Biological and Pathological Studies of Rosmarinic Acid as an Inhibitor of Hemorrhagic Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu) Venom
Abstract
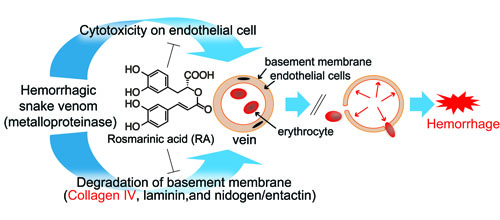
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Rosmarinic Acid
2.3. Anti-hemorrhagic Activity Assay
2.4. Fibrinogen Hydrolytic Activity Assay
2.5. Collagen Hydrolytic Activity Assay
2.6. Cytotoxic Action on HUVEC
2.7. Histopathological Study
2.8. Heat Stability
2.9. Assay for Edema Activity
3. Results
3.1. Inhibitory Activity of RA on Crude Snake Venoms and Purified Hemorrhagic Toxins

3.2. Inhibition of Fibrinogen Hydrolytic Activity

3.3. Inhibition of Venom Cytotoxic Action on HUVEC
3.4. Inhibition of Type IV Collagen Hydrolytic Activity


3.5. Histological Study of T. flavoviridis Venom and the Effect of RA

3.6. Heat Stability of RA

3.7. Inhibition of Venom-Induced Edema
4. Discussion

Acknowledgements
References
- Warrell, D.A. The global problem of snakebite: Its prevention and treatment. In Recent Advances in Toxinology Research; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tu, C.K., Eds.; National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1992; pp. 121–153. [Google Scholar]
- Chippaux, J.P. Snake-bites: Appraisal of the global situation. Bull. World Health Organ. 1998, 76, 515–524. [Google Scholar]
- Swaroop, S.; Grab, B. Snakebite mortality in the world. Bull. World Health Organ. 1954, 10, 35–76. [Google Scholar]
- Theakston, R.D.G.; Reid, H.A. Development of simple standard assay procedures for the characterization of snake venom. Bull. World Health Organ. 1983, 61, 949–956. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, A.T. Venoms: Chemistry and Molecular Biology; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, A.T. Rattlesnake Venoms: Their actions and Treatment; Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Martz, W. Plants with a reputation against snakebite. Toxicon 1992, 30, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar]
- Mors, W.B.; Nascimento, M.C.; Pereira, B.M.; Pereira, N.A. Plant natural products active against snake-bite —the molecular approach. Phytochemistry 2000, 55, 627–642. [Google Scholar]
- Soares, A.M.; Januario, A.H.; Lourenco, M.V.; Pereira, A.M.; Pereira, P.S. Neutralizing effects of Brazilian plants against snake venoms. Drugs Future 2004, 29, 1105–1117. [Google Scholar]
- Aung, H.T.; Nikai, T.; Niwa, M.; Takaya, Y. Rosmarinic acid in Argusia argentea inhibits snake venom-induced hemorrhage. J. Nat. Med. 2010, 64, 482–486. [Google Scholar]
- Komori, Y.; Hagihara, S.; Tu, A.T. Specificity of hemorrhagic proteinase from Crotalus atrox (western diamondback rattlesnake) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 829, 127–130. [Google Scholar]
- Nikai, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Komori, Y.; Sugihara, H. Hemorrhagic toxin, bilitoxin-2, from Agkistrodon bilineatus venom. J. Nat. Toxins 1996, 5, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Nikai, T.; Sugihara, H.; Tanaka, T. Enzymochemical studies on snake venoms II. Purification of lethal protein Ac1-proteinase in the venom of Agkistrodon acutus. Yakugaku Zasshi 1977, 97, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikai, T.; Suzuki, J.; Komori, Y.; Sugihara, H. Biochemical and pathological studies on hemorrhagic toxin. J. Nat. Toxins 1995, 4, 83–96. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason, J.B.; Tu, A.T. Hemorrhagic toxins from western diamondback rattlesnake (Crotalus atrox) venom: Isolation and characterization of five toxins and the role of zinc in hemorrhagic toxin e. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 3395–3404. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, C.; Teng, C.M. Fibrinogenolytic enzymes of Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1976, 420, 298–308. [Google Scholar]
- Ishiyama, M.; Miyazono, Y.; Sasamoto, K.; Ohkura, Y.; Ueno, K. A highly water-soluble disulfonated tetrazolium salt as a chromogenic indicator for NADH as well as cell viability. Talanta 1997, 44, 1299–1305. [Google Scholar]
- Tominaga, H.; Ishiyama, M.; Ohseto, F.; Sasamoto, K.; Hamamoto, T.; Suzuki, K.; Watanabe, M. A water-soluble tetrazolium salt useful for colorimetric cell viability assay. Anal. Commun. 1999, 36, 47–50. [Google Scholar]
