Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
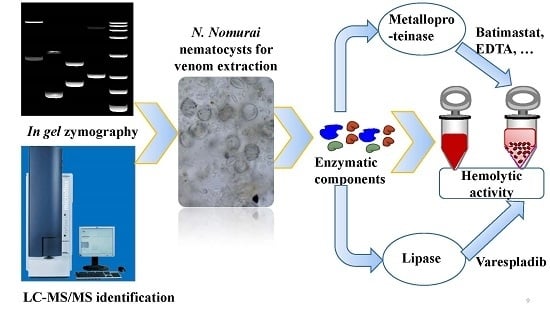
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Evaluation of the Molecular Mass of the Enzymatic Components by Zymography Assays
2.2. Venom Protein Profiling by LC-MS/MS
2.3. Hemolytic Activity and the Roles of Metalloproteinase- and Lipase-Class Species in Hemolysis
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples
4.2. Isolation of Nematocysts and Venom Extraction
4.3. SDS-PAGE Analysis
4.4. In Gel Zymography of Proteases, Lipases and Hyaluronidases
4.4.1. Zymography of Proteases
4.4.2. Zymography of Lipases
4.4.3. Zymography of Hemolytic Proteins
4.4.4. Zymography of Hyaluronidases
4.5. Protein Identification by LC-MS/MS
4.6. Hemolytic Activity In Vitro
4.7. Metalloproteinase Inhibitory Activity
4.8. Phospholipase Inhibitory Activity
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Badre, S. Bioactive toxins from stinging jellyfish. Toxicon 2014, 91, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turk, T.; Kem, W.R. The phylum Cnidaria and investigations of its toxins and venoms until 1990. Toxicon 2009, 54, 1031–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Liu, D.; Keesing, J.K. Jellyfish blooms in China: Dominant species, causes and consequences. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Condon, R.H.; Duarte, C.M.; Pitt, K.A.; Robinson, K.L.; Lucas, C.H.; Sutherland, K.R.; Mianzan, H.W.; Bogeberg, M.; Purcell, J.E.; Decker, M.B.; et al. Recurrent jellyfish blooms are a consequence of global oscillations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 1000–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tibballs, J. Australian venomous jellyfish, envenomation syndromes, toxins and therapy. Toxicon 2006, 48, 830–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, B.J.; Jacups, S.P. Prospective study of Chironex fleckeri and other box jellyfish stings in the “Top End” of Australia’s Northern Territory. Med. J. Aust. 2005, 183, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barnes, J.H. Observations on jellyfish stingings in North Queensland. Med. J. Aust. 1960, 47, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Marino, A.; Morabito, R.; Pizzata, T.; La Spada, G. Effect of various factors on Pelagia noctiluca (Cnidaria, Scyphozoa) crude venom-induced haemolysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2008, 151, 144–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, S.; Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Prange, A. A novel proteinaceous cytotoxin from the Northern Scyphozoa Cyanea capillata (L.) with structural homology to cubozoan haemolysins. Toxicon 2011, 57, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Yue, Y.; Dong, X.; Li, R.; Li, P. The acaricidal activity of venom from the jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai against the carmine spider mite Tetranychus cinnabarinus. Toxins 2016, 8, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Li, R.; Chen, X.; Yue, Y.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, P. Effect of venom from the jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai on the silkworm Bombyx mori L. Toxins 2015, 7, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, K.L.; Fernando, R.; Ramasamy, S.; Seymour, J.E.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. The in vitro vascular effects of two Chirodropid (Chironex fleckeri and Chiropsella bronzie) venoms. Toxicol. Lett. 2007, 168, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, I.; Lee, H.; Pyo, M.-J.; Heo, Y.; Bae, S.K.; Kwon, Y.C.; Yoon, W.D.; Kang, C.; Kim, E. Proteomics approach to examine the cardiotoxic effects of Nemopilema nomurai jellyfish venom. J. Proteom. 2015, 128, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Xia, X.; Lai, Z.; Zhong, T.; Li, G.; Fan, L.; Shu, W. Apoptosis-like cell death induced by nematocyst venom from Chrysaora helvola brandt jellyfish and an in vitro evaluation of commonly used antidotes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 180, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, K.L.; Isbister, G.K.; McGowan, S.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; Seymour, J.E.; Hodgson, W.C. A pharmacological and biochemical examination of the geographical variation of Chironex fleckeri venom. