Co-Occurrence of Microcystins and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Drinking Water Source and Their Removal in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Seasonal Variations of Cyanobacteria, MCs and T&O Compounds in the EDWS
2.2. Relationships among Cyanobacteria, MCs and T&O Compounds in the EDWS
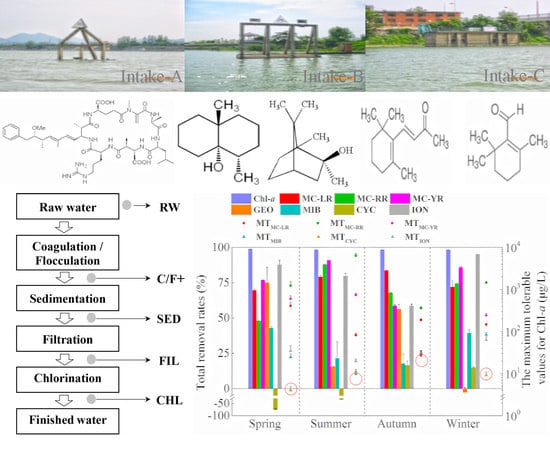
2.3. The Removal of Chlorophyll-a, MCs and T&O Compounds via Treatment Processes in the DWTP
2.3.1. Coagulation/Flocculation (C/F+)
2.3.2. Sedimentation (SED)
2.3.3. Sand Filtration (FIL)
2.3.4. Chlorination (CHL)
2.3.5. Total Removal Rates of Chlorophyll-a and the Metabolites
3. Discussion
3.1. The Co-Occurrence of MCs and T&O Compounds Relating to Different Dominant Cyanobacterial Species in the EDWS
3.2. The Fate of Chlorophyll-a, MCs and T&O Compounds in the Associated DWTP
3.3. The Establishment of Chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) Limits at Intake (CLIs) for DWTP and Reservoir Management
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Method
5.1. Chemicals, Standards and Materials
5.2. Study Site
5.3. Sampling, Sample Preparation and Phytoplankton Analysis
5.4. MCs Extraction and Analysis
5.5. T&O Compounds Analysis
5.6. Statistical Analysis
5.7. Calculation of Removal Rates and CLIs
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- BouhaddaFda, R.; Nelieu, S.; Nasri, H.; Delarue, G.; Bouaicha, N. High diversity of microcystins in a Microcystis bloom from an Algerian Lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 216, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management, 1st ed.; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999; pp. 183–210. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, S.B. Aquatic taste and odor: A primary signal of drinking-water integrity. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Pt. A 2004, 67, 1779–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking Water Quality, Incorporating First Addendum; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- El Herry, S.; Fathalli, A.; Rejeb, A.J.-B.; Bouaïcha, N. Seasonal occurrence and toxicity of Microcystis spp. and Oscillatoria tenuis in the Lebna Dam, Tunisia. Water Res. 2008, 42, 1263–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotto, A.M.; Satchwell, M.F.; Berry, D.L.; Gobler, C.J.; Boyer, G.L. Spatial and temporal diversity of microcystins and microcystin-producing genotypes in Oneida Lake, NY. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinang, S.C.; Reichwaldt, E.S.; Ghadouani, A. Spatial and temporal variability in the relationship between cyanobacterial biomass and microcystins. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 6379–6395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szlag, D.C.; Sinclair, J.L.; Southwell, B.; Westrick, J.A. Cyanobacteria and cyanotoxins occurrence and removal from five high-risk conventional treatment drinking water plants. Toxins 2015, 7, 2198–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Ding, J.; Hou, A.; Li, Y.; Niu, Z.; Su, X.; Xu, Y.; Laws, E.A. The 2007 water crisis in Wuxi, China: Analysis of the origin. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 182, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, J.L.; Loftin, K.A.; Meyer, M.T.; Ziegler, A.C. Cyanotoxin mixtures and taste-and-odor compounds in cyanobacterial blooms from the midwestern united states. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 7361–7368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, K.; Fujioka, H.; Muranaka, M.; Yokoyama, A.; Katagami, Y.; Homma, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Tsujimura, S.; Kumagai, M.; Watanabe, M.F. Spatial distribution and temporal variation of Microcystis species composition and microcystin concentration in Lake Biwa. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Ma, Z.; Niu, Y.; Tao, M.; Deng, X.; Wang, Q. A systematic study on spatial and seasonal patterns of eight taste and odor compounds with relation to various biotic and abiotic parameters in gonghu bay of Lake Taihu, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 409, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghernaout, B.; Ghernaout, D.; Saiba, A. Algae and cyanotoxins removal by coagulation/flocculation: A review. Desalin. Water Treat. 