Lysine Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Application in Food Model Contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
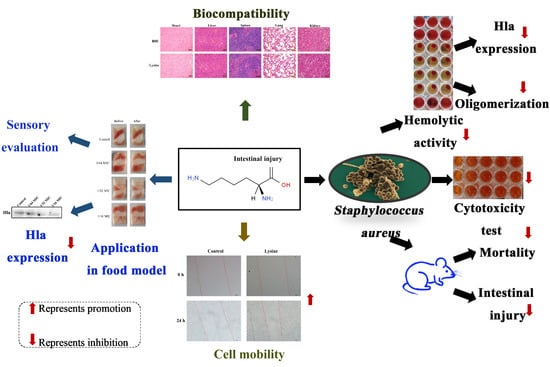
:Highlights
- Lysine inhibits hemolytic activity of S. aureus;
- Lysine inhibits the expression of toxin Hla of S. aureus;
- Lysine inhibits Hla oligomerization;
- Lysine attenuates S. aureus supernatant damage in mice and Caco-2 cells;
- Lysine inhibits the expression of Hla of S. aureus in a food model and had good biocompatibility.
- Lysine has the potential to be used as an anti- S. aureus preparation in the food industry.
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MIC and MBC
2.2. Growth Curves and SIC
2.3. Lys Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of S. aureus
2.4. Lys Inhibits the Hemolytic Activity of Hla and Interferes with the Oligomerization of Hla
2.5. Lys Attenuates the Damage of S. aureus Supernatant to Jejunum and Ileum and Delayed the Mortality of Mice
2.6. Lys Reduces the Cytotoxicity of S. aureus Supernatant and Promotes Caco-2 Cell Migration
2.7. Lys Inhibits the Expression of Hla of S. aureus in a Food Model
2.8. Lys Has Good Biocompatibility
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Strain and Culture
5.2. Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
5.3. Growth Curve
5.4. Hemo-ysis ana Lysis
5.5. Coomassie Brilliant Blue Staining
5.6. Western Blot
5.7. Oligomerization Experiment
5.8. Intestinal Histology Score
5.9. Mortality
5.10. Cytotoxicity Test
5.11. Scratch Test
5.12. Biocompatibility
5.13. Application of Lys in Food Model
5.14. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Muthaiyan, A.; O’Bryan, C.A.; Gustafson, J.E.; Li, Y.; Crandall, P.G.; Ricke, S.C. Use of natural antimicrobials from a food safety perspective for control of Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 1240–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, V.K.; Bahuguna, A.; Kumar, V.; Khan, I.; Alrokayan, S.H.; Khan, H.A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Xiao, J.; Na, M.; Sonwal, S.; et al. Cellular antioxidant potential and inhibition of foodborne pathogens by a sesquiterpene ilimaquinone in cold storaged ground chicken and under temperature-abuse condition. Food Chem. 2021, 373, 131392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.Y.C.; Davis, J.S.; Eichenberger, E.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr. Staphylococcus aureus Infections: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, Clinical Manifestations and Management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2015, 28, 603–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Acton, D.S.; Plat-Sinnige, M.; Wamel, W.V.; Groot, N.D.; Belkum, A.V. Intestinal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus: How does its frequency compare with that of nasal carriage and what is its clinical impact? Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. Off. Publ. Eur. Soc. Clin. Microbiol. 2009, 28, 115. [Google Scholar]
- Tenderis, B.; Kılıç, B.; Yalçın, H.; Şimşek, A. Impact of sodium lactate, encapsulated or unencapsulated polyphosphates and their combinations on Salmonella Typhimurium, Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Staphylococcus aureus growth in cooked ground beef. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2020, 321, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezirtzoglou, E.; Stavropoulou, E. Immunology and probiotic impact of the newborn and young children intestinal microflora. Anaerobe 2011, 17, 369–374. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.K.; Lee, M.J.; Ju, Y.; Lee, S.E.; Yang, K.S.; Sohn, J.W.; Kim, M.J. Determining the clinical significance of co-colonization of vancomycin-resistant enterococci and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in the intestinal tracts of patients in intensive care units: A case–control study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2019, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Squier, C.; Rihs, J.D.; Risa, K.J.; Sagnimeni, A.; Wagener, M.M.; Stout, J.; Murder, R.R.; Singh, N. Staphylococcus Aureus Rectal Carriage and its Association with Infections in Patients in a Surgical Intensive Care Unit and a Liver Transplant Unit. Infect. Control. Hosp. Epidemiol. 2002, 23, 495–501. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, S.; Jain, P.A.; Mishra, R.R. Antigenic sites characterization and in Silico annotation of the Staphylococcus aureus Enterotoxins. Pharma Innov. J. 2018, 7, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Vécsey-Semjén, B.; Möllby, R.; van der Goot, G. Partial C-terminal Unfolding Is Required for Channel Formation by Staphylococcal -toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8655–8660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xuewen, H.; Ping, O.; Zhongwei, Y.; Zhongqiong, Y.; Hualin, F.; Juchun, L.; Changliang, H.; Gang, S.; Zhixiang, Y.; Xu, S.; et al. Eriodictyol protects against Staphylococcus aureus-induced lung cell injury by inhibiting alpha-hemolysin expression. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2018, 34, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiaschi, L.; Di Palo, B.; Scarselli, M.; Pozzi, C.; Tomaszewski, K.; Galletti, B.; Nardi-Dei, V.; Arcidiacono, L.; Mishra, R.P.N. Auto-Assembling Detoxified Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Hemolysin Mimicking the Wild-Type Cytolytic Toxin. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2016, 23, 442–450. [Google Scholar]
