Aflatoxin B1 Detoxification Potentials of Garlic, Ginger, Cardamom, Black Cumin, and Sautéing in Ground Spice Mix Red Pepper Products
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
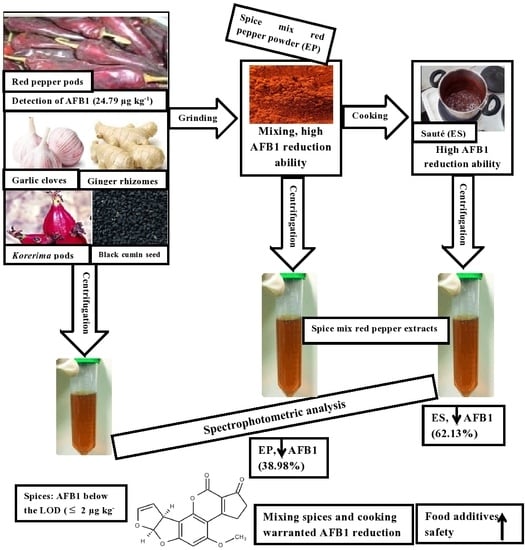
2.1. Aflatoxin B1 Level and Detoxification
2.2. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Contents, and Antioxidant Activities of Entire Samples
2.3. Correlation Analysis
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Experimental Design
5.2. Sample Collection and Experimental Sauté Preparation
5.3. Experimental Section
5.3.1. Aflatoxin B1 Determination
5.3.2. Determination of TPC, TFC, and Antioxidant Activities
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AFB1 | Aflatoxin B1 |
| AFs | Aflatoxins |
| CP | Commercial spice mix red pepper powder |
| CS | Commercial spice mix red pepper sauté |
| DPPH | 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl |
| EP | Experimental spice mix red pepper powder |
| ES | Experimental spice mix red pepper sauté |
| FICA | Ferrous ion chelating activity |
| FRAP | Ferric ion reducing antioxidant power |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| mg GAE g−1 | Milligram gallic acid equivalent per gram |
| mg QE g−1 | Milligram quercetin equivalent per gram |
| RP | Control red pepper powder |
| TFC | Total flavonoid content |
| TPC | Total phenolic content |
References
- Wakhungu, C.N.; Okoth, S.; Wachira, P.O.N. Mycotoxins contaminating herbs and spices in Africa: A review. Afr. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 3, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, C.; Jang, M.; Son, Y.; Lee, S.; Choi, I.; Kim, S.; Kim, D. Food Chemistry Aflatoxins contamination in spices and processed spice products commercialized in Korea. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, A.; Xie, H.; Tang, X.; Qi, Z.; Li, P. Worldwide aflatoxin contamination of agricultural products and foods: From occurrence to control. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2021, 20, 2332–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negera, M.; Washe, A. Use of natural dietary spices for reclamation of food quality impairment by aflatoxin. J. Food Qual. 2019, 10, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhao, L.; Ma, Q.; Ji, C. Novel strategies for degradation of aflatoxins in food and feed: A review. Food Res. Int. 2021, 140, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkerroum, N. Chronic and acute toxicities of aflatoxins: Mechanisms of action. Int. J. Environ. Res. Publ. Health 2020, 17, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Mahato, D.K.; Kamle, M.; Mohanta, T.K.; Kang, S.G. Aflatoxins: A global concern for food safety, human health and their management. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.; Rodríguez, R.; Garcia-Cela, E.; Medina, A.; Magan, N.; Lima, N.; Battilani, P.; Santos, C. Overview of fungi and mycotoxin contamination in capsicum pepper and in its derivatives. Toxins 2019, 11, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tafesse, F.; Addisie, B.; Tesfaye, K.; Nie, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Mycotoxins in Ethiopia: A Review on prevalence, economic and health impacts. Toxins 2020, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herms, S.; Alemahu, A.; Mengesha, B.; van Oort, W. Investment opportunities in the Ethiopian Spices sub-sector. ResearchGate 2015, 6, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismaie, A.A.; Papenbrock, J. Mycotoxins: Producing fungi and mechanisms of phytotoxicity. Agriculture 2015, 5, 492–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, P.; Peles, F.; Brassó, D.L.; Béri, B.; Pusztahelyi, T.; Pócsi, I.; Győri, Z. Physical and chemical methods for reduction in aflatoxin content of feed and food. Toxins 2021, 13, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pankaj, S.K.; Shi, H.; Keener, K.M. A review of novel physical and chemical decontamination technologies for aflatoxin in food. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 71, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Stamatelopoulou, E.; Varzakas, T. Advances in occurrence, importance, and mycotoxin control strategies: Prevention and detoxification in foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, H.; Meneely, J.P.; Quinn, B.; Zhao, Y.; Bourke, P.; Gilmore, B.F.; Zhang, G.; Elliott, C.T. Novel decontamination approaches and their potential application for post-harvest aflatoxin control. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 106, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebo, O.A.; Molelekoa, T.; Makhuvele, R.; Adebiyi, J.A.; Oyedeji, A.B.; Gbashi, S.; Adefisoye, M.A.; Ogundele, O.M.; Njobeh, P.B. A review on novel non-thermal food processing techniques for mycotoxin reduction. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 56, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayanandraj, S.; Brinda, R.; Kannan, K.; Adhithya, R.; Vinothini, S.; Senthil, K.; Chinta, R.R.; Paranidharan, V.; Velazhahan, R. Detoxification of aflatoxin B1 by an aqueous extract from leaves of Adhatoda vasica Nees. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 169, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putriani, N.; Perdana, J.; Meiliana; Nugrahedi, P.Y. Effect of thermal processing on key phytochemical compounds in green leafy vegetables: A review. Food Rev. Int. 2020, 2020, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, M.; Kalita, D.; Bartolo, M.E.; Jayanty, S.S. Capsaicinoids, polyphenols and antioxidant activities of Capsicum annuum: Comparative study of the effect of ripening stage and cooking methods. Antioxidants 2019, 8, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emire, S.A.; Jha, Y.K.; Mekam, F. Role of Anti-nutritional Factors in Food Industry. Beverage Food World 2013, 2013, 23–27. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/280722236 (accessed on 23 September 2022).
- Roncero-ramos, I.; Mendiola-lanao, M.; Pérez-clavijo, M.; Delgado-andrade, C. Effect of different cooking methods on nutritional value and antioxidant activity of cultivated mushrooms. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 68, 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thamkaew, G.; Sjöholm, I.; Galindo, F.G. A review of drying methods for improving the quality of dried herbs. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 1763–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, I.G.; Shin, Y.J.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.; Yoo, S.M. Effects of different cooking methods on the antioxidant properties of red pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2012, 17, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, I.; Chohan, M.; Opara, E.I. Impact of cooking and digestion, In Vitro, on the antioxidant capacity and anti-inflammatory activity of cinnamon, clove and nutmeg. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2013, 68, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Liu, Y.; Lai, S.; Cao, H.; Guan, Y.; San, W. Trends in food science and technology effects of domestic cooking process on the chemical and biological properties of dietary phytochemicals. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 85, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponzilacqua, B.; Corassin, C.H.; Oliveira, C.A.F. Antifungal activity and detoxification of aflatoxins by plant extracts: Potential for food applications. Open Food Sci. J. 2018, 10, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agi, V.N.; Azike, C.A. Antifungal action of garlic (Allium sativum) and ginger (Zingiber officinale) on some pathogenic fungi. Asian J. Res. Biochem. 2019, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forouzanfar, F.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S.; Hosseinzadeh, H. Black cumin (Nigella sativa) and its constituent (thymoquinone): A review on antimicrobial effects. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2014, 17, 929–938. [Google Scholar]
- Macario, E.T.T.; Segundo, E.; Aguilar, V.; Transito, M.; Rojas, A.; Dagoberto, D.G.O.; Quevedo, R.; Díaz, O.M.J.; Montes, B. Garlic (Allium sativum L.) and its beneficial properties for health: A review Elajo (Allium sativum L.) ysus propiedades beneficiosas para la salud: Una revisión. Agroind. Sci. 2020, 10, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ene-obong, H.; Onuoha, N.; Aburime, L.; Mbah, O. Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of some indigenous spices consumed in Nigeria. Food Chem. 2018, 238, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, D. Comparative analysis of spices for their phenolic content, flavonoid content and antioxidant capacity. Am. Int. J. Res. Form. Appl. Nat. Sci. 2013, 11, 38–42. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Deepshikha-Gupta2/publication/272415613 (accessed on 12 February 2023).
- Azzoune, N.; Mokrane, S.; Riba, A.; Bouras, N.; Verheecke, C.; Sabaou, N.; Mathieu, F. Contamination of common spices by aflatoxigenic fungi and aflatoxin B1 in Algeria. Qual. Assur. Saf. Crops Foods 2015, 8, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolde, M. Effects of aflatoxin contamination of grains in Ethiopia. Int. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 7, 1298–1308. Available online: www.internationalscholarsjournals.org (accessed on 19 December 2022).