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 192, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Chen, X.; Li, P. Combined proteomics and transcriptomics identifies sting-related toxins of jellyfish Cyanea nozakii. J. Proteom. 2016, 148, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xue, W.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.; Li, P. Jellyfish venomics and venom gland transcriptomics analysis of Stomolophus meleagris to reveal the toxins associated with sting. J. Proteom. 2014, 106, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, P. Biochemical and kinetic evaluation of the enzymatic toxins from two stinging scyphozoans Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii. Toxicon 2016, 125, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zychar, B.C.; Dale, C.S.; Demarchi, D.S.; Goncalves, L.R.C. Contribution of metalloproteases, serine proteases and phospholipases A(2) to the inflammatory reaction induced by Bothrops jararaca crude venom in mice. Toxicon 2010, 55, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Jung, E.-s.; Kang, C.; Yoon, W.D.; Kim, J.-S.; Kim, E. Scyphozoan jellyfish venom metalloproteinases and their role in the cytotoxicity. Toxicon 2011, 58, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossignol, G.; Merieau, A.; Guerillon, J.; Veron, W.; Lesouhaitier, O.; Feuilloley, M.G.; Orange, N. Involvement of a phospholipase C in the hemolytic activity of a clinical strain of Pseudomonas fluorescens. BMC Microbiol. 2008, 8, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmholz, H.; Ruhnau, C.; Schuett, C.; Prange, A. Comparative study on the cell toxicity and enzymatic activity of two northern scyphozoan species Cyanea capillata (L.) and Cyanea lamarckii (Peron and Leslieur). Toxicon 2007, 50, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nevalainen, T.J.; Peuravuori, H.J.; Quinn, R.J.; Llewellyn, L.E.; Benzie, J.A.H.; Fenner, P.J.; Winkel, K.D. Phospholipase A2 in Cnidaria. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B-Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004, 139, 731–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knittel, P.S.; Long, P.F.; Brammall, L.; Marques, A.C.; Almeida, M.T.; Padilla, G.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M. Characterising the enzymatic profile of crude tentacle extracts from the South Atlantic jellyfish Olindias sambaquiensis (Cnidaria: Hydrozoa). Toxicon 2016, 119, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jungo, F.; Bairoch, A. Tox-prot, the toxin protein annotation program of the Swiss-Prot protein knowledgebase. Toxicon 2005, 45, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, D.; Brinkman, D.L.; Potriquet, J.; Mulvenna, J. Tentacle transcriptome and venom proteome of the pacific sea nettle, Chrysaora fuscescens (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa). Toxins 2016, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Jia, X.; Potriquet, J.; Kumar, D.; Dash, D.; Kvaskoff, D.; Mulvenna, J. Transcriptome and venom proteome of the box jellyfish Chironex fleckeri. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weston, A.J.; Chung, R.; Dunlap, W.C.; Morandini, A.C.; Marques, A.C.; Moura-da-Silva, A.M.; Ward, M.; Padilla, G.; da Silva, L.F.; Andreakis, N.; et al. Proteomic characterisation of toxins isolated from nematocysts of the South Atlantic jellyfish Olindias sambaquiensis. Toxicon 2013, 71, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balasubramanian, P.G.; Beckmann, A.; Warnken, U.; Schnolzer, M.; Schuler, A.; Bornberg-Bauer, E.; Holstein, T.W.; Ozbek, S. Proteome of hydra nematocyst. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9672–9681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, S.; Hayashi, H.; Araki, S. Two vascular apoptosis-inducing proteins from snake venom are members of the metalloprotease/disintegrin family. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 253, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackessy, S.P. Evolutionary trends in venom composition in the Western Rattlesnakes (Crotalus viridis sensu lato): Toxicity vs. Tenderizers. Toxicon 2010, 55, 1463–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Such, D.R.; Souza, F.N.; Meissner, G.O.; Morgon, A.M.; Gremski, L.H.; Ferrer, V.P.; Trevisan-Silva, D.; Matsubara, F.H.; Boia-Ferreira, M.; Sade, Y.B.; et al. Brown spider (Loxosceles genus) venom toxins: Evaluation of biological conservation by immune cross-reactivity. Toxicon 2015, 108, 154–166. [Google Scholar]
