How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. AERONET Aerosol Data Sets
2.2. MODIS Aerosol Data Sets
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Aerosol Optical Properties in Eastern China
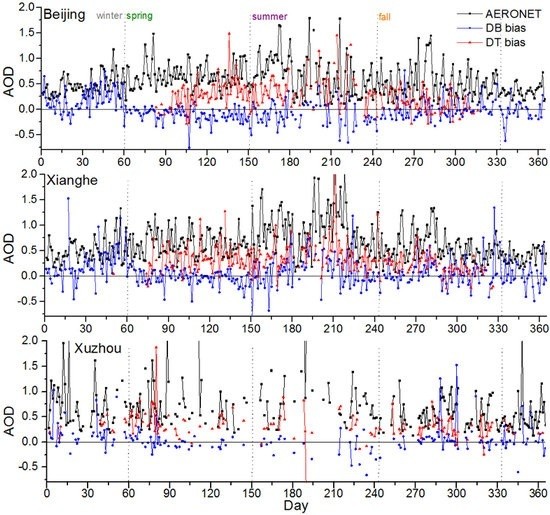
3.2. Temporal Characteristics of MODIS Aerosol Retrieval Bias
3.3. Decadal Variations of the Aerosol Optical Properties and MODIS AOD Bias
4. Discussions
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanre, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M.M.B., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2013; 1535 p. [Google Scholar]
- Holben, B.N.; Eck, T.F.; Slutsker, I.; Tanre, D.; Buis, J.P.; Setzer, A.; Lavenu, F. AERONET—A Federated Instrument Network and Data Archive for Aerosol Characterization. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Remer, L.A.; Vermote, E.F.; Chu, A.; Holben, B.N. Operational remote sensing of tropospheric aerosol over land from EOS moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 17051–17068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diner, D.J.; Martonchik, J.V.; Kahn, R.A.; Pinty, B.; Gobron, N.; Nelson, D.L.; Holben, B.N. Using angular and spectral shape similarity constraints to improve MISR aerosol and surface retrievals over land. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 94, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, O.; Tanskanen, A.; Veihelmann, B.; Ahn, C.; Braak, R.; Bhartia, P.K.; Veefkind, P.; Levelt, P. Aerosols and surface UV products from Ozone Monitoring Instrument observations: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Vaughan, M.A.; Omar, A.; Hu, Y.; Powell, K.A.; Liu, Z.; Hunt, W.H.; Young, S.A. Overview of the CALIPSO Mission and CALIOP Data Processing Algorithms. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2310–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovik, O.; Holben, B.; Eck, T.F.; Smirnov, A.; Kaufman, Y.J.; King, M.D.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I. Variability of absorption and optical properties of key aerosol types observed in worldwide locations. J. Atmos. Sci. 2002, 59, 590–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Tsay, S.C.; King, M.D.; Herman, J.R. Aerosol properties over bright-reflecting source regions. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2004, 42, 557–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Mattoo, S.; Vermote, E.F.; Kaufman, Y.J. Second generation operational algorithm: Retrieval of aerosol properties over land from inversion of Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer spectral reflectance. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, 3710–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, C.; Chen, H.; Tsay, S.C.; Holben, B.; Huang, J.; Xia, X. East Asian Studies of Tropospheric Aerosols and their Impact on Regional Climate (EAST-AIRC): An overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2011, 116, D00K34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Niu, T.; Zhang, X.C.; Gong, S.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Sun, J.Y. Atmospheric aerosol compositions in China: Spatial/temporal variability, chemical signature, regional haze distribution and comparisons with global aerosols. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 11, 779–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tao, M.H.; Chen, L.F.; Su, L.; Tao, J.H. Satellite observation of regional haze pollution over the North China Plain. J. Geophys. Res. 2012, 117, D12203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.H.; Chen, L.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Tao, J.H.; Su, L. Satellite observation of abnormal yellow haze clouds over East China during summer agricultural burning season. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 79, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, H.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xia, X.; Goloub, P.; Holben, B.; Zhao, H.; Damiri, B. Ground-based aerosol climatology of China: Aerosol optical depths from the China Aerosol Remote Sensing Network (CARSNET) 2002–2013. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 7619–7652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, D.; Xu, H.; Li, K. Aerosol Optical and Microphysical Properties of Four Typical Sites of SONET in China Based on Remote Sensing Measurements. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 9928–9953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, J.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Ji, D.; Liu, Z.; Wen, T.; Wang, P. The Campaign on Atmospheric Aerosol Research Network of China: CARE-China. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 1137–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Smirnov, A.; Hoben, B.; Chin, M.; Streets, D.G.; Lu, Z.; Tanre, D. Reduction of aerosol absorption in Beijing since 2007 from MODIS and AERONET. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, L10803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.H.; Chen, L.F.; Wang, Z.F.; Tao, J.H.; Che, H.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Wang, Y. Comparison and evaluation of MODIS Collection 6 aerosol data in China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 6992–7005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Xin, J.Y.; Yin, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Wang, Y.S. The Variations and Trends of MODIS C5 & C6 Products’ Errors in the Recent Decade over the Background and Urban Areas of North China. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 754. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, J.; Xia, X.A.; Wang, J.; Che, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, J.; Ayoub, M. Evaluation of Aerosol Optical Depth and Aerosol Models from VIIRS Retrieval Algorithms over North China Plain. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.; Holben, B.; Reid, J.; Mukelabai, M.; Piketh, S.; Torres, O.; Jethva, H.; Hyer, E.; Ward, D.; Dubovik, O. A seasonal trend of single scattering albedo in southern African biomass-burning particles: Implications for satellite products and estimates of emissions for the world’s largest biomass-burning source. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6414–6432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichoku, C.; Chu, D.A.; Mattoo, S.; Kaufman, Y.J.; Remer, L.A.; Tanre, D.; Slutsker, I.; Holben, B.N. A spatio-temporal approach for global validation and analysis of MODIS aerosol products. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 8006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Mattoo, S.; Munchak, L.A.; Remer, L.A.; Sayer, A.M.; Patadia, F.; Hsu, N.C. The Collection 6 MODIS aerosol products over land and ocean. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2013, 6, 2989–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyapustin, A.; Wang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Meister, G.; Platnick, S.; Levy, R.; Hall, F. Science impact of modis C5 calibration degradation and C6+ improvements. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 4353–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.C.; Remer, L.A.; Dubovik, O. Global aerosol optical properties and application to Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aerosol retrieval over land. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112, D13210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, N.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Bettenhausen, C.; Sayer, A.M.; Hansell, R.; Seftor, C.S.; Huang, J.; Tsay, S.C. Enhanced Deep Blue aerosol retrieval algorithm: The second generation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9296–9315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayer, A.M.; Hsu, N.C.; Bettenhausen, C.; Jeong, M.J. Validation and uncertainty estimates for MODIS Collection 6 “Deep Blue” aerosol data. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 7864–7872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.H.; Chen, L.; Wang, L.; Ma, P.; Tao, J.; Jia, S. A study of urban pollution and haze clouds over northern China during the dusty season based on satellite and surface observations. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 82, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Carlson, B.E.; Lacis, A.A. Using Single Scattering Albedo Spectral Curvature to Characterize East Asian Aerosol Mixtures. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 2037–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Schleicher, N.; Fricker, M.; Cen, K.; Liu, X.L.; Kaminski, U.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.F.; Norra, S. Long-term variation of black carbon and PM2.5 in Beijing, China with respect to meteorological conditions and governmental measures. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Aerosol Model | Algorithm | SSA, 412 nm | SSA, 470 nm | SSA, 660 nm | R, μm | Standard Deviation, μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dust/Spheroid | DT | - | 0.94 | 0.96 | 0.68 | - |
| Absorbing/Smoke | DT | - | 0.88 | 0.85 | 0.256 | - |
| Moderately Absorbing | DT | - | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.261 | - |
| Nonabsorbing/Urban-Industrial | DT | - | 0.95 | 0.94 | 0.207 | - |
| Dust/Spheroid | DB | 0.91 | 0.96 | - | 1.0 | 1.45 |
| Smoke | DB | 0.90 | 0.89 | - | 0.14 | 1.45 |
| “whiter” Dust/Spheroid | DB | 0.98 | 0.99 | ≈1.0 | - | - |
| “redder” Dust/Spheroid | DB | 0.91 | 0.94 | ≈1.0 | - | - |
| Site | Winter DT | Spring DT | Summer DT | Fall DT | Winter DB | Spring DB | Summer DB | Fall DB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | - | 0.3 | 0.38 | 0.04 | 0.24 | −0.11 | −0.095 | −0.003 |
| Xianghe | - | 0.353 | 0.42 | 0.201 | 0.153 | −0.04 | 0.1 | 0.064 |
| Xuzhou | 0.299 | 0.31 | 0.26 | 0.273 | 0.137 | 0.006 | −0.176 | 0.088 |
| Taihu | 0.219 | 0.483 | 0.366 | 0.266 | 0.08 | −0.021 | −0.229 | 0.021 |
| Qiandaohu | −0.192 | 0.108 | 0.082 | −0.027 | −0.293 | −0.21 | −0.347 | −0.251 |
| Hongkong | 0.09 | 0.179 | - | 0.137 | −0.113 | −0.274 | −0.5 | −0.218 |
| Site | Winter DT | Spring DT | Summer DT | Fall DT | Winter DB | Spring DB | Summer DB | Fall DB |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beijing | S−P− | S*P− | S*P− | S−P− | T− | T+ | T* | T− |
| Xianghe | S−P− | S*P− | S*P− | S−P− | T− | T* | T− | T* |
| Xuzhou | S*P− | S+P− | S*P− | S−P− | T− | T* | T+ | T* |
| Taihu | S-P− | S*P− | S*P− | S−P− | T* | T* | T+ | T* |
| Qiandaohu | S−P* | S*P* | S+P* | S−P* | T+ | T* | T+ | T+ |
| Hongkong | S*P* | S*P* | S−P* | S−P* | T+ | T− | T+ | T+ |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, M.; Wang, Z.; Tao, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Hou, C.; Wang, L.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H. How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080800
Tao M, Wang Z, Tao J, Chen L, Wang J, Hou C, Wang L, Xu X, Zhu H. How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(8):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080800
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Minghui, Zifeng Wang, Jinhua Tao, Liangfu Chen, Jun Wang, Can Hou, Lunche Wang, Xiaoguang Xu, and Hao Zhu. 2017. "How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China?" Remote Sensing 9, no. 8: 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080800
APA StyleTao, M., Wang, Z., Tao, J., Chen, L., Wang, J., Hou, C., Wang, L., Xu, X., & Zhu, H. (2017). How Do Aerosol Properties Affect the Temporal Variation of MODIS AOD Bias in Eastern China? Remote Sensing, 9(8), 800. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9080800