Shedding Lights on Crude Venom from Solitary Foraging Predatory Ant Ectatomma opaciventre: Initial Toxinological Investigation
Abstract
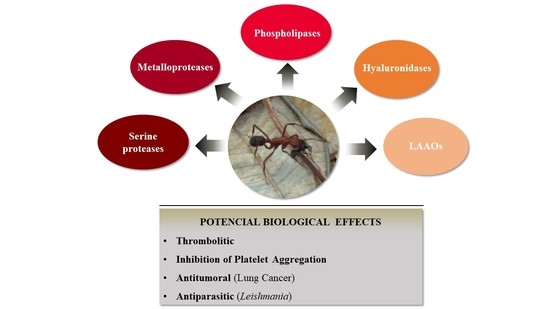
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Peptides, Proteins, and Zymography Profile in Polyacrylamide Gel from E. opaciventre Venom
2.2. Detection of Enzyme Classes Contained in the E. opaciventre Crude Venom and Quantitative Evaluation of Activity
2.3. Evaluation of Effects upon Biochemical Parameters Por E. opaciventre Venom
2.4. Inhibition of Platelet Aggregation by E. opaciventre Venom
2.5. Bioprospecting Characterization
2.5.1. Evaluation of the Toxicity by E. opaciventre Venom on Lung Cancer Cells
2.5.2. Cytotoxic Effect of E. opaciventre Venom on Promastigote Forms of Leishmania
3. Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Enzymatic Profile from E. opaciventre Venom
3.1.1. Hyaluronidases
3.1.2. Proteases
3.1.3. Phospholipases A2
3.1.4. L-Amino Acid Oxidases (LAAOs)
3.2. Analysis of Hemostatic Effects by E. opaciventre Venom
3.3. Biotechnological Potential of E. opaciventre Venom
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Venom Preparation
5.2. Biological Samples
5.3. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
5.4. Enzymatic Activities
5.4.1. Fibrinogenolytic Activity
5.4.2. Azocaseinolytic Activity
5.4.3. Zymography
5.4.4. Hyaluronidase Activity
5.4.5. Phospholipase Activity
5.4.6. L-Amino Acid Oxidase Assay
5.5. Biological Activities
5.5.1. Coagulant Activity
5.5.2. Thrombolytic Activity
5.5.3. Platelet Aggregation Assay
5.5.4. Cell Viability Assay
Cell Culture
MTT Assay
5.5.5. Antiparasitic Activity
Leishmania Promastigote Culture
Evaluation of Susceptibility of Mouse Bone Marrow-Derived Macrophages (BMDM) Treated with E. opaciventre Venom
5.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brady, S.G.; Schultz, T.R.; Fisher, B.; Ward, P.S. Evaluating alternative hypotheses for the early evolution and diversification of ants. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18172–18177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keller, R. A Phylogenetic Analysis of Ant Morphology (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) with Special Reference to the Poneromorph Subfamilies. Bull. Am. Mus. Nat. Hist. 2011, 355, 1–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, P.S. The phylogeny and evolution of ants. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2014, 45, 23–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Escoubas, P.; Padula, M.P.; Orivel, J.; Dejean, A.; Nicholson, G.M. Diversity of peptide toxins from stinging ant venoms. Toxicon 2014, 92, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolay, S.; Boulay, R.; D’Ettorre, P. Regulation of ant foraging: A review of the role of information use and personality. Front. Psychol. 2020, 11, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos-Pinto, J.R.A.; Perez-Riverol, A.; Lasa, A.M.; Palma, M.S. Diversity of peptidic and proteinaceous toxins from social Hymenoptera venoms. Toxicon 2018, 148, 172–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.R.; Fox, E.G.P.; Escoubas, P.; Orivel, J.; Nicholson, G.M.; Dejean, A. The biochemical toxin arsenal from ant venoms. Toxins 2016, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laxme, R.S.; Suranse, V.; Sunagar, K. Arthropod venoms: Biochemistry, ecology and evolution. Toxicon 2019, 158, 84–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, A.M.; Carneiro-Leão, L.; Amaral, L.; Coimbra, A. Hymenoptera venom allergy Re-Sting reactions. Eur. Ann. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 53, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adelmeyer, J.; Pickert, J.; Pfützner, W.; Möbs, C. Long-term impact of hymenoptera venom immunotherapy on clinical course, immune parameters, and psychosocial aspects. Allergol. Sel. 2021, 5, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordon, K.D.C.F.; Cologna, C.T.; Fornari-Baldo, E.C.; Pinheiro-Júnior, E.L.; Cerni, F.