Performance of MODIS C6 Aerosol Product during Frequent Haze-Fog Events: A Case Study of Beijing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sets
2.1. Study Area
2.2. AERONET Data
2.3. MODIS Data
2.4. Air Quality Monitoring Data
3. Analytical Methods
4. Results
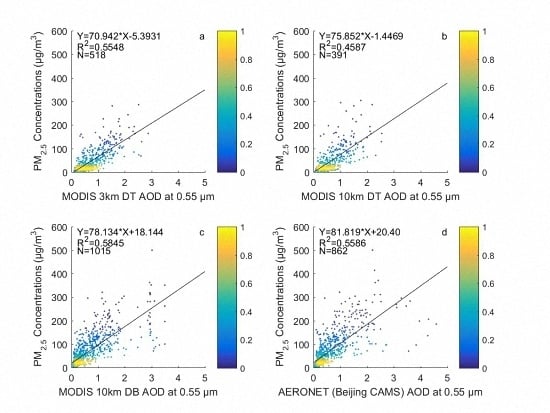
4.1. Performance of the MODIS 10 km DT, 10 km DB, and 3 km DT Products
4.2. Retrieval Statistics under Different Air Quality Situations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lynch, P.; Reid, J.S.; Westphal, D.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Hogan, T.F.; Hyer, E.J.; Curtis, C.A.; Hegg, D.A.; Shi, Y.X.; Campbell, J.R.; et al. An 11-year global gridded aerosol optical thickness reanalysis (v1.0) for atmospheric and climate sciences. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1489–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Mattoo, S.; Chu, D.A.; Martins, J.V.; Li, R.R.; Ichoku, C.; Levy, R.C.; Kleidman, R.G.; et al. The MODIS aerosol algorithm, products, and validation. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 947–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.B.; Meyer, K.; Yu, H.B.; Platnick, S.; Colarco, P.; Liu, Z.Y.; Oreopoulos, L. Shortwave direct radiative effects of above-cloud aerosols over global oceans derived from 8 years of CALIOP and MODIS observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 2877–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.G.; Liu, Y.N.; Wang, L.J.; Kuang, X.Y.; Xu, X.H.; Kan, H.D. Particulate air pollution and mortality in a cohort of Chinese men. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 186, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, R.A.; Gaitley, B.J. An analysis of global aerosol type as retrieved by MISR. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 4248–4281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghan, S.J.; Liu, X.; Easter, R.C.; Zaveri, R.; Rasch, P.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Eaton, B. Toward a Minimal Representation of Aerosols in Climate Models: Comparative Decomposition of Aerosol Direct, Semidirect, and Indirect Radiative Forcing. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 6461–6476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Kaufman, Y.J. Effects of neglecting polarization on the MODIS aerosol retrieval over land. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 2576–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasekamp, O.P.; Litvinov, P.; Butz, A. Aerosol properties over the ocean from PARASOL multiangle photopolarimetric measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Pinty, B.; Gobron, N.; Nelson, D.L.; Holben, B.N. Using angular and spectral shape similarity constraints to improve MISR aerosol and surface retrievals over land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Munchak, L.A.; Hsu, N.C.; Levy, R.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products: Comparison between Aqua’s e-Deep Blue, Dark Target, and “merged” data sets, and usage recommendations. J. Geophys. Res. 2014, 119, 13965–13989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Abdou, W.A.; Bruegge, C.J.; Conel, J.E.; Crean, K.A.; Gaitley, B.J.; Helmlinger, M.C.; Kahn, R.A.; Martonchik, J.V.; Pilorz, S.H.; et al. MISR aerosol optical depth retrievals over southern Africa during the SAFARI-2000 dry season campaign. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2001, 28, 3127–3130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Goloub, P.; Chiapello, I.; Chen, H.; Ducos, F.; Li, Z. Aerosol variability over East Asia as seen by POLDER space-borne sensors. J. Geophys. Res. 2010, 115, D24215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Liu, T.; Cai, H.; Tang, J.; Bu, K.; Yan, F.; Yang, C.; Yang, J.; Zhang, S. Estimating land surface radiation balance using MODIS in northeastern China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2014, 8, 083523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payra, S.; Soni, M.; Kumar, A.; Prakash, D.; Verma, S. Intercomparison of Aerosol Optical Thickness Derived from MODIS and in Situ Ground Datasets over Jaipur, a Semi-arid Zone in India. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9237–9246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, A.; Jayaraman, A.; Ganguly, D. Validation of Version 5.1 MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth (Deep Blue Algorithm and Dark Target Approach) over a Semi-Arid Location in Western India. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties of Four Typical Sites of SONET in China Based on Remote Sensing Measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, E.F.; Tanre, D.; Deuze, J.L.; Herman, M.; Morcrette, J.J. Second Simulation of the Satellite Signal in the Solar Spectrum, 6S: An overview. