Self-Healing Flexible Conductive Film by Repairing Defects via Flowable Liquid Metal Droplets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Electrical Conductivity of the Films
3.2. Flexibility and Self-Healing of the Films
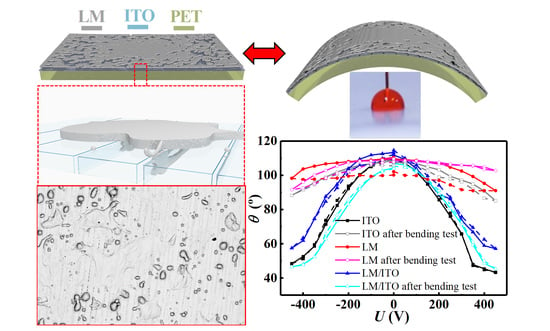
3.3. Electrowetting Performance on the Flexible Conductive Films
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Miao, J.; Wang, Q.; Yu, Z.; Wang, C. Direct Printing for Additive Patterning of Silver Nanowires for Stretchable Sensor and Display Applications. Adv. Mater. Technol.-US. 2017, 3, 1700232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kim, T.; Cho, S.; Lee, Y.; Choe, A.; Walker, B.; Ko, S.-J.; Kim, J.Y.; Ko, H. Capillary printing of highly aligned silver nanowire transparent electrodes for high-performance optoelectronic devices. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 7933–7942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangoi, R.; Smith, C.G.; Seymour, M.D.; Venkataraman, J.N.; Clark, D.M.; Kleper, M.L.; Kahn, B.E. Printing radio frequency identification (RFID) tag antennas using inks containing silver dispersions. J. Disper. Sci. Technol. 2005, 25, 513–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, F.; Fung, M.; Tong, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, S. Flexible organic light-emitting device based on magnetron sputtered indium-tin-oxide on plastic substrate. Thin Solid Films 2004, 466, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.Y.; Duoss, E.B.; Motala, M.J.; Guo, X.; Park, S.-I.; Xiong, Y.; Yoon, J.; Nuzzo, R.G.; Rogers, J.A.; Lewis, J.A. Omnidirectional printing of flexible, stretchable, and spanning silver microelectrodes. Science 2009, 323, 1590–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, C.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, K.; Wang, Z. Electrowetting on liquid-infused film (EWOLF): Complete reversibility and controlled droplet oscillation suppression for fast optical imaging. Sci. Rep.-UK. 2014, 4, 6846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narasimhan, V.; Park, S.Y. An Ion Gel as a Low-Cost, Spin-Coatable, High-Capacitance Dielectric for Electrowetting-on-Dielectric (EWOD). Langmuir 2015, 31, 8512–8518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-W.; Park, J.-W. The cohesive crack and buckle delamination resistances of indium tin oxide (ITO) films on polymeric substrates with ductile metal interlayers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Chiu, S.; Cho, T.; Huang, J. Improved bending fatigue behavior of flexible PET/ITO film with thin metallic glass interlayer. Mater. Lett. 2013, 113, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parekh, D.P.; Ladd, C.; Panich, L.; Moussa, K.; Dickey, M.D. 3D printing of liquid metals as fugitive inks for fabrication of 3D microfluidic channels. Lab Chip. 2016, 16, 1812–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurdesau, F.; Khripunov, G.; Da Cunha, A.; Kaelin, M.; Tiwari, A. Comparative study of ITO layers deposited by DC and RF magnetron sputtering at room temperature. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, L.; Wu, F. Indium tin oxide@ carbon core–shell nanowire and jagged indium tin oxide nanowire. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aouaj, M.A.; Diaz, R.; Belayachi, A.; Rueda, F.; Abd-Lefdil, M. Comparative study of ITO and FTO thin films grown by spray pyrolysis. Mater. Res. Bull. 2009, 44, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.-K.; Tan, S.-S.; Nee, C.-H.; Yap, S.-S.; Kee, Y.-Y.; Sáfrán, G.; Horváth, Z.E.; Moscatello, J.; Yap, Y.-K.; Tou, T.-Y. Pulsed laser deposition of indium tin oxide nanowires in argon and helium. Mater. Lett. 2012, 66, 280–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrero, J.; Guillen, C. Improved ITO thin films for photovoltaic applications with a thin ZnO layer by sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2004, 451, 630–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Du, X.; Logan, J.M.; Sippel, J.; Nikolou, M.; Kamaras, K.; Reynolds, J.R.; Tanner, D.B.; Hebard, A.F. Transparent, conductive carbon nanotube films. Science 2004, 305, 1273–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.; Kim, H.; Lee, Y.; Xu, X.; Park, J.-S.; Zheng, Y.; Balakrishnan, J.; Lei, T.; Kim, H.R.; Song, Y.I. Roll-to-roll production of 30-inch graphene films for transparent electrodes. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, B.; Pei, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Rong, Q.; Lin, Q.; Guo, Y.; Sun, T.; Guo, C.; Carnahan, D. Uniform self-forming metallic network as a high-performance transparent conductive electrode. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 873–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Zhang, L. Transparent conductive ITO/Cu/ITO films prepared on flexible substrates at room temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 3082–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleau, E.; Reece, S.; Desai, S.C.; Smith, M.E.; Dickey, M.D. Self-Healing Stretchable Wires for Reconfi gurable Circuit Wiring and 3D Microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2012, 25, 1589–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.G.; Alrowais, H.; Pavlidis, S.; Brand, O. Size-Scalable and High-Density Liquid-Metal-Based Soft Electronic Passive Components and Circuits Using Soft Lithography. