Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
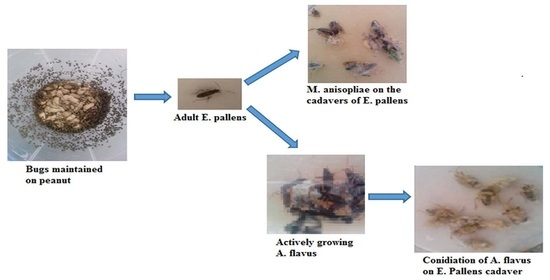
2.1. Fungal Isolates
2.2. Dose–Response Bioassay
2.3. Enzyme Assay
2.4. Correlation between Rates of Mortality and Enzyme Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. E. pallens Collection and Maintenance
4.2. Fungal Isolates
4.3. Fungal Conidia Preparation
4.4. Dose–Response Bioassay
4.5. Production of Cuticle-Degrading Enzymes
4.6. Enzyme Assays
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chandra, K.; Kushwaha, S.; Sambath, S.; Biswas, B. Distribution and Diversity of Hemiptera Fauna of Veerangana Durgavati Wildlife Sanctuary, Damoh, Madhya Pradesh (India). Biol. Forum-Int. J. 2012, 4, 68–74. [Google Scholar]
- Weirauch, C.; Schuh, R.T. Systematics and evolution of Heteroptera: 25 years of progress. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2011, 56, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gad, S.K.M.S.M. Taxonomic review of family Rhyparochromidae (Hemiptera: Lygaeoidea) from Egypt. Egypt. J. Exp. Biol. 2013, 9, 33–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schaefer, C.W.; Panizzi, A.R. Heteroptera of Economic Importance; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ranga Rao, G.; Rameshwar Rao, V.; Nigam, S. Post-Harvest Insect Pests of Groundnut and Their Management; International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics: Patancheru, India, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Senthil-Nathan, S. Natural pesticide research. Physiol. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 101, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Pampapathy, G.; Dwivedi, S.; Reddy, L. Mechanisms and diversity of resistance to insect pests in wild relatives of groundnut. J. Econ. Entomol. 2003, 96, 1886–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Cheng, B.; Du, D.; Hu, X.; Peng, A.; Pu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Z.; Chen, G. Morphological, molecular and virulence characterization of three Lencanicillium species infecting Asian citrus psyllids in Huangyan citrus groves. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 125, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo, D.; Dunlap, C.; Avery, P.; Navarrete, J.; Duncan, R.; Jackson, M.; Behle, R.; Cave, R.; Crane, J.; Rooney, A. Entomopathogenic fungi as biological control agents for the vector of the laurel wilt disease, the redbay ambrosia beetle, Xyleborus glabratus (Coleoptera: Curculionidae). Biol. Control 2015, 81, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.E.; Vega, F.E.; Chandler, D.; Goettel, M.S.; Pell, J.; Wajnberg, E. The Ecology of Fungal Entomopathogens; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Boomsma, J.J.; Jensen, A.B.; Meyling, N.V.; Eilenberg, J. Evolutionary interaction networks of insect pathogenic fungi. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2014, 59, 467–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.; Grzywacz, D.; Shapiro-Ilan, D.; Frutos, R.; Brownbridge, M.; Goettel, M. Insect pathogens as biological control agents: Back to the future. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2015, 132, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaike, S.; Keller, N.P. Aspergillus flavus. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2011, 49, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, F.T.; Shang, B.; Selvaraj, J.N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y. Isolation and characterization of Aspergillus flavus strains in China. J. Microbiol. 2018, 56, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisvad, J.C.; Hubka, V.; Ezekiel, C.; Hong, S.-B.; Nováková, A.; Chen, A.; Arzanlou, M.; Larsen, T.; Sklenář, F.; Mahakarnchanakul, W. Taxonomy of Aspergillus section Flavi and their production of aflatoxins, ochratoxins and other mycotoxins. Stud. Mycol. 2019, 93, 1–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humphrey, J. Food safety, trade, standards and the integration of smallholders into value chains: A review of the literature. IFAD Res. Ser. 2017, 11, 1–72. [Google Scholar]