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1997, 35, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Tang, H.; Zhao, H. Diurnal, weekly and monthly spatial variations of air pollutants and air quality of Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 119, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Shi, G.; Uchiyama, A.; Yamazaki, A.; Chen, H.; Goloub, P.; Zhang, X. Intercomparison between aerosol optical properties by a PREDE skyradiometer and CIMEL sunphotometer over Beijing, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 3199–3214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.B.; Chatenet, B.; Gomes, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Tsay, S.C.; et al. Columnar aerosol optical properties at AERONET sites in central eastern Asia and aerosol transport to the tropical mid-Pacific. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Che, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y. Study of aerosol optical properties at Kunming in southwest China and long-range transport of biomass burning aerosols from North Burma. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Li, Z.Q.; Wang, P.C.; Hao, W.M.; Nordgren, B.L.; Wang, S.G.; Liu, G.R.; Wang, L.L.; Wen, T.X.; et al. Aerosol optical depth (AOD) and Angstrom exponent of aerosols observed by the Chinese Sun Hazemeter Network from August 2004 to September 2005. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D05203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.H.; Kim, Y.J. Satellite remote sensing of Asian aerosols: A case study of clean, polluted, and Asian dust storm days. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2010, 3, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.A.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, P.C.; Zong, X.M.; Qiu, J.H.; Gouloub, P. Aerosol properties and their spatial and temporal variations over North China in spring 2001. Tellus B 2005, 57, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Qi, Q.; Jiang, L.; Zhou, F.; Wang, J. Population Exposure to PM2.5 in the Urban Area of Beijing. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Li, Z.; Gao, W.; Ding, W.; Xu, Q.; Song, X. Diurnal, seasonal, and spatial variation of PM2.5 in Beijing. Sci. Bull. 2015, 60, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.R.; Yin, Y.; Sivakumar, V.; Kang, N.; Yu, X.; Diao, Y.; Adesina, A.J.; Reddy, R.R. Aerosol climatology and discrimination of aerosol types retrieved from MODIS, MISR and OMI over Durban (29.88°S, 31.02°E), South Africa. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 117, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.L.; Zha, Y.; Zhang, J.H.; Gao, J. Aerosol Indices Derived from MODIS Data for Indicating Aerosol-Induced Air Pollution. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 1587–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, L. Comparison and Evaluation of Different MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Products Over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region in China. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2017, 10, 835–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; Cuesta, J.; Ma, Y. Multi-peak accumulation and coarse modes observed from AERONET retrieved aerosol volume size distribution in Beijing. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2016, 128, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.F.; Waller, L.A.; Al-Hamdan, M.Z.; Crosson, W.L.; Estes, M.G.; Estes, S.M.; Quattrochi, D.A.; Sarnat, J.A.; Liu, Y. Estimating ground-level PM2.5 concentrations in the southeastern US using geographically weighted regression. Environ. Res. 2013, 121, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Chatfield, R.B.; Strawa, A.W. Enhancing the Applicability of Satellite Remote Sensing for PM2.5 Estimation Using MODIS Deep Blue AOD and Land Use Regression in California, United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 6546–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Xu, D.D.; Chai, Z.F.; Ouyang, H.; Feng, W.Y.; Mao, X.Y. INAA study for characterization of PM10 and PM2.5 in Beijing and influence of dust storm. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2006, 270, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wang, F.; Xiao, G.; Wu, K.; Zhang, S. Air Quality of Beijing and Impacts of the New Ambient Air Quality Standard. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Jing, J.; Tao, J.; Hsu, S.C.; Wang, G.; Cao, J.; Lee, C.S.L.; Zhu, L.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Chemical characterization and source apportionment of PM2.5 in Beijing: Seasonal perspective. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7053–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.G. Variability of aerosol optical depth and Angstrom wavelength exponent derived from AERONET observations in recent decades. