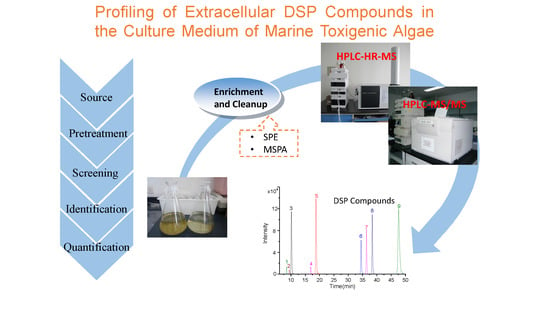
Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
2.2. Method Performance
2.3. Screening and Identification of Extracellular DSP Compounds in the Culture Medium of P. lima
2.4. Contents of Extracellular DSP Compounds in the Culture Medium of P. lima at Different Growth Stages
2.5. Screening of Extracellular DSP Compounds in the Culture Medium of P. minimum
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
4.3. Microalgae Cultivation and Collection
4.4. Sample Preparation
4.4.1. Extraction of DSP Compounds from Toxigenic Algae
4.4.2. Direct Sampling
4.4.3. Solid-Phase Extraction
4.4.4. Macroporous Resin Passive Adsorption
4.5. Instrumental Conditions
4.6. Data Analysis
4.6.1. Screening of Extracellular DSP Compounds
4.6.2. Identification of Extracellular DSP Compounds
4.6.3. Quantification and Semi-quantification of Extracellular DSP Compounds
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Granéli, E.; Turner, J.T. Ecology of harmful algae. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 2007, 88, 304. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, J.L.; Tong, M.; Fux, E.; Anderson, D.M. Toxin production, retention, and extracellular release by Dinophysis acuminate during extended stationary phase and culture decline. Harmful Algae 2012, 19, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, V.L.; Moore, L.; Bill, B.D.; Adams, N.G.; Harrington, N.; Borchert, J.; Silva, D.A.M.D.; Eberhart, B.T.L. Diarrhetic shellfish toxins and Oother lipophilic toxins of human health concern in washington state. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1815–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; McIntyre, L.; Ritson, M.; Stone, J.; Bronson, R.; Bitzikos, O.; Rourke, W.; Galanis, E. Outbreak of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning associated with mussels, British Columbia, Canada. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 1669–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, L.T.; Krock, B.; Hansen, P.J. Production and excretion of okadaic acid, pectenotoxin-2 and a novel dinophysistoxin from the DSP-causing marine dinoflagellate Dinophysis acuta–Effects of light, food availability and growth phase. Harmful Algae 2013, 23, 34–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Baba, M.K.; Sugawara, R.; Kamiyama, T. LC-MS/MS analysis of okadaic acid analogues and other lipophilic toxins in single-cell isolates of several Dinophysis species collected in hokkaido, Japan. Harmful Algae 2009, 8, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; LeBlanc, P.; Burton, I.W.; Walter, J.A.; McCarron, P.; Melanson, J.E.; Strangman, W.K.; Wright, J.L.C. Sulfated diesters of okadaic acid and DTX-1: Self-protective precursors of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins. Harmful Algae 2017, 63, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.F.; Ji, R. Advance in the research of diarrhetic shellfish poisons. China Trop. Med. 2006, 6, 157–159. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.C.H.; Fong, F.L.Y.; Ho, K.C.; Lee, F.W.F. The mechanism of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxin production in Prorocentrum spp.: Physiological and molecular perspectives. Toxins 2016, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanucci, S.; Guerrini, F.; Milandri, A.; Pistocchi, R. Effects of different levels of N- and P-deficiency on cell yield, okadaic acid,DTX-1, protein and carbohydrate dynamics in the benthic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. Harmful Algae 2010, 9, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattenrath-Lehmann, T.K.; Marcoval, M.A.; Mittlesdorf, H.; Goleski, J.A.; Wang, Z.H.; Haynes, B.; Morton, S.L.; Gobler, C.J. Nitrogenous nutrients promote the growth and toxicity of Dinophysis acuminata during Estuarine Bloom events. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Rosales, L.; Gallardo-Rodríguez, J.J.; Sánchez-Mirón, A.; Cerón-García, M.C.; Belarbi, E.H.; García-Camacho, F.; Molina-Grima, E. Simultaneous effect of temperature and irradiance on growth and okadaic acid production from the marine dinoflagellate Prorocentrum belizeanum. Toxins 2014, 6, 229–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajuzie, C.C. Toxic Prorocentrum lima induces abnormal behaviour in juvenile sea bass. J. Appl. Phycol. 2008, 20, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajuzie, C.C. Palatability and fatality of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima to Artemia salina. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vale, P.; Veloso, V.; Amorim, A. Toxin composition of a Prorocentrum lima strain isolated from the Portuguese coast. Toxicon 2009, 54, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nascimento, S.M.; Purdie, D.A.; Morris, S. Morphology, toxin composition and pigment content of Prorocentrum lima strains isolated from a coastal lagoon in southern UK. Toxicon 2005, 45, 633–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; McElhinney, M.A.; Boer, J.D. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 1421–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Li, M.; Pan, J.; Liang, J.; Zhou, Y.; Wu, J. Identification of the okadaic acid-based toxin profile of a marine dinoflagellate strain Prorocentrum lima by LC-MS/MS and NMR spectroscopic data. J. Sep. Sci. 2012, 35, 782–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, G.; Bussche, J.V.; Meulebroek, L.V.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.; Vanhaecke, L. Validation of a confirmatory method for lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish using UHPLC–HR–Orbitrap MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5303–5312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orellana, G.; Meulebroek, L.; Vooren, S.V.; Rijcke, M.D.; Vandegehuchte, M.; Janssen, C.R.; Vanhaecke, L. Quantification and profiling of lipophilic marine toxins in microalgae by UHPLC coupled to high-resolution orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2015, 407, 6345–6356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; Mulder, P.P.; Boer, J.D. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish and algae: Development of a library using liquid chromatography coupled to orbitrap mass spectrometry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 685, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendong, Z.; McCarron, P.; Herrenknecht, C.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Cole, R.B.; Hess, P. High resolution mass spectrometry for quantitative analysis and untargeted screening of algal toxins in mussels and passive samplers. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1416, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerssen, A.; McElhinney, M.A.; Mulder, P.P.; Bire, R.; Hess, P.; Boer, J.D. Solid phase extraction for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine toxin analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 394, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McCarthy, M.; Pelt, F.N.A.M.V.; Bane, V.; O’Halloran, J.; Furey, A. Application of passive (SPATT) and active sampling methods in the profiling and monitoring of marine biotoxins. Toxicon 2014, 89, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Sun, G.; Qiu, J.B.; Ma, Q.; Hess, P.; Li, A. Effect of seawater salinity on pore-size distribution on a poly (styrene)-based HP20 resin and its adsorption of diarrhetic shellfish toxins. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1373, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, Q.; Zhang, R.; Wang, S.; Wang, X. Detection, occurrence and monthly variations of typical lipophilic marine toxins associated with diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in the coastal seawater of Qingdao City, China. Chemosphere 2014, 111, 560–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fux, E.; Marcaillou, C.; Mondeguer, F.; Bire, R.; Hess, P. Field and mesocosm trials on passive sampling for the study of adsorption and desorption behaviour of lipophilic toxins with a focus on OA and DTX1. Harmful Algae 2008, 7, 574–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, F.; Song, X.; Yu, R.; Brissard, C.; Tixier, C.; Mondeguer, F.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P. Dynamic adsorption of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in passive sampling relates to pore size distribution of aromatic adsorbent. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zendong, Z.; Herrenknecht, C.; Abadie, E.; Brissard, C.; Tixier, C.; Mondeguer, F.; Séchet, V.; Amzil, Z.; Hess, P. Extended evaluation of polymeric and lipophilic sorbents for passive sampling of marine toxins. Toxicon 2014, 91, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Chen, J.H.; Wang, S.; Shi, X.X.; Shi, H.H.; Zheng, L. Determination of eight typical lipophilic algae toxins in marine microalgae powder using high-performance liquid chromatography-ion trap mass spectrometry. Mar. Sci. 2016, 40, 113–119. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.H.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, F.R.; Cao, W.; Sun, C.J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.R. Screening of lipophilic marine toxins in marine aquaculture environment using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chemosphere 2017, 168, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Chen, J.