A Systematic Investigation into the Environmental Fate of Microcystins and The Potential Risk: Study in Lake Taihu
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Spatial Differences of MCs in Water and Algal Cells of Lake Taihu
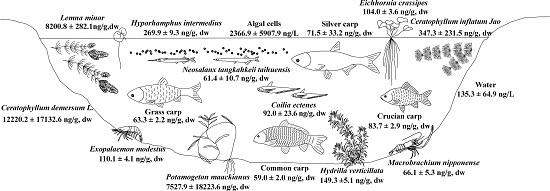
2.2. Accumulation of MCs in Macrophytes of Four Areas of Lake Taihu
2.3. Accumulation of MCs in Shrimp and Fish in MLB of Lake Taihu
2.4. Fate of MCs in the Food Web of Lake Taihu
2.5. Risk of MCs to Local Residents
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Area and Sampling Sites
5.2. Sampling and Processing
5.3. MCs Quantification
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Falconer, I.R. Cyanobacterial Toxins of Drinking Water Supplies: Cylindrospermopsins and Microcystins; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, I.; Webb, P.M.; Schluter, P.J.; Fleming, L.E.; Burns, J.W.; Gantar, M.; Backer, L.C.; Shaw, G.R. Epidemiology of recreational exposure to freshwater cyanobacteria—An international prospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2006, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chorus, I.; Bartram, J. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management; E & FN Spon: London, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Huisman, J. Blooms like it hot. Sci. N. Y. Wash. 2008, 320, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalak, A.M.; Anderson, E.J.; Beletsky, D.; Boland, S.; Bosch, N.S.; Bridgeman, T.B.; Chaffin, J.D.; Cho, K.; Confesor, R.; Daloğlu, I. Record-setting algal bloom in lake erie caused by agricultural and meteorological trends consistent with expected future conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6448–6452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McElhiney, J.; Lawton, L.A. Detection of the cyanobacterial hepatotoxins microcystins. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, M.; von Döhren, H. Cyanobacterial peptides—Nature’s own combinatorial biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 530–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiegand, C.; Pflugmacher, S. Ecotoxicological effects of selected cyanobacterial secondary metabolites a short review. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrão-Filho, A.D.S.; Kozlowsky-Suzuki, B. Cyanotoxins: Bioaccumulation and effects on aquatic animals. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 2729–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skulberg, O.M. Giftvirkninger av Blågrønnalger—Første Tilfelle av Microcystis-Forgiftning Registrert i Norge (Toxic Effects of Blue-Green Algae—First Case of Microcystis Poisoning Reported from Norway); Norsk Institutt for Vannforskning: Oslo, Norway, 1979; p. 42. [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson, J.E.; Meriluoto, J.; Lindholm, T. Can cyanobacterial toxins accumulate in aquatic food chains? In Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium of Microbiol Ecology, Ljubljana, Yugoslavia, 24–26 August 1986; p. 658.
