Object-Oriented Landslide Mapping Using ZY-3 Satellite Imagery, Random Forest and Mathematical Morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China
Abstract
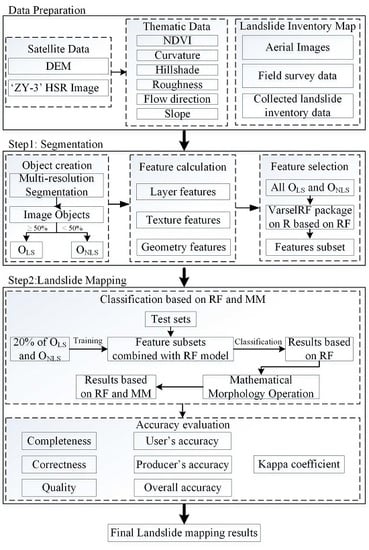
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Landslide Inventory, Image and Thematic Input Layers
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Image Segmentation
2.3.2. Calculation of Object Features
2.3.3. Random Forests-Based Landslide Mapping (RFLM)
2.3.4. Mathematical Morphology Operation
3. Results
3.1. Image Segmentation and Feature Selection
3.2. Landslide Mapping Accuracy Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, C.Z.; Liu, Y.H.; Wen, M.S.; Li, T.F.; Lian, J.F.; Qin, S.W. Geo-Hazard Initiation and Assessment in the Three Gorges Reservoir. In Landslide Disaster Mitigation in Three Gorges Reservoir, China; Wang, F.W., Li, T.L., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 3–40. [Google Scholar]
- Keefer, D.K.; Larsen, M.C. Assessing landslide hazards. Science 2007, 316, 1136–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Fan, X. The landslide story. Nat. Geosci. 2013, 6, 325–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, R.; Wu, X.; Yao, D.; Peng, L.; Ai, L.; Peng, J. Susceptibility assessment of landslides triggered by the Lushan earthquake, April 20, 2013, China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 3979–3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefer, J. Landslide risks rise up agenda. Nature 2014, 511, 272–273. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, R.; Mukherjee, A.; Roy, A.; Khire, M. Technical note temporal remote sensing data and GIS application in landslide hazard zonation of part of Western Ghat, India. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 573–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Westen, C.J.; Castellanos, E.; Kuriakose, S.L. Spatial data for landslide susceptibility, hazard, and vulnerability assessment: An overview. Eng. Geol. 2008, 102, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N. Object-oriented mapping of landslides using Random Forests. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 2564–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaioni, M.; Longoni, L.; Melillo, V.; Papini, M. Remote sensing for landslide investigations: An overview of recent achievements and perspectives. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 9600–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, M.; Ardizzone, F.; Cardinali, M.; Guzzetti, F.; Reichenbach, P. Comparing landslide inventory maps. Geomorphology 2008, 94, 268–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metternicht, G.; Hurni, L.; Gogu, R. Remote sensing of landslides: An analysis of the potential contribution to geo-spatial systems for hazard assessment in mountainous environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 98, 284–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzetti, F.; Mondini, A.C.; Cardinali, M.; Fiorucci, F.; Santangelo, M.; Chang, K.T. Landslide inventory maps: New tools for an old problem. Earth Sci. Rev. 2012, 112, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervas, J.; Barredo, J.I.; Rosin, P.L.; Pasuto, A.; Mantovani, F.; Silvano, S. Monitoring landslides fromoptical remotely sensed imagery: The case history of Tessina landslide, Italy. Geomorphology 2003, 54, 63–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, D.S.; Jibson, R.; Rathje, E.M.; Kelson, K. Landslides triggered by the 2004 Niigata Ken Chuetsu, Japan, earthquake. Earthq. Spectra 2006, 22, 47–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, S.; Kemper, T.; Riedlinger, T.; Kie, R.; Scholte, K.; Mehl, H. Satellite image analysis for disaster and crisis-management support. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2007, 45, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, G.; Liu, S. Forested landslide detection using LiDAR data and the random forest algorithm: A case study of the Three Gorges, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 152, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilley, G.E.; Burgmann, R.; Ferretti, A.; Novali, F.; Rocca, F. Dynamics of slow-moving landslides from permanent scatterer analysis. Science 2004, 304, 1952–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Casagli, N.; Catani, F.; Tofani, V. Persistent Scatterers Interferometry Hotspot and Cluster analysis (PSI-HCA) for detection of extremely slow-moving landslides. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 466–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Mausel, P.; Brondizio, E.; Moran, E. Change detection techniques. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2365–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Shi, W.; Myint, S.W.; Lu, P.; Wang, Q. Semi-automated landslide inventory mapping from bitemporal aerial photographs using change detection and level set method. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travelletti, J.; Malet, J.P.; Delacourt, C. Image-based correlation of Laser Scanning point cloud time series for landslide monitoring. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2014, 32, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, G.; Guo, L.; Zhao, T.; Han, J.; Li, H.; Fang, J. Automatic landslide detection from remote-sensing imagery using a scene classification method based on BoVW and pLSA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 45–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moosavi, V.; Talebi, A.; Shirmohammadi, B. Producing a landslide inventory map using pixel-based and object-oriented approaches optimized by Taguchi method. Geomorphology 2014, 204, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS-J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, P.; Stumpf, A.; Kerle, N.; Casagli, N. Object-oriented change detection for landslide rapid mapping. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2011, 8, 701–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; van Westen, C.J.; Jetten, V.; Kumar, K.V. Segment optimization and data-driven thresholding for knowledge-based landslide detection by object-based image analysis. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2011, 49, 4928–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling, R.; Roessner, S.; Kaufmann, H.; Kleinschmit, B. Automated spatiotemporal landslide mapping over large areas using rapideye time series data. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8026–8055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behling, R.; Roessner, S.; Golovko, D.; Kleinschmit, B. Derivation of long-term spatiotemporal landslide activity—A multi-sensor time series approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 186, 88–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, B.; Jebur, M.N.; Shafri, H.Z.M.; Tehrany, M.S. Data Fusion Technique Using Wavelet Transform and Taguchi Methods for Automatic Landslide Detection From Airborne Laser Scanning Data and QuickBird Satellite Imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2016, 54, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, R.L.; Wood, S.D.; Sheley, R.L. Mapping invasive plants using hyperspectral imagery and Breiman Cutler classifications (randomForest). Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumpf, A.; Lachiche, N.; Malet, J.P.; Kerle, N.; Puissant, A. Active learning in the spatial domain for remote sensing image classification. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2014, 52, 2492–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soille, P. Morphological Image Analysis: Principles and Applications; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.G.; Mason, P.J.; Clerici, N.; Chen, S.; Davis, A.; Miao, F.; Deng, H.; Liang, L. Landslide hazard assessment in the Three Gorges area of the Yangtze river using ASTER imagery: Zigui-Badong. Geomorphology 2004, 61, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duro, D.C.; Franklin, S.E.; Dube, M.G. Multi-scale object-based image analysis and feature selection of multi-sensor earth observation imagery using random forests. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 4502–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baatz, M.; Schäpe, A. Multiresolution segmentation: An optimization approach for high quality multi-scale image segmentation. Available online: http://www.ecognition.com/sites/default/files/405_baatz_fp_12.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2017).
- Definiens Professional Earth (DPE). Definiens Professional 5 User Guide; Definiens AG: München, Germany, 2006; p. 249. [Google Scholar]
- Martha, T.R.; Kerle, N.; van Westen, C.J.; Kumar, K.V. Characterising spectral, spatial and morphometric properties of landslides for semi-automatic detection using object-oriented methods. Geomorphology 2010, 116, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haralick, R.M.; Shanmugam, K.; Dinstein, I.H. Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1973, SMC-3, 610–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laliberte, A.S.; Rango, A. Texture and scale in object-based analysis of subdecimeter resolution unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) imagery. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2009, 47, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble. eCognition Developer 8.64.0 Reference Book; Trimble Documentation; Trimble Germany GmbH: Munich, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, D.R., Jr.; Edwards, T.C.; Beard, K.H.; Cutler, A.; Hess, K.T. Random forests for classification in ecology. Ecology 2007, 88, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Cheng, X.; Chen, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, S. Identification of forested landslides using LiDar data, object-based image analysis, and machine learning algorithms. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9705–9726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kursa, M.B.; Rudnicki, W.R. Feature selection with the Boruta package. J. Stat. Softw. 2010, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohavi, R.; John, G.H. Wrappers for feature subset selection. Artif. Intell. 1997, 97, 273–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Uriarte, R. varSelRF. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/varSelRF/varSelRF.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2017).
- R Development Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Liaw, A. RandomForest: Breiman and Cutler’s Random Forests for Classification and Regression. Version 4.6-12. 2015. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/web/packages/randomForest/randomForest.pdf (accessed on 9 January 2017).
