Exfoliative Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)
3. Toxin Identity
4. Molecular Mechanism of Toxin Activity

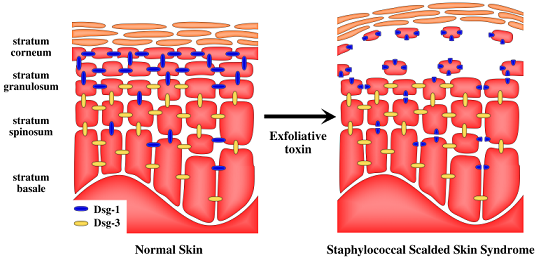
5. Target of Exfoliative Toxins in the Skin


6. Toxin Susceptibility
7. Species-Specific Diversity of ETs
8. Concluding Remarks
Acknowledgements
References and Notes
- Dinges, M.M.; Orwin, P.M.; Schlievert, P.M. Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13 table of contents, 16–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proft, T. In Microbial Toxins: Current Research and Future Trends; Caister Academic Press: Norfolk, UK, 2009; pp. 147–166. [Google Scholar]
- Cribier, B.; Piemont, Y.; Grosshans, E. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in adults. A clinical review illustrated with a new case. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1994, 30, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardwick, N.; Parry, C.M.; Sharpe, G.R. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in an adult. Influence of immune and renal factors. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 132, 468–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ladhani, S.; Joannou, C.L.; Lochrie, D.P.; Evans, R.W.; Poston, S.M. Clinical, microbial, and biochemical aspects of the exfoliative toxins causing staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrom. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 1999, 12, 224–242. [Google Scholar]
- Lyell, A. Toxic epidermal necrolysis. Nurs. Mirror Midwives J. 1973, 136, 42–45. [Google Scholar]
- Payne, A.S.; Hanakawa, Y.; Amagai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Desmosomes and disease: pemphigus and bullous impetigo. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2004, 16, 536–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, W.M.; Tyler, S.D.; Ewan, E.P.; Ashton, F.E.; Pollard, D.R.; Rozee, K.R. Detection of genes for enterotoxins, exfoliative toxins, and toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 in Staphylococcus aureus by the polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1991, 29, 426–430. [Google Scholar]
- Raymond, J.; Bingen, E.; Brahimi, N.; Bergeret, M.; Lepercq, J.; Badoual, J.; Gendrel, D. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in a neonate. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 1997, 16, 453–454. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, S.; Suzuki, H.; Machida, K. Rapid identification by polymerase chain reaction of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin serotype A and B genes. Microbiol. Immunol. 1995, 39, 379–386. [Google Scholar]
- Melish, M.E.; Glasgow, L.A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: the expanded clinical syndrome. J. Pediatr. 1971, 78, 958–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Megevand, C.; Gervaix, A.; Heininger, U.; Berger, C.; Aebi, C.; Vaudaux, B.; Kind, C.; Gnehm, H.P.; Hitzler, M.; Renzi, G.; Schrenzel, J.; Francois, P. Molecular epidemiology of the nasal colonization by methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in Swiss children. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2009. article online in advance of print. [Google Scholar]
- Sila, J.; Sauer, P.; Kolar, M. Comparison of the prevalence of genes coding for enterotoxins, exfoliatins, panton-valentine leukocidin and tsst-1 between methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible isolates of Staphylococcus aureus at the university hospital in olomouc. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky. Olomouc. Czech Repub. 2009, 153, 215–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Yokota, Y.; Terajima, J.; Hayashi, T.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Ohara, M.; Komatsuzawa, H.; Watanabe, H.; Sugai, M. Clonal association of Staphylococcus aureus causing bullous impetigo and the emergence of new methicillin-resistant clonal groups in Kansai district in Japan. J. Infect. Dis. 2002, 185, 1511–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noguchi, N.; Nakaminami, H.; Nishijima, S.; Kurokawa, I.; So, H.; Sasatsu, M. Antimicrobial agent of susceptibilities and antiseptic resistance gene distribution among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with impetigo and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 2119–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Gemmell, C.G. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. J. Med. Microbiol. 1995, 43, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiley, B.B.; Allman, S.; Rogolsky, M.; Norden, C.W.; Glasgow, L.A. taphylococcal scalded skin syndrome: potentiation by immunosuppression in mice; toxin-mediated exfoliation in a healthy adult. Infect. Immun. 1974, 9, 636–640. [Google Scholar]