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1604466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Zhu, T.; Zhu, D.; He, C.; Liu, Y.; Handschuh-Wang, S.; Zhou, X. Liquid metal sponges for mechanically durable, all-soft, electrical conductors. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 1586–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Oudalov, N.; Guo, Q.; Jaeger, H.M.; Brown, E. Effect of oxidation on the mechanical properties of liquid gallium and eutectic gallium-indium. Phy. Fluids 2012, 24, 063101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Cooper, C.; Wang, M.; Adams, J.J.; Genzer, J.; Dickey, M.D. Handwritten, Soft Circuit Boards and Antennas Using Liquid Metal Nanoparticles. Small 2015, 11, 6397–6403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J. Atomized spraying of liquid metal droplets on desired substrate surfaces as a generalized way for ubiquitous printed electronics. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 116, 1091–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.; Hjort, K.; Jeong, S.H. Microfluidic stretchable radio-frequency devices. Proc. IEEE 2015, 103, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaiszik, B.J.; Kramer, S.L.; Grady, M.E.; McIlroy, D.A.; Moore, J.S.; Sottos, N.R.; White, S.R. Autonomic restoration of electrical conductivity. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 398–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsching, U. Droplets and particles in sprays: tailoring particle properties within spray processes. China Part. 2005, 3, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modreanu, M.; Cosmin, P.; Cosmin, S.; Conianu, C.; Dunare, C. Measurement of CVD thin films thickness by sample weighing method. Int. Semicond. Conf. 1996, 2, 409–412. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, E.; Yan, M.; Lane, M.; Ireland, J.; Kannewurf, C.; Chang, R. Properties of multilayer transparent conducting oxide films. Thin Solid Films 2004, 461, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelgawad, M.; Wheeler, A.R. The digital revolution: a new paradigm for microfluidics. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.-K.; Yang, H.; Hsu, W. Droplet-on-a-wristband: Chip-to-chip digital microfluidic interfaces between replaceable and flexible electrowetting modules. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Jiang, H. Fabrication and characterization of flexible electrowetting on dielectrics (EWOD) microlens. Micromachines 2014, 5, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Steckl, A.J. Electrowetting on paper for electronic paper display. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter. 2010, 2, 3318–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welters, W.J.; Fokkink, L.G. Fast electrically switchable capillary effects. Langmuir 1998, 14, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, R.A.; Li, F.; Henzen, A.; Shui, L.; Zhou, G. Influence of fluoropolymer surface wettability on electrowetting display performance. Displays 2018, 53, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.; Cho, S.K.; Garrell, R.L.; Kim, C.-J.C. Low voltage electrowetting-on-dielectric. J. Appl. Phys. 2002, 92, 4080–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, T.; Jiang, H.; Wei, B.; Chen, G.; Fang, X.; Jin, M.; Hayes, R.A.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Screen-printing fabrication of electrowetting displays based on poly (imide siloxane) and polyimide. Displays 2015, 37, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Gruner, G.; Gong, J.; Kim, C.-J.C.; Hornbostel, B. Electrowetting devices with transparent single-walled carbon nanotube electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 093124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Niu, R.; Jin, M.; Cao, J.; Yan, Z.; Gao, J.; Wu, H.; Zhou, G.; Shui, L. Self-Healing Flexible Conductive Film by Repairing Defects via Flowable Liquid Metal Droplets. Micromachines 2019, 10, 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10020113
Niu R, Jin M, Cao J, Yan Z, Gao J, Wu H, Zhou G, Shui L. Self-Healing Flexible Conductive Film by Repairing Defects via Flowable Liquid Metal Droplets. Micromachines. 2019; 10(2):113. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10020113
Chicago/Turabian StyleNiu, Ruiwen, Mingliang Jin, Jieping Cao, Zhibin Yan, Jinwei Gao, Hao Wu, Guofu Zhou, and Lingling Shui. 2019. "Self-Healing Flexible Conductive Film by Repairing Defects via Flowable Liquid Metal Droplets" Micromachines 10, no. 2: 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10020113
APA StyleNiu, R., Jin, M., Cao, J., Yan, Z., Gao, J., Wu, H., Zhou, G., & Shui, L. (2019). Self-Healing Flexible Conductive Film by Repairing Defects via Flowable Liquid Metal Droplets. Micromachines, 10(2), 113. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10020113