Children and Snakebite: Snake Venom Effects on Adult and Paediatric Plasma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
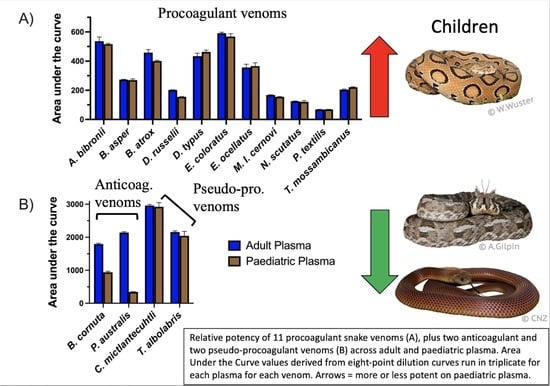
2. Results and Discussion
Conclusions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Plasma Collection and Handling
3.2. Venom Stocks
3.3. Coagulation Tests
3.4. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasturiratne, A.; Wickremasinghe, A.R.; De Silva, N.; Gunawardena, N.K. The Global Burden of Snakebite: A Literature Analysis and Modelling Based on Regional Estimates of Envenoming and Deaths. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, 1591–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, R.A.; Hargreaves, A.; Wagstaff, S.C.; Faragher, B.; Lalloo, D.G. Snake Envenoming: A Disease of Poverty. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009, 3, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohapatra, B.; Warrell, D.A.; Suraweera, W.; Bhatia, P.; Dhingra, N.; Jotkar, R.M.; Rodriguez, P.S.; Mishra, K.; Whitaker, R.; Jha, P. Snakebite Mortality in India: A Nationally Representative Mortality Survey. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiermeier, Q. Snakebite Crisis Gets US$100-Million Boost for Better Antivenoms: Wellcome Trust Launches Research Initiative for Long-Neglected Health Problem. Nat. News 2019. Available online: https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-019-01557-0 (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Solano, G.; Pla, D.; Herrara, M.; Segura, A.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Sanchez, A.; Sanz, L.; Lomonte, B.; et al. Preclinical Evaluation of the Efficacy of Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: State-of-the-Art and Challenges Ahead. Toxins 2017, 9, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Burnouf, T.; Harrison, R.; Calvete, J.; Kuch, U.; Warrell, A. A Multicomponent Strategy to Improve the Availability of Antivenom for Treating Snakebite Envenoming. Policy Pract. 2014, 92, 526–532. [Google Scholar]
- Fry, B.G. Venomous Reptiles and Their Toxins: Evolution, Pathophysiology, and Biodiscovery; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 9788578110796. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Calvete, J.J.; Habib, A.G.; Harrison, R.A.; Williams, D.J.; Warrell, D.A. Snakebite Envenoming. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2017, 3, 17063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.; Kuruppu, S.; Reeve, S.; Ian Smith, A.; Hodgson, W.C. Oxylepitoxin-1, a Reversible Neurotoxin from the Venom of the Inland Taipan (Oxyuranus Microlepidotus). Peptides 2006, 27, 2655–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Duffull, S.B.; Brown, S.G.A. Failure of Antivenom to Improve Recovery in Australian Snakebite Coagulopathy. QJM An Int. J. Med. 2009, 102, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palta, S.; Saroa, R.; Palta, A. Overview of the Coagulation System. Indian J. Anaesth. 2014, 58, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casewell, N.R.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Laustsen, A.H.; Sunagar, K. Causes and Consequences of Snake Venom Variation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 41, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonk, F.J.; Casewell, N.R.; Henkel, C.V.; Heimberg, A.M.; Jansen, H.J.; McCleary, R.J.R.; Kerkkamp, H.M.E.; Vos, R.A.; Guerreiro, I.; Calvete, J.J.; et al. The King Cobra Genome Reveals Dynamic Gene Evolution and Adaptation in the Snake Venom System. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20651–20656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bos, M.H.A.; Boltz, M.; St. Pierre, L.; Masci, P.P.; De Jersey, J.; Lavin, M.F.; Camire, R.M. Venom Factor V from the Common Brown Snake Escapes Hemostatic Regulation through Procoagulant Adaptations. Blood 2009, 114, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, M.A.; Le, T.N.M.; Swarup, S.; Kini, R.M. Molecular Evolution Caught in Action: Gene Duplication and Evolution of Molecular Isoforms of Prothrombin Activators in Pseudonaja Textilis (Brown Snake). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Paes, B.; Johnston, M. Development of the Hemostatic System in the Neonate and Young Infant. Am. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 1990, 12, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrish, M.; Goldner, C.; Silberg, L. Comparison between Snakebites in Children and Adults. Pediatrics 1965, 36, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, D.; Sartorius, B.; Hift, R. Snakebite in North-Eastern South Africa: Clinical Characteristics and Risks for Severity. South African Fam. Pract. 2016, 58, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.; Brown, D. Multiple Thromboembolic Strokes in a Toddler Associated with Australian Eastern Brown Snake Envenomation. Radiol. Case Reports 2019, 14, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenes-Chacón, H.; Gutiérrez, J.M.; Camacho-Badilla, K.; Soriano-Fallas, A.; Ulloa-Gutierrez, R.; Valverde-Muñoz, K.; Ávila-Agüero, M.L. Snakebite Envenoming in Children: A Neglected Tropical Disease in a Costa Rican Pediatric Tertiary Care Center. Acta Trop. 2019, 200, 105176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Variawa, S.; Buitendag, J.; Marais, R.; Wood, D.; Oosthuizen, G. Prospective Review of Cytotoxic Snakebite Envenomation in a Paediatric Population. Toxicon 2021, 190, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buitendag, J.; Variawad, S.; Wood, D.; Oosthuizen, G.V. A Comparison between Adult and Paediatric Snakebites and Their Outcomes in North Eastern South Africa. Toxicon 2022, 208, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, R.; Sula, B.; Cakir, G.; Aktar, F.; Deveci; Yolbas, I.; Çelen, M.K.; Bekcibasi, M.; Palanci, Y.; Dogan, E. Comparison of Snakebite Cases in Children and Adults. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.; Ruha, A.M.; Wolk, B.; Caravati, M.; Brent, J.; Campleman, S.; Wax, P.; Aldy, K.; Akpunonu, P.; Bebarta, V.S.; et al. When It Comes to Snakebites, Kids Are Little Adults: A Comparison of Adults and Children with Rattlesnake Bites. J. Med. Toxicol. 2020, 16, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryanarayana, G.; Rameshkumar, R.; Mahadevan, S. Retrospective Hospital-Based Cohort Study on Risk Factors of Poor Outcome in Pediatric Snake Envenomation. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2021, 67, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagle, P.; Barnes, C.; Ignjatovic, V.; Furmedge, J.; Newall, F.; Chan, A.; De Rosa, L.; Hamilton, S.; Ragg, P.; Robinson, S.; et al. Developmental Haemostasis: Impact for Clinical Haemostasis Laboratories. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 95, 362–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovic, V.; Pelkmans, L.; Kelchtermans, H.; Al Dieri, R.; Hemker, C.; Kremers, R.; Bloemen, S.; Karlaftis, V.; Attard, C.; De Laat, B.; et al. Differences in the Mechanism of Blood Clot Formation and Nanostructure in Infants and Children Compared with Adults. Thromb. Res. 2015, 136, 1303–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attard, C.; Van der Straaten, T.; Karlaftis, V.; Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V. Developmental Hemostasis: Age-Specific Differences in the Levels of Hemostatic Proteins. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1850–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremers, R.M.W.; Wagenvoord, R.J.; de Laat, H.B.; Monagle, P.; Hemker, H.C.; Ignjatovic, V. Low Paediatric Thrombin Generation Is Caused by an Attenuation of Prothrombin Conversion. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 115, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeloffzen, W.W.; Kluin-Nelemans, H.C.; Mulder, A.B.; Veeger, N.J.G.M.; Bosman, L.; De Wolf, J.T. In Normal Controls, Both Age and Gender Affect Coagulability as Measured by Thrombelastography. Anesth. Analg. 