- Opal, S.M.; Johnson-Winegar, A.D.; Cross, A.S. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in two immunocompetent adults caused by exfoliatin B-producing Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1988, 26, 1283–1286. [Google Scholar]
- El Helali, N.; Carbonne, A.; Naas, T.; Kerneis, S.; Fresco, O.; Giovangrandi, Y.; Fortineau, N.; Nordmann, P.; Astagneau, P. Nosocomial outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in neonates: epidemiological investigation and control. J. Hosp. Infect. 2005, 61, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Rittershain, G.R. Die exfoliative dermatitis jungener senglinge. Z. Kinderheilkd 1878, 2, 3–23. [Google Scholar]
- Lyell, A. A review of toxic epidermal necrolysis in Britain. Br. J. Dermatol. 1967, 79, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melish, M.E.; Glasgow, L.A.; Turner, M.D. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome: isolation and partial characterization of the exfoliative toxin. J. Infect. Dis. 1972, 125, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapral, F.A.; Miller, M.M. Product of Staphylococcus aureus responsible for the scalded-skin syndrome. Infect. Immun. 1971, 4, 541–545. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott, J.P.; Kent, J.; Lyell, A.; Gemmell, C.G. Toxic epidermal necrolysis produced by an extracellular product of Staphylococcus aureus. Br. J. Dermatol. 1971, 85, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melish, M.E.; Glasgow, L.A. The staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 1970, 282, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, I.; Sakurai, S.; Sarai, Y. Purification of exfoliatin produced by Staphylococcus aureus of bacteriophage group 2 and its physicochemical properties. Infect. Immun. 1973, 8, 156–164. [Google Scholar]
- Arbuthnott, J.P.; Billcliffe, B.; Thompson, W.D. Isoelectric focusing studies of staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. FEBS Lett. 1974, 46, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.D.; Metzger, J.F.; Spero, L. Production, purification, and chemical characterization of Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin. Infect. Immun. 1975, 12, 1206–1210. [Google Scholar]
- Dimond, R.L.; Wuepper, K.D. Purification and characterization of a staphylococcal epidermolytic toxin. Infect. Immun. 1976, 13, 627–633. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, I.; Sakurai, S.; Sarai, Y. New type of exfoliatin obtained from staphylococcal strains, belonging to phage groups other than group II, isolated from patients with impetigo and Ritter's disease. Infect. Immun. 1974, 10, 851–861. [Google Scholar]
- Wiley, B.B.; Rogolsky, M. Molecular and serological differentiation of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin synthesized under chromosomal and plasmid control. Infect. Immun. 1977, 18, 487–494. [Google Scholar]
- de Azavedo, J.; Arbuthnott, J.P. Prevalence of epidermolytic toxin in clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 1981, 14, 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Adesiyun, A.A.; Lenz, W.; Schaal, K.P. Exfoliative toxin production by Staphylococcus aureus strains isolated from animals and human beings in Nigeria. Microbiologica 1991, 14, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Kondo, I.; Sakurai, S.; Sarai, Y.; Futaki, S. Two serotypes of exfoliatin and their distribution in staphylococcal strains isolated from patients with scalded skin syndrome. J. Clin. Microbiol. 1975, 1, 397–400. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, O.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sugai, M.; Chapuis-Cellier, C.; Arnaud, F.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J.; Lina, G. Clinical manifestations of staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome depend on serotypes of exfoliative toxins. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2005, 43, 1890–1893. [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole, P.W.; Foster, T.J. Molecular cloning and expression of the epidermolytic toxin A gene of Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 1986, 1, 583–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.P.; Iandolo, J.J. Sequence of the exfoliative toxin B gene of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 167, 726–728. [Google Scholar]