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Anjolette, F.A.P.; Cordeiro, F.A.; Wiezel, G.A.; Cardoso, I.A.; et al. From animal poisons and venoms to medicines: Achievements, challenges and perspectives in drug discovery. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.G.P.; Solis, D.R.; dos Santos, L.D.; Pinto, J.R.A.D.S.; Menegasso, A.R.D.S.; Silva, R.C.M.C.; Palma, M.S.; Bueno, O.C.; de Alcântara Machado, E. A simple, rapid method for the extraction of whole fire ant venom (Insecta: Formicidae: Solenopsis). Toxicon 2013, 65, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lima, D.B.; Sousa, P.L.; Torres, A.F.; da França Rodrigues, K.A.; Mello, C.P.; Tessarolo, L.D.; Quinet, Y.P.; de Oliveira, M.R.; Martins, A.M. Antiparasitic effect of Dinoponera quadriceps giant ant venom. Toxicon 2016, 120, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lima, D.; Torres, A.; Mello, C.; Menezes, R.; Sampaio, T.; Canuto, J.; Da Silva, J.; Freire, V.; Quinet, Y.; Havt, A.; et al. Antimicrobial effect of Dinoponera quadriceps (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) venom against Staphylococcus aureus strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 390–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, P.L.; Quinet, Y.; Ponte, E.L.; Vale, J.F.D.; Torres, A.F.C.; Pereira, M.G.; Assreuy, A.M.S. Venom’s antinociceptive property in the primitive ant Dinoponera quadriceps. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 144, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchard, A.; Aili, S.R.; Téné, N.; Barassé, V.; Klopp, C.; Dejean, A.; Kini, R.M.; Mrinalini, M.; Coquet, L.; Jouenne, T.; et al. Venom peptide repertoire of the European myrmicine ant Manica rubida: Identification of Insecticidal Toxins. J. Proteome Res. 2020, 19, 1800–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebaid, H.; Abdel-Salam, B.; Alhazza, I.; Al-Tamimi, J.; Hassan, I.; Rady, A.; Mashaly, A.; Mahmoud, A.; Sammour, R. Samsum ant venom modulates the immune response and redox status at the acute toxic dose in vivo. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2019, 25, e20190020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pie, M.R. Foraging ecology and behaviour of the ponerine ant Ectatomma opaciventre Roger in a Brazilian savannah. J. Nat. Hist. 2004, 38, 717–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arseniev, A.; Pluzhnikov, K.; Nolde, D.; Sobol, A.; Sukhanov, S.; Grishin, E.; Torgov, M. Toxic principle of selva ant venom is a pore-forming protein transformer. FEBS Lett. 1994, 347, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolde, D.; Sobol, A.G.; Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Grishin, E.V.; Arseniev, A.S. Three-dimensional structure of ectatomin from Ectatomma tuberculatum ant venom. J. Biomol. NMR 1995, 5, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluzhnikov, K.A.; Kozlov, S.A.; Vassilevski, A.A.; Vorontsova, O.V.; Feofanov, A.V.; Grishin, E.V. Linear antimicrobial peptides from Ectatomma quadridens ant venom. Biochimie 2014, 107, 211–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.S.R.; De Souza, D.L.N.; Guimaraes, D.O.; Lopes, D.S.; Mamede, C.C.N.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Ache, D.C.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Borges, M.H.; et al. Biochemical and functional characterization of Bothropoidin: The first haemorrhagic metalloproteinase from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom. J. Biochem. 2014, 157, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, F.B.; Gomes, M.S.R.; De Souza, D.L.N.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Castanheira, L.E.; Borges, M.H.