2010, 110, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosquera, A.; Idrovo, L.A.; Tafur, A.; Del Brutto, O.H. Stroke Following Bothrops Spp. Snakebite. Neurology 2003, 60, 1577–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva de Oliveira, S.; Freitas-de-Sousa, L.A.; Alves, E.C.; de Lima Ferreira, L.C.; da Silva, I.M.; de Lacerda, M.V.G.; Fan, H.W.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Monteiro, W.M. Fatal Stroke after Bothrops Snakebite in the Amazonas State, Brazil: A Case Report. Toxicon 2017, 138, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Pardal, P.P.; da Silva Pinheiro, A.C.J.; Cunha Silva, C.T.; Santos, P.R.S.G.; da Costa Gadelha, M.A. Hemorrhagic Stroke in Children Caused by Bothrops Marajoensis Envenoming: A Case Report. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 21, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, H.; Liu, M.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Long, C.; Li, H.; Mwangi, J.; Lu, Q.; Lai, R.; Shen, C. Snake C-Type Lectins Potentially Contribute to the Prey Immobilization in Protobothrops mucrosquamatus and Trimeresurus stejnegeri Venoms. Toxins 2020, 12, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, M.; Fernández, J.; Vargas, M.; Villalta, M.; Segura, Á.; León, G.; Angulo, Y.; Paiva, O.; Matainaho, T.; Jensen, S.D.; et al. Comparative Proteomic Analysis of the Venom of the Taipan Snake, Oxyuranus Scutellatus, from Papua New Guinea and Australia: Role of Neurotoxic and Procoagulant Effects in Venom Toxicity. J. Proteomics 2012, 75, 2128–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loría, G.D.; Rucavado, A.; Kamiguti, A.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Fox, J.W.; Alape, A.; Gutiérrez, J.M. Characterization of “basparin A,” a Prothrombin-Activating Metalloproteinase, from the Venom of the Snake Bothrops Asper That Inhibits Platelet Aggregation and Induces Defibrination and Thrombosis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 418, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.J. On Some Effects upon the Blood Produced by the Injection of the Venom of the Australian Black Snake (Pseudechis Porphyriacus). Proc. R. Soc. New South Wales 1893, 15, 380–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K.; Scorgie, F.E.; O’leary, M.A.; Seldon, M.; Brown, S.G.A.; Lincz, L.F. Factor Deficiencies in Venom-Induced Consumption Coagulopathy Resulting from Australian Elapid Envenomation: Australian Snakebite Project (ASP-10). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 8, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monagle, P.; Ignjatovic, V.; Savoia, H. Hemostasis in Neonates and Children: Pitfalls and Dilemmas. Blood Rev. 2010, 24, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J. Hemostatic Analysis of Simulated Gloydius Ussuriensis Envenomation Using Canine Blood: A Comparison of Thromboelastography and Classical Coagulation Tests. Animals 2022, 12, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oulion, B.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Arbuckle, K.; Lister, C.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Rogalski, A.; Violette, A.; et al. Factor X Activating Atractaspis Snake Venoms and the Relative Coagulotoxicity Neutralising Efficacy of African Antivenoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 288, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Walker, A.; Naude, A.