- Hunduma, T.; Tesfaye, A.; Alemu, M. Aflatoxin contamination of Ethiopian hot red pepper and risk characterization: Dietary exposure assessment and estimated aflatoxin-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Ethiop. J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 30, 63–81. [Google Scholar]
- Pickova, D.; Ostry, V.; Malir, J.; Toman, J.; Malir, F. A review on mycotoxins and microfungi in spices in the light of the last five years. Toxins 2020, 12, 789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barani, A.; Nasiri, Z.; Jarrah, N. Natural occurrence of aflatoxins in commercial pepper in Iran. Food Agric. Immunol. 2016, 33, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanushree, M.P.; Sailendri, D.; Yoha, K.S.; Moses, J.A.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Mycotoxin contamination in food: An exposition on spices. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syamilah, N.; Nurul Afifah, S.; Effarizah, M.E.; Norlia, M. Mycotoxins and mycotoxigenic fungi in spices and mixed spices: A review. Food Res. 2022, 6, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daou, R.; Joubrane, K.; Maroun, R.G.; Khabbaz, L.R.; Ismail, A.; El Khoury, A. Mycotoxins: Factors influencing production and control strategies. AIMS Agric. Food 2021, 6, 416–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Baek, S.G.; Hung, N.B.; Kim, S.; Jang, J. Effects of temperature and humidity on fungal occurrence in dried red pepper during storage. Res. Plant Dis. 2021, 27, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Galani Yamdeu, J.H.; Gong, Y.Y.; Orfila, C. A review of postharvest approaches to reduce fungal and mycotoxin contamination of foods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 1521–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozbey, F.; Kabak, B. Natural co-occurrence of a flatoxins and ochratoxin A in spices. Food Control 2012, 28, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, M.; Paciolla, C.; Logrieco, A.F.; Mulè, G.; Lin, L. Plant bioactive compounds in pre- and postharvest management for aflatoxins reduction. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.Y. The toxification and detoxification mechanisms of aflatoxin B1 in human: An update. In Aflatoxin B1 Occurrence, Detection and Toxicological Effects; Long, X.D., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK; Rijeka, Croatia, 2019; pp. 221–239. Available online: www.intechopen.com (accessed on 21 July 2022).
- Iram, W.; Anjum, T.; Iqbal, M.; Ghaffar, A.; Abbas, M. Structural elucidation and toxicity assessment of degraded products of aflatoxin B1 and B2 by aqueous extracts of Trachyspermum ammi. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Harrasi, M.M.A.; Al-Sadi, A.M.; Al-Sabahi, J.N.; Al-Farsi, K.; Waly, M.I.; Velazhahan, R. Essential oils of Heliotropium bacciferum, Ocimum dhofarense and Zataria multiflora exhibit aflatoxin B1 detoxification potential. All Life 2021, 14, 989–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlovsky, P.; Suman, M.; Berthiller, F.; De Meester, J.; Eisenbrand, G.; Perrin, I.; Oswald, I.P.; Speijers, G.; Chiodini, A.; Recker, T.; et al. Impact of food processing and detoxification treatments on mycotoxin contamination. Mycotoxin Res. 2016, 32, 179–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalili, M. A review on aflatoxins reduction in food. Iran. J. Health Saf. Environ. 2015, 3, 445–459. [Google Scholar]
- Rushing, B.R.; Selim, M.I. Aflatoxin B1: A review on metabolism, toxicity, occurrence in food, occupational exposure, and detoxification methods. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inchuen, S.; Pornchaloempong, P.; Narkrugsa, W.; Tungkananuruk, K. Influence of heat treatment on antioxidant capacity and color of Thai red curry paste. Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 2011, 45, 136–146. [Google Scholar]
- Shaimaa, G.A.; Mahmoud, M.S.; Mohamed, M.R. Effect of heat treatment on phenolic and flavonoid compounds and antioxidant activities of some Egyptian sweet and chili pepper. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2016, 4, 2–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alide, T.; Wangila, P.; Kiprop, A. Effect of cooking temperature and time on total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and total in vitro antioxidant activity of garlic. BMC Res. Notes 2020, 13, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruck De Souza, L.; Leitão Gindri, A.; De Andrade Fortes, T.; Felli Kubiça, T.; Enderle, J.; Roehrs, R.; Moura, E.; Silva, S.; Manfredini, V.; Denardin, E.L.G. Phytochemical analysis, antioxidant activity, antimicrobial activity, and cytotoxicity of Chaptalia nutans leaves. Adv. Pharmacol. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 2020, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.W.C.; Chan, H.J.; Lim, J.E.; Yik, S.H.; Tan, S.F.; Goh, P.C.; Yap, K.Y.; Yee, S.Y. Effects of different cooking methods on the bioactivities of some spices. Emir. J. Food Agric. 2015, 27, 610–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altemimi, A.; Lakhssassi, N.; Baharlouei, A.; Watson, D.G.; Lightfoot, D.A. Phytochemicals: Extraction, isolation, and identification of bioactive compounds from plant extracts. Plants 2017, 6, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guldiken, B.; Ozkan, G.; Catalkaya, G.; Ceylan, F.D.; Ekin Yalcinkaya, I.; Capanoglu, E. Phytochemicals of herbs and spices: Health versus toxicological effects. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 119, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bag, A.; Chattopadhyay, R.R. Evaluation of synergistic antibacterial and antioxidant efficacy of essential oils of spices and herbs in combination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Ghasemi, A. Phytochemical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties of extracts from two spice herbs under different extraction solvents. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2019, 13, 2470–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rita, A.; Mateus, S.; Pena, A.; Silva, A.S. Mycotoxins in pistachios (Pistacia vera L.): Methods for determination, occurrence, decontamination. Toxins 2021, 13, 682–716. [Google Scholar]
- BioTeZ. B-TeZ ELISA Aflatoxin B1 Kit; Berlin-Buch GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2015; Volume 49, pp. 2–10. Available online: www.biotez.de (accessed on 6 May 2022).