- Appel, M.H.; da Silveira, R.B.; Chaim, O.M.; Paludo, K.S.; Silva, D.T.; Chaves, D.M.; da Silva, P.H.; Mangili, O.C.; Senff-Ribeiro, A.; Gremski, W.; et al. Identification, cloning and functional characterization of a novel dermonecrotic toxin (phospholipase D) from brown spider (Loxosceles intermedia) venom. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, D.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Z.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Global transcriptome analysis of the tentacle of the jellyfish Cyanea capillata using deep sequencing and expressed sequence tags: Insight into the toxin- and degenerative disease-related transcripts. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Snake venom hyaluronidase: A therapeutic target. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2006, 24, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, Y.; Kwon, Y.C.; Bae, S.K.; Hwang, D.; Yang, H.R.; Choudhary, I.; Lee, H.; Yum, S.; Shin, K.; Yoon, W.D.; et al. Cloning a Chymotrypsin-like 1 (CTRL-1) protease cDNA from the jellyfish Nemopilema nomurai. Toxins 2016, 8, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Sakamoto, B.; Crow, G.L.; Nakajima, T. Isolation and characterization of a novel protein toxin from the Hawaiian box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea alata. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 589–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa, K.; Nakao, M.; Ito, E.; Miyake, M.; Noda, M.; Nakajima, T. Novel proteinaceous toxins from the box jellyfish (sea wasp) Carybdea rastoni. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 275, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.; Burnell, J. Identification, cloning and sequencing of two major venom proteins from the box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 2007, 50, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentlage, B.; Cartwright, P.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Lewis, C.; Richards, G.S.; Collins, A.G. Evolution of box jellyfish (Cnidaria: Cubozoa), a group of highly toxic invertebrates. Proc. Biol. Sci. R. Soc. 2010, 277, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ames, L.C.; Yanagihara, A.A.; Keil, D.; Lawley, J.W.; Van Blerk, J.; Gillan, B.; Bentlage, B.; Bely, A.; Collins, A.G. Establishing the neotype of the enigmatic oceanic box jellyfish Alatina alata (Reynaud 1830) (Cnidaria: Cubozoa). Integr. Comp. Biol. 2013, 53, E126. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.J.; Ratnapala, L.A.; Cooke, I.M.; Yanagihara, A.A. Partial purification and characterization of a hemolysin (CAH1) from Hawaiian box jellyfish (Carybdea alata) venom. Toxicon 2001, 39, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Cai, S.; Li, P. Partial characterization of the hemolytic activity of the nematocyst venom from the jellyfish Cyanea nozakii kishinouye. Toxicology In Vitro Int. J. Publ. Assoc. BIBRA 2010, 24, 1750–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boukhalfa-Abib, H.; Laraba-Djebari, F. Ccmp-ii, a new hemorrhagic metalloproteinase from Cerastes cerastes snake venom: Purification, biochemical characterization and amino acid sequence analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 167, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, M.S.R.; Naves de Souza, D.L.; Guimaraes, D.O.; Lopes, D.S.; Mamede, C.C.N.; Gimenes, S.N.C.; Ache, D.C.; Rodrigues, R.S.; Yoneyama, K.A.G.; Borges, M.H.; et al. Biochemical and functional characterization of bothropoidin: The first haemorrhagic metalloproteinase from Bothrops pauloensis snake venom. J. Biochem. 2015, 157, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, L.; Marcussi, S.; Marchi-Salvador, D.P.; Silva Jr, F.P.; Fuly, A.L.; Stábeli, R.G.; da Silva, S.L.; González, J.; Monte, A.d.; Soares, A.M. Enzymatic and structural characterization of a basic phospholipase A2 from the sea anemone Condylactis gigantea. Biochimie 2010, 92, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, S.; Takeya, H.; Iwanaga, S. Snake venom metalloproteinases: Structure, function and relevance to the mammalian ADAM/ADAMTS family proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liu, D.; Liu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhou, Y.; He, Q.; Zhang, L. Protective effects of batimastat