Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms
Abstract
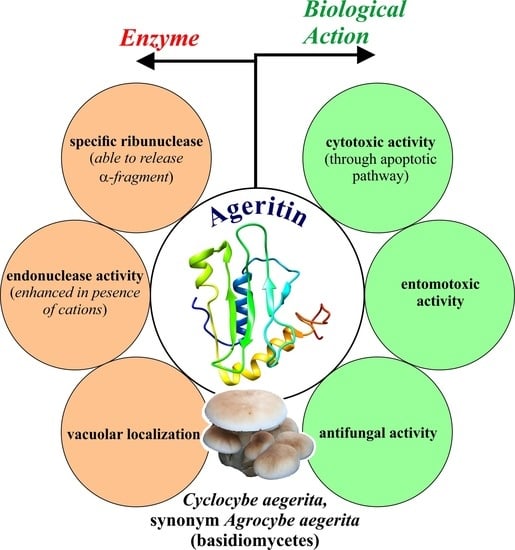
:1. Introduction
2. The Edible Mushroom Cyclocybe aegerita
3. Isolation of Ageritin from Cyclocybe aegerita (V. Brig.) Singer
4. Cellular Localization of Ageritin
5. Structural Properties of Ageritin
5.1. Physicochemical Characteristics of Ageritin
5.2. Metal Dependence
5.3. Protein Structure, 3D Homology Modelling and Phylogenetic Analysis
5.4. Gene Organization
6. Enzymatic Properties of Ageritin
6.1. Ribonucleolytic Activity of Ageritin on Ribosomes
6.2. Ribonuclease Activity on Tobacco Mosaic Virus (TMV) RNA
6.3. Endonuclease Activity on Plasmid and Genomic DNAs
7. Antiproliferative and Defense Activities of Ageritin
7.1. Cytotoxic Activity
7.2. Antifungal Activity
7.3. Entomotoxic and Nematotoxic Activity
7.4. Antibacterial Activity
8. Other Members of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins from Edible Mushrooms
9. Possible Applications of Ageritin in Medicine and Agriculture
10. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cm | GuHCl concentration at half-completion of the transition |
| RL-P | Ribotoxin-like protein |
| Tm | Melting temperature. |
References
- Ferreira, I.C.; Vaz, J.A.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Martins, A. Compounds from wild mushrooms with antitumor potential. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blagodatski, A.; Yatsunskaya, M.; Mikhailova, V.; Tiasto, V.; Kagansky, A.; Katanaev, V.L. Medicinal mushrooms as an attractive new source of natural compounds for future cancer therapy. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 29259–29274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rong, Z.; Zhao Kun, L.; Ye Ni, Z.; Jack Ho, W.; Tzi Bun, N.; Fang, L. Research Progress of Bioactive Proteins from the Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2019, 20, 196–219. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.S.; Huang, H.; Yang, Q.; Liu, W.Y. Purification of alpha-sarcin and an antifungal protein from mold (Aspergillus giganteus) by chitin affinity chromatography. Protein Expr. Purif. 2002, 25, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, R.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Barber, D.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L.; Gonzalez, G.; Mendez, E. Amino acid sequence homologies in alfa-sarcin, restrictocin and mitogillin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982, 108, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazet, I.; Vey, A. Hirsutellin A, a toxic protein produced in vitro by Hirsutella thompsonii. Microbiology 1995, 141 Pt 6, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olombrada, M.; Medina, P.; Budia, F.; Gavilanes, J.G.; Martínez-Del-Pozo, Á.; García-Ortega, L. Characterization of a new toxin from the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae: The ribotoxin anisoplin. Biol. Chem. 2017, 398, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacadena, J.; Alvarez-García, E.; Carreras-Sangrà, N.; Herrero-Galán, E.; Alegre-Cebollada, J.; García-Ortega, L.; Oñaderra, M.; Gavilanes, J.G.; del Pozo, A.M. Fungal ribotoxins: Molecular dissection of a family of natural killers. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2007, 31, 212–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ling, C.; Ermolenko, D.N. Structural insights into ribosome translocation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2016, 7, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.G.; Davies, J.E. Specific cleavage of ribosomal RNA caused by alpha sarcin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977, 4, 1097–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, Y.; Huber, P.W.; Wool, I.G. The ribonuclease activity of the cytotoxin alpha-sarcin. The characteristics of the enzymatic activity of alpha-sarcin with ribosomes and ribonucleic acids as substrates. J. Biol. Chem. 1983, 258, 2662–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olombrada, M.; Lázaro-Gorines, R.; López-Rodríguez, J.C.; Martínez-Del-Pozo, Á.; Oñaderra, M.; Maestro-López, M.; Lacadena, J.; Gavilanes, J.G.; García-Ortega, L. Fungal Ribotoxins: A Review of Potential Biotechnological Applications. Toxins 2017, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Ragucci, S.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J.M. Antifungal Activity of α-Sarcin against Penicillium digitatum: Proposal of a New Role for Fungal Ribotoxins. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1978–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Ragucci, S.; Iglesias, R.; Piccolella, S.; Amici, A.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.A.; Di Maro, A. Purification, characterization and cytotoxicity assessment of Ageritin: The first ribotoxin from the basidiomycete mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pizzo, E.