- Bury, N.R.; Eddy, F.B.; Codd, G.A. The effects of the cyanobacterium microcystis aeruginosa, the cyanobacterial hepatotoxin microcystin-LR, and ammonia on growth rate and ionic regulation of brown trout. J. Fish Biol. 1995, 46, 1042–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, H.; Harada, K.I.; Senma, M.; Ito, Y.; Yasuda, N.; Ushida, S.; Kimura, Y. Possible cause of unnatural mass death of wild birds in a pond in Nishinomiya, Japan: Sudden appearance of toxic cyanobacteria. Nat. Toxins 1999, 7, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paskerová, H.; Hilscherová, K.; Bláha, L. Oxidative stress and detoxification biomarker responses in aquatic freshwater vertebrates exposed to microcystins and cyanobacterial biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 2024–2037. [Google Scholar]
- Gugger, M.; Lenoir, S.; Berger, C.; Ledreux, A.; Druart, J.C.; Humbert, J.F.; Guette, C.; Bernard, C. First report in a river in france of the benthic cyanobacterium phormidium favosum producing anatoxin-A associated with dog neurotoxicosis. Toxicon 2005, 45, 919–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nasri, H.; El Herry, S.; Bouaïcha, N. First reported case of turtle deaths during a toxic microcystis spp. Bloom in Lake Oubeira, Algeria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2008, 71, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pouria, S.; De, A.A.; Barbosa, J.; Cavalcanti, R.L.; Barreto, V.T.S.; Ward, C.J.; Preiser, W.; Poon, G.K.; Neild, G.H.; Codd, G.A. Fatal microcystin intoxication in haemodialysis unit in Caruaru, Brazil. Lancet 1998, 352, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billam, M.; Mukhi, S.; Tang, L.; Gao, W.; Wang, J.S. Toxic response indicators of microcystin-LR in f344 rats following a single-dose treatment. Toxicon 2008, 51, 1068–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.A.; Zhao, Q.; Pu, C.W.; Qiu, Z.Q.; Zhang, R.P.; Shu, W.Q. A cross-sectional investigation of chronic exposure to microcystin in relationship to childhood liver damage in the three gorges reservoir region, China. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1483–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ufelmann, H.; Kruger, T.; Luckas, B.; Schrenk, D. Human and rat hepatocyte toxicity and protein phosphatase 1 and 2A inhibitory activity of naturally occurring desmethyl-microcystins and nodularins. Toxicology 2012, 293, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Z. Primary prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 1995, 10, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.Z. Drinking water and primary liver cancer. In Primary Liver Cancer; Tang, Z.Y., Wu, M.C., Xia, S.S., Eds.; China Academic Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 30–37. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Li, L.; Xu, J. First identification of the hepatotoxic microcystins in the serum of a chronically exposed human population together with indication of hepatocellular damage. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.W.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.Q.; Qiu, T. Transfer, distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in the aquatic food web in Lake Taihu, China, with potential risks to human health. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 2191–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.R.; Chen, W.; Peng, L.; Wan, N.; Gan, N.Q.; Zhang, X.M. Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: A systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in meiliang bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2853–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P. Microcystin accumulation in freshwater bivalves from Lake Taihu, China, and the potential risk to human consumption. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yu, J.W.; Li, Z.