against hemorrhagic injuries in delayed jellyfish envenomation syndrome models. Toxicon 2015, 108, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.M.; Giglio, J.R. Chemical modifications of phospholipases A(2) from snake venoms: Effects on catalytic and pharmacological properties. Toxicon 2003, 42, 855–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewin, M.; Samuel, S.; Merkel, J.; Bickler, P. Varespladib (LY315920) appears to be a potent, broad-spectrum, inhibitor of snake venom phospholipase A2 and a possible pre-referral treatment for envenomation. Toxins 2016, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrovic, N.; Grove, C.; Langton, P.E.; Misso, N.L.A.; Thompson, P.J. A simple assay for a human serum phospholipase A(2) that is associated with high-density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 2001, 42, 1706–1713. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonfim, V.L.; Ponce-Soto, L.A.; de Souza, D.M.; Souza, G.H.M.F.; Baldasso, P.A.; Eberlin, M.N.; Marangoni, S. Structural and functional characterization of myotoxin, Cr-IV 1, a phospholipase A(2) D49 from the venom of the snake Calloselasma rhodostoma. Biologicals 2008, 36, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diz, E.B.S.; Marangoni, S.; Toyama, D.O.; Fagundes, F.H.R.; Oliveira, S.C.B.; Fonseca, F.V.; Calgarotto, A.K.; Joazeiro, P.P.; Toyama, M.H. Enzymatic and structural characterization of new PLA2 isoform isolated from white venom of Crotalus durissus ruruima. Toxicon 2009, 53, 104–114. [Google Scholar]
- Birch, M.; Denning, D.W.; Robson, G.D. Comparison of extracellular phospholipase activities in clinical and environmental Aspergillus fumigatus isolates. Med. Mycol. 2004, 42, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arce-Bejarano, R.; Lomonte, B.; Maria Gutierrez, J. Intravascular hemolysis induced by the venom of the Eastern coral snake, Micrurus fulvius, in a mouse model: Identification of directly hemolytic phospholipases A(2). Toxicon 2014, 90, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radwan, F.F.Y.; Aboul-Dahab, H.M. Milleporin-1, a new phospholipase A(2) active protein from the fire coral Millepora platyphylla nematocysts. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C-Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2004, 139, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdez-Cruz, N.A.; Batista, C.V.F.; Possani, L.D. Phaiodactylipin, a glycosylated heterodimeric phospholipase A(2) from the venom of the scorpion Anuroctonus phaiodactylus. Eur. J. Biochem. 2004, 271, 1453–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razpotnik, A.; Križaj, I.; Šribar, J.; Kordiš, D.; Maček, P.; Frangež, R.; Kem, W.R.; Turk, T. A new phospholipase A2 isolated from the sea anemone Urticina crassicornis—Its primary structure and phylogenetic classification. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2641–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.; Burnell, J. Partial purification of cytolytic venom proteins from the box jellyfish, Chironex fleckeri. Toxicon 2008, 51, 853–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagai, H.; Takuwa-Kuroda, K.; Nakao, M.; Oshiro, N.; Iwanaga, S.; Nakajima, T. A novel protein toxin from the deadly box jellyfish (sea wasp, Habu-kurage) Chiropsalmus quadrigatus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2002, 66, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponce, D.; Brinkman, D.L.; Luna-Ramírez, K.; Wright, C.E.; Dorantes-Aranda, J.J. Comparative study of the toxic effects of Chrysaora quinquecirrha (Cnidaria: Scyphozoa) and Chironex fleckeri (Cnidaria: Cubozoa) venoms using cell-based assays. Toxicon 2015, 106, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Yu, H.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Qing, Y.; Li, K.; Li, B.; Meng, X.; Cui, J.; Li, P. Application of nanoLC-MS/MS to the shotgun proteomic analysis of the nematocyst proteins from jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 899, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachamim, T.; Morgenstern, D.; Aharonovich, D.; Brekhman, V.; Lotan, T.; Sher, D. The dynamically evolving nematocyst content of an anthozoan, a scyphozoan, and a hydrozoan. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrette, T.; Seymour, J. A rapid and repeatable method for venom extraction from cubozoan nematocysts. Toxicon 2004, 44, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloom, D.A.; Burnett, J.W.; Alderslade, P. Partial purification of box jellyfish (Chironex fleckeri) nematocyst venom isolated at the beachside. Toxicon 1998, 36, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Yu, H.H.; Yue, Y.; Liu, S.; Xing, R.G.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, X.Q.; Li, P.C. In depth analysis of the in vivo toxicity of venom from the jellyfish Stomolophus meleagris. Toxicon 2014, 92, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during assembly of head of bacteriophage-T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, L.B.; Pucca, M.B.; Roncolato, E.C.; Bertolini, T.B.; Netto, J.C.; Barbosa, J.E. In vitro comparison of enzymatic effects among brazilian Bothrops spp. Venoms. Toxicon 2013, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.G.; Kho, C.W.; Cho, S.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, S.H.; Park, B.C. A functional proteomic analysis of secreted fibrinolytic enzymes from Bacillus subtilis 168 using a combined method of two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and zymography. Proteomics 2002, 2, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, L.B.; Pucca, M.B.; Roncolato, E.C.; Netto, J.C.; Barbosa, J.E. Analysis of phospholipase A2, L-amino acid oxidase, and proteinase enzymatic activities of the Lachesis muta rhombeata venom. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2012, 26, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Matehuala, R.; Rojas-Molina, A.; Vuelvas-Solorzano, A.A.; Garcia-Arredondo, A.; Alvarado, C.I.; Olguin-Lopez, N.; Aguilar, M. Cytolytic and systemic toxic effects induced by the aqueous extract of the fire coral Millepora alcicornis collected in the Mexican Caribbean and detection of two types of cytolisins. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop Dis. 2015, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girish, K.S.; Jagadeesha, D.K.; Rajeev, K.B.; Kemparaju, K. Snake venom hyaluronidase: An evidence for isoforms and extracellular matrix degradation. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 240, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkman, D.L.; Konstantakopoulos, N.; McInerney, B.V.; Mulvenna, J.; Seymour, J.E.; Isbister, G.K.; Hodgson, W.C. Chironex fleckeri ( box jellyfish) venom proteins expansion of a cnidarian toxin family that elicits variable cytolytic and cardiovascular effects. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4798–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayano, A.M.; Simoes-Silva, R.; Medeiros, P.S.M.; Maltarollo, V.G.; Honorio, K.M.; Oliveira, E.; Albericio, F.; da Silva, S.L.; Aguiar, A.C.C.; Krettli, A.U.; et al. Bbmp-1, a new metalloproteinase isolated from Bothrops brazili snake venom with in vitro antiplasmodial properties. Toxicon 2015, 106, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lomonte, B.; Pla, D.; Sasa, M.; Tsai, W.-C.; Solorzano, A.; Manuel Urena-Diaz, J.; Laura Fernandez-Montes, M.; Mora-Obando, D.; Sanz, L.; Maria Gutierrez, J.; et al. Two color morphs of the pelagic yellow-bellied sea snake, Pelamis platura, from different locations of Costa Rica: Snake venomics, toxicity, and neutralization by antivenom. J. Proteom. 2014, 103, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, Y.; Yu, H.; Li, R.; Xing, R.; Liu, S.; Li, K.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, P. Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography. Toxins 2017, 9, 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020047
Yue Y, Yu H, Li R, Xing R, Liu S, Li K, Wang X, Chen X, Li P. Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography. Toxins. 2017; 9(2):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020047
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Yang, Huahua Yu, Rongfeng Li, Ronge Xing, Song Liu, Kecheng Li, Xueqin Wang, Xiaolin Chen, and Pengcheng Li. 2017. "Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography" Toxins 9, no. 2: 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020047
APA StyleYue, Y., Yu, H., Li, R., Xing, R., Liu, S., Li, K., Wang, X., Chen, X., & Li, P. (2017). Functional Elucidation of Nemopilema nomurai and Cyanea nozakii Nematocyst Venoms’ Lytic Activity Using Mass Spectrometry and Zymography. Toxins, 9(2), 47. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins9020047