The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. SAR Data
3.2. SAR Data Processing
3.3. Multiple-Satellite Combination Technique for the Retrieval of 2D Displacement Time-Series
4. Experimental Results
4.1. SBAS Analysis
4.2. Two-Dimensional (2D) Deformation Time-Series Extraction
5. Discussion
5.1. Lingang New City
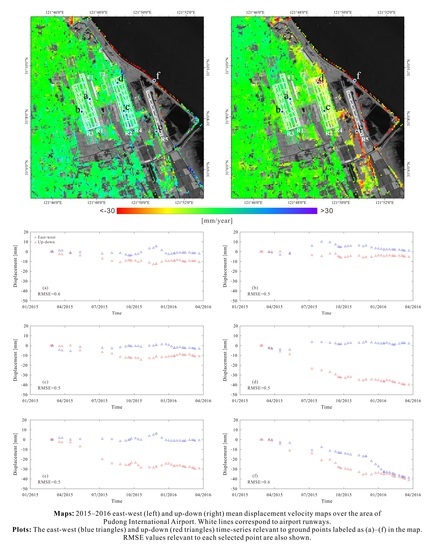
5.2. Pudong International Airport
5.3. Additional Remarks
6. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bürgmann, R.; Rosen, P.A.; Fielding, E.J. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry to measure Earth’s surface topography and its deformation. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2000, 28, 169–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D.; Feigl, K.L. Radar interferometry and its application to changes in the Earth’s surface. Rev. Geophys. 1998, 36, 441–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massonnet, D. The displacement field of the Landers earthquake mapped by radar interferometry. Nature 1993, 364, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, A.; Prati, C.; Rocca, F. Permanent scatterers in SAR interferometry. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2001, 39, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampes, B.M. Radar Interferometry: Springer Persistent Scatterer Technique; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Berardino, P.; Fornaro, G.; Lanari, R.; Sansosti, E. A new algorithm for surface deformation monitoring based on small baseline differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 40, 2375–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werner, C.; Wegmuller, U.; Strozzi, T.; Wiesmann, A. Interferometric Point Target Analysis forDeformation Mapping. In Proceedings of the 2003 IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium, Toulouse, France, 21–25 July 2003; Volume 7, pp. 4362–4364. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, T.J.; Parsons, B.E.; Lu, Z. Toward mapping surface deformation in three dimensions using InSAR. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, L. Using multiple RADARSAT InSAR pairs to estimate a full three-dimensional solution for glacial ice movement. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Sigmundsson, F.; Carstensen, J. Three-dimensional surface motion maps estimated from combined interferometric synthetic aperture radar and GPS data. J. Geophys. Res. 2002, 107, 2250–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialko, Y.; Simons, M.; Agnew, D. The complete (3-D) surface dis-placement field in the epicentral area of the 1999 M(w)7.1 Hector Mine earthquake, California, from space geodetic observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3063–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fialko, Y.; Sandwell, D.; Simons, M.; Rosen, P. Three-dimensional deformation caused by the Bam, Iran, earthquake and the origin of shallow slip deficit. Nature 2005, 435, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Li, Z.W.; Ding, X.L.; Zhu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Sun, Q. 3D coseismic displacement of 2010 Darfield, New Zealand earthquake estimated from multi-aperture InSAR and D-InSAR measurements. J. Geod. 2012, 86, 1029–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, H.; Wei, L.Z.; Jun, Z.J.; Chong, R.X.; Li, X.D. Inferring three-dimensional surface displacement field by combining SAR interferometric phase and amplitude information of ascending and descending orbits. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 53550–53560. [Google Scholar]
- Solari, L.; Ciampalini, A.; Raspini, F.; Bianchini, S.; Zinno, I.; Bonano, M.; Manunta, M.; Moretti, S.; Casagli, N. Combined use of C-and X-Band SAR data for subsidence monitoring in an urban area. Geosciences 2017, 7, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Ding, X.; Li, Z.; Zhu, J.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, L. Kalman-filter based approach for multisensor, multitrack, and multitemporal InSAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4226–4239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsonov, S.; d’Oreye, N. Multidimensional time-series analysis of ground deformation from multiple InSAR data sets applied to Virunga Volcanic Province. Geophys. J. Int. 2012, 191, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa, T.; Ueda, H. Advanced interferometric synthetic aperture radar (InSAR) time series analysis using interferograms of multiple-orbit tracks: A case study on Miyake-jima. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B12407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Solaro, G.; Calò, F.; Dema, C. A Minimum Acceleration Approach for the Retrieval of Multi-Platform InSAR Deformation Time-Series. IEEE J. Sel. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 9, 3883–3898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casu, F.; Manconi, A. Four-dimensional surface evolution of active rifting from spaceborne SAR data. Geosphere 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.X.; Luo, X.J.; Chen, Q.; Huang, J.F.; Ding, X.L. Detecting land subsidence in Shanghai by PS-networking SAR interferometry. Sensors 2008, 8, 4725–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J.; Li, T. Monitoring ground subsidence in shanghai maglev area using two kinds of SAR data. J. Appl. Geod. 2012, 6, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Wu, J.C.; Zhang, L.N.; Zou, J.P.; Liu, G.X.; Zhang, R.; Yu, B. Deformation Trend Extraction Based on Multi-Temporal InSAR in Shanghai. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.C.; Samsonov, S.; Yin, H.W.; Ye, S.J.; Cao, Y.R. Time-series analysis of subsidence associated with rapid urbanization in Shanghai, China measured with SBAS InSAR method. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, J.; Li, T.; Chen, J. Monitoring ground deformation based on small baseline approach in Shanghai. J. Tongji Univ. 2012, 40, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.C.; Hu, F.M. Monitoring Ground Subsidence along the Shanghai Maglev Zone Using TerraSAR-X Images. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. 