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Burch, M.; Lin, T.F. Taihu Lake not to blame for Wuxi’s woes. Science 2008, 319, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.A.; Liu, Y.M.; Chen, W.; Liu, L.M.; Kent, M.; Song, L.R. Health risks associated with consumption of microcystin-contaminated fish and shellfish in three chinese lakes: Significance for freshwater aquacultures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2010, 73, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P. Tissue distributions and seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins-LR and -RR in two freshwater shrimps, palaemon modestus and macrobrachium nipponensis, from a large shallow, eutrophic lake of the subtropical China. Toxicon 2005, 45, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P. Seasonal dynamics of the hepatotoxic microcystins in various organs of four freshwater bivalves from the large eutrophic Lake Taihu of subtropical China and the risk to human consumption. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 572–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Xie, P.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Liang, G. Bioaccumulation of the hepatotoxic microcystins in various organs of a freshwater snail from a subtropical Chinese lake, Taihu Lake, with dense toxic microcystis blooms. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2007, 26, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, D.W.; Xie, P.; Wang, Q.; Ma, Z.M. Simultaneous determination of microcystin contaminations in various vertebrates (fish, turtle, duck and water bird) from a large eutrophic chinese lake, Lake Taihu, with toxic microcystis blooms. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3317–3322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Luo, W.; Lu, Y.; Giesy, J.P. Bioaccumulation of microcystins (MCs) in four fish species from Lake Taihu, China: Assessment of risks to humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 487, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, J.D.; Franklin, R.B.; Garman, G.; McIninch, S.; Porter, A.J.; Bukaveckas, P.A. Exposure to the cyanotoxin microcystin arising from interspecific differences in feeding habits among fish and shellfish in the james river estuary, virginia. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 5194–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehman, P.W.; Teh, S.J.; Boyer, G.L.; Nobriga, M.L.; Bass, E.; Hogle, C. Initial impacts of microcystis aeruginosa blooms on the aquatic food web in the san francisco estuary. Hydrobiologia 2009, 637, 229–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhu, G.; Wu, T.; Li, W.; Shi, K.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, B.; Caruso, A.M. The role of tropical cyclones in stimulating cyanobacterial (microcystis spp.) blooms in hypertrophic Lake Taihu, China. Harmful Algae 2014, 39, 310–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. Report of the Working Group on Chemical Substances in Drinking Water; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, N.; Pant, S.C.; Vijayaraghavan, R.; Rao, P.V.L. Comparative toxicity evaluation of cyanobacterial cyclic peptide toxin microcystin variants (LR, RR, YR) in mice. Toxicology 2003, 188, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotton, B.; Guillard, J.; Anneville, O.; Maréchal, M.; Savichtcheva, O.; Domaizon, I. Trophic transfer of microcystins through the lake pelagic food web: Evidence for the role of zooplankton as a vector in fish contamination. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 466–467, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xie, P.; Chen, J. Biochemical and ultrastructural changes of the liver and kidney of the phytoplanktivorous silver carp feeding naturally on toxic microcystis blooms in Taihu Lake, China. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1042–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filizadeh, Y.; Ahmadi, H.; Zolfinejad, K. The feeding preferences of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella val.) for ten aquatic plants. In Proceedings of The Fourth International Iran & Russia Conference, ShahreKord, Iran, 8–10 September 2004; pp. 1447–1451.
