Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively
Abstract
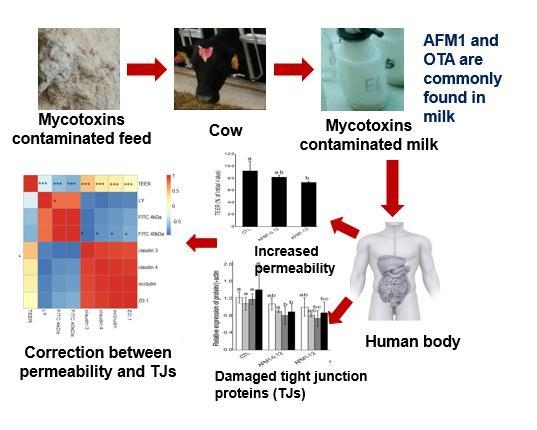
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of AFM1 and OTA Individually or Collectively on the TEER Values of Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
2.2. Effects of AFM1 and OTA Individually or Collectively on the Permeability of Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
2.3. Effects of ATM1 and OTA Individually or Collectively on TJ Protein Levels in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
2.4. Effects of AFM1 and OTA Individually or Collectively on TJ Protein Localization in Caco-2 Cell Monolayers
2.5. The Interactive Effects of the Combination of AFM1 and OTA
2.6. Correlations between TJ Junction and Intestinal Permeability
2.7. AFM1 and OTA Induce Barrier Dysfunction via MAPK-Dependent Mechanism
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Differentiation
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. TEER Measurement
4.5. Permeability Tracer Flux Assay
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescent Staining
4.8. Downregulation of Occludin by siRNA
4.9. Comparison between Expected and Measured Endpoints
4.10. Analysis for Interactions and Correlations
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capriotti, A.L.; Caruso, G.; Cavaliere, C.; Foglia, P.; Samperi, R.; Laganà, A. Multiclass mycotoxin analysis in food, environmental and biological matrices with chromatography/mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2012, 31, 466–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Flores, M.E.; Lizarraga, E.; López de Cerain, A.; González-Peñas, E. Presence of mycotoxins in animal milk: A review. Food Control 2015, 53, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.C.; Zheng, N.; Zheng, B.Q.; Wen, F.; Cheng, J.B.; Han, R.W.; Xu, X.M.; Li, S.L.; Wang, J.Q. Simultaneous determination of aflatoxin M1, ochratoxin A, zearalenone and alpha-zearalenol in milk by UHPLC-MS/MS. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boudra, H.; Barnouin, J.; Dragacci, S.; Morgavi, D.P. Aflatoxin M1 and ochratoxin a in raw bulk milk from French dairy herds. J. Dairy Sci. 2007, 90, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meucci, V.; Razzuoli, E.; Soldani, G.; Massart, F. Mycotoxin detection in infant formula milks in Italy. Food Addit. Contam. 2010, 27, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvito, P.C.; Sizoo, E.A.; Almeida, C.M.M.; van Egmond, H.P. Occurrence of Aflatoxins and Ochratoxin A in Baby Foods in Portugal. Food Anal. Methods 2008, 3, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botta, A.; Martinez, V.; Mitjans, M.; Balboa, E.; Conde, E.; Vinardell, M.P. Erythrocytes and cell line-based assays to evaluate the cytoprotective activity of antioxidant components obtained from natural sources. Toxicol. In Vitro 2014, 28, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, S.L.; Zhang, Y.D.; Zheng, N. Aflatoxin M1 cytotoxicity against human intestinal Caco-2 cells is enhanced in the presence of other mycotoxins. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 96, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bondy, G.S.; Pestka, J.J. Immunomodulation by fungal toxins. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B 2000, 3, 109–143. [Google Scholar]
- Galarza-Seeber, R.; Latorre, J.D.; Bielke, L.R.; Kuttappan, V.A.; Wolfenden, A.D.; Hernandez-Velasco, X.; Merino-Guzman, R.; Vicente, J.L.; Donoghue, A.; Cross, D.; et al. Leaky Gut and Mycotoxins: Aflatoxin B1 Does Not Increase Gut Permeability in Broiler Chickens. Front. Vet. Sci. 2016, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambacorta, L.; Pinton, P.; Avantaggiato, G.; Oswald, I.P.; Solfrizzo, M. Grape Pomace, an Agricultural Byproduct Reducing Mycotoxin Absorption: In Vivo Assessment in Pig Using Urinary Biomarkers. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6762–6771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Applegate, T.J. Modulation of intestinal functions following mycotoxin ingestion: Meta-analysis of published experiments in animals. Toxins 2013, 5, 396–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, M.; Mahfoud, R.; Garmy, N.; Fantini, J. The mycotoxin deoxynivalenol affects nutrient absorption in human intestinal epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qasim, M.; Rahman, H.; Ahmed, R.; Oellerich, M.; Asif, A.R. Mycophenolic acid mediated disruption of the intestinal epithelial tight junctions. Exp. Cell Res. 2014, 322, 277–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, T. Regulation of intestinal epithelial permeability by tight junctions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Mariscal, L.; Betanzos, A.; Avila-Flores, A. MAGUK proteins: structure and role in the tight junction. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2000, 11, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuse, M.; Hirase, T.; Itoh, M.; Nagafuchi, A.; Yonemura, S.; Tsukita, S. Occludin: A Novel Integral Membrane Protein Localizing at Tight Junctions. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1777–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Padura, I.; Lostaglio, S.; Schneemann, M.; Williams, L.; Romano, M.; Fruscella, P.; Panzeri, C.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Ruco, L.; Villa, A.; et al. Junctional Adhesion Molecule, a Novel Member of the Immunoglobulin Superfamily That Distributes at Intercellular Junctions and Modulates Monocyte Transmigration. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitic, L.L.; Anderson, J.M. Molecular architecture of tight junctions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 121–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, P.; Braber, S.; Varasteh, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Garssen, J.; Fink-Gremmels, J. The intestinal barrier as an emerging target in the toxicological assessment of mycotoxins. Arch. Toxicol. 2017, 91, 1007–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artursson, P.; Karlsson, J. Correlation between oral drug absorption in humans and apparent drug permeability coefficients in human intestinal epithelial (Caco-2) cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 175, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P.; Palm, K.; Luthman, K. Caco-2 monolayers in experimental and theoretical predictions of drug transport. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2012, 64, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assuncao, R.; Ferreira, M.; Martins, C.; Diaz, I.; Padilla, B.; Dupont, D.; Braganca, M.; Alvito, P. Applicability of in vitro methods to study patulin bioaccessibility and its effects on intestinal membrane integrity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health A 2014, 77, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, A.; Ares, I.; Ramos, E.; Castellano, V.; Martinez, M.; Martinez-Larranaga, M.R.; Anadon, A.; Martinez, M.A. Mycotoxins modify the barrier function of Caco-2 cells through differential gene expression of specific claudin isoforms: Protective effect of illite mineral clay. Toxicology 2016, 353–354, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, D.; Padfield, P.J.; McLaughlin, J.; Cannell, S.; O’Neill, C.A. Ochratoxin A displaces claudins from detergent resistant membrane microdomains. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 632–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresca, M.; Yahi, N.; Younes-Sakr, L.; Boyron, M.; Caporiccio, B.; Fantini, J. Both direct and indirect effects account for the pro-inflammatory activity of enteropathogenic mycotoxins on the human intestinal epithelium: Stimulation of interleukin-8 secretion, potentiation of interleukin-1beta effect and increase in the transepithelial passage of commensal bacteria. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 228, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranaldi, G.; Mancini, E.; Ferruzza, S.; Sambuy, Y.; Perozzi, G. Effects of red wine on ochratoxin A toxicity in intestinal Caco-2/TC7 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2007, 21, 204–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caloni, F.; Cortinovis, C.; Pizzo, F.; De Angelis, I. Transport of Aflatoxin M(1) in Human Intestinal Caco-2/TC7 Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2012, 3, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangikar, P.B.; Dwivedi, P.; Neeraji, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Telang, A.G. Teratogenic effects in rabbits of simultaneous exposure to ochratoxin A and aflatoxin B1 with special reference to microscopic effects. Toxcology 2005, 215, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zheng, N.; Fan, C.; Cheng, M.; Wang, S.; Jabar, A.; Wang, J.; Cheng, J. Effects of Aflatoxin B1 combined with Ochratoxin A and/or Zearalenone on Metabolism, Immune Function, and Antioxidant Status in Lactating Dairy Goats. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehar, J.; Zimmermann, G.R.; Krueger, A.S.; Molnar, R.A.; Ledell, J.T.; Heilbut, A.M.; Short, G.F.; Giusti, L.C.; Nolan, G.P.; Magid, O.A.; et al. Chemical combination effects predict connectivity in biological systems. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2007, 3, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Sachsenmeier, K.; Zhang, L.; Sult, E.; Hollingsworth, R.E.; Yang, H. A new bliss independence model to analyze drug combination data. J. Biomol. Screen. 2014, 19, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrozzino, F.; Pugnale, P.; Feraille, E.; Montesano, R. Inhibition of basal p38 or JNK activity enhances epithelial barrier function through differential modulation of claudin expression. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C775–C787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshima, T.; Sasaki, M.; Kataoka, H.; Miwa, H.; Takeuchi, T.; John, T. Wip1 protects hydrogen peroxide-induced colonic epithelial barrier dysfunction. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 3139–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinton, P.; Braicu, C.; Nougayrede, J.P.; Laffitte, J.; Taranu, I.; Oswald, I.P. Deoxynivalenol impairs porcine intestinal barrier function and decreases the protein expression of claudin-4 through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent mechanism. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1956–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracarense, A.P.; Lucioli, J.; Grenier, B.; Drociunas Pacheco, G.; Moll, W.D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Oswald, I.P. Chronic ingestion of deoxynivalenol and fumonisin, alone or in interaction, induces morphological and immunological changes in the intestine of piglets. Br. J. Nutr. 2012, 107, 1776–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenier, B.; Bracarense, A.P.; Schwartz, H.E.; Lucioli, J.; Cossalter, A.M.; Moll, W.D.; Schatzmayr, G.; Oswald, I.P. Biotransformation approaches to alleviate the effects induced by fusarium mycotoxins in swine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 6711–6719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bouhet, S.; Oswald, I.P. The effects of mycotoxins, fungal food contaminants, on the intestinal epithelial cell-derived innate immune response. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2005, 108, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratz, S.; Wu, Q.K.; El-Nezami, H.; Juvonen, R.O.; Mykkanen, H.; Turner, P.C. Lactobacillus rhamnosus strain GG reduces aflatoxin B1 transport, metabolism, and toxicity in Caco-2 Cells. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 3958–3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahfoud, R.; Maresca, M.; Garmy, N.; Fantini, J. The Mycotoxin Patulin Alters the Barrier Function of the Intestinal Epithelium: Mechanism of Action of the Toxin and Protective Effects of Glutathione. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2002, 181, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, J.; Padfield, P.J.; Burt, J.P.; O’Neill, C.A. Ochratoxin A increases permeability through tight junctions by removal of specific claudin isoforms. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2004, 287, C1412–C1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madara, J.L. Regulation of the movement of solutes across tight junctions. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 1998, 60, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbari, P.; Braber, S.; Gremmels, H.; Koelink, P.J.; Verheijden, K.A.; Garssen, J.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Deoxynivalenol: A trigger for intestinal integrity breakdown. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 2414–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinton, P.; Nougayrede, J.P.; Del Rio, J.C.; Moreno, C.; Marin, D.E.; Ferrier, L.; Bracarense, A.P.; Kolf-Clauw, M.; Oswald, I.P. The food contaminant deoxynivalenol, decreases intestinal barrier permeability and reduces claudin expression. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2009, 237, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeissig, S.; Bojarski, C.; Buergel, N.; Mankertz, J.; Zeitz, M.; Fromm, M.; Schulzke, J. Downregulation of epithelial apoptosis and barrier repair in active Crohn’s disease by tumour necrosis factor α antibody treatment. Gut 2004, 53, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, A.; Hashegawa, M.; Yagi, K.; Kondoh, M. Homoharringtonine increases intestinal epithelial permeability by modulating specific claudin isoforms in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 89, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, Z.D.; Duan, Z.T.; Wang, S.K.; He, B.S.