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A. The ribotoxin-like protein Ostreatin from Pleurotus ostreatus fruiting bodies: Confirmation of a novel ribonuclease family expressed in basidiomycetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 161, 1329–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D.K.; Rühl, M.; Mishra, B.; Kleofas, V.; Hofrichter, M.; Herzog, R.; Pecyna, M.J.; Sharma, R.; Kellner, H.; Hennicke, F.; et al. The genome sequence of the commercially cultivated mushroom Agrocybe aegerita reveals a conserved repertoire of fruiting-related genes and a versatile suite of biopolymer-degrading enzymes. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhart, M.; Albertó, E. Morphologic characterization of Agrocybe cylindracea (Basidiomyceta, Agaricales) from America, Europe and Asia. Rev. Mex. Micol. 2007, 24, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Vizzini, A.; Angelini, C.; Ercole, V. Le sezioni Velatae e Aporus di Agrocybe sottogenere Aporus: Rivalutazione del genere Cyclocybe Velen. ed un nuova specie. Boll. Assoc. Micol. Ecol. Romana 2014, 92, 21–38. [Google Scholar]
- Nauta, M.M. Genus Agrocybe. In Flora Agaricina Neerlandica; Noordeloos, M.E., Kuyper, T.W., Vellinga, E.C., Eds.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005; Volume 6, pp. 204–211. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Ching, L.T.; Ke, X.; Cheung, P.C. Comparison of the Composition and Antioxidant Activities of Phenolics from the Fruiting Bodies of Cultivated Asian Culinary-Medicinal Mushrooms. Int J. Med. Mushrooms 2016, 18, 871–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaras, M.D.; Richie, J.P.; Calcagnotto, A.; Beelman, R.B. Mushrooms: A rich source of the antioxidants ergothioneine and glutathione. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, H.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Ren, Z.; Gao, Z.; Liu, X.; Jia, L. Polysaccharides with Antioxidative and Antiaging Activities from Enzymatic-Extractable Mycelium by Agrocybe aegerita (Brig.) Sing. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 1584647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhong, J.J.; Xiao, J.H. Secondary metabolites from higher fungi: Discovery, bioactivity, and bioproduction. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol. 2009, 113, 79–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landi, N.; Pacifico, S.; Ragucci, S.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.; Iannuzzi, F.; Zarrelli, A.; Piccolella, S.; Di Maro, A. Pioppino mushroom in southern Italy: An undervalued source of nutrients and bioactive compounds. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 5388–5397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Gu, B.; Huang, J.; Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Yin, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yu, G.; Li, Y.; Wong, B.H.; et al. Transcriptome and proteome exploration to provide a resource for the study of Agrocybe aegerita. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Jin, Y.; Yin, Y.; Yu, G.; Lan, X.; Cui, M.; Liang, Y.; Wong, B.H.C.; Guo, L. Purification and characterization of an antitumor protein with deoxyribonuclease activity from edible mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2012, 56, 1729–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Sun, H. Antitumor activity of the protein and small molecule component fractions from Agrocybe aegerita through enhancement of cytokine production. J. Med. Food 2014, 17, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labarère, J.; Noël, T. Mating type switching in the tetrapolar basidiomycete Agrocybe aegerita. Genetics 1992, 131, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.-Q.; Zhao, R.-L.; Hyde, K.D.; Begerow, D.; Kemler, M.; Yurkov, A.; McKenzie, E.H.C.; Raspé, O.; Kakishima, M.; Sánchez-Ramírez, S.; et al. Notes, outline and divergence times of Basidiomycota. Fungal Divers. 2019, 99, 105–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frings, R.A.; Maciá-Vicente, J.G.; Buße, S.; Čmoková, A.; Kellner, H.; Hofrichter, M.; Hennicke, F. Multilocus phylogeny- and fruiting feature-assisted delimitation of European Cyclocybe aegerita from a new Asian species complex and related species. Mycol. Prog. 2020, 19, 1001–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.M.; Hinsinger, D.D.; Jiang, G.F. The complete mitochondrial genome of the Agrocybe aegerita, an edible mushroom. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2017, 2, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Endo, Y.; Wool, I.G. The site of action of alpha-sarcin on eukaryotic ribosomes. The sequence at the alpha-sarcin cleavage site in 28 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 9054–9060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maro, A.; Valbonesi, P.; Bolognesi, A.; Stirpe, F.; De Luca, P.; Gigliano, G.S.; Gaudio, L.; Delli Bovi, P.; Ferranti, P.; Malorni, A.; et al. Isolation and characterization of four type-1 ribosome-inactivating proteins, with polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase activity, from leaves of Phytolacca dioica L. Planta 1999, 208, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragucci, S.; Pacifico, S.; Ruocco, M.R.; Crescente, G.; Nasso, R.; Simonetti, M.; Masullo, M.; Piccolella, S.; Pedone, P.V.; Landi, N.; et al. Ageritin from poplar mushrooms: Scale-up purification and cytotoxicity towards undifferentiated and differentiated SH-SY5Y cells. Food Funct. 2019, 10, 6342–6350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Citores, L.; Iglesias, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. Effect of an additional N-terminal methionyl residue on enzymatic and antifungal activities of Ageritin purified from Agrocybe aegerita fruiting bodies. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1226–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baglivo, I.; Ragucci, S.; D’Incecco, P.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Faoro, F.; Pedone, P.V.; Di Maro, A. Gene Organization, Expression, and Localization of Ribotoxin-Like Protein Ageritin in Fruiting Body and Mycelium of Agrocybe aegerita. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reindl, M.; Hänsch, S.; Weidtkamp-Peters, S.; Schipper, K. A Potential Lock-Type Mechanism for Unconventional Secretion in Fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabouille, C. Pathways of Unconventional Protein Secretion. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampitella, E.; Landi, N.; Oliva, R.; De Lise, F.; Bosso, A.; Gaglione, R.; Ragucci, S.; Arciello, A.; Petraccone, L.; Pizzo, E.; et al. Toxicity of ribotoxin-like protein Ageritin is related to its differential interaction with target cell membranes. J. Biochem. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero, A.; García-Ortega, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Landi, N.; Berisio, R.; Di Maro, A. Structural and enzymatic properties of Ageritin, a novel metal-dependent ribotoxin-like protein with antitumor activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2018, 1862, 2888–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasset, M. α-Sarcin and related toxins (Aspergillus). In Guidebook to Protein Toxins and Their Use in Cell Biology; Rappuoli, R., Montecucco, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 58–60. [Google Scholar]
- Herrero-Galán, E.; Lacadena, J.; Martínez del Pozo, A.; Boucias, D.G.; Olmo, N.; Oñaderra, M.; Gavilanes, J.G. The insecticidal protein hirsutellin A from the mite fungal pathogen Hirsutella thompsonii is a ribotoxin. Proteins 2008, 72, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Bigelow, C.C. Estimation of the free energy of stabilization of ribonuclease A, lysozyme, alpha-lactalbumin, and myoglobin. J. Biol. Chem. 1982, 257, 12935–12938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korennykh, A.V.; Piccirilli, J.A.; Correll, C.C. The electrostatic character of the ribosomal surface enables extraordinarily rapid target location by ribotoxins. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 436–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ruggiero, A.; García-Ortega, L.; Moreira, M.; Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Di Maro, A.; Berisio, R. Binding and enzymatic properties of Ageritin, a fungal ribotoxin with novel zinc-dependent function. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 136, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staats, C.; Kmetzsch, L.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M. Fungal zinc metabolism and its connections to virulence. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2013, 3, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tayyrov, A.; Azevedo, S.; Herzog, R.; Vogt, E.; Arzt, S.; Lüthy, P.; Müller, P.; Rühl, M.; Hennicke, F.; Künzler, M. Heterologous Production and Functional Characterization of Ageritin, a Novel Type of Ribotoxin Highly Expressed during Fruiting of the Edible Mushroom Agrocybe aegerita. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2019, 85, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Ruiz, A.; García-Ortega, L.; Kao, R.; Lacadena, J.; Oñaderra, M.; Mancheño, J.M.; Davies, J.; Martínez del Pozo, Á.; Gavilanes, J.G. RNase U2 and α-Sarcin: A Study of Relationships. In Methods in Enzymology; Nicholson, A.W., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; Volume 341, pp. 335–351. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Pedone, P.V.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A. Structural insights into nucleotide and protein sequence of Ageritin: A novel prototype of fungal ribotoxin. J. Biochem. 2018, 165, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Di Giuseppe, A.M.; Russo, R.; Poerio, E.; Severino, V.; Di Maro, A. Nutritional profiling of Eurasian woodcock meat: Chemical composition and myoglobin characterization. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 5120–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmo, N.; Turnay, J.; de Buitrago, G.G.; de Silanes, I.L.; Gavilanes, J.G.; Lizarbe, M.A. Cytotoxic mechanism of the ribotoxin alpha-sarcin. Induction of cell death via apoptosis. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 2113–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Ferreras, J.M.; Di Maro, A.; Iglesias, R. Ageritin, a Ribotoxin from Poplar Mushroom (Agrocybe aegerita) with Defensive and Antiproliferative Activities. ACS Chem. Biol. 2019, 14, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, E.; Akata, I. Viruses infecting macrofungi. Virusdisease 2018, 29, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, L.; Michel, F.; Westhof, E. Involvement of a GNRA tetraloop in long-range RNA tertiary interactions. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 236, 1271–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, I.-G.; Lee, S.-H.; Sim, D.-W.; Won, H.-S.; Lee, B.-J. Structure-based functional identification of Helicobacter pylori HP0268 as a nuclease with both DNA nicking and RNase activities. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5194–5207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J. Biological activities of the antiviral protein BE27 from sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Planta 2014, 241, 421–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesias, R.; Citores, L.; Ragucci, S.; Russo, R.; Di Maro, A.; Ferreras, J. Biological and antipathogenic activities of ribosome-inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2016, 1860, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aceto, S.; Di Maro, A.; Conforto, B.; Siniscalco, G.G.; Parente, A.; Delli Bovi, P.; Gaudio, L. Nicking activity on pBR322 DNA of ribosome inactivating proteins from Phytolacca dioica L. leaves. Biol. Chem. 2005, 386, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, A.B.; Del Pozo, A.M.; San Segundo, B. Biotechnologically relevant enzymes and proteins. Antifungal mechanism of the Aspergillus giganteus AFP against the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2006, 72, 883–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakoff, A.M. Perturbation of vesicular traffic with the carboxylic ionophore monensin. Cell 1983, 32, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasset, M.; Oñaderra, M.; Thomas, P.G.; Gavilanes, J.G. Fusion of phospholipid vesicles produced by the anti-tumour protein alpha-sarcin. Biochem. J. 1990, 265, 815–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Turnay, J.; Olmo, N.; Jiménez, A.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Gavilanes, J.G. Kinetic study of the cytotoxic effect of alpha-sarcin, a ribosome inactivating protein from Aspergillus giganteus, on tumour cell lines: Protein biosynthesis inhibition and cell binding. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 1993, 122, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancheño, J.M.; Gasset, M.; Oñaderra, M.; Gavilanes, J.G.; D’Alessio, G. Bovine seminal ribonuclease destabilizes negatively charged membranes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1994, 199, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notomista, E.; Mancheño, J.M.; Crescenzi, O.; Di Donato, A.; Gavilanes, J.; D’Alessio, G. The role of electrostatic interactions in the antitumor activity of dimeric RNases. FEBS J. 2006, 273, 3687–3697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzo, E.; Oliva, R.; Morra, R.; Bosso, A.; Ragucci, S.; Petraccone, L.; Del Vecchio, P.; Di Maro, A. Binding of a type 1 RIP and of its chimeric variant to phospholipid bilayers: Evidence for a link between cytotoxicity and protein/membrane interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2017, 1859, 2106–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.Y.; Choi, J.N.; Sharma, P.K.; Lee, W.H. Isolation and Identification of Mushroom Pathogens from Agrocybe aegerita. Mycobiology 2010, 38, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrero-Galán, E.; García-Ortega, L.; Olombrada, M.; Lacadena, J.; Del Pozo, Á.M.; Gavilanes, J.G.; Oñaderra, M. Hirsutellin A: A Paradigmatic Example of the Insecticidal Function of Fungal Ribotoxins. Insects 2013, 4, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boddy, L.; Jones, T.H. Chapter 9 Interactions between basidiomycota and invertebrates. In British Mycological Society Symposia Series; Boddy, L., Frankland, J.C., van West, P., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2008; Volume 28, pp. 155–179. [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher, J.T.; Gaze, R.H. Mushroom Pest and Disease Control: A Colour Handbook; CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2007; pp. 1–193. [Google Scholar]