- Romero-Oliva, C.S.; Contardo-Jara, V.; Block, T.; Pflugmacher, S. Accumulation of microcystin congeners in different aquatic plants and crops—A case study from Lake Amatitlan, Guatemala. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 102, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Huang, J.; Li, D.; Liu, Y. Microcystin-rr uptake and its effects on the growth of submerged macrophyte Vallisneria natans (lour.) hara. Environ. Toxicol. 2005, 20, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Oliva, C.S.; Contardo-Jara, V.; Pflugmacher, S. Time dependent uptake, bioaccumulation and biotransformation of cell free crude extract microcystins from lake amatitlan, guatemala by ceratophyllum demersum, egeria densa and hydrilla verticillata. Toxicon 2015, 105, 62–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedergreen, N.; Madsen, T.V. Nitrogen uptake by the floating macrophyte lemna minor. New Phytol. 2002, 155, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, P.; Cooke, G.D. Ceratophyllum demersum–phosphorus interactions in nutrient enriched aquaria. Hydrobiologia 2003, 497, 79–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pflugmacher, S.; Wiegand, C.; Beattie, K.A.; Krause, E.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Codd, G.A. Uptake, effects, and metabolism of cyanobacterial toxins in the emergent reed plant Phragmites australis (Cav.) trin. Ex steud. Environm. Toxicol. Chem. 2001, 20, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Oliva, C.S.; Contardo-Jara, V.; Pflugmacher, S. Antioxidative response of the three macrophytes ceratophyllum demersum, egeria densa, and hydrilla verticillata to a time dependent exposure of cell-free crude extracts containing three microcystins from cyanobacterial blooms of Lake Amatitlan, Guatemala. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 163, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Figueiredo, D.R.; Azeiteiro, U.M.; Esteves, S.M.; Gonçalves, F.J.M.; Pereira, M.J. Microcystin-producing blooms—A serious global public health issue. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2004, 59, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codd, G.A.; Morrison, L.F.; Metcalf, J.S. Cyanobacterial toxins: Risk management for health protection. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 203, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saqrane, S.; Ghazali, I.E.; Ouahid, Y.; Hassni, M.E.; Hadrami, I.E.; Bouarab, L.; del Campo, F.F.; Oudra, B.; Vasconcelos, V. Phytotoxic effects of cyanobacteria extract on the aquatic plant lemna gibba: Microcystin accumulation, detoxication and oxidative stress induction. Aquat. Toxicol. 2007, 83, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, M.; Azevedo, J.; Pinto, E.; Neves, J.; Campos, A.; Vasconcelos, V. Effects of microcystin-LR, cylindrospermopsin and a microcystin-LR/cylindrospermopsin mixture on growth, oxidative stress and mineral content in lettuce plants (Lactuca sativa L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 116, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.Q.; Ni, L.Y.; Cao, T.; Xie, P. Ammonium, microcystins, and hypoxia of blooms in eutrophic water cause oxidative stress and C–N imbalance in submersed and floating-leaved aquatic plants in Lake Taihu, China. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitrovic, S.M.; Allis, O.; Furey, A.; James, K.J. Bioaccumulation and harmful effects of microcystin-LR in the aquatic plants lemna minor and wolffia arrhiza and the filamentous alga chladophora fracta. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2005, 61, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferr ao-Filho, A.S.; Domingos, P.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Influences of a Microcystis aeruginosakützing bloom on zooplankton populations in Jacarepagu’a Lagoon (Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2002, 32, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva Ferr ao-Filho, A.; Azevedo, S.M.F.O. Effects of unicellular and colonial forms of toxic microcystis aeruginosa from laboratory cultures and natural populations on tropical cladocerans. Aquat. Ecol. 2003, 37, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beattie, K.A.; Ressler, J.; Wiegand, C.; Krause, E.; Codd, G.A.; Steinberg, C.E.W.; Pflugmacher, S. Comparative effects and metabolism of two microcystins and nodularin in the brine shrimp artemia salina. Aquat. Toxicol. 2003, 62, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaney, J.M.; Wilkins, R.M. Toxicity of microcystin-LR, isolated from microcystis aeruginosa, against various insect species. Toxicon 1995, 33, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiripi, L.; Nagy, L.; Kalmar, T.; Kovacs, A.; Vörös, L. Insect (Locusta migratoria migratorioides) test monitoring the toxicity of cyanobacteria. Neurotoxicology 1997, 19, 605–608. [Google Scholar]
