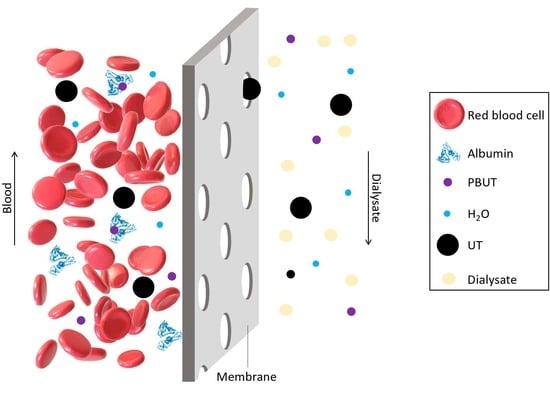
Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Adsorptive Membranes
3. Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of PBUTs
3.1. Infusion of Binding Competitors
3.2. Competitive Binding Membranes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations:
References
- Hill, N.R.; Fatoba, S.T.; Oke, J.L.; Hirst, J.A.; O’Callaghan, C.A.; Lasserson, D.S.; Hobbs, F.D.R. Global Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sundström, J.; Bodegard, J.; Bollmann, A.; Vervloet, M.G.; Mark, P.B.; Karasik, A.; Taveira-Gomes, T.; Botana, M.; Birkeland, K.I.; Thuresson, M.; et al. Prevalence, Outcomes, and Cost of Chronic Kidney Disease in a Contemporary Population of 2·4 Million Patients from 11 Countries: The CaReMe CKD Study. Lancet Reg. Health-Eur. 2022, 20, 100438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faria, M.; de Pinho, M.N. Challenges of Reducing Protein-Bound Uremic Toxin Levels in Chronic Kidney Disease and End Stage Renal Disease. Transl. Res. 2021, 229, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanholder, R.; Laecke, S.; Glorieux, G. What Is New in Uremic Toxicity? Pediatr. Nephrol. 2008, 23, 1211–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vanholder, R.; Fouque, D.; Glorieux, G.; Heine, G.H.; Kanbay, M.; Mallamaci, F.; Massy, Z.A.; Ortiz, A.; Rossignol, P.; Wiecek, A.; et al. Clinical Management of the Uraemic Syndrome in Chronic Kidney Disease. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duranton, F.; Cohen, G.; De Smet, R.; Rodriguez, M.; Jankowski, J.; Vanholder, R.; Argiles, A. Normal and Pathologic Concentrations of Uremic Toxins. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1258–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pappa, T.; Refetoff, S. Thyroid Hormone Transport Proteins: Thyroxine-Binding Globulin, Transthyretin, and Albumin; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 9780128093245. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, E.; Saigusa, D.; Mishima, E.; Uchida, T.; Miura, D.; Morikawa-Ichinose, T.; Kisu, K.; Sekimoto, A.; Saito, R.; Oe, Y.; et al. Impact of the Oral Adsorbent AST-120 on Organ-Specific Accumulation of Uremic Toxins: LC-MS/MS and MS Imaging Techniques. Toxins 2018, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.-H.; Chiang, C.-K. Uremic Toxins and Protein-Bound Therapeutics in AKI and CKD: Up-to-Date Evidence. Toxins 2021, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduell, F. Hemodiafiltration versus Conventional Hemodialysis: Should “Conventional” Be Redefined? Semin. Dial. 2018, 31, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Clark, W.R. Haemodialysis Membranes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 394–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.S.; Tsai, Y.C.; Chen, T.W.; Li, S.Y. Artificial Kidney Engineering: The Development of Dialysis Membranes for Blood Purification. Membranes 2022, 12, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Brendolan, A.; Crepaldi, C.; Rodighiero, M.; Scabardi, M. Blood and Dialysate Flow Distributions in Hollow-Fiber Hemodialyzers Analyzed by Computerized Helical Scanning Technique. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ficheux, A.; Kerr, P.G.; Brunet, P.; Argilés, À. The Ultrafiltration Coefficient of a Dialyser (KUF) Is Not a Fixed Value, and It Follows a Parabolic Function: The New Concept of KUF Max. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2011, 26, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drioli, E.; Giorno, L. Comprehensive Membrane Science and Engineering, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; ISBN 9780444532046. [Google Scholar]
- Hung, Y.H.; Lai, T.S.; Belmouaz, M.; Tu, Y.C.; Lai, C.F.; Lin, S.L.; Chen, Y.M. Effects of Medium Cut-Off Polyarylethersulfone and Polyvinylpyrrolidone Blend Membrane Dialyzers in Hemodialysis Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Membranes 2022, 12, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Su, B. Effects of Expanded Hemodialysis with Medium Cut-Off Membranes on Maintenance Hemodialysis Patients: A Review. Membranes 2022, 12, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweigart, C.; Boschetti-de-Fierro, A.; Hulko, M.; Nilsson, L.G.; Beck, W.; Storr, M.; Krause, B. Medium Cut-off Membranes—Closer to the Natural Kidney Removal Function. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 40, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Said, N.; Lau, W.J.; Ho, Y.C.; Lim, S.K.; Zainol Abidin, M.N.; Ismail, A.F. A Review of Commercial Developments and Recent Laboratory Research of Dialyzers and Membranes for Hemodialysis Application. Membranes 2021, 11, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fresenius Medical Care FX High-Flux and FX Low-Flux Dialyzers. Available online: https://www.freseniusmedicalcare.com/en/healthcare-professionals/hemodialysis/dialyzers/fx-high-and-low-flux-dialyzers (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Baxter Polyflux L. Available online: https://renalcare.baxter.com/products/polyflux-l (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Baxter Polyflux H. Available online: https://renalcare.baxter.com/products/polyflux-h (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Nipro Sureflux. Available online: https://www.nipro-group.com/en/our-offer/products-services/surefluxtm (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Nipro Salacea. Available online: https://www.nipro-group.com/en/our-offer/products-services/solaceatm-dialyzer (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Itoh, Y.; Ezawa, A.; Kikuchi, K.; Tsuruta, Y.; Niwa, T. Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins in Hemodialysis Patients Measured by Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry and Their Effects on Endothelial ROS Production. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 403, 1841–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.A.; Ou, S.M.; Lin, C.C. Influence of Dialysis Membranes on Clinical Outcomes: From History to Innovation. Membranes 2022, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R. New Uremic Toxins—Which Solutes Should Be Removed? Hemodiafiltration-A New Era 2010, 168, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekawanvijit, S. Cardiotoxicity of Uremic Toxins: A Driver of Cardiorenal Syndrome. Toxins 2018, 10, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zare, F.; Janeca, A.; Jokar, S.M.; Faria, M.; Gonçalves, M.C. Interaction of Human Serum Albumin with Uremic Toxins: The Need of New Strategies Aiming at Uremic Toxins Removal. Membranes 2022, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krediet, R.T. Preservation of Residual Kidney Function and Urine Volume in Patients on Dialysis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leong, S.C.; Sao, J.N.; Taussig, A.; Plummer, N.S.; Meyer, T.W.; Sirich, T.L. Residual Function Effectively Controls Plasma Concentrations of Secreted Solutes in Patients on Twice Weekly Hemodialysis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 1979–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.C.; Tomino, Y.; Lu, K.C. Impacts of Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresol Sulfate on Chronic Kidney Disease and Mitigating Effects of AST-120. Toxins 2018, 10, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, T.T.; Jang, K.; Her, N.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, I.S. Fabrication of Hollow Fiber Membranes with Different Inner Diameters for Enhanced Uremic Toxins Removal in Hemodialysis: Exploring from High-Flux to High Molecular Weight Retention Onset Classes. J. Membr. Sci. 2022, 663, 121065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Biesen, W.; Eloot, S. Enhanced Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins Using Displacers: Road to Success? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, X.; Song, Z.; Lu, K.; Zhu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, W.; Jin, J. Microporous Polymer Adsorptive Membranes with High Processing Capacity for Molecular Separation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qalyoubi, L.; Al-Othman, A.; Al-Asheh, S. Recent Progress and Challenges on Adsorptive Membranes for the Removal of Pollutants from Wastewater. Part I: Fundamentals and Classification of Membranes. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2021, 3, 100086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijink, M.S.L.; Wester, M.; Sun, J.; Saris, A.; Bolhuis-Versteeg, L.A.M.; Saiful, S.; Joles, J.A.; Borneman, Z.; Wessling, M.; Stamatialis, D.F. A Novel Approach for Blood Purification: Mixed-Matrix Membranes Combining Diffusion and Adsorption in One Step. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijink, M.S.L.; Wester, M.; Glorieux, G.; Gerritsen, K.G.F.; Sun, J.; Swart, P.C.; Borneman, Z.; Wessling, M.; Vanholder, R.; Joles, J.A.; et al. Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membranes for Removal of Protein-Bound Toxins from Human Plasma. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7819–7828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavlenko, D.; Van Geffen, E.; Van Steenbergen, M.J.; Glorieux, G.; Vanholder, R.; Gerritsen, K.G.F.; Stamatialis, D. New Low-Flux Mixed Matrix Membranes That Offer Superior Removal of Protein-Bound Toxins from Human Plasma. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.L.; Stamatialis, D. High Flux Mixed Matrix Membrane with Low Albumin Leakage for Blood Plasma Detoxification. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 609, 118187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Beek, O.E.M.; van Gelder, M.K.; Lokhorst, C.; Hazenbrink, D.H.M.; Lentferink, B.H.; Gerritsen, K.G.F.; Stamatialis, D. In Vitro Study of Dual Layer Mixed Matrix Hollow Fiber Membranes for Outside-in Filtration of Human Blood Plasma. Acta Biomater. 2021, 123, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Hou, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ye, S.; Wang, M.; Ren, L. Adsorptive Removal of Uremic Toxins Using Zr-Based MOFs for Potential Hemodialysis Membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2022, 57, 2909–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; Yeow, J.T.W. An Adsorption Study of Indoxyl Sulfate by Zeolites and Polyethersulfone–Zeolite Composite Membranes. Mater. Des. 2017, 120, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Rodríguez-Reinoso, F. Nanoporous Materials for Gas Storage; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; ISBN 9789811335037. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Chen, C.; Samarasekera, C.; Yeow, J.T.W. Influence of Zeolite Shape and Particle Size on Their Capacity to Adsorb Uremic Toxin as Powders and as Fillers in Membranes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res.-Part B Appl. Biomater. 2017, 105, 1594–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, Y.; Hao, M.; Li, Z. Chapter 17—Metal–Organic Frameworks for Photocatalysis. In Interface Science and Technology; Surface Science of Photocatalysis; Yu, J., Jaroniec, M., Jiang, C., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; Volume 31, pp. 541–579. [Google Scholar]
- Petitpas, I.; Bhattacharya, A.A.; Twine, S.; East, M.; Curry, S. Crystal Structure Analysis of Warfarin Binding to Human Serum Albumin. Anatomy of Drug Site I. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22804–22809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fasano, M.; Curry, S.; Terreno, E.; Galliano, M.; Fanali, G.; Narciso, P.; Notari, S.; Ascenzi, P. The Extraordinary Ligand Binding Properties of Human Serum Albumin. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Miyamoto, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Update on the Pharmacokinetics and Redox Properties of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2011, 100, 3682–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Noguchi, T.; Miyamoto, Y.; Kadowaki, D.; Kotani, S.; Nakajima, M.; Miyamura, S.; Ishima, Y.; Otagiri, M.; Maruyama, T. Interaction between Two Sulfate-Conjugated Uremic Toxins, p-Cresyl Sulfate and Indoxyl Sulfate, during Binding with Human Serum Albumin. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1423–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P.; Ho, C.H.; Henrie, M.; Stroup, E.; Handelman, G. Improved Dialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uraemic Toxins with Use of Albumin Binding Competitors: An in Vitro Human Whole Blood Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, X.; Cao, W.; Shen, Z.; Wang, N.; Leng, J.; Zou, N.; Shang, E.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Improved Dialysis Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Salvianolic Acids. Phytomedicine 2019, 57, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Loor, H.; Meijers, B.K.I.; Meyer, T.W.; Bammens, B.; Verbeke, K.; Dehaen, W.; Evenepoel, P. Sodium Octanoate to Reverse Indoxyl Sulfate and P-Cresyl Sulfate Albumin Binding in Uremic and Normal Serum during Sample Preparation Followed by Fluorescence Liquid Chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4684–4688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.; Thijssen, S.; Levin, N.; Kotanko, P.; Handelman, G. Enhanced Indoxyl Sulfate Dialyzer Clearance with the Use of Binding Competitors. Blood Purif. 