The Contribution of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinases to the Synergistic Action of Viper Venom on the Bioenergetic Profile of Vero Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
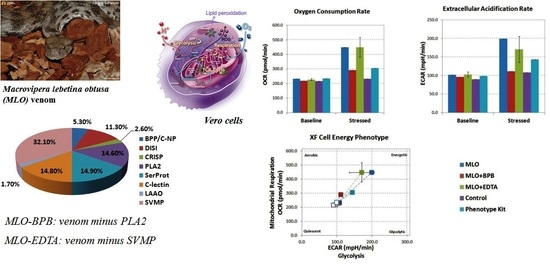
2.1. Macrovipera Lebetina Obtusa Venom Drives an Increase in Both Glycolysis and Mitochondrial Respiration, While the Venom Preincubated with BPB or EDTA Only Impacts Oxidative Phosphorylation, and Not Rate of Glycolysis
2.2. During the MTT Test, the BPB-Blocked Venom Demonstrates the Most Cytotoxic Activity Even at Very Low Concentrations
2.3. ROS Overproduction Is Noticed Both in the BPB-Blocked and Crude Venom, While after Switching off the SVMPs, the Venom Became an Antioxidant
2.4. Lipid Peroxidation Processes Are Also Remarkably Higher in PLA2-Inhibited Venom
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Venom
4.2. Preparation of PLA2 and/or Metalloproteinases Inhibited Venom
4.3. Analysis of the Oxygen Consumption Rate (OCR) and the Extracellular Acidification Rate (ECAR)
4.4. Chemiluminescence Analysis and Lipid Peroxidation
4.5. MTT-Assessed Cytotoxic Effect on Vero Cells
4.6. Statistics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Madsen, J.M. Toxins as weapons of mass destruction. A comparison and contrast with biological-warfare and chemical-warfare agents. Clin. Lab. Med. 2001, 21, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escoubas, P.; King, G.F. Venomics as a drug discovery platform. Expert Rev. Proteom. 2009, 6, 221–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.F. Venoms as a platform for human drugs: Translating toxins into therapeutics. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 1469–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna, N.; Sanchez-Garcia, L.; Unzueta, U.; Diaz, R.; Vazquez, E.; Mangues, R.; Villaverde, A. Protein-Based Therapeutic Killing for Cancer Therapies. Trends Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 318–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovsepian, S.V.; O’Leary, V.B.; Ayvazyan, N.M.; Al-Sabi, A.; Ntziachristos, V.; Dolly, J.O. Neurobiology and Therapeutic Applications of Neurotoxins Targeting Transmitter Release. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 193, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Garcia, M.L. Therapeutic potential of venom peptides. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbri, A.; Travaglione, S.; Falzano, L.; Fiorentini, C. Bacterial protein toxins: Current and potential clinical use. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1116–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doley, R.; Kini, R.M. Protein complexes in snake venom. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 2851–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghazaryan, N.A.; Simonyan, K.V.; Danielyan, M.H.; Zakaryan, N.A.; Ghulikyan, L.A.; Kirakosyan, G.R.; Chavushyan, V.A.; Ayvazyan, N.M. Study of the neuroprotective impact and free radical processes of Macrovipera lebetina obtusa snake venom in the model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurophysiology 2017, 49, 412–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvazyan, N.M.; O’Leary, V.B.; Dolly, J.O.; Ovsepian, S.V. Neurobiology and therapeutic utility of neurotoxins targeting postsynaptic mechanisms of neuromuscular transmission. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1968–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landová, E.; Bakhshaliyeva, N.; Janovcová, M.; Peléšková, Š.; Suleymanova, M.; Polák, J.; Guliev, A.; Frynta, D. Association Between Fear and Beauty Evaluation of Snakes: Cross-Cultural Findings. Front Psychol. 2018, 9, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pla, D.; Quesada-Bernat, S.; Rodríguez, Y.; Sánchez, A.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Mesén, S.; Segura, Á.; Mustafin, D.O.; Fomina, Y.A.; et al. Dagestan blunt-nosed viper, Macrovipera lebetina obtusa (Dwigubsky, 1832), venom. Venomics, antivenomics, and neutralization assays of the lethal and toxic venom activities by anti-Macrovipera lebetina turanica and anti-Vipera berus berus antivenoms. Toxicon X 2020, 6, 100035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazaryan, N.A.; Ghulikyan, L.A.; Kishmiryan, A.V.; Kirakosyan, G.R.; Nazaryan, O.H.; Ghevondyan, T.H.; Zaqaryan, N.A.; Ayvazyan, N.M. Anti-tumor effect investigation of obtustatin and crude Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom in S-180 sarcoma bearing mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 764, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatulian, S.A. Toward Understanding Interfacial Activation of Secretory Phospholipase A2 (PLA2): Membrane Surface Properties and Membrane-Induced Structural Changes in the Enzyme Contribute Synergistically to PLA2 Activation. Biophys. J. 2001, 80, 789–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kini, R.M. Venom Phospholipase A2 Enzymes: Structure, Function and Mechanism; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Mackessy, S.P. Handbook of Venoms and Toxins of Reptiles; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; Taylor & Francis Group: Oxfordshire, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.W.; Gutierrez, J.M. Snake Venom Metalloproteinases; MDPI: Basel, Switzerland, 2017; 264p. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, L.; Ayvazyan, N.; Calvete, J.J. Snake venomics of the Armenian mountain vipers Macrovipera lebetina obtusa and Vipera raddei. J. Proteom. 