- Diaz-Uriarte, R.; Alvarez de Andres, S. Gene selection and classification of microarray data using random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragut, L.; Csillik, O.; Eisank, C.; Tiede, D. Automated parameterisation for multi-scale image segmentation on multiple layers. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2014, 88, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myint, S.W.; Gober, P.; Brazel, A.; Grossman-Clarke, S.; Weng, Q. Per-pixel vs. object-based classification of urban land cover extraction using high spatial resolution imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1145–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, B.; Ercanoglu, M. Landslide identification and classification by object-based image analysis and fuzzy logic: An example from the Azdavay region (Kastamonu, Turkey). Comput. Geosci. 2012, 38, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Input Layer Derived from Satellite Images (Pixel Size) | Input Layer Derived from Digital Elevation Model (DEM) (Pixel Size) |
|---|---|
| Panchromatic (Pan) (2.1 m) | Curvature (5.8 m) |
| Red (5.8 m) | Hillshade (5.8 m) |
| Green (5.8 m) | Roughness (5.8 m) |
| Blue (5.8 m) | Flow direction (5.8 m) |
| Near Infrared (NIR) (5.8 m) | Slope (5.8 m) |
| Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) (5.8 m) |
| Object-Feature Domains (No.) | Features (No.) |
|---|---|
| Layer features (57) | Max (11), Min (11), Stdv (standard deviation) (11), Mean (11), Ratio (11), Brightness (1), MaxDiff (1) |
| Texture features (60) | GLCMall dir. (Ent (12), Mean (12), Cor (12), Con (12), Stdv (12)) |
| Geometry features (7) | Shape index (1), Density (1), Main direction (1), Roundness (1), Length-width ratio (1), Area (1), Number of Pixels (1) |
| Features (No.) | Layers |
|---|---|
| Mean (7) | Pan, Hillshade, Roughness, Blue, Green, NIR, Flow Direction |
| Min (7) | Pan, Hillshade, Roughness, Blue, Green, NIR, Flow Direction |
| Max (6) | Hillshade, Roughness, Blue, Green, NIR, Flow Direction |
| Ratio (4) | Hillshade, Blue, NIR, Flow Direction |
| Stdv (2) | Roughness, NIR |
| Methods | Completeness (%) | Correctness (%) | Quality (%) | UA (%) | PA (%) | OA (%) | KAPPA (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RFLM | 71.9 ± 0.13 | 91.5 ± 0.07 | 67.1 ± 0.45 | 89.7 ± 0.44 | 72.9 ± 0.72 | 95.0 ± 0.08 | 77.6 ± 0.43 |
| RFCLM | 84.1 ± 0.36 | 90.9 ± 0.11 | 77.0 ± 0.48 | 89.2 ± 0.52 | 84.2 ± 0.61 | 96.3 ± 0.09 | 84.4 ± 0.38 |
| RFOLM | 63.8 ± 0.88 | 97.6 ± 0.13 | 61.2 ± 0.56 | 96.9 ± 0.42 | 64.1 ± 0.97 | 94.6 ± 0.13 | 74.3 ± 0.76 |
| RFOCLM | 67.8 ± 0.89 | 97.4 ± 0.12 | 65.9 ± 0.69 | 96.9 ± 0.44 | 67.6 ± 0.97 | 95.1 ± 0.13 | 77.0 ± 0.74 |
| RFCOLM | 81.5 ± 0.47 | 93.5 ± 0.08 | 77.6 ± 0.39 | 92.8 ± 0.53 | 83.0 ± 0.66 | 96.7 ± 0.1 | 85.7 ± 0.44 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.; Trinder, J.C.; Niu, R. Object-Oriented Landslide Mapping Using ZY-3 Satellite Imagery, Random Forest and Mathematical Morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040333
Chen T, Trinder JC, Niu R. Object-Oriented Landslide Mapping Using ZY-3 Satellite Imagery, Random Forest and Mathematical Morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(4):333. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040333
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tao, John C. Trinder, and Ruiqing Niu. 2017. "Object-Oriented Landslide Mapping Using ZY-3 Satellite Imagery, Random Forest and Mathematical Morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China" Remote Sensing 9, no. 4: 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040333
APA StyleChen, T., Trinder, J. C., & Niu, R. (2017). Object-Oriented Landslide Mapping Using ZY-3 Satellite Imagery, Random Forest and Mathematical Morphology, for the Three-Gorges Reservoir, China. Remote Sensing, 9(4), 333. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9040333