2015, 39, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madero, M.; Cano, K.B.; Campos, I.; Tao, X.; Maheshwari, V.; Brown, J.; Cornejo, B.; Handelman, G.; Thijssen, S.; Kotanko, P. Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins during Hemodialysis Using a Binding Competitor. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Guo, J.M.; Hua, Y.Q.; Zhu, K.Y.; Tang, Y.P.; Zhao, B.C.; Jia, L.F.; Zhao, J.; Tang, Z.S.; Duan, J.A. The Mixture of Salvia Miltiorrhiza-Carthamus Tinctorius (Danhong Injection) Alleviates Low-Dose Aspirin Induced Gastric Mucosal Damage in Rats. Phytomedicine 2016, 23, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Yi, X.; Huang, P.; Chen, S.; Wu, Y. Drug-Protein Binding of Danhong Injection and the Potential Influence of Drug Combination with Aspirin: Insight by Ultrafiltration LC–MS and Molecular Modeling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 134, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, H.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Ding, F. Improved Dialytic Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins by Intravenous Lipid Emulsion in Chronic Kidney Disease Rats. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1842–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes, G.; Faria, M.; Carvalho, A.; Gonçalves, M.C.; de Pinho, M.N. Structure of Water in Hybrid Cellulose Acetate-Silica Ultrafiltration Membranes and Permeation Properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 189, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faria, M.; Moreira, C.; Eusébio, T.; Brogueira, P.; de Pinho, M.N. Hybrid Flat Sheet Cellulose Acetate/Silicon Dioxide Ultrafiltration Membranes for Uremic Blood Purification. Cellulose 2020, 27, 3847–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, M.C.; Pereira, J.C.; de Almeida, N.; Marques, P.; Faria, M.; Gonçalves, M.C. Improving Hydraulic Permeability, Mechanical Properties, and Chemical Functionality of Cellulose Acetate-Based Membranes by Co-Polymerization with Tetraethyl Orthosilicate and 3-(Aminopropyl)Triethoxysilane. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 261, 117813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeca, A.; Rodrigues, S.C.; Gonçalves, M.C. Novel Cellulose Acetate-Based Monophasic Hybrid Membranes for Improved Blood Purification Devices: Characterization under Dynamic Conditions. Membranes 2021, 11, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, P.; Pires, R.F.; Serpa, J.; Bonifácio, V.D.B. L-Buthionine Sulfoximine Detection and Quantification in Polyurea Dendrimer Nanoformulations. Molecules 2019, 24, 3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rastegar, A.J.; Vosgueritchian, M.; Doll, J.C.; Mallon, J.R.; Pruitt, B.L. Nanomechanical Actuation of a Silicon Cantilever Using an Azo Dye, Self-Assembled Monolayer. Langmuir 2013, 29, 7118–7124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tacke, R.; Burschka, C.; Richter, I.; Wagner, B.; Willeke, R. Pentacoordinate Silicon Compounds with SiO5 Skeletons Containing SiOH or SiOSi Groups: Derivatives of the Pentahydroxosilicate(1-) Anion [Si(OH)5]- and Its Anhydride [(HO)4Si-O-Si(OH)4]2-. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 8480–8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, M. Towards Nanostructured Membranes for the Artificial Kidney, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa: Lisbon, Portugal. 2021. Available online: https://fenix.tecnico.ulisboa.pt/cursos/meq/dissertacao/1691203502344730 (accessed on 23 January 2023).




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodrigues, F.S.C.; Faria, M. Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins 2023, 15, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020110
Rodrigues FSC, Faria M. Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020110
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodrigues, Flávia S. C., and Mónica Faria. 2023. "Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins" Toxins 15, no. 2: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020110
APA StyleRodrigues, F. S. C., & Faria, M. (2023). Adsorption- and Displacement-Based Approaches for the Removal of Protein-Bound Uremic Toxins. Toxins, 15(2), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020110