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Brandeburgo, M.I.H.; Rodrigues, V.M. Molecular cloning and pharmacological properties of an acidic PLA2 from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom. Toxins 2013, 5, 2403–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, R.S.; da Silva, J.; França, J.B.; Fonseca, F.P.; Otaviano, A.R.; Silva, F.H.; Hamaguchi, A.; Magro, A.J.; Braz, A.S.K.; Dos Santos, J.I. Structural and functional properties of Bp-LAAO, a new l-amino acid oxidase isolated from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom. Biochimie 2009, 91, 490–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, A.A. The evolutionary dynamics of venom toxins made by insects and other animals. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2020, 48, 1353–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J. Venomics: Integrative venom proteomics and beyond. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 611–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaas, Q.; Craik, D.J. Bioinformatics-aided venomics. Toxins 2015, 7, 2159–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, A.F.C.; Huang, C.; Chong, C.-M.; Leung, S.W.; Prieto, A.; Havt, A.; Quinet, Y.P.; Martins, A.M.C.; Lee, S.M.Y.; Rádis-Baptista, G. Transcriptome analysis in venom gland of the predatory giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps: Insights into the polypeptide toxin arsenal of hymenopterans. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Touchard, A.; Téné, N.; Song, P.C.T.; Lefranc, B.; Leprince, J.; Treilhou, M.; Bonnafé, E. Deciphering the molecular diversity of an ant venom peptidome through a venomics approach. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 3503–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Hayward, R.; Robinson, S.D.; Pineda, S.S.; Lalagüe, H.; Vetter, I.; Undheim, E.A.B.; Kini, R.M.; Escoubas, P.; et al. An integrated proteomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals the venom complexity of the bullet ant Paraponera clavata. Toxins 2020, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, S.R.; Touchard, A.; Petitclerc, F.; Dejean, A.; Orivel, J.; Padula, M.P.; Escoubas, P.; Nicholson, G.M. Combined peptidomic and proteomic analysis of electrically stimulated and manually dissected venom from the South American bullet ant Paraponera clavata. J. Proteome Res. 2017, 16, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanandy, T.; Wilson, R.; Gell, D.; Rose, H.E.; Gueven, N.; Davies, N.W.; Brown, S.G.A.; Wiese, M.D. Towards complete identification of allergens in Jack Jumper (Myrmecia pilosula) ant venom and their clinical relevance: An immunoproteomic approach. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2018, 48, 1222–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, J.-L.; Belghazi, M.; Legeai, F.; Ravallec, M.; Frayssinet, M.; Robin, S.; Aboubakar-Souna, D.; Srinivasan, R.; Tamò, M.; Poirié, M.; et al. Proteo-trancriptomic analyses reveal a large expansion of metalloprotease-like proteins in atypical venom Vesicles of the wasp Meteorus pulchricornis (Braconidae). Toxins 2021, 13, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuma, K.; Masuko, K.; Konno, K.; Inagaki, H. Combined venom gland transcriptomic and venom peptidomic analysis of the predatory ant Odontomachus monticola. Toxins 2017, 9, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Wang, W.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Fan, Q. Transcriptome profiling of venom gland from wasp species: De novo assembly, functional annotation, and discovery of molecular markers. BMC Genom. 2020, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aeberhard, J.; Haeberli, G.; Müller, U.; Helbling, A. Specific immunotherapy in hymenoptera venom allergy and concomitant malignancy: A retrospective follow-up focusing on effectiveness and safety. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arias, T.A.; Gómis, V.S.; Mera, T.S.; Castro, A.V.; Gutiérrez, J.V.; Llamazares, A.A.; Amérigo, D.A.; Gonzalez, F.C.; Noche, C.D.; Fernandez, D.G.; et al. Key issues in hymenoptera venom allergy: An update. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 27, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baptista-Saidemberg, N.B.; Saidemberg, D.M.; Palma, M.S. Profiling the peptidome of the venom from the social wasp Agelaia pallipes pallipes. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucca, M.B.; Cerni, F.A.; Oliveira, I.S.; Jenkins, T.P.; Argemí, L.; Sørensen, C.V.; Ahmadi, S.; Barbosa, J.E.; Laustsen, A.H. Bee updated: Current knowledge on bee venom and bee envenoming therapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zamith-Miranda, D.; Fox, E.G.P.; Monteiro, A.P.; Gama, D.; Poublan, L.E.; de Araujo, A.F.; Araujo, M.F.C.; Atella, G.C.; Machado, E.A.; Diaz, B.L. The allergic response mediated by fire ant venom proteins. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Wahed, A.A.; Yosri, N.; Sakr, H.; Du, M.; Algethami, A.; Zhao, C.; Abdelazeem, A.; Tahir, H.; Masry, S.; Abdel-Daim, M.; et al. Wasp venom biochemical components and their potential in biological applications and nanotechnological interventions. Toxins 2021, 13, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologna, C.T.; dos Santos Cardoso, J.; Jourdan, E.; Degueldre, M.; Upert, G.; Gilles, N.; Uetanabaro, A.P.T.; Costa Neto, E.M.; Thonart, P.; de Pauw, E.; et al. Peptidomic comparison and characterization of the major components of the venom of the giant ant Dinoponera quadriceps collected in four different areas of Brazil. J. Proteom. 2013, 94, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluzhinikov, K.A.; Nol’de, D.E.; Tertyshnikova, S.M.; Sukhanov, S.V.; Sobol’, A.G.; Torgov, M.; Filippov, A.K.; Arsen’ev, A.S.; Grishin, E.V. Structure-activity study of the basic toxic component of venom from the ant Ectatomma tuberculatum. Bioorganicheskaia Khimiia 1994, 20, 857–871. [Google Scholar]
- Bordon, K.C.F.; Wiezel, G.A.; Amorim, F.G.; Arantes, E.C. Arthropod venom Hyaluronidases: Biochemical properties and potential applications in medicine and biotechnology. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Silva, M.F.; Mota, C.M.; Miranda, V.D.S.; Cunha, A.D.O.; Silva, M.C.; Naves, K.S.C.; De Oliveira, F.; Silva, D.A.D.O.; Mineo, T.W.P.; Santiago, F.M. Biological and enzymatic characterization of proteases from crude venom of the ant Odontomachus bauri. Toxins 2015, 7, 5114–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevallos, M.; Navarro-Duque, C.; Varela-Julia, M.; Alagon, A. Molecular mass determination and assay of venom hyaluronidases by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Toxicon 1992, 30, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungsa, P.; Incamnoi, P.; Sukprasert, S.; Uawonggul, N.; Klaynongsruang, S.; Daduang, J.; Patramanon, R.; Roytrakul, S.; Daduang, S. Cloning, structural modelling and characterization of VesT2s, a wasp venom hyaluronidase (HAase) from Vespa tropica. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2016, 22, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacomini, D.L.J.; Pereira, F.D.C.; Pinto, J.R.A.D.S.; dos Santos, L.D.; Neto, A.J.D.S.; Giratto, D.T.; Palma, M.S.; Zollner, R.D.L.; Braga, M.R.B. Hyaluronidase from the venom of the social wasp Polybia paulista (Hymenoptera, Vespidae): Cloning, structural modeling, purification, and immunological analysis. Toxicon 2013, 64, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wurm, Y.; Wang, J.; Riba-Grognuz, O.; Corona, M.; Nygaard, S.; Hunt, B.; Ingram, K.K.; Falquet, L.; Nipitwattanaphon, M.; Gotzek, D.; et al. The genome of the fire ant Solenopsis invicta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 5679–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonasio, R.; Zhang, G.; Ye, C.; Mutti, N.S.; Fang, X.; Qin, N.; Donahue, G.; Yang, P.; Li, Q.; Li, C.; et al. Genomic comparison of the ants Camponotus floridanus and Harpegnathos saltator. Science 2010, 329, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariano, D.O.C.; de Oliveira, U.C.; Zaharenko, A.J.; Pimenta, D.C.; Rádis-Baptista, G.; Da Silva, P.; Álvaro, R.D.B. Bottom-Up Proteomic Analysis of Polypeptide Venom Components of the Giant Ant Dinoponera Quadriceps. Toxins 2019, 11, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dos Santos Pinto, J.R.; Fox, E.G.P.; Saidemberg, D.M.; Santos, L.D.; Menegasso, A.R.D.S.; Costa-Manso, E.; Machado, E.A.; Bueno, O.C.; Palma, M.S. Proteomic view of the venom from the fire ant Solenopsis invicta Buren. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 4643–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Pinto, J.R.; Games, P.D.; Azevedo, D.O.; Barros, E.; De Oliveira, L.L.; Ramos, H.J.D.O.; Baracat-Pereira, M.C.; Serrão, J.E. Proteomic analysis of the venom of the predatory ant Pachycondyla striata (Hymenoptera: Formicidae). Arch. Insect Biochem. Physiol. 2017, 96, e21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schmidt, J.O.; Blum, M.S.; Overal, W.L. Comparative enzymology of venoms from stinging Hymenoptera. Toxicon 1986, 24, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordon, K.; Perino, M.G.; Giglio, J.R.; Arantes, E.C. Isolation, enzymatic characterization and antiedematogenic activity of the first reported rattlesnake hyaluronidase from Crotalus durissus terrificus venom. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2740–2748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiren, N.; de Graaf, D.C.; Vanrobaeys, F.; Danneels, E.L.; Devreese, B.; Van Beeumen, J.; Jacobs, F.J. Proteomic analysis of the honey bee worker venom gland focusing on the mechanisms of protection against tissue damage. Toxicon 2008, 52, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-M.; Zhao, Y.-J.; Xu, Z.-W.; Zhu, J.-Y. Venom serine proteinase homolog of the ectoparasitoid Scleroderma guani impairs host phenoloxidase cascade. Toxicon 2020, 183, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R. Hymenoptera Venom Allergens. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 30, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winningham, K.M.; Fitch, C.D.; Schmidt, M.; Hoffman, D.R. Hymenoptera venom protease allergens. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004, 114, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitworth, S.T.; Blum, M.S.; Travis, J. Proteolytic Enzymes from Larvae of the Fire Ant, Solenopsis invicta. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 14430–14434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zóia, M.A.P.; Azevedo, F.V.P.D.V.; Vecchi, L.; Mota, S.T.S.; Rodovalho, V.; Cordeiro, A.O.; Correia, L.I.V.; Silva, A.C.A.; Ávila, V.D.; De Araújo, T.G.; et al. Inhibition of triple-negative breast cancer cell aggressiveness by cathepsin D blockage: Role of Annexin A1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valentin, E.; Ghomashchi, F.; Gelb, M.H.; Lazdunski, M.; Lambeau, G. Novel Human Secreted Phospholipase A2 with Homology to the Group III Bee Venom Enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 7492–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Sicard, N.; Candy, D.; Anderson, M. The biochemical composition of venom from the pavement ant (Tetramorium caespitum L.). Toxicon 1989, 27, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nidamarthi, H.V.K.; Choudhury, M.; Velmurugan, D. Understanding the binding mechanism of succinic acid against phospholipase A 2 from bee venom. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2021, 35, e22715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, A.; Tomono, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Inui, M.; Morita, N.; Ichimonji, I.; Takagi, H.; Nagaoka, F.; Matsumoto, M.; Ito, Y.; et al. Phospholipase A2 from bee venom increases poly(I:C)-induced activation in human keratinocytes. Int. Immunol. 2020, 32, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komi, D.E.A.; Shafaghat, F.; Zwiener, R. Immunology of Bee Venom. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 54, 386–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourgeois, E.A.; Subramaniam, S.; Cheng, T.-Y.; de Jong, A.; Layre, E.; Ly, D.; Salimi, M.; Legaspi, A.; Modlin, R.L.; Salio, M.; et al. Bee venom processes human skin lipids for presentation by CD1a. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 149–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sukprasert, S.; Rungsa, P.; Uawonggul, N.; Incamnoi, P.; Thammasirirak, S.; Daduang, J.; Daduang, S. Purification and structural characterisation of phospholipase A1 (Vespapase, Ves a 1) from Thai banded tiger wasp (Vespa affinis) venom. Toxicon 2013, 61, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.R.; Sakell, R.H.; Schmidt, M. Sol i 1, the phospholipase allergen of imported fire ant venom. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005, 115, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikodijević, D.D.; Jovankić, J.V.; Cvetković, D.M.; Anđelković, M.Z.; Nikezić, A.G.; Milutinović, M.G. L-amino acid oxidase from snake venom: Biotransformation and induction of apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 910, 174466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, I.S.; Cardoso, I.A.; Bordon, K.D.C.F.; Carone, S.E.I.; Boldrini-França, J.; Pucca, M.B.; Zoccal, K.F.; Faccioli, L.H.; Sampaio, S.V.; Rosa, J.C.; et al. Global proteomic and functional analysis of Crotalus durissus collilineatus individual venom variation and its impact on envenoming. J. Proteom. 2019, 191, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Miura, T. Antibacterial properties of l-amino acid oxidase: Mechanisms of action and perspectives for therapeutic applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 7847–7857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izidoro, L.F.M.; Sobrinho, J.C.; Mendes, M.M.; Costa, T.R.; Grabner, A.N.; Rodrigues, V.D.M.; Da Silva, S.L.; Zanchi, F.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Fernandes, C.F.; et al. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: Trends in pharmacology and biochemistry. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 196754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perumal Samy, R.; Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Thwin, M.M.; Chow, T.K.V.; Bow, H.; Yap, E.H.; Thong, T.W.J. Antibacterial activity of snake, scorpion and bee venoms: A comparison with purified venom phospholipase A2 enzymes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2007, 102, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.-J. Acurhagin-C, an ECD disintegrin, inhibits integrin αvβ3-mediated human endothelial cell functions by inducing apoptosis via caspase-3 activation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 1338–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yeh, C.H.; Peng, H.C.; Huang, T.F. Accutin, a new disintegrin, inhibits angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo by acting as integrin alphavbeta3 antagonist and inducing apoptosis. Blood 1998, 92, 3268–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachetto, A.T.A.; Mackman, N. Modulation of the mammalian coagulation system by venoms and other proteins from snakes, arthropods, nematodes and insects. Thromb. Res. 2019, 178, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bade, B.C.; Cruz, C.S.D. Lung Cancer. Clin. Chest Med. 2020, 41, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.S.; Baldwin, D.R. Recent advances in the management of lung cancer. Clin. Med. 2018, 18, s41–s46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, G.; Garraud, O.; Daghestani, M.; Al-Khalifa, M.S.; Richard, Y. Human breast carcinoma cells are induced to apoptosis by samsum ant venom through an IGF-1-dependant pathway, PI3K/AKT and ERK signaling. Cell. Immunol. 