Fusing Observational, Satellite Remote Sensing and Air Quality Model Simulated Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Exposure in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Description
2.1.1. PM2.5 Monitoring Data
2.1.2. Satellite Remote Sensing of AOD
2.1.3. Satellite Remote Sensing Covariates for AOD-Derived PM2.5
2.1.4. WRF-CMAQ Simulation
2.2. Statistical Analysis
2.2.1. Step 1.1: AOD-Derived PM2.5
2.2.2. Step 1.2: Calibrated-CMAQ PM2.5
2.2.3. Step 2: Inversed Deviation Weighted Averages
2.2.4. Step 3: Spatiotemporal Kriging of the Residuals
2.3. Model Evaluation
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics for Inputs of Data Fusion
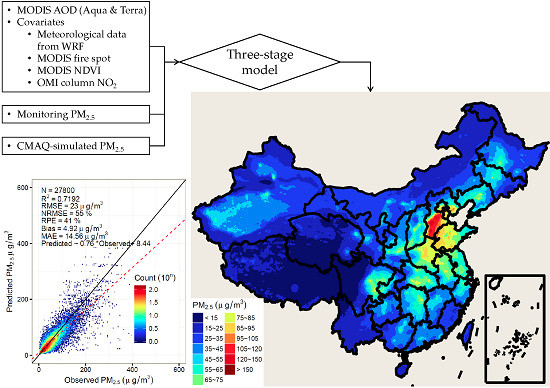
3.2. Cross-Validation Results for the Estimates of the Three-Stage Model
3.3. The Fitted Spatial and Seasonal Patterns of PM2.5 in China
3.4. Exposure Assessments Based on the Fused Estimates
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dominici, F.; Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Pham, L.; Mcdermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M. Fine particulate air pollution and hospital admission for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases. JAMA 2006, 295, 1127–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, R.D.; Bell, M.L.; Geyh, A.S.; Mcdermott, A.; Zeger, S.L.; Samet, J.M.; Dominici, F. Emergency admissions for cardiovascular and respiratory diseases and the chemical composition of fine particle air pollution. Environ. Health Perspect. 2009, 117, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritz, B.; Yu, F.; Fruin, S.; Chapa, G.; Shaw, G.M.; Harris, J.A. Ambient air pollution and risk of birth defects in southern california. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2002, 155, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salam, M.T.; Millstein, J.; Li, Y.; Lurmann, F.; Margolis, H.G.; Gilliland, F.D. Birth outcomes and prenatal exposure to ozone, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter: Results from the children’s health study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1638–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapkota, A.; Chelikowsky, A.P.; Nachman, K.E.; Cohen, A.; Ritz, B. Exposure to particulate matter and adverse birth outcomes: A comprehensive review and meta-analysis. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2010, 5, 369–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Han, I.; Shao, M.; Hu, M.; Zhang, J.; Tang, X. PM2.5 constituents and oxidative DNA damage in humans. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 4757–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, C.; Park, S.K.; Vokonas, P.S.; Sparrow, D.; Wilker, E.H.; Baccarelli, A.; Suh, H.H.; Tucker, K.L.; Wright, R.O.; Schwartz, J. Air pollution and homocysteine: More evidence that oxidative stress-related genes modify effects of particulate air pollution. Epidemiology 2010, 21, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laden, F.; Schwartz, J.; Speizer, F.E.; Dockery, D.W. Reduction in fine particulate air pollution and mortality: Extended follow-up of the harvard six cities study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2006, 173, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Turner, M.C.; Cohen, A.; Krewski, D.; Jerrett, M.; Gapstur, S.M.; Thun, M.J. Lung cancer and cardiovascular disease mortality associated with ambient air pollution and cigarette smoke: Shape of the exposure–response relationships. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1616–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Zhu, T.; Liang, S.; Ezzati, M.; Remais, J.V. Environmental health in china: Progress towards clean air and safe water. Lancet 2010, 375, 1110–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; He, K.; Huo, H. Policy: Cleaning china’s air. Nature 2012, 484, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Yang, X.; Yuan, X. Public awareness and willingness to pay for tackling smog pollution in china: A case study. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Zhou, M.G.; Zhang, Y.J.; Cai, Y.; Pan, X.C. Seasonal effects of PM10 concentrations on mortality in tianjin, china: A time-series analysis. J. Public Health 2012, 21, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Xu, X.; Kan, H. Acute effect of ambient air pollution on stroke mortality in the China air pollution and health effects study. Stroke 2013, 44, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, S.; Tian, Z.; Pan, X.; Zhang, J.; Williams, G.M. The burden of air pollution on years of life lost in Beijing, China, 2004-08: Retrospective regression analysis of daily deaths. BMJ 2013, 347, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, R.; Li, W.; Wang, M.; Cao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Xu, Q. The association between ambient air pollution and daily mortality in Beijing after the 2008 Olympics: A time series study. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Deng, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Shima, M.; Wang, X.; Qin, Y.; Zheng, C.; Wei, H.; Yu, H. Blood pressure changes and chemical constituents of particulate air pollution: Results from the healthy volunteer natural relocation (HVNR) study. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Han, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhu, T. Estimating adult mortality attributable to PM2.5 exposure in China with assimilated PM2.5 concentrations based on a ground monitoring network. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 568, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerrett, M.; Burnett, R.T.; Ma, R.; Pope, C.A.; Krewski, D.; Newbold, K.B.; Thurston, G.D.; Shi, Y.; Finkelstein, N.; Calle, E.E. Spatial analysis of air pollution and mortality in los angeles. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercer, L.D.; Szpiro, A.A.; Sheppard, L.; Lindstrom, J.; Adar, S.D.; Allen, R.; Avol, E.L.; Oron, A.P.; Larson, T.V.; Liu, L.J.S. Comparing universal kriging and land-use regression for predicting concentrations of gaseous oxides of nitrogen (NOx) for the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis and air pollution (MESA air). Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 4412–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, S.B.; Beckerman, B.; Jerrett, M.; Brauer, M. Application of land use regression to estimate long-term concentrations of traffic-related nitrogen oxides and fine particulate matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2422–2428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eeftens, M.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Bellander, T.; Cesaroni, G.; Cirach, M.; Declercq, C.; Dedele, A.; Dons, E.; de Nazelle, A.; et al. Development of land use regression models for PM2.5, PM2.5 absorbance, PM10 and PMcoarse in 20 European study areas; results of the ESCAPE project. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11195–11205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.V. Satellite remote sensing of surface air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7823–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paciorek, C.J.; Liu, Y.; Morenomacias, H.; Kondragunta, S. Spatiotemporal associations between goes aerosol optical depth retrievals and ground-level PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5800–5806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kloog, I.; Nordio, F.; Coull, B.A.; Schwartz, J. Incorporating local land use regression and satellite aerosol optical depth in a hybrid model of spatiotemporal PM2.5 exposures in the Mid-Atlantic states. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11913–11921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Huang, L.; Bi, J.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 in China using satellite remote sensing. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7436–7444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beloconi, A.; Kamarianakis, Y.; Chrysoulakis, N. Estimating urban PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations, based on synergistic MERIS/AATSR aerosol observations, land cover and morphology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 172, 148–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Park, R.J. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 using aerosol optical depth determined from satellite remote sensing. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Brauer, M.; Kahn, R.A.; Levy, R.C.; Verduzco, C.; Villeneuve, P.J. Global estimates of ambient fine particulate matter concentrations from satellite-based aerosol optical depth: Development and application. Environ. Health Perspect. 2010, 118, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, D.W.; Schere, K.L. Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawahda, A.; Yamashita, K.; Ohara, T.; Kurokawa, J.; Yamaji, K. Evaluation of premature mortality caused by exposure to PM2.5 and ozone in East Asia: 2000, 2005, 2020. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 3445–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lelieveld, J.; Evans, J.S.; Fnais, M.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. The contribution of outdoor air pollution sources to premature mortality on a global scale. Nature 2015, 525, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bravo, M.A.; Fuentes, M.; Zhang, Y.; Burr, M.J.; Bell, M.L. Comparison of exposure estimation methods for air pollutants: Ambient monitoring data and regional air quality simulation. Environ. Res. 2012, 116, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckerman, B.S.; Jerrett, M.; Serre, M.L.; Martin, R.V.; Lee, S.; Van Donkelaar, A.; Ross, Z.; Su, J.; Burnett, R.T. A hybrid approach to estimating national scale spatiotemporal variability of PM2.5 in the contiguous United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 7233–7241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mcmillan, N.J.; Holland, D.M.; Morara, M.; Feng, J. Combining numerical model output and particulate data using Bayesian space-time modeling. Environmetrics 2010, 21, 48–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friberg, M.; Zhai, X.; Holmes, H.A.; Chang, H.H.; Strickland, M.J.; Sarnat, S.E.; Tolbert, P.E.; Russell, A.G.; Mulholland, J.A. Method for fusing observational data and chemical transport model simulations to estimate spatiotemporally resolved ambient air pollution. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3695–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- China Environmental Monitoring Center. Available online: http://113.108.142.147:20035/emcpublish/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Beijing Municipal Environmental Monitoring Center. Available online: http://zx.bjmemc.com.cn/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Guangdong Environmental Monitoring Center. Available online: http://113.108.142.147:20031/AQIPublish/AQI.html (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Atmosphere Archive and Distribution System. Available online: http://ladsweb.nascom.nasa.gov (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.C.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-based spatiotemporal trends in PM2.5 concentrations: China 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Land Process Distributed Active Archive Center. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Modis Active Fire and Burned Area Products. Available online: http://modis-fire.umd.edu/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. Available online: http://disc.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- The Weather Research and Forecasting Model. Available online: http://www.wrf-model.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Bey, I.; Jacob, D.J.; Yantosca, R.M.; Logan, J.A.; Field, B.D.; Fiore, A.M.; Li, Q.; Liu, H.Y.; Mickley, L.J.; Schultz, M.G. Global modeling of tropospheric chemistry with assimilated meteorology: Model description and evaluation. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 23073–23095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Multi-Resolution Emission Inventory of China. Available online: http://www.meicmodel.org/ (accessed on 1 March 2017).
- Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, K.B.; Wang, K.; Zheng, G.T.; Duan, F.K.; Ma, Y.; Kimoto, T. Heterogeneous chemistry: A mechanism missing in current models to explain secondary inorganic aerosol formation during the January 2013 haze episode in North China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2031–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N. Statistics for spatial data. Terra Nova 1993, 4, 613–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randriamiarisoa, H.; Chazette, P.; Couvert, P.; Sanak, J.; Megie, G. Relative humidity impact on aerosol parameters in a Paris suburban area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2006, 6, 1389–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chen, L.; Tao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Su, L. Satellite-based estimation of regional particulate matter (PM) in Beijing using vertical-and-RH correcting method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Geng, G.; He, K. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations over three megalopolises in China using satellite-derived aerosol optical depth measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 124, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressie, N.; Johannesson, G. Fixed rank kriging for very large spatial data sets. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat. Methodol. 2008, 70, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, S. Generalized Additive Models: An Introduction with R; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cressie, N.; Wikle, C.K. Statistics for Spatio-Temporal Data; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Bunke, O.; Droge, B. Bootstrap and cross-validation estimates of the prediction error for linear regression models. Ann. Stat. 1984, 12, 1400–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Hu, Y.; Chang, H.H.; Russell, A.G.; Bai, Y. Improving the accuracy of daily PM2.5 distributions derived from the fusion of ground-level measurements with aerosol optical depth observations, a case study in North China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4752–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Huo, H.; Che, H.; Lin, J.; He, K. Estimating long-term PM2.5 concentrations in china using satellite-based aerosol optical depth and a chemical transport model. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 166, 262–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zhu, J.; Wang, Z.; Gbaguidi, A. Improvement of ozone forecast over Beijing based on ensemble kalman filter with simultaneous adjustment of initial conditions and emissions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 12901–12916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Maeda, T.; Hayashi, M.; Hsiao, L.-F.; Liu, K.-Y. A nested air quality prediction modeling system for urban and regional scales: Application for high-ozone episode in Taiwan. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2001, 130, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-J.; Serre, M.L.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Burnett, R.T.; Jerrett, M. Comparison of geostatistical interpolation and remote sensing techniques for estimating long-term exposure to ambient PM2.5 concentrations across the continental United States. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, T.; Zheng, Y.; Geng, G.; Zheng, B.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, Q.; He, K. Fusing Observational, Satellite Remote Sensing and Air Quality Model Simulated Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Exposure in China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030221
Xue T, Zheng Y, Geng G, Zheng B, Jiang X, Zhang Q, He K. Fusing Observational, Satellite Remote Sensing and Air Quality Model Simulated Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Exposure in China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(3):221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030221
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Tao, Yixuan Zheng, Guannan Geng, Bo Zheng, Xujia Jiang, Qiang Zhang, and Kebin He. 2017. "Fusing Observational, Satellite Remote Sensing and Air Quality Model Simulated Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Exposure in China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 3: 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030221
APA StyleXue, T., Zheng, Y., Geng, G., Zheng, B., Jiang, X., Zhang, Q., & He, K. (2017). Fusing Observational, Satellite Remote Sensing and Air Quality Model Simulated Data to Estimate Spatiotemporal Variations of PM2.5 Exposure in China. Remote Sensing, 9(3), 221. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9030221