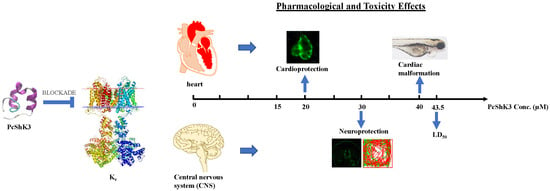
A Novel ShK-Like Toxic Peptide from the Transcriptome of the Cnidarian Palythoa caribaeorum Displays Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection in Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. PcShK3 Is Identified as a Novel ShK-Like Peptide through Molecular Phylogenetic Analysis
2.2. PcShK3 Has the Potential to Block to Kv1.3 and KCa3.1 through Docking Analysis
2.3. PcShK3 Distributed across Vitelline Membrane and Accumulated in the Yolk Sac Stripe of Zebrafish Larvae
2.4. PcShK3 Hold the Potential to Improve or Restore the Cardiovascular Function at Lower Concentration
2.5. PcShK3 Could Prevent the In Vivo Dopaminergic (DA) Neuron Loss Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) in Zebrafish
3. Discussions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Primary Sequence Analysis, Structure Modeling and Molecular Dynamics Simulation
4.2. Molecular Docking Analysis
4.3. Peptide Synthesis
4.4. Zebrafish Maintenance
4.5. Assessment of Survival Rate and Biodistribution of Peptides in Zebrafish Larvae
4.6. Measurement of Morphology and Functions of Zebrafish Heart
4.7. Anti-Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH) Whole-Mount Immunostaining
4.8. Locomotion Behavioral Test
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jouiaei, M.; Sunagar, K.; Federman Gross, A.; Scheib, H.; Alewood, P.F.; Moran, Y.; Fry, B.G. Evolution of an ancient venom: Recognition of a novel family of cnidarian toxins and the common evolutionary origin of sodium and potassium neurotoxins in sea anemone. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G. Venoms to Drugs: Venom as a Source for the Development of Human Therapeutics; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Wulff, H.; Singh, S.; Nugent, D.; Crossley, G.; Khaytin, I.; Calabresi, P.A.; Chen, C.Y.; Gutman, G.A.; et al. Targeting effector memory T cells with a selective peptide inhibitor of Kv1.3 channels for therapy of autoimmune diseases. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1369–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalman, K.; Pennington, M.W.; Lanigan, M.D.; Nguyen, A.; Rauer, H.; Mahnir, V.; Paschetto, K.; Kem, W.R.; Grissmer, S.; Gutman, G.A. ShK-Dap22, a potent Kv1.3-specific immunosuppressive polypeptide. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32697–32707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, L.; Herrington, J.; Goldberg, E.; Dulski, P.M.; Bugianesi, R.M.; Slaughter, R.S.; Banerjee, P.; Brochu, R.M.; Priest, B.T.; Kaczorowski, G.J.; et al. Stichodactyla helianthus peptide, a pharmacological tool for studying Kv3.2 channels. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeton, C.; Wulff, H.; Singh, S.; Botsko, S.; Crossley, G.; Gutman, G.A.; Cahalan, M.D.; Pennington, M.; Chandy, K.G. A novel fluorescent toxin to detect and investigate Kv1.3 channel up-regulation in chronically activated T lymphocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9928–9937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Beeton, C.; Galea, C.A.; Smith, B.J.; Chi, V.; Monaghan, K.P.; Garcia, A.; Rangaraju, S.; Giuffrida, A.; Plank, D.; et al. Engineering a stable and selective peptide blocker of the Kv1.3 channel in T lymphocytes. Mol. Pharmacol. 2009, 75, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Harunur Rashid, M.; Tajhya, R.B.; Beeton, C.; Kuyucak, S.; Norton, R.S. AC-terminally amidated analogue of ShK is a potent and selective blocker of the voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3996–4001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Lu, K.; Li, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Hu, B.; Xu, P.; Shi, X.; Zhou, B.; Pennington, M.; et al. Blockade of Kv1.3 channels ameliorates radiation-induced brain injury. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 528–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergara, C.; Latorre, R.; Marrion, N.V.; Adelman, J.P. Calcium-activated potassium channels. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1998, 8, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.L.; Yang, H.Y.; Chan, P.; Cheng, T.H.; Liu, J.C.; Hsu, F.L.; Liu, I.M.; Cheng, Y.W.; Cheng, J.T. Isosteviol as a potassium channel opener to lower intracellular calcium concentrations in cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jow, F.; Zhang, Z.H.; Kopsco, D.C.; Carroll, K.C.; Wang, K. Functional coupling of intracellular calcium and inactivation of voltage-gated Kv1.1/Kvbeta1.1 A-type K+ channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 15535–15540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.; Gwack, Y.; Prakriya, M.; Srikanth, S.; Puppel, S.H.; Tanasa, B.; Hogan, P.G.; Lewis, R.S.; Daly, M.; Rao, A. A mutation in Orai1 causes immune deficiency by abrogating CRAC channel function. Nature 2006, 441, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feske, S.; Prakriya, M.; Rao, A.; Lewis, R.S. A severe defect in CRAC Ca2+ channel activation and altered K+ channel gating in T cells from immunodeficient patients. J. Exp. Med. 2005, 202, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.L.; Yu, Y.; Roos, J.; Kozak, J.A.; Deerinck, T.J.; Ellisman, M.H.; Stauderman, K.A.; Cahalan, M.D. STIM1 is a Ca2+ sensor that activates CRAC channels and migrates from the Ca2+ store to the plasma membrane. Nature 2005, 437, 902–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakriya, M.; Feske, S.; Gwack, Y.; Srikanth, S.; Rao, A.; Hogan, P.G. Orai1 is an essential pore subunit of the CRAC channel. Nature 2006, 443, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vig, M.; Peinelt, C.; Beck, A.; Koomoa, D.L.; Rabah, D.; Koblan-Huberson, M.; Kraft, S.; Turner, H.; Fleig, A.; Penner, R.; et al. CRACM1 is a plasma membrane protein essential for store-operated Ca2+ entry. Science 2006, 312, 1220–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeromin, A.V.; Zhang, S.L.; Jiang, W.; Yu, Y.; Safrina, O.; Cahalan, M.D. Molecular identification of the CRAC channel by altered ion selectivity in a mutant of Orai. Nature 2006, 443, 226–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lis, A.; Peinelt, C.; Beck, A.; Parvez, S.; Monteilh-Zoller, M.; Fleig, A.; Penner, R. CRACM1, CRACM2, and CRACM3 are store-operated Ca2+ channels with distinct functional properties. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentis, P.J.; Pavasovic, A.; Norton, R.S. Sea Anemones: Quiet Achievers in the Field of Peptide Toxins. Toxins (Basel) 2018, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayal, E.; Bastian, B.; Pankey, M.S.; Ohdera, A.; Medina, M.; Plachetzki, D.C.; Collins, A.; Ryan, J.F. Comprehensive phylogenomic analyses resolve cnidarian relationships and the origins of key organismal traits. PeerJ Preprints 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, S.; Siu, S.W.I.; Yang, B.; Huang, C.; Chan, J.Y.-W.; Morlighem, J.-É.; Wong, C.T.T.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Novel Kunitz-like peptides discovered in the zoanthid Palythoa caribaeorum through transcriptome sequencing. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Morlighem, J.-É.R.; Zhou, H.; Lima, É.P.; Gomes, P.B.; Cai, J.; Lou, I.; Pérez, C.D.; Lee, S.M.; Rádis-Baptista, G. The Transcriptome of the Zoanthid Protopalythoa variabilis (Cnidaria, Anthozoa) Predicts a Basal Repertoire of Toxin-like and Venom-Auxiliary Polypeptides. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3045–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennington, M.W.; Byrnes, M.E.; Zaydenberg, I.; Khaytin, I.; de Chastonay, J.; Krafte, D.S.; Hill, R.; Mahnir, V.M.; Volberg, W.A.; Gorczyca, W.; et al. Chemical synthesis and characterization of ShK toxin: A potent potassium channel inhibitor from a sea anemone. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1995, 46, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauer, H.; Pennington, M.; Cahalan, M.; Chandy, K.G. Structural conservation of the pores of calcium-activated and voltage-gated potassium channels determined by a sea anemone toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 21885–21892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierce, B.G.; Hourai, Y.; Weng, Z. Accelerating protein docking in ZDOCK using an advanced 3D convolution library. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Chung, S.H. Engineering a potent and specific blocker of voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3, a target for autoimmune diseases. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 1976–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Chung, S.H. Molecular dynamics simulations of scorpion toxin recognition by the Ca2+-activated potassium channel KCa3.1. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 1829–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Robinson, A.; Gordon, D.; Chung, S.H. Modeling the binding of three toxins to the voltage-gated potassium channel (Kv1.3). Biophys. J. 2011, 101, 2652–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Tong, W.; Mintseris, J.; Li, L.; Weng, Z. ZDOCK predictions for the CAPRI challenge. Proteins 2003, 52, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rink, E.; Wullimann, M.F. The teleostean (zebrafish) dopaminergic system ascending to the subpallium (striatum) is located in the basal diencephalon (posterior tuberculum). Brain Res. 2001, 889, 316–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanigan, M.D.; Kalman, K.; Lefievre, Y.; Pennington, M.W.; Chandy, K.G.; Norton, R.S. Mutating a critical lysine in ShK toxin alters its binding configuration in the pore-vestibule region of the voltage-gated potassium channel, Kv1.3. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 11963–11971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, A.; Giller, K.; Hornig, S.; Martin-Eauclaire, M.F.; Pongs, O.; Becker, S.; Baldus, M. Toxin-induced conformational changes in a potassium channel revealed by solid-state NMR. Nature 2006, 440, 959–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, V.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S.; Tarcha, E.J.; Londono, L.M.; Sims-Fahey, B.; Upadhyay, S.K.; Lakey, J.T.; Iadonato, S.; Wulff, H.; et al. Development of a sea anemone toxin as an immunomodulator for therapy of autoimmune diseases. Toxicon 2012, 59, 529–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beeton, C.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S. Analogs of the sea anemone potassium channel blocker ShK for the treatment of autoimmune diseases. Inflamm. Allergy Drug Targets 2011, 10, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Kurtz, G.; Vianna-Jorge, R.; Pereira, B.F.; Garcia, M.L.; Kaczorowski, G.J. Peptidyl inhibitors of shaker-type Kv1 channels elicit twitches in guinea pig ileum by blocking kv1.1 at enteric nervous system and enhancing acetylcholine release. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 289, 1517–1522. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tucker, K.; Overton, J.M.; Fadool, D.A. Kv1.3 gene-targeted deletion alters longevity and reduces adiposity by increasing locomotion and metabolism in melanocortin-4 receptor-null mice. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2008, 32, 1222–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Koni, P.A.; Wang, P.; Li, G.; Kaczmarek, L.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Flavell, R.A.; Desir, G.V. The voltage-gated potassium channel Kv1.3 regulates energy homeostasis and body weight. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.S.; Pennington, M.W.; Beeton, C. Case study 2: Transforming a toxin into a therapeutic: The sea anemone potassium channel blocker ShK toxin for treatment of autoimmune diseases. In Venoms to Drugs; IMB: Wollongong, Austraia, 2015; pp. 255–274. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Wei, H.; Lu, J.; Wong, P.; Shim, W. Identification and characterization of calcium sparks in cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55266. [Google Scholar]
- Marks, A.R. Calcium and the heart: A question of life and death. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 111, 597–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morad, M.; Tung, L. Ionic events responsible for the cardiac resting and action potential. Am. J. Cardiol. 1982, 49, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, G. Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias. J. Arrhythm. 2016, 32, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, C.Y.; Kini, R.M. From snake venom toxins to therapeutics—Cardiovascular examples. Toxicon 2012, 59, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furman, B.L. The development of Byetta (exenatide) from the venom of the Gila monster as an anti-diabetic agent. Toxicon 2012, 59, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miljanich, G.P. Ziconotide: Neuronal calcium channel blocker for treating severe chronic pain. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidtko, A.; Lotsch, J.; Freynhagen, R.; Geisslinger, G. Ziconotide for treatment of severe chronic pain. Lancet 2010, 375, 1569–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogita, K.; Okuda, H.; Watanabe, M.; Nagashima, R.; Sugiyama, C.; Yoneda, Y. In vivo treatment with the K+ channel blocker 4-aminopyridine protects against kainate-induced neuronal cell death through activation of NMDA receptors in murine hippocampus. Neuropharmacology 2005, 48, 810–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taherian, R.; Ahmadi, M.A. 4-aminopyridine decreases MPTP-induced behavioral disturbances in animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Int. Clin. Neurosci. J. 2016, 2, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: Multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 1792–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. MUSCLE: A multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinform. 