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Wang, S.; Shi, Q.; Cao, W.; Zheng, X.L.; Sun, C.J.; Wang, X.R.; Zheng, L. Determination of typical lipophilic marine toxins in marine sediments from three coastal bays of China using liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry after accelerated solvent extraction. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 101, 954–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.H.; Wang, Y.L.; Pan, L.; Shen, H.H.; Fu, D.; Fu, B.Q.; Sun, C.J.; Zheng, L. Separation and purification of two minor typical diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins from harmful marine microalgae via combined liquid chromatography with mass spectrometric detection. J. Sep. Sci. 2017, 40, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- These, A.; Scholz, J.; Preiss-Weigert, A. Sensitive method for the determination of lipophilic marine biotoxins in extracts of mussels and processed shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based on enrichment by solid-phase extraction. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 4529–4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Broadwater, M.H.; Ramsdell, J.S. Analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxin-2 in the bottlenose dolphin (Tursiops truncatus) by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2015, 1416, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruve, A.; Leito, I.; Herodes, K. Combating matrix effects in LC/ESI/MS: the extrapolative dilution approach. Anal. Chim. Acta 2009, 651, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marr, J.C.; Jackson, A.E.; Mclachlan, J.L. Occurrence of Prorocentrum lima, a DSP toxin-producing species from the Atlantic coast of Canada. J. Appl. Phycol. 1992, 4, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Marr, J.; Freitas, A.S.W.D.; Quilliam, M.A.; Walter, J.A.; Wright, J.L.C.; Pleasance, S. New diol esters isolated from cultures of the dinoflagellates Prorocentrum lima and Prorocentrum concavum. J. Nat. Prod. 1992, 55, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz, B.; Daranas, A.H.; Cruz, P.G.; Franco, J.M.; Pizarro, G.; Souto, M.L.; Norte, M.; Fernández, J.J. Characterisation of okadaic acid related toxins by liquid chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2007, 50, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, S.; Suzuki, T.; Nishikawa, T. Differences in the production and excretion kinetics of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1, and pectenotoxin-2 between cultures of Dinophysis acuminata and Dinophysis fortii isolated from western Japan. J. Phycol. 2011, 47, 1326–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, L.J.; Huang, X.Y.; Huang, B.Q.; Qi, Y.Z.; Lu, S.H. Growth and competition for different forms of organic phosphorus by the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum donghaiense with the dinoflagellate Alexandrium catenella and the diatom Skeletonema costatum s.l. Hydrobiologia 2015, 754, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witek, B.; Plinski, M. The first recorded bloom of Prorocentrum minimum (Pavillard) Schiller in the coastal zone of the Gulf of Gdańsk. Oceanologia 2000, 42, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.Y.; Liu, L.; Liang, Y.B.; Yu, J.; Xu, D.Y.; Wei, N.; Yang, L.; Guo, H. The distribution, impacts and risks of toxic microalgae and phycotoxins in China. Mar. Environ. Res. 2016, 35, 787–800. [Google Scholar]
- Guillard, R.R.; Ryther, J.H. Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 1962, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Toxins | Peak Area (Matrix) | Relative Standard Deviation (RSD%) | Peak Area (Methanol) | (RSD%) | Signal Suppression (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 11,759,724 | 3.32 | 10,220,561 | 1.14 | +15.06 |
| DTX1 | 13,774,916 | 2.98 | 15,896,689 | 2.16 | −13.35 |
| Peak | Retention Time (min) | Detected Ion | Measured (m/z) | Theoretial (m/z) | Error (ppm) | Chemical Fomula | Toxin ID | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 8.5 | [M + Na]+ | 827.4576 | 827.4552 | −2.97 | C44H68O13 | 19-epi-OA /DTX2/DTX2b/DTX2c | [31,37] |
| 2 | 9.4 | [M + Na]+ | 827.4578 | 827.4552 | −3.22 | C44H68O13 | ||
| 3 | 10.2 | [M + Na]+ | 827.4569 | 827.4552 | −2.1 | C44H68O13 | OA | [20,31,37] |
| 4 | 16.9 | [M + Na]+ | 841.4723 | 841.4709 | −1.76 | C45H70O13 | 35S DTX1 | [31] |
| 5 | 18.8 | [M + Na]+ | 841.4729 | 841.4709 | −2.49 | C45H70O13 | DTX1 | [20,31,37] |
| 6 | 34.6 | [M + Na]+ | 937.5300 | 937.5284 | −1.77 | C51H78O14 | OA-D7b | [31,38] |
| 7 | 36.4 | [M + Na]+ | 965.5624 | 965.5597 | −2.89 | C53H82O14 | OA-D9b | [31,38,39] |
