Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Distribution of Cereulide within a Milk Matrix and Milk Matrix with Increased Lipid Contents
2.2. Discussion and Conclusions
3. Materials and Methods
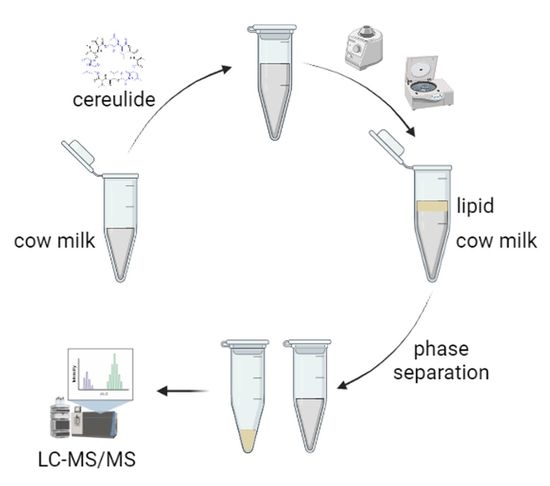
3.1. Chemicals and Samples
3.2. Sample Workup
3.3. Technical Data on Mass Spectrometry and NMR-Spectroscopy
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Lereclus, D.; Koehler, T.M. The Bacillus cereus Group: Bacillus Species with Pathogenic Potential. Microbiol. Spectr. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altayar, M.; Sutherland, A.D. Bacillus cereus is common in the environment but emetic toxin producing isolates are rare. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 100, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnands, L.M.; Dufrenne, J.B.; Rombouts, F.M.; in ’t Veld, P.H.; van Leusden, F.M. Prevalence of potentially pathogenic Bacillus cereus in food commodities in The Netherlands. J. Food Prot. 2006, 69, 2587–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoton, F.M.; Fornelos, N.; N’Guessan, E.; Hu, X.; Swiecicka, I.; Dierick, K.; Jääskeläinen, E.; Salkinoja-Salonen, M.; Mahillon, J. Family portrait of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus weihenstephanensis cereulide-producing strains. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2009, 1, 177–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messelhäusser, U.; Zucker, R.; Kampf, P.; Frenzel, E.; Blochinger, C.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Emetic Bacillus cereus are more volatile than thought: Recent foodborne outbreaks and prevalence studies in Bavaria (2007–2013). BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 465603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Agata, N.; Mori, M.; Ohta, M.; Suwan, S.; Ohtani, I.; Isobe, M. A novel dodecadepsipeptide, cereulide, isolated from Bacillus cereus causes vacuole formation in HEp-2 cells. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1994, 121, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makarasen, A.; Yoza, K.; Isobe, M. Higher structure of cereulide, an emetic toxin from Bacillus cereus, and special comparison with valinomycin, an antibiotic from Streptomyces fulvissimus. Chem. Asian J. 2009, 4, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suwan, S.; Lisobe, M.; Ohtani, I.; Agata, N.; Mori, M.; Ohta, M. Structure of cereulide, a cyclic dodecadepsipeptide toxin from Bacillus cereus, and studies on NMR characteristics of its alkali metal complexes including a conformational structure of the K+ complex. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1995, 1, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Rütschle, A.; Lücking, G.; Frenzel, E.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Scherer, S.; Hofmann, T. Depsipeptide Intermediates Interrogate Proposed Biosynthesis of Cereulide, the Emetic Toxin of Bacillus cereus. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stenfors Arnesen, L.P.; Fagerlund, A.; Granum, P.E. From soil to gut: Bacillus cereus and its food poisoning toxins. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2008, 32, 579–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ehling-Schulz, M.; Fricker, M.; Scherer, S. Bacillus cereus, the causative agent of an emetic type of food-borne illness. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2004, 48, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouzeau-Szynalski, K.; Stollewerk, K.; Messelhäusser, U.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Why be serious about emetic Bacillus cereus: Cereulide production and industrial challenges. Food Microbiol. 2020, 85, 103279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranzler, M.; Stollewerk, K.; Rouzeau-Szynalski, K.; Blayo, L.; Sulyok, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M. Temperature Exerts Control of Bacillus cereus Emetic Toxin Production on Post-transcriptional Levels. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahler, H.; Pasi, A.; Kramer, J.M.; Schulte, P.; Scoging, A.C.; Bär, W.; Krähenbühl, S. Fulminant liver failure in association with the emetic toxin of Bacillus cereus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1142–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierick, K.; van Coillie, E.; Swiecicka, I.; Meyfroidt, G.; Devlieger, H.; Meulemans, A.; Hoedemaekers, G.; Fourie, L.; Heyndrickx, M.; Mahillon, J. Fatal family outbreak of Bacillus cereus-associated food poisoning. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 4277–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Posfay-Barbe, K.M.; Schrenzel, J.; Frey, J.; Studer, R.; Korff, C.; Belli, D.C.; Parvex, P.; Rimensberger, P.C.; Schappi, M.G. Food poisoning as a cause of acute liver failure. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2008, 27, 846–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Gakumazawa, M.; Inaba, A.; Shiga, K.; Takeshita, S.; Mori, M.; Kikuchi, N. Acute encephalopathy of Bacillus cereus mimicking Reye syndrome. Brain Dev. 2010, 32, 688–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, M.; Saitou, K.; Mizumoto, H.; Matsusaka, M.; Agata, N.; Nakayama, M.; Kage, M.; Tatsumi, S.; Okamoto, A.; Yamaguchi, S.; et al. Rapid detoxification of cereulide in Bacillus cereus food poisoning. Pediatrics 2010, 125, e951–e955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, M.; Al, N.M.; Doloy, A.; Jacqmin, S.; Ghiglione, S.; Verroust, N.; Poyart, C.; Ozier, Y. Bacillus cereus, an unusual cause of fulminant liver failure: Diagnosis may prevent liver transplantation. J. Med. Microbiol. 