- White, S.H.; Duivenvoorden, L.; Fabbro, L.D. A decision-making framework for ecological impacts associated with the accumulation of cyanotoxins (cylindrospermopsin and microcystin). Management 2005, 10, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malbrouck, C.; Kestemont, P. Effects of microcystins on fish. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2006, 25, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimba, P.; Khoo, L.; Gaunt, P.; Brittain, S.; Carmichael, W. Confirmation of catfish, ictalurus punctatus (rafinesque), mortality from microcystis toxins. J. Fish Dis. 2001, 24, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Xie, P.; Ke, Z.; Li, L.; Guo, L. In situ studies on physiological and biochemical responses of four fishes with different trophic levels to toxic cyanobacterial blooms in a large chinese lake. Toxicon 2007, 50, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christoffersen, K. Ecological implications of cyanobacterial toxins in aquatic food webs. Phycologia 1996, 35, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.P.; Li, K.; Chen, T.Y.; Dai, X.L.; Jiang, M.; Diana, J.S. Effects of microcystis aeruginosa on life history of water flea daphnia magna. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2011, 29, 892–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Tao, M.; Qin, B.; Qi, M.; Niu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, Z.; Xie, P. Large-scale field evidence on the enhancement of small-sized cladocerans by microcystis blooms in Lake Taihu, China. J. Plankton Res. 2012, 34, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, R.I.; Ho, L.; Brookes, J.D. Effect of chlorination on microcystis aeruginosa cell integrity and subsequent microcystin release and degradation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4447–4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, G.J.; Orr, P.T. Release and degradation of microcystin following algicide treatment of a microcystis aeruginosa bloom in a recreational lake, as determined by HPLC and protein phosphatase inhibition assay. Water Res. 1994, 28, 871–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xie, P.; Zhang, D.W.; Ke, Z.X.; Yang, H. In situ studies on the bioaccumulation of microcystins in the phytoplanktivorous silver carp (Hypophthalmichthys molitrix) stocked in Lake Taihu with dense toxic microcystis blooms. Aquaculture 2006, 261, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvenna, V.; Dale, K.; Priestly, B.; Mueller, U.; Humpage, A.; Shaw, G.; Allinson, G.; Falconer, I. Health risk assessment for cyanobacterial toxins in seafood. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2012, 9, 807–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.; Liu, H.; Qu, J.; Ru, J.; Hou, Y. Cyanobacteria and their toxins in guanting reservoir of Beijing, China. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, C.; Dai, R.; Liu, H.; Zhao, X.; Qu, J. Effects of different phosphorus sources and its concentrations on the growth and toxin production of microcystis aeruginosa. Acta Sci. Circumst. 2013, 33, 2546–2551. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, L.Q.; Xie, P.; Ozawa, K.; Honma, T.; Yokoyama, A.; Park, H.D. Dynamics of microcystins-LR and -RRin the phytoplanktivorous silver carp in a sub-chronic toxicity experiment. Environ. Pollut. 2004, 127, 431–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Z. Agilent 1260 Uhplc/6460qqq used for the detection of microcystins. Environ. Chem. 2011, 30, 731–733. [Google Scholar]