| 8 | 38.6 | [M + Na]+ | 977.5624 | 977.5597 | −3.53 | C54H82O14 | OA-D10a/b | [18,31] |
| 9 | 48.6 | [M + NH4]+ | 976.6049 | 976.5992 | −5.86 | C53H82O15 | 5,7-dihydroxy-2,4-dimethylene-heptyl okadaate | [20,31,39] |
| Incubation Time (Days) | 8 | 16 | 22 | 25 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algae density (×104 cells/mL) | 1.31 | 2.58 | 1.78 | 1.28 | |
| OA (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 2.26 | 9.62 | 9.85 | 14.45 |
| Extracellular | 1.65 | 0.82 | 1.12 | 2.66 | |
| Total | 3.91 | 10.44 | 10.97 | 17.11 | |
| Intracellular/Extracellular | 1.37 | 11.73 | 8.79 | 5.43 | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 21.63 | 21.10 | 19.93 | 34 | |
| Compound 1 (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 5.78 × 10−2 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.32 |
| Extracellular | 2.05 × 10−2 | 9.34 × 10−3 | 1.52 × 10−2 | 3.49 × 10−2 | |
| Total | 7.83 × 10−2 | 0.21 | 0.19 | 0.35 | |
| Intracellular/Extracellular | 2.82 | 21.41 | 11.18 | 9.17 | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.27 | 0.46 | |
| 35S DTX1 (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 2.14 × 10−2 | 5.21 × 10−2 | 7.84 × 10−2 | 0.14 |
| Extracellular | 3.43 × 10−3 | 1.58 × 10−3 | 4.60 × 10−3 | 8.58 × 10−3 | |
| Total | 2.48 × 10−2 | 6.92 × 10−2 | 8.30 × 10−2 | 0.15 | |
| Intracellular/Extracellular | 6.24 | 32.97 | 17.04 | 15.99 | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 4.49 × 10−2 | 4.07 × 10−2 | 8.17 × 10−2 | 0.11 | |
| DTX1 (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 19.56 | 32.70 | 50.91 | 66.25 |
| Extracellular | 2.13 | 0.59 | 1.32 | 1.91 | |
| Total | 21.69 | 33.29 | 52.23 | 68.16 | |
| Intracellular/Extracellular | 9.18 | 55.42 | 38.57 | 34.69 | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 27.90 | 15.15 | 23.55 | 24.35 | |
| OA-D7b (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 0.09 | 0.67 | 1.01 | 0.68 |
| Extracellular | 3.54 × 10−3 | — | — | — | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 4.64 × 10−2 | — | — | — | |
| OA-D9b (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 3.66 | 7.54 | 14.57 | 16.93 |
| Extracellular | 1.91 × 10−3 | — | — | — | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 2.50 × 10−2 | — | — | — | |
| 5,7-dihydroxy-2,4-dimethylene-heptyl okadaate (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 0.105 | 0.15 | 0.18 | — |
| Extracellular | 0.594 | 1.17 | 1.53 | 1.62 | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 7.78 | 30.13 | 27.196 | 20.695 | |
| OA-D10a/b (pg/cell) | Intracellular | 1.25 | 2.93 | 5.41 | 6.23 |
| Extracellular | 1.1 × 10−3 | — | — | — | |
| Extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 1.44 × 10−2 | — | — | — | |
| Total extracellular concentration (μg/L) | 57.70 | 66.72 | 70.92 | 79.63 | |
| Toxins | Retention Time (min) | Chemical Formula | Precursor Ion (m/z) | Product Ions (m/z) | Collision Energy Ampl/V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OA | 10.2 | C44H68O13 | [M + Na]+ (827.5) | 809.6/723.6 | 1.0 |
| DTX1 | 18.8 | C47H70O14 | [M + Na]+ (841.5) | 737.6/823.6 | 1.5 |
| 19-epi-OA/DTX2/DTX2b/DTX2c | 8.5 | C44H68O13 | [M + Na]+ (827.5) | 809.6/723.6 | 1.0 |
| 9.4 | C44H68O13 | [M + Na]+ (827.5) | 809.6/723.6 | 1.0 | |
| 35S DTX1 | 16.9 | C47H70O14 | [M + Na]+ (841.5) | 737.6/823.6 | 1.5 |
| OA-D7b | 34.6 | C51H78O14 | [M + Na]+ (937.5) | 827.7/809.6 | 1.5 |
| OA-D9b | 36.4 | C53H82O14 | [M + Na]+ (965.6) | 827.7/809.6 | 1.5 |
| OA-D10a/b | 38.6 | C54H82O14 | [M + Na]+ (977.6) | 827.7/809.6 | 1.5 |
| 5,7-dihydroxy-2,4-dimethylene-heptyl okadaate | 48.6 | C53H82O15 | [M + NH4]+ (976.6) | 822.7/804.6 | 1.5 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, L.; Chen, J.; Shen, H.; He, X.; Li, G.; Song, X.; Zhou, D.; Sun, C. Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Toxins 2017, 9, 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100308
Pan L, Chen J, Shen H, He X, Li G, Song X, Zhou D, Sun C. Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Toxins. 2017; 9(10):308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100308
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Lei, Junhui Chen, Huihui Shen, Xiuping He, Guangjiu Li, Xincheng Song, Deshan Zhou, and Chengjun Sun. 2017. "Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry" Toxins 9, no. 10: 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100308
APA StylePan, L., Chen, J., Shen, H., He, X., Li, G., Song, X., Zhou, D., & Sun, C. (2017). Profiling of Extracellular Toxins Associated with Diarrhetic Shellfish Poison in Prorocentrum lima Culture Medium by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with Mass Spectrometry. Toxins, 9(10), 308. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9100308