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Xie, H.G. Attenuated expression of the tight junction proteins is involved in clopidogrel-induced gastric injury through p38 MAPK activation. Toxicology 2013, 304, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, C.H.; Seok, J.S.; Petriello, M.C.; Han, S.G. Arsenic downregulates tight junction claudin proteins through p38 and NF-kappaB in intestinal epithelial cell line, HT-29. Toxicology 2017, 379, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balda, M.S.; Matter, K. Tight junctions as regulators of tissue remodelling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 42, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speijers, G.J.; Speijers, M.H. Combined toxic effects of mycotoxins. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 153, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Bartsch, H.; Azémar, B.; Mohr, U.; Estève, J.; Castegnaro, M. MESNA protects rats against nephrotoxicity but not carcinogenicity induced by ochratoxin A, implicating two separate pathways. Facta Univ. Ser. Med. Biol. 2002, 9, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Tavares, A.M.; Alvito, P.; Loureiro, S.; Louro, H.; Silva, M.J. Multi-mycotoxin determination in baby foods andin vitrocombined cytotoxic effects of aflatoxin M1and ochratoxin A. World Mycotoxin J. 2013, 6, 375–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wild, C.; Turner, P. The toxicology of aflatoxins as a basis for public health decisions. Mutagenesis 2002, 17, 471–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faucet-Marquis, V.; Pont, F.; Størmer, F.C.; Rizk, T.; Castegnaro, M.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A. Evidence of a new dechlorinated ochratoxin A derivative formed in opossum kidney cell cultures after pretreatment by modulators of glutathione pathways: Correlation with DNA-adduct formation. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2006, 50, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heidtmann-Bemvenuti, R.; Mendes, G.; Scaglioni, P.; Badiale-Furlong, E.; Souza Soares, L. Biochemistry and metabolism of mycotoxins: A review. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2011, 5, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tozlovanu, M.; Canadas, D.; Pfohl-Leszkowicz, A.; Frenette, C.; Paugh, R.J.; Manderville, R.A. Glutathione conjugates of ochratoxin A as biomarkers of exposure. Arch. Ind. Hyg. Toxicol. 2012, 63, 417–427. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrer, E.; Juan-Garcia, A.; Font, G.; Ruiz, M.J. Reactive oxygen species induced by beauvericin, patulin and zearalenone in CHO-K1 cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1504–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciolla, C.; Florio, A.; Mulè, G.; Logrieco, A.F. Combined effect of beauvericin and T-2 toxin on antioxidant defence systems in cherry tomato shoots. World Mycotoxin J. 2014, 7, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, F.; Freudinger, R.; Schwerdt, G.; Gekle, M. A rapid screening method to test apoptotic synergisms of ochratoxin A with other nephrotoxic substances. Toxicol. In Vitro 2005, 19, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Luo, C.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, N. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins 2018, 10, 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010013
Gao Y, Li S, Wang J, Luo C, Zhao S, Zheng N. Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins. 2018; 10(1):13. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010013
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Yanan, Songli Li, Jiaqi Wang, Chaochao Luo, Shengguo Zhao, and Nan Zheng. 2018. "Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively" Toxins 10, no. 1: 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010013
APA StyleGao, Y., Li, S., Wang, J., Luo, C., Zhao, S., & Zheng, N. (2018). Modulation of Intestinal Epithelial Permeability in Differentiated Caco-2 Cells Exposed to Aflatoxin M1 and Ochratoxin A Individually or Collectively. Toxins, 10(1), 13. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010013