Zearalenone Removal from Corn Oil by an Enzymatic Strategy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Construction of ZEN Degrading Enzyme
2.2. Expression of ZEN Degrading Enzyme
2.3. Preparation of ZEN Degrading Enzyme
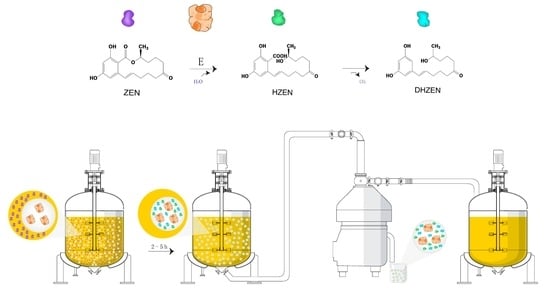
2.4. Detoxification of ZEN in Corn Oil by the Degrading Enzyme
2.5. Distribution of Degradation Products
2.6. Analysis of Tocopherol and Sterol Contents
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plasmids, Strains, Chemicals, and Reagents
5.2. Preparation of ZEN Degrading Enzyme
5.2.1. Construction and Screening of the Recombinant Strain
5.2.2. Expression and Preparation of ZEN Degrading Enzyme
5.3. Retreatment of Crude Corn Oil
5.4. Experimental Design and Treatment
5.4.1. Detoxification of ZEN in Corn Oil
5.4.2. Extraction and Analysis for ZEN in Corn Oil
5.4.3. Analysis for the Distribution of Degradation Products
5.4.4. Analysis of Tocopherols and Sterols
5.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kowalska, K.; Habrowska-Górczynska, D.E.; Piastowska-Ciesielska, A.W. Zearalenone as an endocrine disruptor in humans. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 48, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggblom, P.; Nordkvist, E. Deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, and Fusarium graminearum contamination of cereal straw; field distribution; and sampling of big bales. Mycotoxin Res. 2015, 31, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.H. Occurrence, toxicity, and analysis of major mycotoxins in Food. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gallo, A.; Giuberti, G.; Frisvad, J.C.; Bertuzzi, T.; Nielsen, K.F. Review on mycotoxin issues in ruminants: Occurrence in forages, effects of mycotoxin ingestion on health status and animal performance and practical strategies to counteract their negative effects. Toxins 2015, 7, 3057–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogowska, A.; Pomastowski, P.; Sagandykova, G.; Buszewski, B. Centre Zearalenone and its metabolites: Effect on human health, metabolism and neutralisation methods. Toxicon 2019, 15, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appell, M.; Wang, L.C.; Bosma, W.B. Analysis of the photophysical properties of zearalenone using density functional theory. J. Lumines. 2017, 188, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueza, I.M.; Raspantini, P.C.F.; Raspantini, L.E.R.; Latorre, A.O.; Górniak, S.L. Zearalenone, an Estrogenic Mycotoxin, Is an Immunotoxic Compound. Toxins 2014, 6, 1080–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinedine, A.; Soriano, J.M.; Molto, J.C.; Manes, J. Review on the toxicity, occurrence, metabolism, detoxification, regulations and intake of zearalenone: An oestrogenic mycotoxin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumsantea, S.; Aryusuk, K.; Lilitchan, S.; Jeyashoke, N.; Krisnangkura, K. Reducing Oil Losses in Alkali Refining. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 89, 1913–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R.; Reddy, K.R. Challenges and issues concerning mycotoxins contamination in oil seeds and their edible oils: Updates from last decade. Food Chem. 2017, 215, 425–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Y. Occurrence of deoxynivalenol in maize germs from North China Plain and the distribution of deoxynivalenol in the processed products of maize germs. Food Chem. 2018, 15, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakan, B.; Melcion, D.; Richard-Molard, D.; Cahagnier, B. Fungal growth and Fusarium mycotoxin content in isogenic traditional maize and genetically modified maize grown in France and Spain. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 728–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schollenberger, M.; Müller, H.M.; Rüfle, M.; Drochner, W. Natural occurrence of 16 Fusarium toxins in edible oil marketed in Germany. Food Control. 2008, 19, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EC). No 1126/2007 amending Regulation (EC) No 1881/2006 setting maximum levels for certain contaminants in foodstuffs as regards Fusarium toxins in maize and maize products. Off. J. Eur. Union. 2007, L255, 14–17. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, X.; Sun, C.; Xu, J.; Liu, D.; Han, Y.; Wu, S.; Luo, X. Detoxification of zearalenone from corn oil by adsorption of functionalized functionalized GO systems. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 430, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; He, B.; Zhang, L.; Li, P.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, X.; Zhang, W. A Structure Identification and Toxicity Assessment of the Degradation Products of Aflatoxin B1 in Peanut Oil under UV Irradiation. Toxins 2016, 8, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, X. Molecular Reaction Mechanism for Elimination of Zearalenone during Simulated Alkali Neutralization Process of Corn Oil. Food Chem. 2020, 307, 125546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, G.; Liu, X. Formation of glycidyl fatty acid esters both in real edible oils during laboratory-scale refining and in chemical model during high temperature exposure. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 5919–5927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingle, U.; Lali, A. Design of High-Productivity Mixed Tocopherol Purification from Deodorized Distillates by Tandem Reverse Phase Chromatography. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2019, 96, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlovsky, P.; Suman, M.; Berthiller, F.; De Meester, J.; Eisenbrand, G.; Perrin, I.; Oswald, I.P.; Speijers, G.; Chiodini, A.; Recker, T.; et al. Impact of food processing and detoxification treatments on mycotoxin contamination. Mycotoxin Res. 2016, 32, 179–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; Dordick, J.S.; Hauer, B.; Kiener, A.; Wubbolts, M.; Witholt, B. Industrial biocatalysis today and tomorrow. Nature. 