Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Bv8-AJ Purification
2.2. Bv8-AJ Structural Characterization and Sequence Alignment
2.3. Bv8-AJ Accelerated Full-thickness Wound Healing in Mice
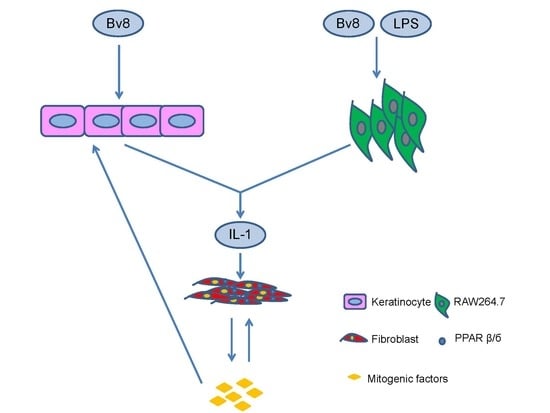
2.4. Bv8-AJ Promoted Cell Proliferation
2.5. Bv8-AJ Induced IL-1 Production
2.6. IL-1 Receptor Antagonist Inhibited Bv8-AJ-induced Cell Proliferation
2.7. Bv8-AJ activated MAPK Signaling Pathway in KC and RAW 264.7 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Animals
5.2. Collection of Frog Skin Secretions
5.3. Peptide Purification
5.4. Structural Analysis
5.5. cDNA Cloning
5.6. Effects of Bv8-AJ on Full-thickness Wounds in Mice
5.7. Isolation of Fibroblasts and Keratinocytes from Newborn Mice
5.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
5.9. Effects of Bv8-AJ on Cytokines Production
5.10. Effects of IL-1ra on Bv8-AJ-induced Cell Proliferation
5.11. Western Blot Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Negri, L.; Lattanzi, R.; Giannini, E.; Melchiorri, P. Bv8/Prokineticin proteins and their receptors. Life Sci. 2007, 81, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullock, C.M.; Li, J.D.; Zhou, Q.Y. Structural determinants required for the bioactivities of prokineticins and identification of prokineticin receptor antagonists. Mol. Pharmacol. 2004, 65, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.Y.; Meidan, R. Biological function of prokineticins. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2008, 46, 181–199. [Google Scholar]
- Mollay, C.; Wechselberger, C.; Mignogna, G.; Negri, L.; Melchiorri, P.; Barra, D.; Kreil, G. Bv8, a small protein from frog skin and its homologue from snake venom induce hyperalgesia in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 374, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, P. Wound healing—Aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 1997, 276, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wechselberger, C.; Puglisi, R.; Engel, E.; Lepperdinger, G.; Boitani, C.; Kreil, G. The mammalian homologues of frog bv8 are mainly expressed in spermatocytes. FEBS Lett. 1999, 462, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, B.T. The natural history of amphibian skin secretions, their normal functioning and potential medical applications. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1997, 72, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. Why do we study animal toxins? Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 183–222. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Lai, R. The chemistry and biological activities of peptides from amphibian skin secretions. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 1760–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yang, S.; Wei, L.; Liu, R.; Lai, R.; Rong, M. Antimicrobial peptide diversity in the skin of the torrent frog, Amolops jingdongensis. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Lin, G.; Lai, R. The first antimicrobial peptide from sea amphibian. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 678–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Yang, J.; He, X.; Mo, G.; Hong, J.; Yan, X.; Lin, D.; Lai, R. Structure and function of a potent lipopolysaccharide-binding antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory peptide. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 3546–3556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.; Hou, X.; Wang, L.; Gao, Y.; Wu, D.; Xi, X.; Zhou, M.; Kwok, H.F.; Duan, J.; Chen, T.; et al. Two novel dermaseptin-like antimicrobial peptides with anticancer activities from the skin secretion of Pachymedusa dacnicolor. Toxins 2016, 8, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Cheng, P.; Ma, C.; Xi, X.; Wang, L.; Zhou, M.; Bian, H.; Chen, T. Evaluating the bioactivity of a novel broad-spectrum antimicrobial peptide brevinin-1gha from the frog skin secretion of hylarana guentheri and its analogues. Toxins 2018, 10, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mwangi, J.; Hao, X.; Lai, R.; Zhang, Z.Y. Antimicrobial peptides: New hope in the war against multidrug resistance. Zool. Res. 2019, 40, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Shen, C.; Lu, Q.; Li, J.; Wei, Y.; He, L.; Bai, R.; Zheng, J.; Luan, N.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Prokineticin 2 plays a pivotal role in psoriasis. EBioMedicine 2016, 13, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prosser, H.M.; Bradley, A.; Chesham, J.E.; Ebling, F.J.; Hastings, M.H.; Maywood, E.S. Prokineticin receptor 2 (prokr2) is essential for the regulation of circadian behavior by the suprachiasmatic nuclei. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Negri, L.; Lattanzi, R.; Giannini, E.; De Felice, M.; Colucci, A.; Melchiorri, P. Bv8, the amphibian homologue of the mammalian prokineticins, modulates ingestive behaviour in rats. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2004, 142, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chong, H.C.; Tan, M.J.; Philippe, V.; Tan, S.H.; Tan, C.K.; Ku, C.W.; Goh, Y.Y.; Wahli, W.; Michalik, L.; Tan, N.S. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal il-1 signaling by pparbeta/delta is essential for skin homeostasis and wound healing. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 817–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Mu, L.; Tang, J.; Shen, C.; Gao, C.; Rong, M.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, X.; Yu, H.; et al. A potential wound healing-promoting peptide from frog skin. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 49, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.H.; Deng, C.J.; Xie, Y.Y.; Guo, X.L.; Wang, Q.Q.; Liu, L.Z.; Lee, W.H.; Li, S.A.; Zhang, Y. Pore-forming toxin-like protein complex expressed by frog promotes tissue repair. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Yang, Y.; Mu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; et al. A frog-derived immunomodulatory peptide promotes cutaneous wound healing by regulating cellular response. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Duan, Z.; Tang, J.; Lv, Q.; Rong, M.; Lai, R. A short peptide from frog skin accelerates diabetic wound healing. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4633–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, G.; Xiang, Y.; Wu, J.; Jiang, P.; Lee, W.; Zhang, Y. Bm-tff2, a toad trefoil factor, promotes cell migration, survival and wound healing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Liu, C.; Gong, W.; Zhao, Z.; Hong, J.; Lin, D.; Wang, Y.; et al. Antioxidant peptidomics reveals novel skin antioxidant system. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2009, 8, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, W.B.; Hakim, M.; Luo, L.; Li, B.W.; Yang, S.L.; Song, Y.Z.; Lai, R.; Lu, Q.M. Purification and characterization of cholecystokinin from the skin of salamander Tylototriton verrucosus. Zool. Res. 2015, 36, 174–177. [Google Scholar]
- Murayama, N.; Hayashi, M.A.; Ohi, H.; Ferreira, L.A.; Hermann, V.V.; Saito, H.; Fujita, Y.; Higuchi, S.; Fernandes, B.L.; Yamane, T.; et al. Cloning and sequence analysis of a Bothrops jararaca cDNA encoding a precursor of seven bradykinin-potentiating peptides and a C-type natriuretic peptide. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, H.; Wei, L.; He, X.; Liu, H.; Yang, S.; Lai, R.; Rao, D. A novel myotropic peptide from the skin secretions of the tree frog, Polypedates pingbianensis. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1718–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Kamau, P.M.; Han, Y.; Hu, J.; Luo, A.; Luo, L.; Zheng, J.; Tian, Y.; Lai, R. The latoia consocia caterpillar induces pain by targeting nociceptive ion channel trpv1. Toxins 2019, 11, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.H.; Chen, Y.; Bai, X.W.; Yao, H.M.; Zhang, X.G.; Yan, X.W.; Lai, R. Identification and characterization of a novel neuropeptide (neuropeptide y-hs) from leech salivary gland of Haemadipsa sylvestris. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2016, 14, 677–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichti, U.; Anders, J.; Yuspa, S.H. Isolation and short-term culture of primary keratinocytes, hair follicle populations and dermal cells from newborn mice and keratinocytes from adult mice for in vitro analysis and for grafting to immunodeficient mice. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 799–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Farhangfar, F.; Zimmer, M.; Zhang, Y. Enhanced keratinocyte proliferation and migration in co-culture with fibroblasts. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, J.; He, X.; Hu, J.; Kamau, P.M.; Lai, R.; Rao, D.; Luo, L. Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway. Toxins 2020, 12, 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010015
Chang J, He X, Hu J, Kamau PM, Lai R, Rao D, Luo L. Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway. Toxins. 2020; 12(1):15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010015
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Jiajia, Xiaoqin He, Jingmei Hu, Peter Muiruri Kamau, Ren Lai, Dingqi Rao, and Lei Luo. 2020. "Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway" Toxins 12, no. 1: 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010015
APA StyleChang, J., He, X., Hu, J., Kamau, P. M., Lai, R., Rao, D., & Luo, L. (2020). Bv8-Like Toxin from the Frog Venom of Amolops jingdongensis Promotes Wound Healing via the Interleukin-1 Signaling Pathway. Toxins, 12(1), 15. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12010015