| Year | Areas | MC-RR (ng/L) | MC-LR (ng/L) | MC-YR (ng/L) | MCs (ng/L) | MC-RR Cell (ng/L) | MC-LR Cell (ng/L) | MC-YR Cell (ng/L) | MCs Cell (ng/L) | Total MCs (ng/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | WC | 46.9 ± 17.2 | 44.9 ± 17.7 | 36.9 ± 10.9 | 128.8 ± 24.0 | 1796.2 ± 2300.6 | 248.4 ± 266.5 | 446.4 ± 548.0 | 2491.0 ± 1486.1 b | 2619.8 ± 1510.1 b |
| 2013 | SC | 37.5 ± 0.31 | 113.9 ± 66.9 | 50.6 ± 4.8 | 202.0 ± 71.4 | 87.0 ± 62.2 | 20.9 ± 0.1 | 39.0 ± 23.8 | 146.9 ± 38.6 a | 348.9 ± 110.0 ab |
| 2013 | LC | 35.5 ± 0.8 | 47.0 ± 17.0 | 33.3 ± 5.6 | 115.8 ± 16.2 | 60.5 ± 46.0 | 115.2 ± 111.3 | 27.8 ± 3.9 | 203.6 ± 113.2 a | 319.3 ± 108.3 a |
| 2013 | MLB | 36.3 ± 5.1 | 38.2 ± 2.7 | 30.0 ± 0.5 | 104.5 ± 7.3 | 137.6 ± 148.7 | 345.4 ± 334.8 | 44.1 ± 30.6 | 527.2 ± 452.9 ab | 631.7 ± 445.6 ab |
| 2014 | WC | 35.1 ± 2.5 | 27.8 ± 3.3 | 14.4 ± 0.5 | 77.3 ± 5.3 | 626.1 ± 365.9 | 280.9 ± 165.5 | 43.7 ± 18.7 | 950.8 ± 550.1 AB | 1028.1 ± 555.4 A |
| 2014 | SC | 90.7 ± 15.4 | 95.1 ± 42.2 | 20.7 ± 0.7 | 206.4 ± 58.3 | 487.5 ± 481.7 | 261.2 ± 235.6 | 35.0 ± 24.8 | 783.7 ± 742.1 A | 990.1 ± 800.4 A |
| 2014 | LC | 53.8 ± 24.1 | 45.3 ± 20.0 | 13.9 ± 7.0 | 112.9 ± 47.6 | 1087.7 ± 1552.1 | 454.0 ± 620.4 | 68.2 ± 76.5 | 1609.8 ± 2248.5 A | 1722.8 ± 2291.0 A |
| 2014 | MLB | 111.5 ± 94.0 | 86.5 ± 66.0 | 20.5 ± 8.0 | 218.5 ± 168.0 | 11,624.8 ± 9689.1 | 5679.4 ± 4597.4 | 759.1 ± 687.7 | 18,063.3 ± 14,974.3 B | 18,281.9 ± 15,142.3 B |
| Correlations | Ceratophyllum | Potamogeton maackianus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MC-RR | MC-LR | MC-YR | MCs | MC-RR | MC-LR | MC-YR | MCs | |
| MC-RR (water) | 0.83 | 0.06 | −0.36 | −0.51 | 0.55 | −0.53 | −0.58 | −0.38 |
| MC-LR (water) | −0.19 | 0.36 | −0.92 | 0.64 | −0.02 | −0.24 | −0.33 | −0.37 |
| MC-YR (water) | 0.54 | 0.21 | −0.69 | −0.09 | −0.19 | −0.01 | 0.59 | 0.19 |
| MCs(water) | 0.1 | −0.35 | 0.92 | −0.57 | 0.27 | −0.46 | −0.4 | −0.4 |
| MC-RR (cells) | −0.93 | 0.21 | −0.33 | 0.96 * | −0.27 | 0.02 | 0.36 | −0.45 |
| MC-LR (cells) | 0.95 | −0.18 | 0.24 | −0.93 | −0.03 | 0.03 | 0.52 | 0.5 |
| MC-YR (cells) | 0.95 * | −0.17 | 0.22 | −0.92 | −0.14 | 0.35 | 0.28 | 0.71 |
| MCs(cells) | −0.76 | 0.32 | −0.65 | 0.98 * | −0.29 | −0.07 | 0.44 | −0.54 |
| Total MC-RR | −0.36 | −0.27 | 0.8 | −0.12 | −0.56 | 0.51 | −0.07 | 0.21 |
| Total MC-LR | −0.64 | −0.16 | 0.6 | 0.24 | −0.68 | 0.49 | −0.38 | −0.12 |
| Total MC-YR | −0.89 | 0.003 | 0.22 | 0.65 | −0.07 | −0.31 | −0.11 | −0.55 |
| Total MCs | 0.95 | −0.09 | −0.01 | −0.8 | −0.08 | 0.39 | 0.04 | 0.75 |
| Species | MC in Edible Parts (MC-LReq ng/g) | Daily Intake for a 60 kg Person (MC-LR eqμg/kg Body Weight) | ×Lifetime TDI (0.04 μg/kg Body Weight/day) | Max Daily Intake Not Exceeding the Guideline (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exopalaemon modestus | 12.5 | 0.0625 | 1.6 | 192 |
| Macrobrachium nipponense | 6.2 | 0.031 | 0.8 | 387 |
| Neosalanx tangkahkeii taihuensis | 5.4 | 0.027 | 0.7 | 444 |
| Coiliaectenes | 8.4 | 0.042 | 1.1 | 286 |
| Hyporhamphusintermedius | 45.8 | 0.229 | 5.7 | 52 |
| Hypophthalmichthys molitrix | 6.3 | 0.032 | 0.8 | 381 |
| Carassius carassius | 8.6 | 0.043 | 1.1 | 279 |
| Cyprinus carpio | 4.2 | 0.021 | 0.5 | 571 |
| Ctenopharyngodon idella | 4.9 | 0.025 | 0.6 | 490 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jia, J.; Chen, Q.; Lauridsen, T.L. A Systematic Investigation into the Environmental Fate of Microcystins and The Potential Risk: Study in Lake Taihu. Toxins 2016, 8, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060170
Jia J, Chen Q, Lauridsen TL. A Systematic Investigation into the Environmental Fate of Microcystins and The Potential Risk: Study in Lake Taihu. Toxins. 2016; 8(6):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060170
Chicago/Turabian StyleJia, Junmei, Qiuwen Chen, and Torben L. Lauridsen. 2016. "A Systematic Investigation into the Environmental Fate of Microcystins and The Potential Risk: Study in Lake Taihu" Toxins 8, no. 6: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060170
APA StyleJia, J., Chen, Q., & Lauridsen, T. L. (2016). A Systematic Investigation into the Environmental Fate of Microcystins and The Potential Risk: Study in Lake Taihu. Toxins, 8(6), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins8060170