran software package for radiative transfer calculations—Description and examples of use. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2005, 5, 1855–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kylling, A.; Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.-C. A reliable and efficient two-stream algorithm for spherical radiative transfer: Documentation of accuracy in realistic layered media. J. Atmos. Chem. 1995, 21, 115–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.C.; Wiscombe, W.; Jayaweera, K. Numerically stable algorithm for discrete-ordinate-method radiative transfer in multiple scattering and emitting layered media. Appl. Opt. 1988, 27, 2502–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamnes, K.; Tsay, S.-C.; Wiscombe, W.; Laszlo, I. DISORT, a General-Purpose Fortran Program for Discrete-Ordinate-Method Radiative Transfer in Scattering and Emitting Layered Media: Documentation of Methodology; Department of Physics and Engineering Physics, Stevens Institute of Technology: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Lucht, W.; Roujean, J.L. Considerations in the parametric modeling of brdf and albedo from multiangular satellite sensor observations. Remote Sens. Rev. 2000, 18, 343–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, E.G.; King, M.D.; Platnick, S.; Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F. Spatially complete global spectral surface albedos: Value-added datasets derived from terra modis land products. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2005, 43, 144–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Hu, Z.; Holben, B.; Guo, Z. Investigating the aerosol optical and radiative characteristics of heavy haze episodes in Beijing during january of 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 9884–9900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateos, D.; Antón, M.; Toledano, C.; Cachorro, V.E.; Aladosarboledas, L.; Sorribas, M.; Costa, M.J.; Baldasano, J.M. Aerosol radiative effects in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared spectral ranges using long-term aerosol data series over the iberian peninsula. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 13497–13514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, Y.K.; Holsen, T.M.; Hopke, P.K. Comparison of hybrid receptor models to locate pcb sources in Chicago. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, M.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Wang, Z. Formation process of the widespread extreme haze pollution over Northern China in January 2013: Implications for regional air quality and climate. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Wang, L.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Hu, B.; Liu, B. Aerosol radiative effect in uv, vis, nir, and sw spectra under haze and high-humidity urban conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevasagulló, E. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Y.; Ge, J.; Huang, J. Spatial and temporal distribution of modis and misr aerosol optical depth over Northern China and comparison with aeronet. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.B.; Ju, W.M.; Chen, J.M.; Zhu, G.L.; Xing, B.L.; Zhu, J.F.; He, M.Z. Spatial and temporal variations of forest lai in China during 2000–2010. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2012, 57, 2846–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H. Impact of urbanization and land-use change on surface climate in middle and lower reaches of the yangtze river, 1988–2008. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, Y.; Gong, W.; Zhang, M. Observations of aerosol color ratio and depolarization ratio over Wuhan. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.A.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, P.C.; Zhang, W.X.; Goloub, P.; Chatenet, B.; Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N. Variation of column-integrated aerosol properties in a Chinese urban region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, 769–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Mao, J.; Lau, K.-H.A.; Chen, J.-C.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Zhu, A.; Liu, G. Characteristics of distribution and seasonal variation of aerosol optical depth in Eastern China with modis products. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2003, 48, 2488–2495. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z. Transmission and division of total optical depth method: A universal calibration method for sun photometric measurements. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 2974–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ma, X.; Wang, W. Characteristics of PM1.0, PM2.5, and PM10, and their relation to black carbon in Wuhan, central China. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1377–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.; Che, H.; Zhu, J.; Chen, H.; Cong, Z.; Deng, X.; Fan, X.; Fu, Y.; Goloub, P.; Jiang, H. Ground-based remote sensing of aerosol climatology in China: Aerosol optical properties, direct radiative effect and its parameterization. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mie, G. Beitrage zur optik truber medien, speziell kolloidaler metallosungen. Ann. Phys. 1908, 25, 377–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldering, A.; Cass, G.R.; Moon, K.C. An air monitoring network using continuous particle size distribution monitors: Connecting pollutant properties to visibility via mie scattering calculations. Atmos. Environ. 1994, 28, 2733–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, Y.; Niu, Y.; Salazar, G.A.; Gong, W. Analysis of atmospheric turbidity in clear skies at Wuhan, central China. J. Earth Sci. 2017, 28, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loeb, N.G.; Su, W. Direct aerosol radiative forcing uncertainty based on a radiative perturbation analysis. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 5288–5293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



















| Parameter | Perturbation | Change of ARE in Wuhan W/m2 (%) | Change of ARE in Dengfeng W/m2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AOD | 0.01|−0.01 | −3.57 (4.66)|3.62 (−4.72) | −3.13 (8.00)|3.18 (−8.13) |
| SSA | 0.03|−0.03 | 8.51 (−9.85)|−8.25 (9.70) | 6.21 (−9.17)|−6.40 (10.10) |
| AF | 0.02|−0.02 | 1.98 (−2.35)|−1.93 (2.30) | 1.57 (−2.60)|−1.52 (2.50) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, M.; Wang, L.; Gong, W.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B. Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9100997
Zhang M, Wang L, Gong W, Ma Y, Liu B. Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(10):997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9100997
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ming, Lunche Wang, Wei Gong, Yingying Ma, and Boming Liu. 2017. "Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 10: 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9100997
APA StyleZhang, M., Wang, L., Gong, W., Ma, Y., & Liu, B. (2017). Aerosol Optical Properties and Direct Radiative Effects over Central China. Remote Sensing, 9(10), 997. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9100997