2012, 61, 743–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tschiedel, E.; Rath, P.-M.; Steinmann, J.; Becker, H.; Dietrich, R.; Paul, A.; Felderhoff-Müser, U.; Dohna-Schwake, C. Lifesaving liver transplantation for multi-organ failure caused by Bacillus cereus food poisoning. Pediatr. Transplant. 2015, 19, E11–E14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, T.; Sipos, W.; Stark, T.D.; Käser, T.; Knecht, C.; Brunthaler, R.; Saalmüller, A.; Hofmann, T.; Ehling-Schulz, M. First Insights Into Within Host Translocation of the Bacillus cereus Toxin Cereulide Using a Porcine Model. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellouze, M.; Da Buss Silva, N.; Rouzeau-Szynalski, K.; Coisne, L.; Cantergiani, F.; Baranyi, J. Modeling Bacillus cereus Growth and Cereulide Formation in Cereal-, Dairy-, Meat-, Vegetable-Based Food and Culture Medium. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 639546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.L.S.; Montanhini, M.T.M.; Bittencourt, J.V.M.; Destro, M.T.; Bersot, L.S. Gene detection and toxin production evaluation of hemolysin BL of Bacillus cereus isolated from milk and dairy products marketed in Brazil. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2013, 44, 1195–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yobouet, B.A.; Kouamé-Sina, S.M.; Dadié, A.; Makita, K.; Grace, D.; Djè, K.M.; Bonfoh, B. Contamination of raw milk with Bacillus cereus from farm to retail in Abidjan, Côte d’Ivoire and possible health implications. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2014, 94, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ačai, P.; Valík, Ľ.; Liptáková, D. Quantitative risk assessment of Bacillus cereus in pasteurised milk produced in the Slovak Republic. Czech J. Food Sci. 2014, 32, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chaves, J.Q.; de Paiva, E.P.; Rabinovitch, L.; Vivoni, A.M. Molecular Characterization and Risk Assessment of Bacillus cereus Sensu Lato Isolated from Ultrahigh-Temperature and Pasteurized Milk Marketed in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1060–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owusu-Kwarteng, J.; Wuni, A.; Akabanda, F.; Tano-Debrah, K.; Jespersen, L. Prevalence, virulence factor genes and antibiotic resistance of Bacillus cereus sensu lato isolated from dairy farms and traditional dairy products. BMC Microbiol. 2017, 17, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S. Identification of contamination sources of Bacillus cereus in pasteurized milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 1998, 43, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, Y.; Liu, X.; Dietrich, R.; Märtlbauer, E.; Cao, J.; Ding, S.; Zhu, K. Characterization of Bacillus cereus isolates from local dairy farms in China. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2016, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, S.; Sarkar, P.K. Bacillus cereus hazard and control in industrial dairy processing environment. Food Control 2016, 69, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh-Lakha, S.; Leon-Velarde, C.G.; Chen, S.; Lee, S.; Shannon, K.; Fabri, M.; Downing, G.; Keown, B. A Study To Assess the Numbers and Prevalence of Bacillus cereus and Its Toxins in Pasteurized Fluid Milk. J. Food Prot. 2017, 80, 1085–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marxen, S.; Stark, T.D.; Rütschle, A.; Lücking, G.; Frenzel, E.; Scherer, S.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Hofmann, T. Multiparametric Quantitation of the Bacillus cereus Toxins Cereulide and Isocereulides A-G in Foods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 8307–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walser, V.; Kranzler, M.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Stark, T.D.; Hofmann, T.F. Structure Revision of Isocereulide A, an Isoform of the Food Poisoning Emetic Bacillus cereus Toxin Cereulide. Molecules 2021, 26, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frank, O.; Kreissl, J.K.; Daschner, A.; Hofmann, T. Accurate Determination of Reference Materials and Natural Isolates by Means of Quantitative 1H NMR Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Walser, V.; Kranzler, M.; Dawid, C.; Ehling-Schulz, M.; Stark, T.D.; Hofmann, T.F. Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk. Toxins 2021, 13, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080528
Walser V, Kranzler M, Dawid C, Ehling-Schulz M, Stark TD, Hofmann TF. Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk. Toxins. 2021; 13(8):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080528
Chicago/Turabian StyleWalser, Veronika, Markus Kranzler, Corinna Dawid, Monika Ehling-Schulz, Timo D. Stark, and Thomas F. Hofmann. 2021. "Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk" Toxins 13, no. 8: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080528
APA StyleWalser, V., Kranzler, M., Dawid, C., Ehling-Schulz, M., Stark, T. D., & Hofmann, T. F. (2021). Distribution of the Emetic Toxin Cereulide in Cow Milk. Toxins, 13(8), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins13080528