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; Fry, B.G. Varespladib (LY315920) Neutralises Phospholipase A2 Mediated Prothrombinase-Inhibition Induced by Bitis Snake Venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 236, 108818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.; op den Brouw, B.; Coimbra, F.; Gillett, A.; Del-Rei, T.; Chalkidis, H.; Sant’Anna, S.; Teixeira-da-Rocha, M.; et al. Coagulotoxicity of Bothrops (Lancehead Pit-Vipers) Venoms from Brazil: Differential Biochemistry and Antivenom Efficacy Resulting from Prey-Driven Venom Variation. Toxins 2018, 10, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seneci, L.; Zdenek, C.N.; Bourke, L.A.; Cochran, C.; Elda, E.S.; Frank, N.; Fry, B.G.; Neri-castro, E.; Melisa, B.; Alag, A. A Symphony of Destruction: Dynamic Differential Fibrinogenolytic Toxicity by Rattlesnake (Crotalus and Sistrurus) Venoms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2021, 245, 109034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Wu, Z.; Shen, S.; Liu, J.; Xiang, N.; Liao, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, L.; Chen, Q. Purification, Partial Characterizations, and N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence of a Procoagulant Protein FV-2 from Daboia Russelli Siamensis (Myanmar) Venom. J Biochem Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Dashevsky, D.; Nouwens, A.; Fry, B.G. The Sweet Side of Venom: Glycosylated Prothrombin Activating Metalloproteases from Dispholidus typus (Boomslang) and Thelotornis mossambicanus (Twig Snake). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2020, 227, 108625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morita, T.; Iwanaga, S. Purification and Properties of Prothrombin Activator from the Venom of Echis Carinatus. J. Biochem. 1978, 83, 559–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasson, S.S.; Theakston, R.D.G.; Harrison, R.A. Cloning of a Prothrombin Activator-like Metalloproteinase from the West African Saw-Scaled Viper, Echis Ocellatus. Toxicon 2003, 42, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Dobson, J.S.; Bourke, L.A.; Soria, R.; Fry, B.G. Clinical Implications of Differential Procoagulant Toxicity of the Palearctic Viperid Genus Macrovipera, and the Relative Neutralization Efficacy of Antivenoms and Enzyme Inhibitors. Toxicol. Lett. 2021, 340, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kini, R.M. The Intriguing World of Prothrombin Activators from Snake Venom. Toxicon 2005, 45, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Youngman, N.J.; Hay, C.; Dobson, J.; Dunstan, N.; Allen, L.; Milanovic, L.; Fry, B.G. Anticoagulant Activity of Black Snake (Elapidae: Pseudechis) Venoms: Mechanisms, Potency, and Antivenom Efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 330, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masci, P.P.; Whitaker, A.N.; de Jersey, J. Purification and Characterization of a Prothrombin Activator from the Venom of the Australian Brown Snake, Pseudonaja Textilis Textilis. Biochem Int. 1988, 17, 825–835. [Google Scholar]
- Bourke, L.A.; Youngman, N.J.; Zdenek, C.N.; op den Brouw, B.; Violette, A.; Fourmy, R.; Fry, B.G. Trimeresurus Albolabris Snakebite Treatment Implications Arising from Ontogenetic Venom Comparisons of Anticoagulant Function, and Antivenom Efficacy. Toxicol. Lett. 2020, 327, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debono, J.; Bos, M.H.A.; Frank, N.; Fry, B. Clinical Implications of Differential Antivenom Efficacy in Neutralising Coagulotoxicity Produced by Venoms from Species within the Arboreal Viperid Snake Genus Trimeresurus. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 316, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ignjatovic, V.; Ilhan, A.; Monagle, P. Evidence for Age-Related Differences in Human Fibrinogen. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2011, 22, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clauss, A. Rapid Physiological Coagulation Method in Determination of Fibrinogen. Acta Haematol. 1957, 17, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warrell, D.A. Snake Venoms in Science and Clinical Medicine * 1. Russell’s Viper: Biology, Venom and Treatment of Bites. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 1989, 83, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alirol, E.; Lechevalier, P.; Zamatto, F.; Chappuis, F.; Alcoba, G.; Potet, J. Antivenoms for Snakebite Envenoming: What Is in the Research Pipeline? PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaudas, X. Natural History of a Highly Medically Important Snake, Russell’s Viper (Daboia Russelii), in a Human-Dominated Indian Rural Landscape. J. Herpetol. 