- O'Toole, P.W.; Foster, T.J. Nucleotide sequence of the epidermolytic toxin A gene of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 3910–3915. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.Y.; Schmidt, J.J.; Johnson-Winegar, A.D.; Spero, L.; Iandolo, J.J. Sequence determination and comparison of the exfoliative toxin A and toxin B genes from Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 1987, 169, 3904–3909. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, A.D.; Spero, L.; Cades, J.S.; de Cicco, B.T. Purification and characterization of different types of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Immun. 1979, 24, 679–684. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, G.J.; Novick, R.P. Peptide signaling in Staphylococcus aureus and other Gram-positive bacteria. Peptides 2004, 25, 1389–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, B.J.; Foster, T.J.; Dorman, C.J.; Park, S.; Stewart, G.S. Osmotic and growth-phase dependent regulation of the eta gene of Staphylococcus aureus: a role for DNA supercoiling. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1992, 232, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarraud, S.; Lyon, G.J.; Figueiredo, A.M.; Gerard, L.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J.; Muir, T.W.; Novick, R.P. Exfoliatin-producing strains define a fourth agr specificity group in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 6517–6522. [Google Scholar]
- Jarraud, S.; Mougel, C.; Thioulouse, J.; Lina, G.; Meugnier, H.; Forey, F.; Nesme, X.; Etienne, J.; Vandenesch, F. Relationships between Staphylococcus aureus genetic background, virulence factors, agr groups (alleles), and human disease. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 631–641. [Google Scholar]
- Lillibridge, C.B.; Melish, M.E.; Glasgow, L.A. Site of action of exfoliative toxin in the staphylococcal scaled-skin syndrome. Pediatrics 1972, 50, 728–738. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Takami, H.; Ohnishi, M.; Murata, T.; Nakayama, K.; Asakawa, K.; Ohara, M.; Komatsuzawa, H.; Sugai, M. Complete nucleotide sequence of a Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxin B plasmid and identification of a novel ADP-ribosyltransferase, EDIN-C. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 7760–7771. [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai, S.; Suzuki, H.; Kondo, I. DNA sequencing of the eta gene coding for staphylococcal exfoliative toxin serotype A. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1988, 134, 711–717. [Google Scholar]
- Dancer, S.J.; Garratt, R.; Saldanha, J.; Jhoti, H.; Evans, R. The epidermolytic toxins are serine proteases. FEBS Lett. 1990, 268, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, J.A.; Saldanha, J.W.; Garratt, R.C. Novel features of serine protease active sites and specificity pockets: sequence analysis and modelling studies of glutamate-specific endopeptidases and epidermolytic toxins. Protein Eng. 1996, 9, 591–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, C.J.; Redpath, M.B. The esterolytic activity of epidermolytic toxins. Biochem. J. 1992, 284 (Pt 1), 177–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Prevost, G.; Rifai, S.; Chaix, M.L.; Piemont, Y. Functional evidence that the Ser-195 residue of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin A is essential for biological activity. Infect. Immun. 1991, 59, 3337–3339. [Google Scholar]
- Redpath, M.B.; Foster, T.J.; Bailey, C.J. The role of the serine protease active site in the mode of action of epidermolytic toxin of Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1991, 65, 151–155. [Google Scholar]
- Rago, J.V.; Vath, G.M.; Tripp, T.J.; Bohach, G.A.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Schlievert, P.M. Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins cleave alpha- and beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormones. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 2366–2368. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey, C.J.; Smith, T.P. The reactive serine residue of epidermolytic toxin A. Biochem. J. 1990, 269, 535–537. [Google Scholar]