- Santi, L.; e Silva, L.A.D.; da Silva, W.O.B.; Corrêa, A.P.F.; Rangel, D.E.N.; Carlini, C.R.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. Virulence of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae using soybean oil formulation for control of the cotton stainer bug, Dysdercus peruvianus. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 27, 2297–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, U.; Kaur, G. Extracellular enzyme production in Metarhizium anisopliae isolates. Folia Microbiol. 2009, 54, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santi, L.; da Silva, W.O.B.; Berger, M.; Guimarães, J.A.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. Conidial surface proteins of Metarhizium anisopliae: Source of activities related with toxic effects, host penetration and pathogenesis. Toxicon 2010, 55, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. Metarhizium anisopliae enzymes and toxins. Toxicon 2010, 56, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Tian, M.-Y.; He, Y.-R.; Bland, J.M.; Gu, W.-X. Behavioral and electrophysiological responses of Coptotermes formosanus Shiraki towards entomopathogenic fungal volatiles. Biol. Control 2010, 55, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Rizwan-ul-Haq, M.; Al-Ayedh, H.; AlJabr, A.M. Susceptibility and immune defence mechanisms of Rhynchophorus ferrugineus (Olivier)(Coleoptera: Curculionidae) against entomopathogenic fungal infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, A.R.F.; Martins, J.N.; Furlaneto, M.C.; Barros, N.M.d. Production of cuticle-degrading proteases by Nomuraea rileyi and its virulence against Anticarsia gemmatalis. Ciênc. Rural 2010, 40, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, T.; Coates, C.; Dubovskiy, I.; Ratcliffe, N. Entomopathogenic fungi: New insights into host–pathogen interactions. Adv. Genet. 2016, 94, 307–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Morton, J.C.; Ramirez, J.L.; Souza-Neto, J.A.; Dimopoulos, G. The entomopathogenic fungus Beauveria bassiana activate toll and JAK-STAT pathway-controlled effector genes and anti-dengue activity in Aedes aegypti. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Munguía, A.M.; Garza-Hernández, J.A.; Rebollar-Tellez, E.A.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M.A.; Reyes-Villanueva, F. Transmission of Beauveria bassiana from male to female Aedes aegypti mosquitoes. Parasites Vectors 2011, 4, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karthi, S.; Vaideki, K.; Shivakumar, M.S.; Ponsankar, A.; Thanigaivel, A.; Chellappandian, M.; Vasantha-Srinivasan, P.; Muthu-Pandian, C.K.; Hunter, W.B.; Senthil-Nathan, S. Effect of Aspergillus flavus on the mortality and activity of antioxidant enzymes of Spodoptera litura Fab.(Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) larvae. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2018, 149, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, G. Review on safety of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2007, 17, 879–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polar, P.; Kairo, M.T.; Moore, D.; Pegram, R.; John, S.-A. Comparison of water, oils and emulsifiable adjuvant oils as formulating agents for Metarhizium anisopliae for use in control of Boophilus microplus. Mycopathologia 2005, 160, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inglis, D.; Jaronski, S.T.; Wraight, S.P.; Beattie, A.; Watson, D.; Stevens, M.; Rae, D. Use of spray oils with entomopathogens. In Spray Oils Beyond 2000: Sustainable Pest and Disease Management; University of Western Sydney: Sydney, Australia, 2002; pp. 302–312. [Google Scholar]
- Batta, Y. Production and testing of novel formulations of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae (Metschinkoff) Sorokin (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes). Crop Prot. 2003, 22, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomer, C.; Bateman, R.; Johnson, D.; Langewald, J.; Thomas, M. Biological control of locusts and grasshoppers. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2001, 46, 667–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaya, G.P.; Hassan, S. Entomogenous fungi as promising biopesticides for tick control. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2000, 24, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camargo, M.G.; Golo, P.S.; Angelo, I.C.; Perinotto, W.M.; Sá, F.A.; Quinelato, S.; Bittencourt, V.R. Effect of oil-based formulations of acaripathogenic fungi to control Rhipicephalus microplus ticks under laboratory conditions. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 188, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balogun, S.; Fagade, O. Entomopathogenic fungi in population of Zonocerus variegatus (l) in Ibadan, south west, Nigeria. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2004, 3, 382–386. [Google Scholar]