2012, 273, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taslimi, Y.; Zahedifard, F.; Rafati, S. Leishmaniasis and various immunotherapeutic approaches. Parasitolology 2018, 145, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhoundi, M.; Downing, T.; Votypka, J.; Kuhls, K.; Lukeš, J.; Cannet, A.; Ravel, C.; Marty, P.; Delaunay, P.; Kasbari, M.; et al. Leishmania infections: Molecular targets and diagnosis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2017, 57, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of Structural Proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, V.M.; Soares, A.; Guerra-Sá, R.; Rodrigues, V.; Fontes, M.; Giglio, J.R. Structural and functional characterization of neuwiedase, a nonhemorrhagic fibrin(ogen)olytic metalloprotease from Bothrops neuwiedi snake venom. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2000, 381, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Ferrante, N. Turbidimetric measurement of acid mucopoly-saccharides and hyaluronidase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1956, 220, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Haas, G.; Postema, N.; Nieuwenhuizen, W.; van Deenen, L. Purification and properties of phospholipase a from porcine pancreas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Enzym. 1968, 159, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, E.; Lübke, K.; Lehmann, M.; Beetz, I. Haemolytic activity and action on the surface tension of aqueous solutions of synthetic melittins and their derivatives. Experientia 1971, 27, 764–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, N.-H.; Ponnudurai, G. An investigation on the antigenic cross-reactivity of Calloselasma rhodostoma (Malayan pit viper) venom hemorrhagin, thrombin-like enzyme and l-amino acid oxidase using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Toxicon 1994, 32, 1265–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assakura, M.T.; Salomão, M.D.G.; Puorto, G.; Mandelbaum, F.R. Hemorrhagic, fibrinogenolytic and edema-forming activities of the venom of the colubrid snake Philodryas olfersii (green snake). Toxicon 1992, 30, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Amino Acids | E. opaciventre |
|---|---|
| Serine | 384.18 |
| Valine | 310.43 |
| Glutamine | 290.05 |
| Alanine | 259.49 |
| Arginine | 161.48 |
| Asparagine | 153.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Correia, L.I.V.; Azevedo, F.V.P.d.V.; Amorim, F.G.; Cirilo Gimenes, S.N.; Polloni, L.; Zoia, M.A.P.; Costa, M.S.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Santos, J.C.; et al. Shedding Lights on Crude Venom from Solitary Foraging Predatory Ant Ectatomma opaciventre: Initial Toxinological Investigation. Toxins 2022, 14, 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010037
Correia LIV, Azevedo FVPdV, Amorim FG, Cirilo Gimenes SN, Polloni L, Zoia MAP, Costa MS, Rodrigues JP, Yoneyama KAG, Santos JC, et al. Shedding Lights on Crude Venom from Solitary Foraging Predatory Ant Ectatomma opaciventre: Initial Toxinological Investigation. Toxins. 2022; 14(1):37. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010037
Chicago/Turabian StyleCorreia, Lucas Ian Veloso, Fernanda Van Petten de Vasconcelos Azevedo, Fernanda Gobbi Amorim, Sarah Natalie Cirilo Gimenes, Lorena Polloni, Mariana Alves Pereira Zoia, Mônica Soares Costa, Jéssica Peixoto Rodrigues, Kelly A. Geraldo Yoneyama, Jean Carlos Santos, and et al. 2022. "Shedding Lights on Crude Venom from Solitary Foraging Predatory Ant Ectatomma opaciventre: Initial Toxinological Investigation" Toxins 14, no. 1: 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010037
APA StyleCorreia, L. I. V., Azevedo, F. V. P. d. V., Amorim, F. G., Cirilo Gimenes, S. N., Polloni, L., Zoia, M. A. P., Costa, M. S., Rodrigues, J. P., Yoneyama, K. A. G., Santos, J. C., Arantes, E. C., Rodrigues, V. d. M., Goulart, L. R., & Rodrigues, R. S. (2022). Shedding Lights on Crude Venom from Solitary Foraging Predatory Ant Ectatomma opaciventre: Initial Toxinological Investigation. Toxins, 14(1), 37. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14010037