2021, 55, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, P.V.; Muthukumarana, T.G.W.; Aslam, W.A.M.; Chaminda, S.A.A.; Munasinghe, T.S.; Kularatne, S.A.M. An Unusual Case of Gross Myoglobinuria in a Child Following Russell’s Viper (Daboia Russelii) Envenomation. Toxicon 2019, 157, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, A.K. The Pro-Coagulant Fibrinogenolytic Serine Protease Isoenzymes Purified from Daboia Russelii Russelii Venom Coagulate the Blood through Factor V Activation: Role of Glycosylation on Enzymatic Activity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Das, D.; Iyer, J.K.; Kini, R.M.; Doley, R. Unveiling the Complexities of Daboia Russelii Venom, a Medically Important Snake of India, by Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Toxicon 2015, 107, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kini, R.M.; Rao, V.S.; Joseph, , J.S. Procoagulant Proteins from Snake Venoms. Haemostasis 2002, 31, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Vegh, P.; Johnston, M.; Bowker, J.; Ofosu, F.; Mitchell, L. Maturation of the Hemostatic System during Childhood. Blood 1992, 80, 1998–2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, K.K.; Martinage, A. Post-Translational Chemical Modification(S) of Proteins. Int. J. Biochem. 1992, 24, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevers, E.M.; Williamson, P.L. Getting to the Outer Leaflet: Physiology of Phosphatidylserine Exposure at the Plasma Membrane. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 605–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zdenek, C.N.; Hay, C.; Arbuckle, K.; Jackson, T.N.W.; Bos, M.H.A.; op den Brouw, B.; Debono, J.; Allen, L.; Dunstan, N.; Morley, T.; et al. Coagulotoxic Effects by Brown Snake (Pseudonaja) and Taipan (Oxyuranus) Venoms, and the Efficacy of a New Antivenom. Toxicol. Vitr. 2019, 58, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, H.; Rosenkranz, A.; Novak, M.; Leschnik, B.; Petritsch, M.; Rehak, T.; Köfeler, H.; Ulrich, D.; Muntean, W. No Differences in Support of Thrombin Generation by Neonatal or Adult Platelets. Hamostaseologie 2009, 29, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youngman, N.J.; Debono, J.; Dobson, J.S.; Zdenek, C.N.; Harris, R.J.; den Brouw, B.O.; Coimbra, F.C.P.; Naude, A.; Coster, K.; Sundman, E.; et al. Venomous Landmines: Clinical Implications of Extreme Coagulotoxic Diversification and Differential Neutralization by Antivenom of Venoms within the Viperid Snake Genus Bitis. Toxins 2019, 11, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrew, M.; Paes, B.; Milner, R.; Johnston, M.; Mitchell, L.; Tollefsen, D.; Castle, V.; Powers, P. Development of the Human Coagulation System in the Healthy Premature Infant. Blood 1988, 72, 1651–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Pierre, L.; Masci, P.P.; Filippovich, I.; Sorokina, N.; Marsh, N.; Miller, D.J.; Lavin, M.F. Comparative Analysis of Prothrombin Activators from the Venom of Australian Elapids. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2005, 22, 1853–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.M.; Vargas, M.; Segura, A.; Herrera, M.; Villalta, M.; Solano, G.; Sánchez, A.; Herrera, C.; León, G. In Vitro Tests for Assessing the Neutralizing Ability of Snake Antivenoms: Toward the 3Rs Principles. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, L.P.; Ignjatovic, V.; Winkel, K.D.; Summerhayes, R.; Monagle, P. The Differences of Platelet Response to Snake Venoms: A Comparative Study of Children and Adults. Toxicon 2008, 52, 960–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Q.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.Y.; Han, K.S.; Kim, H.K. Influence of ABO Type on Global Coagulation Assay Results: Effect of Coagulation Factor VIII. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2015, 53, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underhill, D. Snake Species. In Australia’s Dangerous Creatures; Sutherland, S.K., Ed.; Reader’s Digest: Sydney, Australia, 1993; ISBN 0864380186. [Google Scholar]
