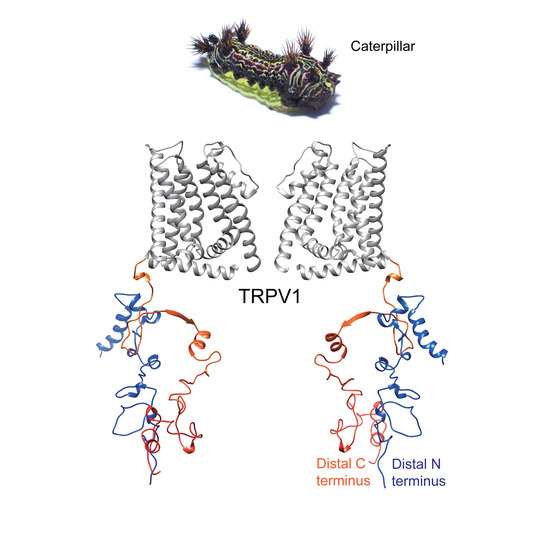
The Latoia consocia Caterpillar Induces Pain by Targeting Nociceptive Ion Channel TRPV1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Caterpillar Venom Induces Pain in a Mouse Model In Vivo
2.2. Caterpillar Venom Targets TRPV1 Ion Channel
2.3. Calcium Signal from Sensory Neurons Challenged with Caterpillar Venom
2.4. L. consocia Crude Venom Induces Pain Behaviors in WT but Not TRPV1 KO Mice
2.5. Transcriptome Analysis of the Caterpillar L. consocia Venom Glands
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Experimental Section
5.1. Animals
5.2. Venom Collection
5.3. Venom Purification
5.4. Dorsal Root Ganglion Isolation
5.5. Cell Preparation and Transient Transfection
5.6. Calcium Fluorescence Imaging
5.7. Electrophysiological Recordings
5.8. Paw Licking Behavior Test
5.9. Transcriptome Sequencing Analysis
5.10. Data Analysis
5.11. Data Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balit, C.R.; Geary, M.J.; Russell, R.C.; Isbister, G.K. Prospective study of definite caterpillar exposures. Toxicon 2003, 42, 657–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimaldi, D.E.; Engel, M.S. Evolution of the Insects; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA; Melbourne, Australia, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Diaz, J.H. The evolving global epidemiology, syndromic classification, management, and prevention of caterpillar envenoming. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2005, 72, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veiga, A.B.; Blochtein, B.; Guimaraes, J.A. Structures involved in production, secretion and injection of the venom produced by the caterpillar lonomia obliqua (lepidoptera, saturniidae). Toxicon 2001, 39, 1343–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrijo-Carvalho, L.C.; Chudzinski-Tavassi, A.M. The venom of the lonomia caterpillar: An overview. Toxicon 2007, 49, 741–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Why do we study animal toxins? Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 183–222. [Google Scholar]
- Julius, D. Trp channels and pain. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2013, 29, 355–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemmie, J.A.; Taugher, R.J.; Kreple, C.J. Acid-sensing ion channels in pain and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013, 14, 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibbs, G.R.; Posson, D.J.; Goldstein, P.A. Voltage-gated ion channels in the pns: Novel therapies for neuropathic pain? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2016, 37, 522–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Xiao, Y.; Kang, D.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Undheim, E.A.; Klint, J.K.; Rong, M.; Lai, R.; King, G.F. Discovery of a selective nav1.7 inhibitor from centipede venom with analgesic efficacy exceeding morphine in rodent pain models. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17534–17539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J. Molecular mechanism of trp channels. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 221–242. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Wei, N.; Hong, J.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Rong, M.; Yarov-Yarovoy, V.; Zheng, J.; Wang, K.; et al. A pain-inducing centipede toxin targets the heat activation machinery of nociceptor trpv1. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.A.; Jiang, W.; Luo, L.; Li, B.; Yang, S.; Song, Y.; Lai, R. Scorpion toxin, bmp01, induces pain by targeting trpv1 channel. Toxins 2015, 7, 3671–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohlen, C.J.; Priel, A.; Zhou, S.; King, D.; Siemens, J.; Julius, D. A bivalent tarantula toxin activates the capsaicin receptor, trpv1, by targeting the outer pore domain. Cell 2010, 141, 834–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arocha-Pinango, C.L.; Marval, E.; Guerrero, B. Lonomia genus caterpillar toxins: Biochemical aspects. Biochimie 2000, 82, 937–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, J.A.; Rodrigues, G.; Nascimento-Silva, V.; Renovato-Martins, M.; Berger, M.; Guimaraes, J.A.; Barja-Fidalgo, C. Effects of lonomia obliqua venom on vascular smooth muscle cells: Contribution of nadph oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Toxins 2017, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro Bastos, L.; Veiga, A.B.; Guimaraes, J.A.; Tonussi, C.R. Nociceptive and edematogenic responses elicited by a crude bristle extract of lonomia obliqua caterpillars. Toxicon 2004, 43, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funakoshi, K.; Nakano, M.; Atobe, Y.; Goris, R.C.; Kadota, T.; Yazama, F. Differential development of trpv1-expressing sensory nerves in peripheral organs. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 323, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villas-Boas, I.M.; Bonfa, G.; Tambourgi, D.V. Venomous caterpillars: From inoculation apparatus to venom composition and envenomation. Toxicon 2018, 153, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombati, R.; Wang, Y.; Du, C.; Lu, X.; Li, B.; Nyachieo, A.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Lai, R. A membrane disrupting toxin from wasp venom underlies the molecular mechanism of tissue damage. Toxicon 2018, 148, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Yang, F.; Zhang, B.; Lee, B.H.; Li, B.; Luo, L.; Zheng, J.; Lai, R. A bimodal activation mechanism underlies scorpion toxin-induced pain. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geron, M.; Hazan, A.; Priel, A. Animal toxins providing insights into trpv1 activation mechanism. Toxins 2017, 9, 326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez, N.J.; Senff, S.; Jensen, J.E.; Er, S.Y.; Herzig, V.; Rash, L.D.; King, G.F. Spider-venom peptides as therapeutics. Toxins 2010, 2, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.F.; Hardy, M.C. Spider-venom peptides: Structure, pharmacology, and potential for control of insect pests. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2013, 58, 475–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Undheim, E.A.; Fry, B.G.; King, G.F. Centipede venom: Recent discoveries and current state of knowledge. Toxins 2015, 7, 679–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakim, M.A.; Yang, S.; Lai, R. Centipede venoms and their components: Resources for potential therapeutic applications. Toxins 2015, 7, 4832–4851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Rong, M.; Liang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; King, G.F.; Lai, R. Chemical punch packed in venoms makes centipedes excellent predators. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2012, 11, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santibanez-Lopez, C.E.; Francke, O.F.; Ureta, C.; Possani, L.D. Scorpions from mexico: From species diversity to venom complexity. Toxins 2016, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, K.N.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Tan, P.T.; Chew, K.C.; Cheng, B.; Kini, R.M.; Koh, J.L.; Seah, S.H.; Brusic, V. Scorpion, a molecular database of scorpion toxins. Toxicon 2002, 40, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Pajak, A.; Kolosowska, N.; Kucharczyk, M.; Starowicz, K. The importance of trpv1-sensitisation factors for the development of neuropathic pain. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Yang, K.Y.; Nam, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Bae, Y.C.; Ahn, D.K. Differential regulation of peripheral il-1beta-induced mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in rats. Pain 2014, 155, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Li, B.; Wang, S.; Wu, F.; Wang, X.; Liang, P.; Ombati, R.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; Cui, J.; et al. Centipedes subdue giant prey by blocking kcnq channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1646–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Xu, L.; Kamau, P.M.; Zheng, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, S.; Lai, R. Molecular basis for heat desensitization of trpv1 ion channels. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yao, Z.; Kamau, P.M.; Han, Y.; Hu, J.; Luo, A.; Luo, L.; Zheng, J.; Tian, Y.; Lai, R. The Latoia consocia Caterpillar Induces Pain by Targeting Nociceptive Ion Channel TRPV1. Toxins 2019, 11, 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120695
Yao Z, Kamau PM, Han Y, Hu J, Luo A, Luo L, Zheng J, Tian Y, Lai R. The Latoia consocia Caterpillar Induces Pain by Targeting Nociceptive Ion Channel TRPV1. Toxins. 2019; 11(12):695. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120695
Chicago/Turabian StyleYao, Zhihao, Peter Muiruri Kamau, Yalan Han, Jingmei Hu, Anna Luo, Lei Luo, Jie Zheng, Yuhua Tian, and Ren Lai. 2019. "The Latoia consocia Caterpillar Induces Pain by Targeting Nociceptive Ion Channel TRPV1" Toxins 11, no. 12: 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120695
APA StyleYao, Z., Kamau, P. M., Han, Y., Hu, J., Luo, A., Luo, L., Zheng, J., Tian, Y., & Lai, R. (2019). The Latoia consocia Caterpillar Induces Pain by Targeting Nociceptive Ion Channel TRPV1. Toxins, 11(12), 695. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins11120695