2001, 409, 258–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruhauf, S.; Schwartz, H.; Ottner, F.; Krska, R.; Vekiru, E. Yeast cell based feed additives: Studies on aflatoxin B1and zearalenone. Food Addit. Contam. Part A 2012, 29, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Takahashi-Ando, N.; Ohsato, S.; Shibata, T.; Hamamoto, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Kimura, M. Metabolism of Zearalenone by Genetically Modified Organisms Expressing the Detoxification Gene from Clonostachys rosea. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2004, 70, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vekiru, E.; Fruhauf, S.; Hametner, C.; Schatzmayr, G.; Krska, R.; Moll, W.D.; Schuhmacher, R. Isolation and characterisation of enzymatic zearalenone hydrolysis reaction products. World Mycotoxin J. 2016, 9, 353–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhauf, S.; Novak, B.; Nagl, V.; Hackl, M.; Hartinger, D.; Rainer, V.; Labudová, S.; Adam, G.; Aleschko, M.; Moll, W.D.; et al. Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin Zearalenone to its Metabolites Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (HZEN) and Decarboxylated Hydrolyzed Zearalenone (DHZEN) Diminishes its Estrogenicity In Vitro and In Vivo. Toxins 2019, 11, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi-Ando, N.; Kimura, M.; Kakeya, H.; Osada, H.; Yamaguchi, I. A novel lactonohydrolase responsible for the detoxification of zearalenone: Enzyme purification and gene cloning. Biochem. J. 2002, 365, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Yin, L.; Hu, H.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, G. Expression, functional analysis and mutation of a novel neutral zearalenone-degrading enzyme. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, K.; Zhang, W.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, D. Characterization, expression and application of a zearalenone degrading enzyme from Neurospora crassa. AMB Express. 2018, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z. Engineering strategies for enhanced production of protein and bio-products in Pichia pastoris: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, L.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, L.; Zhang, G.; Ma, Y. High-level expression of a ZEN-detoxifying gene by codon optimization and biobrick in Pichia pastoris. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sharkawy, S.; Abul-Hajj, Y.J. Microbial cleavage of zearalenone. Xenobiotica 1988, 18, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higa-Nishiyama, A.; Takahashi-Ando, N.; Shimizu, T.; Kudo, T.; Yamaguchi, I.; Kimura, M. A model transgenic cereal plant with detoxification activity for the estrogenic mycotoxin zearalenone. Transgenic Res. 2005, 14, 713–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Ando, N.; Tokai, T.; Hamamoto, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; Kimura, M. Efficient decontamination of zearalenone, the mycotoxin of cereal pathogen, by transgenic yeasts through the expression of a synthetic lactonohydrolase gene. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 67, 838–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakeya, H.; Takahashi-Ando, N.; Kimura, M.; Onose, R.; Yamaguchi, I.; Osada, H. Biotransformation of the Mycotoxin, Zearalenone, to a Non-estrogenic Compound by a Fungal Strain of Clonostachys sp. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 2723–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- De Ruyck, K.; De Boevre, M.; Huybrechts, I.; De Saeger, S. Dietary mycotoxins, co-exposure, and carcinogenesis in humans: Short review. Mutat. Res. Rev. Mutat. Res. 2015, 766, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peng, W.; Ko, T.P.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, C.C.; Zhu, Z.; Huang, C.H.; Zeng, Y.F.; Huang, J.W.; Wang, H.J.; et al. Crystal structure and substrate-binding mode of the mycoestrogen-detoxifying lactonase ZHD from Clonostachys rosea. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62321–62325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Yang, W.; Zhou, H.; Ming, D.; Sun, K.; Xu, T.; Hu, X.; Lv, H. The structure of a complex of the lactonohydrolase zearalenone hydrolase with the hydrolysis product of zearalenone at 1.60 A˚ resolution. Acta Crystallogr. F Struct. Biol. Commun. 2017, 73, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shier, W.T.; Shier, A.C.; Xie, W.; Mirocha, C.J. Structure-activity relationships for human estrogenic activity in zearalenone mycotoxins. Toxicon 2001, 39, 1435–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Yu, Z.; Tian, X.; Han, J.; Zhang, Z.; Han, W. Theoretical Study on Zearalenol Compounds Binding with Wild Type Zearalenone Hydrolase and V153H Mutant. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hao, X.; Chang, X.; Wu, S.; Wu, Z.; Sun, C. Study on the factors to affect the activity of zearalenone degrading enzyme ZLHY6. Sci. Technol. Cereals Oils Foods 2013, 21, 99–101. [Google Scholar]
- Patrick, A. Immobilisation and application of lipases in organic media. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 6406–6436. [Google Scholar]
- Joint FAO/WHO Food Standards Committee of the Codex Alimentarius. JECFA (Food and Agriculture Organization/ World Health Organization). 2014. Available online: http://www.codexalimentarius.org/input/download/report/776/REP12_CFe.pdf (accessed on 6 January 2020).