- Ali, A.; Wu, H.; Ponnampalam, E.N.; Cottrell, J.J.; Dunshea, F.R.; Suleria, H.A.R. Comprehensive profiling of most widely used spices for their phenolic compounds through LC-ESI-QTOF-MS2 and their antioxidant potential. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, G.M.; Mahajan, R.T. Comparative antioxidant activity of twenty traditional Indian medicinal plants and its correlation with total flavonoid and phenolic content. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res. 2015, 30, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Wang, J.; Al-Qadiri, H.M.; Ross, C.F.; Powers, J.R.; Tang, J.; Rasco, B.A. Determination of total phenolic content and antioxidant activity of garlic (Allium sativum) and elephant garlic (Allium ampeloprasum) by Attenuated total reflectance: Fourier Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 5215–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Treatment | % Detoxification SE |
|---|---|
| Control red pepper (RP) | 0.00 0.05 d |
| Experimental spice mix red pepper (EP) | 38.98 0.05 b |
| Experimental spice mix red pepper sauté (ES) | 62.13 0.05 a |
| Commercial spice mix red pepper (CP) | 23.47 0.05 c |
| Commercial spice mix red pepper sauté (CS) | 65.95 0.05 a |
| Variable | By Variable | Correlation (r) | Count (n) | Signif Prob |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Detoxification of AFB1 (%) | TPC (mg GAE g−1 dw) | 0.9 | 10 | 0.0004 |
| Detoxification of AFB1 (%) | TFC (mg QE g−1 dw) | 0.68 | 10 | 0.0305 |
| Detoxification of AFB1 (%) | DPPH free radical scavenging activity (IC50) | 0.87 | 10 | 0.0008 |
| Detoxification of AFB1 (%) | FRAP (mg TE g−1 dw) | 0.82 | 10 | 0.0037 |
| Detoxification of AFB1 (%) | Chelating potential of FICA (mg QE g−1 dw) | 0.86 | 10 | 0.0013 |
| Treatments | RP (%) | GA (%) | GI (%) | CA (%) | BC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control red pepper (RP) | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Garlic (GA) | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ginger (GI) | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| Cardamom (CA) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| Black cumin (BC) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| Experimental spice mix red pepper (EP) | 67.5 | 13.5 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 2.7 |
| Experimental spice mix red pepper sauté (ES) | 67.5 | 13.5 | 9.5 | 6.8 | 2.7 |
| Commercial spice mix red pepper (CP) | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
| Commercial spice mix red pepper sauté (CS) | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown | unknown |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Medalcho, T.H.; Abegaz, K.; Dessalegn, E.; Mate, J. Aflatoxin B1 Detoxification Potentials of Garlic, Ginger, Cardamom, Black Cumin, and Sautéing in Ground Spice Mix Red Pepper Products. Toxins 2023, 15, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15050307
Medalcho TH, Abegaz K, Dessalegn E, Mate J. Aflatoxin B1 Detoxification Potentials of Garlic, Ginger, Cardamom, Black Cumin, and Sautéing in Ground Spice Mix Red Pepper Products. Toxins. 2023; 15(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleMedalcho, Tadewos Hadero, Kebede Abegaz, Engida Dessalegn, and Juan Mate. 2023. "Aflatoxin B1 Detoxification Potentials of Garlic, Ginger, Cardamom, Black Cumin, and Sautéing in Ground Spice Mix Red Pepper Products" Toxins 15, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15050307
APA StyleMedalcho, T. H., Abegaz, K., Dessalegn, E., & Mate, J. (2023). Aflatoxin B1 Detoxification Potentials of Garlic, Ginger, Cardamom, Black Cumin, and Sautéing in Ground Spice Mix Red Pepper Products. Toxins, 15(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins15050307