- Scully, L.R.; Bidochka, M.J. Serial passage of the opportunistic pathogen Aspergillus flavus through an insect host yields decreased saprobic capacity. Can. J. Microbiol. 2005, 51, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seye, F.; Bawin, T.; Boukraa, S.; Zimmer, J.-Y.; Ndiaye, M.; Delvigne, F.; Francis, F. Effect of entomopathogenic Aspergillus strains against the pea aphid, Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2014, 49, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leger, R.J.S.; Screen, S.E.; Shams-Pirzadeh, B. Lack of Host Specialization inAspergillus flavus. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 320–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peng, G.; Xia, Y. The mechanism of the mycoinsecticide diluent on the efficacy of the oil formulation of insecticidal fungus. BioControl 2011, 56, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umaru, F.F.; Simarani, K. Evaluation of the Potential of Fungal Biopesticides for the Biological Control of the Seed Bug, Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas)(Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae). Insects 2020, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, S.S.; Sharma, A.K.; Beniwal, V.; Goel, G.; Batra, P.; Kumar, A.; Jaglan, S.; Sharma, A.K.; Malhotra, S. Myco-biocontrol of insect pests: Factors involved, mechanism, and regulation. J. Pathog. 2012, 2012, 126819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihara, F.; Yaginuma, K.; Kobayashi, N.; Mishiro, K.; Sato, T. Screening of entomopathogenic fungi against the brown-winged green bug, Plautia stali Scott (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2001, 36, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moraes, C.K.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. Regulation of extracellular chitinases and proteases in the entomopathogen and acaricide Metarhizium anisopliae. Curr. Microbiol. 2003, 46, 0205–0210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, G.; Coudron, T.; Ignoffo, C.; Riba, G. Chitinolytic activity and virulence associated with native and mutant isolates of an entomopathogenic fungus, Nomuraea rileyi. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1989, 54, 394–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beys da silva, W.O.; Santi, L.; Corrêa, A.P.F.; Silva, L.A.D.; Bresciani, F.R.; Schrank, A.; Vainstein, M.H. The entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae can modulate the secretion of lipolytic enzymes in response to different substrates including components of arthropod cuticle. Fungal Biol. 2010, 114, 911–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grewal, G.K.; Joshi, N.; Suneja, Y. Pathogenicity of Metarhizium rileyi (Farlow) Kepler, S.A. Rehner and Humber isolates against Spodoptera litura (Fabricius) and their extracellular enzymatic activities. Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2021, 31, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, A.-R.; Ibrahim, R.A. Assessment of the virulence and proteolytic activity of three native entomopathogenic fungi against the larvae of Oryctes agamemnon (Burmeister)(Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest Control 2019, 29, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supakdamrongkul, P.; Bhumiratana, A.; Wiwat, C. Characterization of an extracellular lipase from the biocontrol fungus, Nomuraea rileyi MJ, and its toxicity toward Spodoptera litura. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010, 105, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bidochka, M.J.; Khachatourians, G.G. Protein hydrolysis in grasshopper cuticles by entomopathogenic fungal extracellular proteases. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1994, 63, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembe, S.; Shouche, Y.; Ghate, H. DNA barcoding of Pentatomomorpha bugs (Hemiptera: Heteroptera) from Western Ghats of India. Meta Gene 2014, 2, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinelato, S.; Golo, P.S.; Perinotto, W.M.; Sá, F.A.; Camargo, M.G.; Angelo, I.C.; Moraes, A.M.; Bittencourt, V.R. Virulence potential of Metarhizium anisopliae sl isolates on Rhipicephalus (Boophilus) microplus larvae. Vet. Parasitol. 2012, 190, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, L.R.; Enkerli, J. Effect of seed treatment duration on growth and colonization of Vicia faba by endophytic Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium brunneum. Biol. Control 2016, 103, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.C.; Lee, M.R.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.J.; Park, S.E.; Nai, Y.-S.; Lee, G.S.; Shin, T.Y.; Kim, J.S. Tenebrio molitor-mediated entomopathogenic fungal library construction for pest management. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2018, 21, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.C.; Park, S.; Lee, D.G. Purification and characterization of a novel chitinase from the entomopathogenic fungus, Metarhizium anisopliae. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 1999, 73, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, W. A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J. Econ. Entomol. 1925, 18, 265–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Throne, J.E.; Weaver, D.K.; Chew, V.; Baker, J.E. Probit analysis of correlated data: Multiple observations over time at one concentration. J. Econ. Entomol. 1995, 88, 1510–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Oil-Formulated Conidia | Tween 80 Formulation | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conidia/mL | Mean ± S.E. | |||