2004, 5, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Peterson, D.; Filipski, A.; Kumar, S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Gallo Cassarino, T.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, J.; Schwede, T. The SWISS-MODEL Repository: New features and functionalities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D315–D318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudor, J.E.; Pallaghy, P.K.; Pennington, M.W.; Norton, R.S. Solution structure of ShK toxin, a novel potassium channel inhibitor from a sea anemone. Nat. Struct. Biol. 1996, 3, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pronk, S.; Pall, S.; Schulz, R.; Larsson, P.; Bjelkmar, P.; Apostolov, R.; Shirts, M.R.; Smith, J.C.; Kasson, P.M.; van der Spoel, D.; et al. GROMACS 4.5: A high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 845–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Spoel, D.; Lindahl, E.; Hess, B.; Groenhof, G.; Mark, A.E.; Berendsen, H.J. GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005, 26, 1701–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E. Crystal contacts as nature’s docking solutions. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: Visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graph. 1996, 14, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerfield, M. A Guide for the Laboratory Use of Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Eugene, 4th ed.; University of Oregon Press: Eugene, OR, USA, 2000; pp. 1.1, 9.7, 10.16. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, J.Y.; Zhou, H.; Kwan, Y.W.; Chan, S.W.; Radis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M. Evaluation in zebrafish model of the toxicity of rhodamine B-conjugated crotamine, a peptide potentially useful for diagnostics and therapeutics. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2017, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Chan, J.Y.; Shan, L.; Cui, G.; Cui, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A Novel Danshensu Derivative Prevents Cardiac Dysfunction and Improves the Chemotherapeutic Efficacy of Doxorubicin in Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 117, 94–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.Q.; Sa, F.; Chong, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Chang, R.C.; Chan, S.W.; Hoi, P.M.; Yuen Lee, S.M. Schisantherin A protects against 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neuron damage in zebrafish and cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through the ROS/NO and AKT/GSK3beta pathways. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 170, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.J.; Cheang, L.C.; Wang, M.W.; Li, G.H.; Chu, I.K.; Lin, Z.X.; Lee, S.M. Ethanolic extract of fructus Alpinia oxyphylla protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced damage of PC12 cells in vitro and dopaminergic neurons in zebrafish. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 32, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Q.; Gong, G.; Siu, S.W.I.; Wong, C.T.T.; Yu, H.; Tse, Y.C.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Lee, S.M.-Y. A Novel ShK-Like Toxic Peptide from the Transcriptome of the Cnidarian Palythoa caribaeorum Displays Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection in Zebrafish. Toxins 2018, 10, 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060238
Liao Q, Gong G, Siu SWI, Wong CTT, Yu H, Tse YC, Rádis-Baptista G, Lee SM-Y. A Novel ShK-Like Toxic Peptide from the Transcriptome of the Cnidarian Palythoa caribaeorum Displays Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection in Zebrafish. Toxins. 2018; 10(6):238. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060238
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Qiwen, Guiyi Gong, Shirley Weng In Siu, Clarence Tsun Ting Wong, Huidong Yu, Yu Chung Tse, Gandhi Rádis-Baptista, and Simon Ming-Yuen Lee. 2018. "A Novel ShK-Like Toxic Peptide from the Transcriptome of the Cnidarian Palythoa caribaeorum Displays Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection in Zebrafish" Toxins 10, no. 6: 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060238
APA StyleLiao, Q., Gong, G., Siu, S. W. I., Wong, C. T. T., Yu, H., Tse, Y. C., Rádis-Baptista, G., & Lee, S. M. -Y. (2018). A Novel ShK-Like Toxic Peptide from the Transcriptome of the Cnidarian Palythoa caribaeorum Displays Neuroprotection and Cardioprotection in Zebrafish. Toxins, 10(6), 238. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins10060238