2017, 14, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perissin, D.; Wang, Z.; Lin, H. Shanghai subway tunnels and highways monitoring through Cosmo-SkyMed Persistent Scatterers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. 2012, 73, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, K.; Liu, G.X.; Li, Z.H.; Li, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.W.; Singleton, A. Extracting Vertical Displacement Rates in Shanghai (China) with Multi-Platform SAR Images. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9542–9562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Pepe, A.; Gao, W.; Lu, Z.; Bonano, M.; He, M.; Tang, X. A DInSAR Investigation of the Ground Settlement Time Evolution of Ocean-Reclaimed Lands in Shanghai. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2015, 8, 1763–1781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebker, H.A.; Villasenor, J. Decorrelation in interferometric radar echoes. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1992, 30, 950–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agram, P.S.; Simons, M. A noise model for InSAR time-series. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2015, 120, 2752–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.N.; Liao, M.S.; Wang, H.M.; Zhang, L.; Balz, T. Deformation Monitoring and Analysis of the Geological Environment of Pudong International Airport with Persistent Scatterer SAR Interferometry. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Bonano, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, T.; Wang, H. The Use of C-/X-Band Time-Gapped SAR Data and Geotechnical Models for the Study of Shanghai’s Ocean-Reclaimed Lands through the SBAS-DInSAR Technique. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Tang, Y.Q.; Zhou, N.Q.; Wang, J.X. Consolidation settlement of Shanghai dredger fill under self-weight using centrifuge modeling test. J. Cent. South Univ. Technol. 2008, 39, 862–866. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor, R.N. Geothecnical Centrifuge Technology; Blackie Academic and Professional: Glasgow, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Z.D.; Tang, Y.Q. Land subsidence and pore structure of soils caused by the high-rise building group through centrifuge model test. Eng. Geol. 2010, 113, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, J.; Wu, J.; Hu, C.; Grafaren, E.; Chen, J. Horizontal deformation rate analysis based on multiepoch GPS measurements in Shanghai. J. Surv. Eng. 2008, 134, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R. GMES Sentinel-1 mission. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 120, 9–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.D.; Han, L.M.; Chai, Z.L. Subgrade settlement rules of first runway of Pudong airport in Shanghai. J. Eng. Geol. 2012, 20, 131–137. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.H.; Yin, C.L.; Si, B.F.; Li, J.S.; Liu, S.; Su, E.H. Foundation bed treatment for high-grade taking-off and landing runway-study on construction proposal for the third runway of Shanghai Pudong international airport building construction. Build. Constr. 2007, 29, 275–277. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, D.; Guarnieri, F.; Monti, A. TOPSAR: Terrain observation by progressive scans. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2352–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small Baseline Subset Algorithm (SBAS). Available online: http://www.irea.cnr.it (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- ENVI’s SARScape Modules from EXELIS VIS Information Solutions. Available online: http://www.sarmap.ch/page.php?page=sarscape (accessed on 1 January 2017).
- Rosen, P.A. Synthetic aperture radar interferometry. Proc. IEEE 2000, 88, 333–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strang, G. Linear Algebra and Its Applications; Harcourt Brace Jovanovich: Orlando, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Pepe, A.; Yang, Y.; Manzo, M.; Lanari, R. Improved EMCF-SBAS Processing Chain Based on Advanced Techniques for the Noise-Filtering and Selection of Small Baseline Multi-look DInSAR Interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2015, 53, 4394–4417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franceschetti, G.; Lanari, R. Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Casu, F.; Manconi, A.; Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. Deformation time-series generation in areas characterized by large displacement dynamics: The SAR amplitude Pixel-Offset SBAS technique. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 2752–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldstein, R.M.; Werner, C.L. Radar interferogram filtering for geophysical applications. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4035–4038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, M. A novel phase unwrapping method based on network programming. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1998, 36, 813–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pepe, A.; Lanari, R. On the extension of the minimum cost flow algorithm for phase unwrapping of multi-temporal differential SAR interferograms. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanghai Institute of Geological Survey (SIGS). The Geological Hazard Risk Assessment Report of Pudong International Airport (PD4); Shanghai Institute Geologocal Survey: Shanghai, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]












© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, L.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, M.; Pepe, A. The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111194
Yu L, Yang T, Zhao Q, Liu M, Pepe A. The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(11):1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111194
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Lei, Tianliang Yang, Qing Zhao, Min Liu, and Antonio Pepe. 2017. "The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis" Remote Sensing 9, no. 11: 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111194
APA StyleYu, L., Yang, T., Zhao, Q., Liu, M., & Pepe, A. (2017). The 2015–2016 Ground Displacements of the Shanghai Coastal Area Inferred from a Combined COSMO-SkyMed/Sentinel-1 DInSAR Analysis. Remote Sensing, 9(11), 1194. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9111194