- Vath, G.M.; Earhart, C.A.; Rago, J.V.; Kim, M.H.; Bohach, G.A.; Schlievert, P.M.; Ohlendorf, D.H. The structure of the superantigen exfoliative toxin A suggests a novel regulation as a serine protease. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 1559–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Cavarelli, J.; Prevost, G.; Bourguet, W.; Moulinier, L.; Chevrier, B.; Delagoutte, B.; Bilwes, A.; Mourey, L.; Rifai, S.; Piemont, Y.; Moras, D. The structure of Staphylococcus aureus epidermolytic toxin A, an atypic serine protease, at 1.7 A resolution. Structure 1997, 5, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vath, G.M.; Earhart, C.A.; Monie, D.D.; Iandolo, J.J.; Schlievert, P.M.; Ohlendorf, D.H. The crystal structure of exfoliative toxin B: a superantigen with enzymatic activity. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 10239–10246. [Google Scholar]
- Papageorgiou, A.C.; Plano, L.R.; Collins, C.M.; Acharya, K.R. Structural similarities and differences in Staphylococcus aureus exfoliative toxins A and B as revealed by their crystal structures. Protein Sci. 2000, 9, 610–618. [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya, J.; Ito, Y.; Takiuchi, I. Purification of protease from a mixture of exfoliative toxin and newborn-mouse epidermis. Infect. Immun. 2000, 68, 5044–5049. [Google Scholar]
- Vaishnani, J. Superantigen. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2009, 75, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morlock, B.A.; Spero, L.; Johnson, A.D. Mitogenic activity of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin. Infect. Immun. 1980, 30, 381–384. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.W.; Kotzin, B.; Herron, L.; Callahan, J.; Marrack, P.; Kappler, J. Interaction of Staphylococcus aureus toxin "superantigens" with human T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 8941–8945. [Google Scholar]
- Schrezenmeier, H.; Fleischer, B. Mitogenic activity of staphylococcal protein A is due to contaminating staphylococcal enterotoxins. J. Immunol. Methods 1987, 105, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleischer, B.; Bailey, C.J. Recombinant epidermolytic (exfoliative) toxin A of Staphylococcus aureus is not a superantigen. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 1992, 180, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Rago, J.V.; Vath, G.M.; Bohach, G.A.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Schlievert, P.M. Mutational analysis of the superantigen staphylococcal exfoliative toxin A (ETA). J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 2207–2213. [Google Scholar]
- Monday, S.R.; Vath, G.M.; Ferens, W.A.; Deobald, C.; Rago, J.V.; Gahr, P.J.; Monie, D.D.; Iandolo, J.J.; Chapes, S.K.; Davis, W.C.; Ohlendorf, D.H.; Schlievert, P.M.; Bohach, G.A. Unique superantigen activity of staphylococcal exfoliative toxins. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 4550–4559. [Google Scholar]
- Nishifuji, K.; Sugai, M.; Amagai, M. Staphylococcal exfoliative toxins: "molecular scissors" of bacteria that attack the cutaneous defense barrier in mammals. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2008, 49, 21–31. [Google Scholar]
- Hanakawa, Y.; Schechter, N.M.; Lin, C.; Nishifuji, K.; Amagai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Enzymatic and molecular characteristics of the efficiency and specificity of exfoliative toxin cleavage of desmoglein 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 5268–5277. [Google Scholar]
- Jordon, R.E.; Sams, W.M., Jr.; Diaz, G.; Beutner, E.H. Negative complement immunofluorescence in pemphigus. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1971, 57, 407–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanley, J.R.; Koulu, L.; Thivolet, C. Distinction between epidermal antigens binding pemphigus vulgaris and pemphigus foliaceus autoantibodies. J. Clin. Invest. 1984, 74, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyre, R.W.; Stanley, J.R. Human autoantibodies against a desmosomal protein complex with a calcium-sensitive epitope are characteristic of pemphigus foliaceus patients. J. Exp. Med. 1987, 165, 1719–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getsios, S.; Huen, A.C.; Green, K.J. Working out the strength and flexibility of desmosomes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, B.D.; Marcozzi, C.; Magee, A.I. The cadherin superfamily: diversity in form and function. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 629–641. [Google Scholar]