- Howie, S.R.C. Blood Sample Volumes in Child Health Research: Review of Safe Limits. Bull. World Health Organ. 2011, 89, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maduwage, K.; Isbister, G.K. Current Treatment for Venom-Induced Consumption Coagulopathy Resulting from Snakebite. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2014, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isbister, G.K. Snakebite Doesn’t Cause Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation: Coagulopathy and Thrombotic Microangiopathy in Snake Envenoming. Semin Thromb Hemost 2010, 36, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laxme, R.R.S.; Khochare, S.; Attarde, S.; Suranse, V.; Iyer, A.; Casewell, N.R.; Whitaker, R.; Martin, G.; Sunagar, K. Biogeographic Venom Variation in Russell’s Viper (Daboia Russelii) and the Preclinical Inefficacy of Antivenom Therapy in Snakebite Hotspots. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2021, 15, e0009247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Children, A.; Adelaide, N.; Museum, S.A.; Terrace, N.; Terrace, N. Variation in Venom Proteins from Isolated Populations of Tiger Snakes (Notechis Ater Niger, N. Scutatus) in South Australia. Toxicon 1988, 26, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Flight, S.; Mirtschin, P.; Masci, P.P. Comparison of Active Venom Components between Eastern Brown Snakes Collected from South Australia and Queensland. Ecotoxicology 2006, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourke, L.A.; Zdenek, C.N.; Tanaka-azevedo, A.M.; Perez, G.; Silveira, M.; Sant, S.; Grego, K.F.; Fabri, C.; Rodrigues, B.; Fry, B.G. Clinical and Evolutionary Implications of Dynamic Coagulotoxicity Divergences in Bothrops (Lancehead Pit Viper) Venoms. Toxins 2022, 14, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdell, R.; Wagner, R.; Brinkhous, K. Effect of Antihemophilic Factor on One-Stage Clotting Tests. J. Lab. Clin. Med. 1953, 41, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Yekutieli, D. Quantitative Trait Loci Analysis Using the False Discovery Rate. Genetics 2005, 171, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]




| Scientific Name | Common Name | Broad Distribution | Coagulotoxic Activity and Mechanism | Source of Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atractaspis bibronii | Bibron’s Stiletto Snake | Southern Africa | FX activating | [41] |
| Bitis cornuta | Many-horned Adder | Atlantic coast of South Africa | Prothrombinase inhibition via PLA2s | [42] |
| Bothrops atrox | Lancehead Viper | South America | FX and PRT activating via SVMP | [43] |
| Bothrops asper | Terciopelo | Central America | FX and PRT activating via SVMP | [36] |
| Crotalus mictlantecuhtli | Veracruz Neotropical Rattlesnake | Mexico | Fibrinogen cleavage (pseudo-procoagulant) | [44] |
| Daboia russelii | Russell’s Viper | South Asia | FX activating | [45] |
| Dispholidus typus | Boomslang | Sub-Saharan Africa | PRT activating | [46] |
| Echis coloratus | Painted Saw-scaled Viper | Middle East and Arabian Peninsula | PRT activating via P-IIId SVMP (Ca-dependent) | [47] |
| Echis ocellatus | West African Saw-scaled Viper | West Africa | PRT activating via P-IIIa SVMP (Ca-independent) | [48] |
| Macrovipera lebetina cernovi | Lebetine Viper | Middle East | FX activating | [49] |
| Notechis scutatus | Tiger Snake | South and SE Australia | PRT activating via venom FXa | [50] |
| Pseudechis australis | Mulga Snake | South and SE Australia | Prothrombinase and/or FVa inhibition via PLA2s | [51] |
| Pseudonaja textilis | Eastern Brown Snake | Eastern & Southern Australia | PRT activating via venom FVa:FXa | [52] |