- Kwak, Y.K.; Vikström, E.; Magnusson, K.E.; Vécsey-Semjén, B.; Colque-Navarro, P.; Möllby, R. The Staphylococcus aureus Alpha-Toxin Perturbs the Barrier Function in Caco-2 Epithelial Cell Monolayers by Altering Junctional Integrity. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayamizu, K.; Oshima, I.; Nakano, M. Comprehensive Safety Assessment of l-Lysine Supplementation from Clinical Studies: A Systematic Review. J. Nutr. 2020, 150, 2561S–2569S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachirasiri, K.; Wanlapa, S.; Uttapap, D.; Rungsardthong, V. Use of amino acids as a phosphate alternative and their effects on quality of frozen white shrimps (Penaeus vanamei). LWT 2016, 69, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, L.; Su, L.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Jutte, P.C.; Ren, Y.; Busscher, H.J. Nanotechnology-based antimicrobials and delivery systems for biofilm-infection control. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 428–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Zhang, N.; Liu, S.; Chen, M.; Xie, J. ε-Polylysine Inhibits Shewanella putrefaciens with Membrane Disruption and Cell Damage. Molecules 2019, 24, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abril, A.G.; Gonzalez-Villa, T.; Barros-Velázquez, J.; Cañas, B.; Sánchez-Pérez, A.; Calo-Mata, P.; Carrera, M. Staphylococcus aureus Exotoxins and Their Detection in the Dairy Industry and Mastitis. Toxins 2020, 12, 537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J.; Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, L.; Yi, T.; Shen, Z.; Teng, Z.; Wang, J. Aloe-emodin Attenuates Staphylococcus aureus Pathogenicity by Interfering with the Oligomerization of α-Toxin. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Liu, S.; Li, G.; Shi, L.; Dong, J.; Li, W.; Deng, X.; Niu, X. Morin hydrate attenuates Staphylococcus aureus virulence by inhibiting the self-assembly of α-hemolysin. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 118, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christine, T.; Hamilton, M.M.; Vivekananda, D.; Yang, X.P.; Hilliard, J.J.; Stephens, G.L.; Agnieszka, S.; Hua, L.; Terrence, O.; Joann, S. Staphylococcus aureus Alpha Toxin Suppresses Effective Innate and Adaptive Immune Responses in a Murine Dermonecrosis Model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75103. [Google Scholar]
- von Hoven, G.; Qin, Q.; Neukirch, C.; Husmann, M.; Hellmann, N. S. aureus α-toxin: Small pore, large consequences. Biol. Chem. 2018, 400, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, Q.; Niu, X.; Liu, Z.; Kang, X.; Mao, Y.; Li, N.; Wang, G. Inhibitory Effect of Andrographis paniculata Lactone on Staphylococcus aureus α-Hemolysin. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 891943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worlitzsch, D.; Kaygin, H.; Steinhuber, A.; Dalhoff, A.; Botzenhart, K.; Doring, G. Effects of amoxicillin, gentamicin and moxifloxacin on the hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, T.S.; Hilliard, J.J.; Jones-Nelson, O.; Keller, A.E.; O’Day, T.; Tkaczyk, C.; DiGiandomenico, A.; Hamilton, M.; Pelletier, M.; Wang, Q.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus α toxin potentiates opportunistic bacterial lung infections. Sci. Transl. Med. 2016, 8, 329ra31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, H.; Zhang, J.; KuoLee, R.; Patel, G.B.; Chen, W. Intestinal M cells: The fallible sentinels? World J. Gastroenterol. 2007, 13, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar]
- Ceriotti, F.; Zakowski, J.; Sine, H.; Altaie, S.; Horowitz, G.; Pesce, A.J.; Boyd, J.; Horn, P.; Gard, U.; Horowitz, G. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). 2012. Available online: https://www.scienceopen.com/document?vid=1d021ccc-8583-4e6b-a47c-8735734df154 (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- Johny, A.K.; Hoagland, T.; Venkitanarayanan, K. Effect of Subinhibitory Concentrations of Plant-Derived Molecules in Increasing the Sensitivity of Multidrug-Resistant Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium DT104 to Antibiotics. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2010, 7, 1165–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.L.; Ono, H.; Isayama, S.; Okada, R.; Okamura, M.; Lei, L.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Liu, M.; Cui, J.; et al. Biological characteristics of staphylococcal enterotoxin Q and its potential risk for food poisoning. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 122, 1672–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Li, Q.; Lin, T. Lycopene attenuates Staphylococcus aureus-induced inflammation via inhibiting α-hemolysin expression. Microbes Infect. 2021, 23, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Cao, Y.; Li, Z.; Lu, X.; Pang, B.; Wang, S.; Kan, B. Salmonella enterica subsp. II serovar 4,5,12:a:- may cause gastroenteritis infections in humans. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2089007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.; Liu, Z.; Yan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Hao, K.; Liu, C.; Wang, J. Subinhibitory concentrations of Honokiol reduce α-Hemolysin (Hla) secretion by Staphylococcus aureus and the Hla-induced inflammatory response by inactivating the NLRP3 inflammasome. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2019, 8, 707–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, J.; Niu, X.; Dong, J.; Wang, D.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Luo, M.; Li, S.; Feng, H.; Deng, X. Baicalin Protects Mice from Staphylococcus aureus Pneumonia via Inhibition of the Cytolytic Activity of α-Hemolysin. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 206, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iida, T.; Takagi, T.; Katada, K.; Mizushima, K.; Fukuda, W.; Uchiyama, K.; Handa, O.; Ichikawa, H.; Naito, Y.; Itoh, Y. Rapamycin Improves Mortality Following Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion via the Inhibition of Remote Lung Inflammation in Mice. Digestion 2015, 92, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, L. Tanshinone I attenuates the malignant biological properties of ovarian cancer by inducing apoptosis and autophagy via the inactivation of PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell Prolif. 2019, 53, e12739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Lee, S.K.; Kim, H.; Kim, T.M. Exosomes Secreted from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Accelerate Skin Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, J.-H.; Wang, S.; Gu, M.; Luan, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Gu, X. Biocompatibility and biosafety of butterfly wings for the clinical use of tissue-engineered nerve grafts. Neural Regen. Res. 2021, 16, 1606–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, M.; Kou, M.; Shi, C.; Peng, X.; Wang, X. Control of Foodborne Staphylococcus aureus by Shikonin, a Natural Extract. Foods 2021, 10, 2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanišová, E.; Drevková, B.; Tokár, M.; Terentjeva, M.; Kačániová, M. Physicochemical and sensory evaluation of biscuits enriched with chicory fiber. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2020, 26, 38–43. [Google Scholar]






| Strain | MIC (mM) | MBC (mM) | Original Source of Strain |
|---|---|---|---|
| ATCC29213 | 400 | 400 | American Type Culture Collection |
| 265 | 400 | 400 | Patient vomit |
| 265Δsea | 400 | 400 | Constructed and preserved in this laboratory |
| 265Δhla | 400 | 400 | Constructed and preserved in this laboratory |
| Sample | Average Sensory Score (Points) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color | Organization Status | Odor | Overall Acceptabilit | Total | |
| A | 8.214 ± 1.075 | 7.857 ± 1.424 | 7.810 ± 1.030 | 8.024 ± 1.270 | 8.092 ± 0.258 |
| B | 7.762 ± 1.758 | 7.548 ± 1.870 | 8.024 ± 1.346 | 7.595 ± 1.338 | 7.810 ± 0.188 |
| C | 8.405 ± 1.114 | 8.071 ± 1.132 | 8.429 ± 1.087 | 8.190 ± 1.066 | 8.089 ± 0.222 |
| D | 7.929 ± 1.734 | 7.762 ± 1.602 | 8.095 ± 1.633 | 7.619 ± 1.387 | 7.857 ± 0.257 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wan, Y.; Wang, X.; Bai, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, X. Lysine Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Application in Food Model Contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins 2022, 14, 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120867
Wan Y, Wang X, Bai T, Zheng X, Yang L, Li Q, Wang X. Lysine Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Application in Food Model Contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins. 2022; 14(12):867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120867
Chicago/Turabian StyleWan, Yangli, Xiaowen Wang, Tianyi Bai, Xuting Zheng, Liu Yang, Qianhong Li, and Xin Wang. 2022. "Lysine Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Application in Food Model Contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus" Toxins 14, no. 12: 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120867
APA StyleWan, Y., Wang, X., Bai, T., Zheng, X., Yang, L., Li, Q., & Wang, X. (2022). Lysine Inhibits Hemolytic Activity of Staphylococcus aureus and Its Application in Food Model Contaminated with Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins, 14(12), 867. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14120867