2008, 71, 98–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghazaryan, N.A.; Ghulikyan, L.A.; Kishmiryan, A.V.; Andreeva, T.V.; Utkin, Y.u.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Lomonte, B.; Ayvazyan, N.M. Phospholipases a2 from Viperidae snakes: Differences in membranotropic activity between enzymatically active toxin and its inactive isoforms. BBA Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazarian, N.A.; Gulikyan, L.; Lomonte, B.; Andreeva, T.V.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.u.N.; Aivazyan, N.M. Comparative Analysis of Membranotropic Properties of Various Phospholipases A2 from Venom of Snakes of the Family Viperidae. Dokl. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 457, 111–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, O.G.; Tsai, M.D.; Gelb, M.H.; Jain, M.K. Interfacial enzymology: The secreted phospholipase A2-paradigm. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2613–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, E.A.; Cao, J.; Hsu, Y.H.; Magrioti, V.; Kokotos, G. Phospholipase A2 enzymes: Physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6130–6185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brahma, R.K.; McCleary, R.J.; Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Venom gland transcriptomics for identifying, cataloging, and characterizing venom proteins in snakes. Toxicon 2015, 93, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šribar, J.; Kovačič, L.; Oberčkal, J.; Ivanušec, A.; Petan, T.; Fox, J.W.; Križaj, I. The neurotoxic secreted phospholipase A2 from the Vipera a. ammodytes venom targets cytochrome c oxidase in neuronal mitochondria. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Križaj, I. Ammodytoxin: A window into understanding presynaptic toxicity of secreted phospholipases A2 and more. Toxicon. 2011, 58, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calvete, J.J.; Sanz, L.; Angulo, Y.; Lomonte, B.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Venoms, venomics, antivenomics. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tasoulis, T.; Isbister, G.K. A review and database of snake venom proteomes. Toxins 2017, 9, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brown, M.C.; Staniszewska, I.; Del Valle, L.; Tuszynski, G.P.; Marcinkiewicz, C. Angiostatic activity of obtustatin as alpha1beta1 integrin inhibitor in experimental melanoma growth. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 2195–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghazaryan, N.; Movsisyan, N.; Macedo, J.C.; Vaz, S.; Ayvazyan, N.; Pardo, L.; Logarinho, E. The antitumor efficacy of monomeric disintegrin obtustatin in S-180 sarcoma mouse model. Investig. New Drugs 2019, 193, 135–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McLane, M.A.; Marcinkiewicz, C.; Vijay-Kumar, S.; Wierzbicka-Patynowski, I.; Niewiarowski, S. Viper Venom Disintegrins and Related Molecules. Exp. Biol. Med. 1998, 219, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerencser, A.A.; Neilson, A.; Choi, S.W.; Edman, U.; Yadava, N.; Oh, R.J.; Ferrick, D.A.; Nicholls, D.G.; Brand, M.D. Quantitative microplate-based respirometry with correction for oxygen diffusion. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6868–6878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nadanaciva, S.; Rana, P.; Beeson, G.C.; Chen, D.; Ferrick, D.A.; Beeson, C.C.; Will, Y. Assessment of drug-induced mitochondrial dysfunction via altered cellular respiration and acidification measured in a 96-well platform. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2012, 44, 421–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, D.G.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; Wu, M.; Jensen, P.B.; Rogers, G.W.; Ferrick, D.A. Bioenergetic profile experiment using C2C12 myoblast cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2010, 46, e2511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diepart, C.; Verrax, J.; Calderon, P.B.; Feron, O.; Jordan, B.F.; Gallez, B. Comparison of methods for measuring oxygen consumption in tumor cells in vitro. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 396, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mookerjee, S.A.; Goncalves, R.L.S.; Gerencser, A.A.; Nicholls, D.G.; Brand, M.D. The contributions of respiration and glycolysis to extracellular acid production. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 2015, 1847, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finkel, T.; Holbrook, N. 2000. Oxidants, Oxidative Stress and the Biology of Aging. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonarduzzi, G.; Arkan, M.; Başağa, H.; Chiarpotto, E.; Sevanian, A.; Poli, G. Lipid Oxidation Products in Cell Signaling. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2000, 28, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.W.; Serrano, S.M.T. Snake Toxins and Haemostasis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 951–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, M.; Clemetson, K.; Markland, F.S.; McLane, M.A.; Morita, T. Toxins and Hemostasis: From Bench to Bedside; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, D.C.I.; Armugam, A.; Jeyaseelan, K. Snake venom components and their applications in biomedicine. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 3030–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M.; Evans, H.J. Structural domains in venom proteins: Evidence that metalloproteinases and nonenzymatic platelet aggregation inhibitors (disintegrins) from snake venoms are derived by proteolysis from a common precursor. Toxicon 1992, 30, 265–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskanyan, A.V.; Darbinyan, A.A.; Parseghyan, L.M. Hemorrhagic changes and microglia activation induced by Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom with the inhibited enzymatic activity in rat brain. Toxicol Res. 2022, 38, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcussi, S.; Sant’Ana, C.D.; Oliveira, C.Z.; Rueda, A.Q.; Menaldo, D.L.; Beleboni, R.O.; Stabeli, R.G.; Giglio, J.R.; Fontes, M.R.; Soares, A.M. Snake venom phospholipase A2 inhibitors: Medicinal chemistry and therapeutic potential. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtović, T.; Lang Balija, M.; Ayvazyan, N.; Halassy, B. Paraspecificity of Vipera a. ammodytes-specific antivenom towards Montivipera raddei and Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venoms. Toxicon 2014, 78, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaqaryan, N.A.; Ghazaryan, N.A.; Ayvazyan, N.M. Dynamic changes in lipid peroxidation and antioxidant level in rat’s tissues with Macrovipera lebetina obtusa and Montivipera raddei venom intoxication. J. Biophys. Chem. 2014, 5, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuke, K.; Nakamura, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Kayanoki, Y.; Tatsumi, H.; Taniguchi, N. Induction of Apoptotic Cell Death in Human Endothelial Cells Treated with Snake Venom: Implication of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species and Protective Effects of Glutathione and Superoxide Dismutases. J. Biochem. 1997, 122, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Chadwick, A.E.; Dart, C.; Kamishima, T.; Quayle, J.M. Bioenergetic profile of human coronary artery smooth muscle cells and effect of metabolic intervention. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0177951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mookerjee, S.A.; Nicholls, D.G.; Brand, M.D. Determining maximum glycolytic capacity using extracellular flux measurements. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hesterberg, R.S.; Cleveland, J.L.; Epling-Burnette, P.K. Role of polyamines in immune cell functions. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bilz, N.C.; Jahn, K.; Lorenz, M.; Ludtke, A.; Hübschen, J.M.; Geyer, H.; Mankertz, A.; Hubner, D.; Liebert, U.G.; Claus, C. Rubella viruses shift cellular bioenergetics to a more oxidative and glycolytic phenotype with a strain-specific requirement for glutamine. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00934-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, M.; Neilson, A.; Swift, A.L.; Moran, R.; Tamagnine, J.; Parslow, D.; Armistead, S.; Lemire, K.; Orrell, J.; Teich, J.; et al. Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link between attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am. J. Physiol. 2006, 292, C125–C136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, G.N.; Morofuji, Y.; Banks, W.A.; Price, T.O. High glucose-induced mitochondrial respiration and reactive oxygen species in mouse cerebral pericytes is reversed by pharmacological inhibition of mitochondrial carbonic anhydrases: Implications for cerebral microvascular disease in diabetes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 440, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dier, U.; Shin, D.-H.; Hemachandra, L.P.M.P.; Uusitalo, L.M.; Hempel, N. Bioenergetic analysis of ovarian cancer cell lines: Profiling of histological subtypes and identification of a mitochondria-defective cell line. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benavides, G.A.; Liang, Q.; Dodson, M.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Zhang, J. Inhibition of autophagy and glycolysis by nitric oxide during hypoxia–reoxygenation impairs cellular bioenergetics and promotes cell death in primary neurons. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 65, 1215–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellen, K.E.; Lu, C.; Mancuso, A.; Lemons, J.M.; Ryczko, M.; Dennis, J.W.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Coller, H.A.; Thompson, C.B. The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway couples growth factor-induced glutamine uptake to glucose metabolism. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 2784–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- DeBerardinis, R.J.; Cheng, T. Q’s next: The diverse functions of glutamine in metabolism, cell biology, and cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, D.Y.; Xie, F.Z.; Zhai, C.; Stern, J.S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.L. The role of cellular oxidative stress in regulating glycolysis energy metabolism in hepatoma cells. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arestakesyan, H.; Karabekian, Z.I. Adhesion properties of cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibroblasts are affected by Macrovipera lebetina obtusa venom. Issues Theor. Clin. Medicine. J. Sci. Pract. Med. 2017, 20, 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Arestakesyan, N.V. Specific Effect of Macrovipera Lebetina Obtuse Snake Venom on Cultured Myocardial Cells. PhD Thesis, Orbeli Institute of Physiology of NAS RA, Yerevan, Armenia, 2017. Available online: http://www.physiol.sci.am/Publ/autoreferat_HovA.pdf (accessed on 24 July 2017).