- Landi, N.; Ragucci, S.; Culurciello, R.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pedone, P.V.; Pizzo, E.; Di Maro, A. Ribotoxin-like proteins from Boletus edulis: Structural properties, cytotoxicity and in vitro digestibility. Food Chem. 2021. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Allahyari, H.; Heidari, S.; Ghamgosha, M.; Saffarian, P.; Amani, J. Immunotoxin: A new tool for cancer therapy. Tumour Biol. 2017, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taneja, P.; Sharma, S.; Sinha, V.B.; Yadav, A.K. Advancement of nanoscience in development of conjugated drugs for enhanced disease prevention. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Mr (Da) | pI | IC50 (pM) | Tm (°C) | Cm ([GuHCl]1/2/M) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exp | Theor | Exp | Theor | pH 7.4 | pH 7.4 | ||
| Ageritin | 14,801.8 | 14,800.8 | >9.5 | 9.3 | 133 | 78.1 | 5.5 |
| ITC Experimental Values | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| N of Sites | KITC (M−1) | ΔH (Kcal mol−1) | |
| Mg2+ | 3 | 3.25 × 106 | −1.6 |
| Ca2+ | 1 | 7.68 × 105 | −13.1 |
| Zn2+ | 4 | 1.77 × 107 | −9.9 |
| Amino Acid Residues | Cys | Lys + Arg | Extinction Coefficient | GRAVY * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asp + Glu | 0.1% | |||
| 135 | 1 Free | 1.4 | 1.47 | −0.26 |
| Cell Line | Organism | Tissue | Morphology | Disease | Culture Properties | IC50 at 48 h | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| µg/mL | µM | |||||||
| SH-SY5Y | Human | Bone marrow | Epithelial | Neuroblastoma | Mixed, adherent/suspension | 77.30 | 5.15 | [34] |
| SK-N-BE(2)-C | Human | Bone marrow | Neuroblast | Neuroblastoma | Mixed, adherent/suspension | 8.41 | 0.56 | [14] |
| C6 | Rat | Brain | Fibroblast | Glioma | Adherent | 4.58 | 0.30 | [14] |
| U-251 | Human | Brain | Pleomorphic/ astrocytoid | Glioblastoma | Adherent | 9.46 | 0.63 | [14] |
| HeLa | Human | Cervix | Epithelial | Carcinoma | Adherent | 0.06 | 0.004 | [52] |
| Colo 320 | Human | Colon | rounded and refractile | Adenocarcinoma | Mixed, adherent/suspension | 28.50 | 1.90 | [52] |
| Raji | Human | Lymphoblast | Lymphoblast | Lymphoma | Suspension | 15.00 | 1.00 | [52] |
| SVT2 * | Mouse | Embryo | Fibroblast | - | Adherent | 26.00 | 1.73 | [39] |
| Balb/c 3T3 ** | Mouse | Embryo | Fibroblast | - | Adherent | 78.00 | 5.20 | [39] |
| Sf21 | Fall armyworm | Ovary | - | - | Suspension | n.r. | n.r. | [47] |
| Organism | Strain | Observation in Petri Dish | (°C) ** | Medium | Growth Conditions | Toxin Final Concentration (µM) | Growth Inhibition (%) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Filamentous fungus | Penicillium digitatum * |  | 26 | PDB a; 150 µL | 100 spores/well | 2.9 | 79.0 | [52] |
| 1.8 | 76.0 | |||||||
| 0.6 | 63.0 | |||||||
| 0.3 | 49.0 | |||||||
| Filamentous fungus | Trichoderma asperellum (TC74) |  | 26 | PDB a; 150 µL | 100 spores/well | 13.3 | 46.6 | [35] |
| 6.7 | 29.2 | |||||||
| 3.3 | 23.7 | |||||||
| Unicellular fungus | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (BY4741) |  | 30 | YPD b; 5 mL | 0.1 O. D. c | 13.3 | ~10 | [35] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ragucci, S.; Landi, N.; Russo, R.; Valletta, M.; Pedone, P.V.; Chambery, A.; Di Maro, A. Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms. Toxins 2021, 13, 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040263
Ragucci S, Landi N, Russo R, Valletta M, Pedone PV, Chambery A, Di Maro A. Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms. Toxins. 2021; 13(4):263. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040263
Chicago/Turabian StyleRagucci, Sara, Nicola Landi, Rosita Russo, Mariangela Valletta, Paolo Vincenzo Pedone, Angela Chambery, and Antimo Di Maro. 2021. "Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms" Toxins 13, no. 4: 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040263
APA StyleRagucci, S., Landi, N., Russo, R., Valletta, M., Pedone, P. V., Chambery, A., & Di Maro, A. (2021). Ageritin from Pioppino Mushroom: The Prototype of Ribotoxin-Like Proteins, a Novel Family of Specific Ribonucleases in Edible Mushrooms. Toxins, 13(4), 263. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13040263