| A. flavus | M. ansopliae | A. flavus | M. ansopliae | |
| 108 | 54.56 a ± 10.92 | 71.45 a ± 10.88 | 52.64 a ± 11.70 | 58.91 a ± 12.84 |
| 107 | 45.91 a ±10.19 | 59.73 ab± 10.38 | 39.27 ab ± 10.23 | 53.18 a ± 12.03 |
| 106 | 43.46 a ± 7.06 | 49.64 bc ± 8.92 | 30.56 bc ± 9.77 | 48.00 ab ± 10.35 |
| 105 | 36.27 ab ± 7.06 | 39.18 bcd ± 7.81 | 24.56 bc ± 8.36 | 35.82 bc ± 9.28 |
| 104 | 31.09 bc ± 5.76 | 29.27 cd ± 7.30 | 20.00 bc ± 6.95 | 31.46 cb ± 8.80 |
| Control | 1.27 d ± 0.62 | 1.09 e ± 0.49 | 1.09 d ± 0.63 | 2.18 d ± 0.95 |
| Skewness and kurtosis: ± 0.141 & ± 0.808 | ||||
| Fungal Conidia Formulated in Oil | Fungal Conidia Formulated in Tween 80 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates | ||||
| A. flavus | M. anisopliae | A. flavus | M. anisopliae | |
| LC50 (conidia/mL) | 1.95 × 106 | 3.92 × 106 | 9.36 × 107 | 6.85 × 106 |
| 95% fiducial limits (lower–upper) | 2.17 × 104–1.12 × 107 | 1.86×104–7.23 × 106 | 1.37 × 107–3.22 × 108 | 1.33 × 106–1.55 × 106 |
| LC90 (conidia/mL) | 3.66 × 109 | 5.37 × 108 | 6.50 × 109 | 2.57 × 108 |
| 95% fiducial limits (lower–upper) | 8.56 × 108–11.16 × 109 | 1.78 × 108–1.45 × 109 | 4.16 × 109–1.35 × 1012 | 1.15 × 108–1.24 × 109 |
| Toxicity regression equation | Y = 4.13 + 0.71 × X | Y = 4.82 + 0.82 × X | Y = 4.72 + 1.02 × X | Y = 5.21 + 0.99 × X |
| Slope ± standard error | 0.39 ± 0.09 | 0.60 ± 0.16 | 0.48 ± 0.19 | 0.43 ± 0.09 |
| Fungal Conidia Formulated in Oil | Fungal Conidia Formulated in Tween 80 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolates | ||||
| A. flavus | M. anisopliae | A. flavus | M. anisopliae | |
| LT50 (days)/95% fiducial limits (lower–upper) | 3.3 (1.3–4.1) | 3.6 (1.3–4.2) | 5.0 (4.1–5.5) | 3.8 (3.1–4.2) |
| LT90 (days)/95% fiducial limits (lower–upper) | 6.6 (5.9–8.1) | 5.4 (5.3–6.3) | 8.8 (7.6–12.1) | 5.7 (5.1–6.1) |
| Toxicity regression equation | Y = 0.25 + 1.45 × X | Y = 0.63 + 1.66 × X | Y = 1.45 + 0.11 × X | Y = 2.97 + 1.62 × X |
| Slope ± standard error | 0.34 ± 0.11 | 0.56 ± 0.16 | 0.44 ± 0.19 | 0.49 ± 0.09 |
| Enzyme Activity on Alternate Days (U/mL) (Mean ± S.E.) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Isolate | Enzyme | 2nd Day | 4th Day | 6th Day | 8th Day | 10th Day | Mean |
| A. flavus | Protease | 0.49 ± 0.14 a | 0.99 ± 0.20 ab | 1.79 ± 0.43 bc | 2.51 ± 0.34 bc | 2.02 ± 0.45 cd | 1.56 |
| Chitinase | 0.63 ± 0.22 ab | 0.87 ± 0.03 ba | 0.95 ± 0.65 bc | 0.98 ± 0.36 bc | 0.37 ± 0.32 da | 0.76 | |
| Lipase | 1.26 ± 0.42 ab | 2.51 ± 0.02 bc | 3.22 ± 0.14 cb | 2.44 ±0.56 cb | 1.11 ± 0.65 dac | 2.18 | |
| M. anisopliae | Protease | 0.68 ± 0.32 a | 0.94 ± 0.16 ba | 2.43 ± 0.28 cb | 2.12 ±0.12 cb | 1.87 ± 0.42 abd | 1.61 |
| Chitinase | 0.52 ± 0.18 ab | 0.89 ± 0.12 bc | 0.92 ± 0.16 cb | 0.93 ±0.45 cb | 0.85 ± 0.54 ad | 0.82 | |
| Lipase | 1.09 ± 0.31 a | 1.59 ± 0.12 bc | 3.46 ± 0.23 cb | 2.78 ± 0.43 cb | 1.21 ± 0.41 abd | 2.02 | |
| Entomopathogen | Protease | Chitinase | Lipase | (n) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. flavus | r = 0.96, p = 0.03 | r = 0.85, p = 0.19 | r = 0.99, p = 0.006 | 27 |
| M. anisopliae | r = 0.87, p = 0.16 | r = 0.91, p = 0.06 | r = 0.97, p = 0.04 | 27 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Umaru, F.F.; Simarani, K. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities. Toxins 2022, 14, 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090584
Umaru FF, Simarani K. Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities. Toxins. 2022; 14(9):584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090584
Chicago/Turabian StyleUmaru, Fredrick Fidelis, and Khanom Simarani. 2022. "Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities" Toxins 14, no. 9: 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090584
APA StyleUmaru, F. F., & Simarani, K. (2022). Efficacy of Entomopathogenic Fungal Formulations against Elasmolomus pallens (Dallas) (Hemiptera: Rhyparochromidae) and Their Extracellular Enzymatic Activities. Toxins, 14(9), 584. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins14090584