- Amagai, M.; Matsuyoshi, N.; Wang, Z.H.; Andl, C.; Stanley, J.R. Toxin in bullous impetigo and staphylococcal scalded-skin syndrome targets desmoglein 1. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 1275–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amagai, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Hanakawa, Y.; Nishifuji, K.; Sugai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Staphylococcal exfoliative toxin B specifically cleaves desmoglein 1. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2002, 118, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Nishifuji, K.; Sasaki, M.; Fudaba, Y.; Aepfelbacher, M.; Takata, T.; Ohara, M.; Komatsuzawa, H.; Amagai, M.; Sugai, M. Identification of the Staphylococcus aureus etd pathogenicity island which encodes a novel exfoliative toxin, ETD, and EDIN-B. Infect. Immun. 2002, 70, 5835–5845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanakawa, Y.; Schechter, N.M.; Lin, C.; Garza, L.; Li, H.; Yamaguchi, T.; Fudaba, Y.; Nishifuji, K.; Sugai, M.; Amagai, M.; Stanley, J.R. Molecular mechanisms of blister formation in bullous impetigo and staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 110, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
- Schechter, I.; Berger, A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1967, 27, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanakawa, Y.; Selwood, T.; Woo, D.; Lin, C.; Schechter, N.M.; Stanley, J.R. Calcium-dependent conformation of desmoglein 1 is required for its cleavage by exfoliative toxin. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 383–389. [Google Scholar]
- Arnemann, J.; Sullivan, K.H.; Magee, A.I.; King, I.A.; Buxton, R.S. Stratification-related expression of isoforms of the desmosomal cadherins in human epidermis. J. Cell Sci. 1993, 104(Pt 3), 741–750. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plano, L.R.; Adkins, B.; Woischnik, M.; Ewing, R.; Collins, C.M. Toxin levels in serum correlate with the development of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in a murine model. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 5193–5197. [Google Scholar]
- O'Keefe, R.; Dagg, J.H.; MacKie, R.M. The staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in two elderly immunocompromised patients. Br. Med. J. (Clin. Res. Ed.) 1987, 295, 179–180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Richard, M.; Mathieu-Serra, A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in a homosexual adult. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1986, 15, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzelbauer, P.; Konrad, K.; Wolff, K. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in 2 adults with acute kidney failure. Hautarzt 1989, 40, 90–93. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melish, M.E.; Chen, F.S.; Sprouse, S.; Stuckey, M.; Murata, M.S. Epidermolyic toxin in staphylococcal infection: toxin levels and host response. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. Suppl. 1981, 10, 287–298. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, G.A.; Waugh, J.A.; Hall, B.M. Expression of HLA antigens on renal tubular cells in culture. II. Effect of increased HLA antigen expression on tubular cell stimulation of lymphocyte activation and on their vulnerability to cell-mediated lysis. Transplantation 1988, 46, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahl, P.; Schoop, R.; Bilic, G.; Neuweiler, J.; Le Hir, M.; Yoshinaga, S.K.; Wuthrich, R.P. Renal tubular epithelial expression of the costimulatory molecule B7RP-1 (inducible costimulator ligand). J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodjosudjadi, W.; Gerritsma, J.S.; Klar-Mohamad, N.; Gerritsen, A.F.; Bruijn, J.A.; Daha, M.R.; van Es, L.A. Production and cytokine-mediated regulation of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 by human proximal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 1995, 48, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, K.; Friedrich, A.W.; Lubritz, G.; Weilert, M.; Peters, G.; Von Eiff, C. Prevalence of genes encoding pyrogenic toxin superantigens and exfoliative toxins among strains of Staphylococcus aureus isolated from blood and nasal specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 1434–1439. [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly, M.; Dougan, G.; Foster, T.J.; Arbuthnott, J.P. Plasmids in epidermolytic strains of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1981, 124, 99–107. [Google Scholar]