- Durmaz, G.; Gökmen, V. Effect of refining on bioactive composition and oxidative stability of hazelnut oil. Food Res. Int. 2019, 116, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaisali, C.; Charanyaa, S.; Belur, P.D.; Regupathi, I. Refining of edible oils: A critical appraisal of current and potential technologies. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Zhu, H.; Chen, Z. Plant Sterols: Chemical and Enzymatic Structural Modifications and Effects on Their Cholesterol-Lowering Activity. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3047–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freudl, R. Beyond amino acids: Use of the Corynebacterium glutamicum cell factory for the secretion of heterologous proteins. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 258, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Fu, G.; Dong, H.; Li, J.; Du, Y.; Zhang, D. High-efficiency secretion of beta-Mannanase in Bacillus subtilis through protein synthesis and secretion optimization. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 2540–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Hirz, M.; Pichler, H.; Schwab, H. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: Recent achievements and perspectives for heterologous protein production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 5301–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin-Cereghino, G.P.; Stark, C.M.; Kim, D.; Chang, J.; Shaheen, N.; Poerwanto, H.; Agari, K.; Moua, P.; Low, L.K.; Tran, N.; et al. The effect of alpha-mating factor secretion signal mutations on recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Gene 2013, 519, 311–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sleight, S.C.; Bartley, B.A.; Lieviant, J.A.; Sauro, H.M. In-Fusion BioBrick assembly assembly and re-engineering. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 2624–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, W.; Liu, G.; Liu, X. Effects of Fe3+ and antioxidants on glycidyl ester formation in plant oil at high temperature and their influencing mechanisms. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 4167–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wang, M.; Wu, J.; Tao, F.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Q.; Zou, X. Quantitative assessment of zearalenone in maize using multivariate algorithms coupled to Raman spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2019, 286, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Primer Name | Amplicon Gene | Primer Sequence (5’→3’) | Restriction Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| zlhy-6O-5’ | zlhy-6O | CGGAATTC ATGAGAACTA GATCCACTAT | EcoR I |
| zlhy-6O-3’ | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTACAAGTACTTCTGAGTGA | Not I | |
| GS- zlhy-6O-5’ | GS+ zlhy-6O | CGCGGATCCATGTCTTTTAGATCCTTGTTGGCTTTGTCTGGTTTGGTTTGTTCTGGTTTGGCTATGAGAACTA GATCCACTAT | BamH I |
| zlhy-6O-3’ | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTACAAGTACTTCTGAGTGA | Not I | |
| IP-zlhy-6O-5’ | IP+ zlhy-6O | CGCGGATCCATGAAGTTAGCATACTCCTTGTTGCTTCCATTGGCAGGAGTCAGTGCTATGAGAACTAGATCCACTAT | BamH I |
| zlhy-6O-3’ | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGCTTACAAGTACTTCTGAGTGA | Not I | |
| IS-zlhy-6O-5’ | IS+ zlhy-6O | CGCGGATCCATGCTTTTGCAAGCTTTCCTTTTCCTTTTGGCTGGTTTTGCAGCCAAAATATCTGCAATGAGAACTA GATCCACTAT | BamH I |
| zlhy-6O-3’ | ATAAGAATGCGGCCGC TTACAAGTACTTCTGAGTGA | Not I |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, X.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Sun, C. Zearalenone Removal from Corn Oil by an Enzymatic Strategy. Toxins 2020, 12, 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020117
Chang X, Liu H, Sun J, Wang J, Zhao C, Zhang W, Zhang J, Sun C. Zearalenone Removal from Corn Oil by an Enzymatic Strategy. Toxins. 2020; 12(2):117. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020117
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Xiaojiao, Hujun Liu, Jing Sun, Jun Wang, Chengcheng Zhao, Wan Zhang, Jie Zhang, and Changpo Sun. 2020. "Zearalenone Removal from Corn Oil by an Enzymatic Strategy" Toxins 12, no. 2: 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020117
APA StyleChang, X., Liu, H., Sun, J., Wang, J., Zhao, C., Zhang, W., Zhang, J., & Sun, C. (2020). Zearalenone Removal from Corn Oil by an Enzymatic Strategy. Toxins, 12(2), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins12020117