2010, 20, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamyadi, A.; Dorner, S.; Sauvé, S.; Ellis, D.; Bolduc, A.; Bastien, C.; Prévost, M. Species-dependence of cyanobacteria removal efficiency by different drinking water treatment processes. Water Res. 2013, 47, 2689–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Hobson, P.; Ho, L.; Daly, R.; Brookes, J. The effects of various control and water treatment processes on the membrane integrity and toxin fate of cyanobacteria. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 264, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, R.; Sorial, G.A. Treatment of taste and odor causing compounds 2-methyl isoborneol and geosmin in drinking water: A critical review. J. Environ. Sci. 2011, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczak, T.; Tarczynska, M.; Izydorczyk, K.; Mankiewicz, J.; Zalewski, M.; Meriluoto, J. Elimination of microcystins by water treatment processes-examples from sulejow reservoir, Poland. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamyadi, A.; MacLeod, S.L.; Fan, Y.; McQuaid, N.; Dorner, S.; Sauve, S.; Prevost, M. Toxic cyanobacterial breakthrough and accumulation in a drinking water plant: A monitoring and treatment challenge. Water Res. 2012, 46, 1511–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Feng, M.; Liu, F.; Xu, X.; Ke, F.; Chen, X.; Li, W. The establishment of preliminary safety threshold values for cyanobacteria based on periodic variations in different microcystin congeners in Lake Chaohu, China. Environ. Sci. Process. Impact. 2015, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, W.; Bornmann, K.; Imhof, L.; Mankiewicz, J.; Izydorczyk, K. Assessing drinking water treatment systems for safety against cyanotoxin breakthrough using maximum tolerable values. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietsch, J.; Bornmann, K.; Schmidt, W. Relevance of intra-and extracellular cyanotoxins for drinking water treatment. Acta Hydrochim. Hydrobiol. 2002, 30, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoudi, E.; Prévost, M.; Vo Duy, S.; Sauvé, S.; Dorner, S. Adsorption characteristics of multiple microcystins and cylindrospermopsin on sediment: Implications for toxin monitoring and drinking water treatment. Toxicon 2015, 103, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pestana, C.J.; Reeve, P.J.; Sawade, E.; Voldoire, C.F.; Newton, K.; Praptiwi, R.; Collingnon, L.; Dreyfus, J.; Hobson, P.; Gaget, V.; et al. Fate of cyanobacteria in drinking water treatment plant lagoon supernatant and sludge. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 565, 1192–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, N.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Li, C. Aqueous chlorination of algal odorants: Reaction kinetics and formation of disinfection by-products. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höckelmann, C.; Jüttner, F. Off-flavours in water: Hydroxyketones and β-ionone derivatives as new odour compounds of freshwater cyanobacteria. Flavour Fragr. J. 2005, 20, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Gao, N.; Yen, H.; Chiu, Y.; Lin, T. Degradation and formation of wood odorant β-cyclocitral during permanganate oxidation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 194, 362–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.M.; Wang, D.H.; Xu, X.; Wang, Z.J. Formation of known and unknown disinfection by-products from natural organic matter fractions during chlorination, chloramination, and ozonation. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantoral Uriza, E.; Asencio, A.; Aboal, M. Are we underestimating benthic cyanotoxins? Extensive sampling results from Spain. Toxins 2017, 9, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Liu, C.; Yang, F.; Hung, H. Effect of residual chlorine on the analysis of geosmin, 2-MIB and MTBE in drinking water using the SPME technique. Water Res. 2003, 37, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wei, Y. The Freshwater Algae of China: Systematics, Taxonomy and Ecology; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Jeffrey, S.W.; Humphrey, G.F. New spectrophotometric equations for determining chlorophylls a, b, c1 and c2 in higher plants, algae and natural phytoplankton. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanz. 1975, 167, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barco, M.; Lawton, L.A.; Rivera, J.; Caixach, J. Optimization of intracellular microcystin extraction for their subsequent analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1074, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, S.B.; Brownlee, B.; Satchwill, T.; Hargesheimer, E.E. Quantitative analysis of trace levels of geosmin and MIB in source and drinking water using headspace SPME. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2818–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, C.T.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: Software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). In Section on Permutation Methods; Microcomputer Power: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]






| Spring | Summer | Autumn | Winter | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyll-a (μg/L) | 9.0 (5.4–13.7) | 38.5 (22.2–68.0) | 22.2 (8.0–55.7) | 24.6 (5.7–47.9) |
| Phytoplankton density (×104 cells/mL) | 1.7 (0.5–4.0) | 19.1 (18.0–20.2) | 12.7 (5.7–17.2) | 12.2 (7.0–22.1) |
| Cyanobacterial density (×104 cells/mL) | 1.5 (0.3–3.9) | 18.5 (18.6–19.5) | 12.5 (5.4–17.0) | 12.0 (6.7–21.9) |
| Microcystis density (×104 cells/mL) | 0.1 (n.d.–0.3) | 11.6 (2.8–16.5) | 8.8 (3.0–13.1) | 2.3 (0.9–4.8) |
| Dolichospermum density (×104 cells/mL) | 1.4 (0.2–3.8) | 2.8 (0.6–5.2) | 1.6 (1.1–2.2) | 9.4 (5.7–15.5) |
| EMC-LR (μg/L) | 0.05 (0.03–0.06) | 0.98 (0.07–2.80) | 0.65 (0.07–1.04) | 0.14 (0.02–0.55) |
| IMC-LR (μg/L) | 0.04 (0.02–0.08) | 1.15 (0.12–3.22) | 0.11 (0.03–0.18) | 0.36 (0.04–1.31) |
| EMC-RR (μg/L) | 0.12 (0.06–0.17) | 0.31 (0.21–0.59) | 1.42 (0.08–2.45) | 0.12 (0.06–0.22) |
| IMC-RR (μg/L) | 0.07 (0.05–0.11) | 0.16 (0.11–0.25) | 0.56 (0.03–1.47) | 0.41 (0.10–1.20) |
| EMC-YR (μg/L) | 0.07 (n.d.–0.12) | 0.18 (0.11–0.27) | 1.34 (0.21–2.83) | 0.46 (n.d.–0.74) |
| IMC-YR (μg/L) | 0.01 (n.d.–0.02) | 0.37 (0.02–1.07) | 0.82 (0.05–1.35) | 0.11 (0.01–0.31) |
| d-geosmin (ng/L) | 16.8 (1.6–47.8) | 8.1 (4.8–12.1) | 3.7 (1.3–7.2) | 7.7 (n.d.–17.2) |
| p-geosmin (ng/L) | 0.7 (0.2–1.7) | 0.6 (0.2–1.1) | n.d. | 0.4 (n.d.–0.9) |
| d-2-methyl isoborneol (ng/L) | 11.1 (4.5–30.7) | 60.2 (n.d.–193.4) | 14.1 (0.7–27.5) | 5.4 (n.d.–11.8) |
| p-2-methyl isoborneol (ng/L) | 1.3 (0.4–2.0) | 12.6 (0.6–4.0) | 0.5 (n.d.–1.3) | 0.5 (n.d.–1.7) |
| d-β-cyclocitral (ng/L) | 26.5 (8.0–50.1) | 21.9 (8.4–49.2) | 14.9 (8.2–33.8) | 10.6 (n.d.–20.0) |
| p-β-cyclocitral (ng/L) | 4.7 (1.0–10.9) | 26.3 (5.4–53.4) | 4.0 (0.9–8.7) | 42.5 (5.4–106.3) |
| d-β-ionone (ng/L) | 5.8 (0.4–28.4) | 10.8 (3.3–23.2) | 7.3 (n.d.–21.8) | 0.4 (n.d.–1.1) |
| p-β-ionone (ng/L) | 14.5 (1.8–30.1) | 53.4 (2.6–152.7) | 4.8 (0.7–11.6) | 47.1 (3.5–115.8) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shang, L.; Feng, M.; Xu, X.; Liu, F.; Ke, F.; Li, W. Co-Occurrence of Microcystins and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Drinking Water Source and Their Removal in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Toxins 2018, 10, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010026
Shang L, Feng M, Xu X, Liu F, Ke F, Li W. Co-Occurrence of Microcystins and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Drinking Water Source and Their Removal in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Toxins. 2018; 10(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleShang, Lixia, Muhua Feng, Xiangen Xu, Feifei Liu, Fan Ke, and Wenchao Li. 2018. "Co-Occurrence of Microcystins and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Drinking Water Source and Their Removal in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant" Toxins 10, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010026
APA StyleShang, L., Feng, M., Xu, X., Liu, F., Ke, F., & Li, W. (2018). Co-Occurrence of Microcystins and Taste-and-Odor Compounds in Drinking Water Source and Their Removal in a Full-Scale Drinking Water Treatment Plant. Toxins, 10(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10010026