| Thelotornis mossambicanus | Eastern Twig Snake | Eastern Africa | PRT activating | [46] |
| Trimeresurus albolabris | White-lipped Pit Viper | India and SE Asia | Fibrinogen cleavage (pseudo-procoagulant) | [53,54] |
| Species | Common Name | Adult Plasma | Paediatric Plasma | t-Test * q-Value | t Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atractaspis bibronii | Bibron’s stiletto snake | 536.3 ± 29.2 | 516.1 ± 5.6 | q = 0.43 | 1.18 |
| Bitis cornuta | Many-horned adder | 1794.0 ± 25.3 | 940.6 ± 33.1 | q < 0.0001 | 35.43 |
| Bothrops asper | Terciopelo | 272.7 ± 2.5 | 270.0 ± 8.0 | q = 0.53 | 0.56 |
| Bothrops atrox | Fur-de-lance | 458.2 ± 21.5 | 401.1 ± 5.0 | q = 0.08 | 4.49 |
| Crotalus mictlantecuhtli | Veracruz Neotropical rattlesnake | 2962.0 ± 33.4 | 2924.0 ± 126.8 | q = 0.53 | 0.05 |
| Daboia russelii | Russell’s viper | 202.0 ± 1.5 | 154.1 ± 2.8 | q < 0.001 | 26.21 |
| Dispholidus typus | Boomslang | 434.2 ± 19.8 | 462.8 ± 12.1 | q = 0.20 | 2.14 |
| Echis coloratus | Painted saw-scaled viper | 591.1 ± 6.6 | 568.3 ± 19.6 | q = 0.26 | 1.90 |
| Echis ocellatus | West African carpet viper | 356.1 ± 22.6 | 366.1 ± 22.7 | q = 0.53 | 0.54 |
| Macrovipera lebentina cernovi | Lebetine viper | 167.1 ± 2.8 | 154.3 ± 2.6 | q = 0.01 | 5.77 |
| Notechis scutatus | Tiger snake | 124.6 ± 1.9 | 120.3 ± 9.0 | q = 0.53 | 0.81 |
| Pseudechis australis | Mulga snake | 2142.0 ± 28.1 | 342.8 ± 9.9 | q < 0.0001 | 104.6 |
| Pseudonaja textilis | Eastern brown snake | 67.7 ± 1.6 | 68.3 ± 0.98 | q = 0.53 | 0.58 |
| Thelotornis mossambicanus | Eastern twig snake | 204.4 ± 4.4 | 220.5 ± 3.2 | q = 0.02 | 5.13 |
| Trimeresurus albolabris | White-lipped pit viper | 2158.0 ± 33.5 | 2045.0 ± 133.5 | q = 0.38 | 1.41 |
| Assay | Methodology |
|---|---|
| Standard coagulation tests | |
| aPTT | Step 1: 50 µL plasma + 50 µL kaolin/phospholipid (Stago # 00597) Step 2: 240 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 50 µL 0.025 M calcium (Stago # 00367) |
| PT | Step 1: 50 µL human plasma Step 2: 240 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 100 µL Neoplastine (Stago #00606) |
| Fibrinogen levels | Step 1: 150 µL plasma (diluted 1:20 by Owren–Koller (OK) Buffer (isotonic saline) (Stago # 00360) Step 2: 240 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 50 µL Thrombin (Stago #00611) |
| Venom tests | |
| Procoag. venom | Step 1: 50 µL 0.1 µg/mL venom (diluted in OK for dose-response curves) + 50 µL 0.025 M calcium + 50 µL phospholipid (phospholipid bottle in Stago kit #00597) + 25 µL OK buffer Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 75 µL plasma |
| Anticoag. venom | Step 1: 25 µL 0.2 µg/mL venom (diluted in OK for dose-response curves) + 50 µL 0.025 M calcium + 50 µL phospholipid + 25 µL OK Buffer + 75 µL plasma Step 2: 120 s incubation at 37 °C Step 3: Addition of 25 µL FXa (FXa bottle in Stago kit # 00311) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zdenek, C.N.; Rodrigues, C.F.B.; Bourke, L.A.; Tanaka-Azevedo, A.M.; Monagle, P.; Fry, B.G. Children and Snakebite: Snake Venom Effects on Adult and Paediatric Plasma. Toxins 2023, 15, 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020158
Zdenek CN, Rodrigues CFB, Bourke LA, Tanaka-Azevedo AM, Monagle P, Fry BG. Children and Snakebite: Snake Venom Effects on Adult and Paediatric Plasma. Toxins. 2023; 15(2):158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020158
Chicago/Turabian StyleZdenek, Christina N., Caroline F. B. Rodrigues, Lachlan A. Bourke, Anita Mitico Tanaka-Azevedo, Paul Monagle, and Bryan G. Fry. 2023. "Children and Snakebite: Snake Venom Effects on Adult and Paediatric Plasma" Toxins 15, no. 2: 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020158
APA StyleZdenek, C. N., Rodrigues, C. F. B., Bourke, L. A., Tanaka-Azevedo, A. M., Monagle, P., & Fry, B. G. (2023). Children and Snakebite: Snake Venom Effects on Adult and Paediatric Plasma. Toxins, 15(2), 158. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15020158