- Komori, Y.; Nikai, T.; Taniguchi, K.; Masuda, K.; Sugihara, H. Vascular endothelial growth factor VEGF-like heparin-binding protein from the venom of Vipera aspis aspis (Aspic Viper). Int. J. Biochem. 1999, 38, 11796–11803. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, C.L.; Hwang, L.L.; Chen, C.T. Edema-inducing activity of a lethal protein with phospholipase A1 activity isolated from the black-bellied hornet (Vespa basalis) venom. Toxicon 1993, 31, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Laing, G.D.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Jararhagin and its multiple effects on hemostasis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 987–996. [Google Scholar]
- Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Hemorrhagic metalloproteinases from snake venoms. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 62, 325–372. [Google Scholar]
- Markland, F.S. Snake venoms and the hemostatic system. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1749–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Baramova, E.N.; Shannon, J.D.; Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Degradation of extracellular matrix proteins by hemorrhagic metalloproteinases. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 275, 63–71. [Google Scholar]
- Baramova, E.N.; Shannon, J.D.; Bjarnason, J.B.; Fox, J.W. Identification of the cleavage sites by a hemorrhagic metalloproteinase in type IV collagen. Matrix 1990, 10, 91–97. [Google Scholar]
- Mashiko, H.; Takahashi, H. Haemorrhagic factors from snake venoms. II. Structures of haemorrhagic factors and types and mechanisms of haemorrhage. J. Toxicol. Toxin Rev. 1998, 17, 493–512. [Google Scholar]
- Ticli, F.K.; Hage, L.I.S.; Cambraia, R.S.; Pereira, P.S.; Magro, A.J.; Fontes, M.R.M.; Stábeli, R.G.; Giglio, J.R.; França, S.C.; Soares, A.M.; Sampaio, S.V. Rosmarinic acid, a new snake venom phospholipase A2 inhibitor from Cordia verbenacea (Boraginaceae): Antiserum action potentiation and molecular interaction. Toxicon 2005, 46, 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara, K.; Miyagi, Y.; Higa, M.; Yogi, S. Pyrrolizidine alkaloids from Messerschmidia argentea. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 545–547. [Google Scholar]
- Noro, T.; Nishihara, G.N.; Terada, R.; Yoropiy, A. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning in Ulithi Atoll, Yap State, Micronesia. Kagoshima Univ. Res. Ctr. Pac. Isl. Occas. Pap. 2003, 39, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara, K.; Nakazato, R.; Nishi, Y.; Higa, M.; Yogi, S. DPPH-radical scavenging constituents from the twigs of Messerschmidia argentea. Bull. Fac. Sci. Univ. Ryukyus 2002, 74, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Warrell, D.A. Russell’s viper: biology, venom and treatment of bites. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1989, 83, 732–740. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Aung, H.T.; Nikai, T.; Komori, Y.; Nonogaki, T.; Niwa, M.; Takaya, Y. Biological and Pathological Studies of Rosmarinic Acid as an Inhibitor of Hemorrhagic Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu) Venom. Toxins 2010, 2, 2478-2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2102478
Aung HT, Nikai T, Komori Y, Nonogaki T, Niwa M, Takaya Y. Biological and Pathological Studies of Rosmarinic Acid as an Inhibitor of Hemorrhagic Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu) Venom. Toxins. 2010; 2(10):2478-2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2102478
Chicago/Turabian StyleAung, Hnin Thanda, Toshiaki Nikai, Yumiko Komori, Tsunemasa Nonogaki, Masatake Niwa, and Yoshiaki Takaya. 2010. "Biological and Pathological Studies of Rosmarinic Acid as an Inhibitor of Hemorrhagic Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu) Venom" Toxins 2, no. 10: 2478-2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2102478
APA StyleAung, H. T., Nikai, T., Komori, Y., Nonogaki, T., Niwa, M., & Takaya, Y. (2010). Biological and Pathological Studies of Rosmarinic Acid as an Inhibitor of Hemorrhagic Trimeresurus flavoviridis (habu) Venom. Toxins, 2(10), 2478-2489. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2102478