- Elias, P.M.; Fritsch, P.; Mittermayer, H. Staphylococcal toxic epidermal necrolysis: species and tissue susceptibility and resistance. J. Invest. Dermatol. 1976, 66, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machida, K.; Sakurai, S.; Kondo, I.; Ikawa, S. Relationship between susceptibility and immune response to staphylococcal exfoliative toxin A in mammalian species. Microbiol. Immunol. 1988, 32, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Matsumori, Y.; Tanabe, T.; Saito, H.; Shimizu, A.; Kawano, J. A new type of staphylococcal exfoliative toxin from a Staphylococcus aureus strain isolated from a horse with phlegmon. Infect. Immun. 1994, 62, 3780–3785. [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki, O.; Tristan, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sugai, M.; Lina, G.; Bes, M.; Vandenesch, F.; Etienne, J. Distribution of the exfoliative toxin D gene in clinical Staphylococcus aureus isolates in France. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 585–588. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Tanabe, T.; Kuramoto, M.; Tanaka, K.; Hashimoto, T.; Saito, H. Isolation of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus and its exfoliative activity in the piglet. Vet. Microbiol. 1991, 27, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Murata, Y.; Ohtake, A.; Nakamura, M.; Aizawa, C.; Saito, H.; Maehara, N. New exfoliative toxin produced by a plasmid-carrying strain of Staphylococcus hyicus. Infect. Immun. 1999, 67, 4014–4018. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen, L.O. Differentiation and distribution of three types of exfoliative toxin produced by Staphylococcus hyicus from pigs with exudative epidermitis. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 1998, 20, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrens, P.; Andresen, L.O. Cloning and sequence analysis of genes encoding Staphylococcus hyicus exfoliative toxin types A, B, C, and D. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1833–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Watanabe, T.; Higuchi, K.; Teruya, K.; Ohtake, A.; Murata, Y.; Saito, H.; Aizawa, C.; Danbara, H.; Maehara, N. Chromosomal and extrachromosomal synthesis of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus hyicus. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 4096–4100. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, H.; Kuramoto, M.; Tanabe, T.; Saito, H. Susceptibility of various animals and cultured cells to exfoliative toxin produced by Staphylococcus hyicus subsp. hyicus. Vet. Microbiol. 1991, 28, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terauchi, R.; Sato, H.; Hasegawa, T.; Yamaguchi, T.; Aizawa, C.; Maehara, N. Isolation of exfoliative toxin from Staphylococcus intermedius and its local toxicity in dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Hirose, K.; Terauchi, R.; Abe, S.; Moromizato, I.; Kurokawa, S.; Maehara, N. Purification and characterization of a novel Staphylococcus chromogenes exfoliative toxin. J. Vet. Med. B. Infect. Di.s Vet. Public Health 2004, 51, 116–122. [Google Scholar]
- Andresen, L.O.; Ahrens, P.; Daugaard, L.; Bille-Hansen, V. Exudative epidermitis in pigs caused by toxigenic Staphylococcus chromogenes. Vet. Microbiol. 2005, 105, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futagawa-Saito, K.; Makino, S.; Sunaga, F.; Kato, Y.; Sakurai-Komada, N.; Ba-Thein, W.; Fukuyasu, T. Identification of first exfoliative toxin in Staphylococcus pseudintermedius. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 301, 176–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Takami, H.; Nakasone, K.; Ohnishi, M.; Nakayama, K.; Yamada, S.; Komatsuzawa, H.; Sugai, M. Phage conversion of exfoliative toxin A production in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 38, 694–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dryla, A.; Prustomersky, S.; Gelbmann, D.; Hanner, M.; Bettinger, E.; Kocsis, B.; Kustos, T.; Henics, T.; Meinke, A.; Nagy, E. Comparison of antibody repertoires against Staphylococcus aureus in healthy individuals and in acutely infected patients. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2005, 12, 387–398. [Google Scholar]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Bukowski, M.; Wladyka, B.; Dubin, G. Exfoliative Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins 2010, 2, 1148-1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051148
Bukowski M, Wladyka B, Dubin G. Exfoliative Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins. 2010; 2(5):1148-1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051148
Chicago/Turabian StyleBukowski, Michal, Benedykt Wladyka, and Grzegorz Dubin. 2010. "Exfoliative Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus" Toxins 2, no. 5: 1148-1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051148
APA StyleBukowski, M., Wladyka, B., & Dubin, G. (2010). Exfoliative Toxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Toxins, 2(5), 1148-1165. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins2051148