- Bazaa, A.; Marrakchi, N.; El Ayeb, M.; Sanz, L.; Calvete, J.J. Snake Venomics: Comparative Analysis of the Venom Proteomes of the Tunisian Snakes Cerastes cerastes, Cerastes vipera, Macrovipera lebetina. Proteomics 2005, 5, 4223–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvete, J.J.; Moreno-Murciano, M.P.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Kisiel, D.G.; Marcinkiewicz, C. Snake Venom Disintegrins: Novel Dimeric Disintegrins and Structural Diversification by Disulphide Bond Engineering. Biochem. J. 2003, 372, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, R.J.; Polokoff, M.A.; Friedman, P.A.; Huang, T.-F.; Holt, J.C.; Cook, J.J.; Niewiarowski, S. Disintegrins: A Family of Integrin Inhibitory Proteins from Viper Venoms. Exp. Biol. Med. 1999, 195, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, H.W. Oxygen Radical Chemistry of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 1989, 7, 65–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghulikyan, L.; Mohamadvarzi, M.; Ghukasyan, G.; Kishmiryan, A.; Zaqaryan, N.; Kirakosyan, G.; Ayvazyan, N. Molecular Events Associated with Vipera latifi Venom Effect on Condition of Human Red Blood Cells. Proc. Yerevan State Univ. 2016, 2, 43–50. Available online: http://ysu.am/science/hy/1465212714 (accessed on 26 December 2017). [CrossRef]
- Siigur, J.; Aaspõllu, A.; Siigur, E. Biochemistry and pharmacology of proteins and peptides purified from the venoms of the snakes Macrovipera lebetina subspecies. Toxicon 2019, 158, 16–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayvazian, N.M.; Zakarian, A.E.; Zakarian, N.A. Intensity of Lipid’s Free-Radical Oxidation Processes and Superoxiddismutase’s Activity in Nerve Tissue of Vertebrates. Neurochemistry 2002, 4, 278–284. [Google Scholar]
- Stalnaja, I.D.; Garishvili, T.G. Method of Malonic Dialdehide Determination with Thiobarbituroacid. Biokhimicheskie Metod. Issled. (Biochem. Methods Investig.) 1985, 66–68. [Google Scholar]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ayvazyan, N.; Ghukasyan, G.; Ghulikyan, L.; Kirakosyan, G.; Sevoyan, G.; Voskanyan, A.; Karabekyan, Z. The Contribution of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinases to the Synergistic Action of Viper Venom on the Bioenergetic Profile of Vero Cells. Toxins 2022, 14, 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110724
Ayvazyan N, Ghukasyan G, Ghulikyan L, Kirakosyan G, Sevoyan G, Voskanyan A, Karabekyan Z. The Contribution of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinases to the Synergistic Action of Viper Venom on the Bioenergetic Profile of Vero Cells. Toxins. 2022; 14(11):724. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110724
Chicago/Turabian StyleAyvazyan, Naira, Gevorg Ghukasyan, Lusine Ghulikyan, Gayane Kirakosyan, Gohar Sevoyan, Armen Voskanyan, and Zaruhi Karabekyan. 2022. "The Contribution of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinases to the Synergistic Action of Viper Venom on the Bioenergetic Profile of Vero Cells" Toxins 14, no. 11: 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110724
APA StyleAyvazyan, N., Ghukasyan, G., Ghulikyan, L., Kirakosyan, G., Sevoyan, G., Voskanyan, A., & Karabekyan, Z. (2022). The Contribution of Phospholipase A2 and Metalloproteinases to the Synergistic Action of Viper Venom on the Bioenergetic Profile of Vero Cells. Toxins, 14(11), 724. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14110724