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 044011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Xia, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Z.; Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Goloub, P.; Chen, H.; Estelles, V.; Cuevas-Agullo, E.; et al. Column aerosol optical properties and aerosol radiative forcing during a serious haze-fog month over North China Plain in 2013 based on ground-based sunphotometer measurements. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 2125–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Dubovik, O.; Slutsker, I. Cloud-screening and quality control algorithms for the AERONET database. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 73, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; Holben, B.N.; King, M.D.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I. Accuracy assessments of aerosol optical properties retrieved from Aerosol Robotic Network (AERONET) Sun and sky radiance measurements. J. Geophys. Res. 2000, 105, 9791–9806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Gordon, H.R.; Nakajima, T.; Lenoble, J.; Frouin, R.; Grassl, H.; Herman, B.M.; King, M.D.; Teillet, P.M. Passive remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol and atmospheric correction for the aerosol effect. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16815–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second-generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Tomaso, E.; Schutgens, N.A.J.; Jorba, O.; Garcia-Pando, C.P. Assimilation of MODIS Dark Target and Deep Blue observations in the dust aerosol component of NMMB-MONARCH version 1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2017, 10, 1107–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distribution of Real Time Air Qulaity of China. Available online: http://113.108.142.147:20035/emcpublish/ (accessed on 15 May 2017).
- Petrenko, M.; Ichoku, C.; Leptoukh, G. Multi-sensor Aerosol Products Sampling System (MAPSS). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2012, 5, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, Y.; Zhao, C.S.; Tao, J.C.; Ma, N. Diurnal variations of aerosol optical properties in the North China Plain and their influences on the estimates of direct aerosol radiative effect. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 5761–5772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Levy, R.C.; Munchak, L.A. MODIS 3 km aerosol product: Algorithm and global perspective. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 1829–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.; Bilal, M. Validation of MODIS 3 km Resolution Aerosol Optical Depth Retrievals over Asia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Romero, A.; Gonzalez, J.A.; Calbo, J.; Sanchez-Lorenzo, A.; Michalsky, J. Aerosol optical depth in a western Mediterranean site: An assessment of different methods. Atmos. Res. 2016, 174, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Shi, W.; Luo, N.; Zhao, W. A new method of satellite-based haze aerosol monitoring over the North China Plain and a comparison with MODIS Collection 6 aerosol products. Atmos. Res. 2016, 171, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Son, Y.-S. Spatial Variability of AERONET Aerosol Optical Properties and Satellite Data in South Korea during NASA DRAGON-Asia Campaign. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 3954–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Validation of MODIS Aerosol Optical Depth Retrieval over Mountains in Central China Based on a Sun-Sky Radiometer Site of SONET. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, M.L.; Diner, D.J.; Garay, M.J. Satellite assessment of sea spray aerosol productivity: Southern Ocean case study. J. Geophys. Res. 2016, 121, 872–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, T.; Chen, H.; Gu, X.; Yu, T.; Guo, J.; Guo, H. The inter-comparison of MODIS, MISR and GOCART aerosol products against AERONET data over China. J. Quant. Spectrosc. Radiat. 2012, 113, 2135–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Ge, J.M.; Huang, J.P. Spatial and temporal distribution of MODIS and MISR aerosol optical depth over northern China and comparison with AERONET. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.G.; Yuan, H.S.; Feng, N.; Tao, S. Comparing MODIS and AERONET aerosol optical depth over China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 6519–6529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Chen, L.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Che, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Comparison and evaluation of the MODIS Collection 6 aerosol data in China. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 6992–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.H.; Huang, C.L.; Li, Z.Q.; Chen, H. Development and Validation of a Robust Algorithm for Retrieving Aerosol Optical Depth over Land From MODIS Data. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2015, 8, 1152–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E. Evaluation of MODIS aerosol retrieval algorithms over the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region during low to very high pollution events. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 7941–7957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xin, J.Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, Y.S. The Variations and Trends of MODIS C5 & C6 Products' Errors in the Recent Decade over the Background and Urban Areas of North China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilal, M.; Nichol, J.E.; Nazeer, M. Validation of Aqua-MODIS C051 and C006 Operational Aerosol Products Using AERONET Measurements over Pakistan. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. 2016, 9, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Alexandri, G.; Kourtidis, K.A.; Lelieveld, J.; Zanis, P.; Amiridis, V. Differences between the MODIS Collection 6 and 5.1 aerosol datasets over the greater Mediterranean region. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belle, J.H.; Liu, Y. Evaluation of Aqua MODIS Collection 6 AOD Parameters for Air Quality Research over the Continental United States. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hu, X.; Sayer, A.M.; Levy, R.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, Y.; Tong, S.; Bi, J.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y. Satellite-Based Spatiotemporal Trends in PM2.5 Concentrations: China, 2004–2013. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J.; Meister, G. Effect of MODIS Terra radiometric calibration improvements on Collection 6 Deep Blue aerosol products: Validation and Terra/Aqua consistency. J. Geophys. Res. 2015, 120, 12157–12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, K.; Dong, W.; Lv, B.; Bai, Y. Daily Estimation of Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations over Beijing Using 3 km Resolution MODIS AOD. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12280–12288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, D.; Lang, J.; Wang, G.; Xu, T.; Wang, X.; Yao, S. Temporal and Spatial Characteristics of Ambient Air Quality in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 1868–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Station | AOD Products/PM2.5 | PM2.5 Concentrations | Retrieval Counts (Percentage) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | MODIS 3 km DT | <75 µg/m3 | 396 (76.6%) |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 97 (18.6%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 25 (4.8%) | ||
| MODIS 10 km DT | <75 µg/m3 | 422 (72.5%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 123 (21.1%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 37 (6.4%) | ||
| MODIS 10 km DB | <75 µg/m3 | 716 (70.5%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 203 (20.0%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 96 (9.5%) | ||
| AERONET | <75 µg/m3 | 601 (68.6%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 171 (19.5%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 104 (11.9%) | ||
| PM2.5 | <75 µg/m3 | 1151 (60.0%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 455 (23.7%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 314 (16.3%) | ||
| Beijing-CAMS | MODIS 3 km DT | <75 µg/m3 | 352 (82.2%) |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 61 (14.3%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 15 (3.5%) | ||
| MODIS 10 km DT | <75 µg/m3 | 400 (73.8%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 106 (19.6%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 36 (6.6%) | ||
| MODIS 10 km DB | <75 µg/m3 | 728 (70.7%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 203 (19.6%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 100 (9.7%) | ||
| AERONET | <75 µg/m3 | 556 (76.0%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 153 (20.9%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 23 (3.1%) | ||
| PM2.5 | <75 µg/m3 | 1203 (59.3%) | |
| 75–150 µg/m3 | 479 (23.6%) | ||
| >150 µg/m3 | 346 (17.1%) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.; Fan, A.; Yan, L. Performance of MODIS C6 Aerosol Product during Frequent Haze-Fog Events: A Case Study of Beijing. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050496
Chen W, Fan A, Yan L. Performance of MODIS C6 Aerosol Product during Frequent Haze-Fog Events: A Case Study of Beijing. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(5):496. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050496
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wei, Aiping Fan, and Lei Yan. 2017. "Performance of MODIS C6 Aerosol Product during Frequent Haze-Fog Events: A Case Study of Beijing" Remote Sensing 9, no. 5: 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050496
APA StyleChen, W., Fan, A., & Yan, L. (2017). Performance of MODIS C6 Aerosol Product during Frequent Haze-Fog Events: A Case Study of Beijing. Remote Sensing, 9(5), 496. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9050496