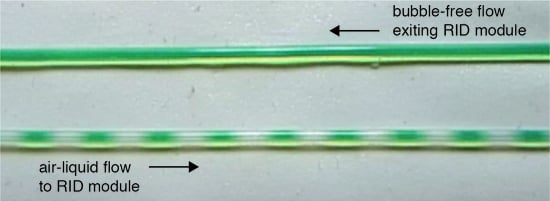
A Low-Cost, Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Module for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Fabrication and Assembly
2.2. RID Operating Principle
2.3. RID Characterization and Automated Image Analysis
2.4. RID Opening Pressure Popen and Membrane Liquid Entry Pressure Pcritical
2.5. Fluid Properties, Contact Angle, and Interfacial Tension Measurements
2.6. Cell Culture
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteriation of RID Bubble Removal Capabilities
3.2. Cell Damage Resulting from Bubble Introduction
3.3. RID Operating Pressure Range and Chip-To-World Interconnections
3.4. Device Fabrication Workflow
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vilkner, T.; Janasek, D.; Manz, A. Micro total analysis systems. Recent developments. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3373–3386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janasek, D.; Franzke, J.; Manz, A. Scaling and the design of miniaturized chemical-analysis systems. Nature 2006, 442, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benam, K.H.; Dauth, S.; Hassell, B.; Herland, A.; Jain, A.; Jang, K.-J.; Karalis, K.; Kim, H.J.; MacQueen, L.; Mahmoodian, R.; et al. Engineered In Vitro Disease Models. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2015, 10, 195–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Osaki, T.; Shin, Y.; Sivathanu, V.; Campisi, M.; Kamm, R.D. In Vitro Microfluidic Models for Neurodegenerative Disorders. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1700489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edington, C.D.; Chen, W.L.K.; Geishecker, E.; Kassis, T.; Soenksen, L.R.; Bhushan, B.M.; Freake, D.; Kirschner, J.; Maass, C.; Tsamandouras, N.; et al. Interconnected Microphysiological Systems for Quantitative Biology and Pharmacology Studies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanyeri, M.; Tay, S. Viable cell culture in PDMS-based microfluidic devices. Methods Cell Biol. 2018, 148, 3–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Helm, M.W.; van der Meer, A.D.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; van den Berg, A.; Segerink, L.I. Microfluidic organ-on-chip technology for blood-brain barrier research. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1142493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, S.N.; Ingber, D.E. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelley, A.M.; Voldman, J. An active bubble trap and debubbler for microfluidic systems. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, D.; Fujioka, H.; Tung, Y.-C.; Futai, N.; Paine, R.; Grotberg, J.B.; Takayama, S. Acoustically detectable cellular-level lung injury induced by fluid mechanical stresses in microfluidic airway systems. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 18886–18891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lochovsky, C.; Yasotharan, S.; Günther, A. Bubbles no more: In-plane trapping and removal of bubbles in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Fujioka, H.; Bian, S.; Torisawa, Y.; Huh, D.; Takayama, S.; Grotberg, J.B. Liquid plug propagation in flexible microchannels: A small airway model. Cit. Phys. Fluids 2009, 21, 071903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lee, D.; Zhang, L.; Jeon, H.; Mendoza-Elias, J.E.; Harvat, T.A.; Hassan, S.Z.; Zhou, A.; Eddington, D.T.; Oberholzer, J. Systematic prevention of bubble formation and accumulation for long-term culture of pancreatic islet cells in microfluidic device. Biomed. Microdevices 2012, 14, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Christoforidis, T.; Ng, C.; Eddington, D.T. Bubble removal with the use of a vacuum pressure generated by a converging-diverging nozzle. Biomed. Microdevices 2017, 19, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Vaillant, R.; Attinger, D. Use of a porous membrane for gas bubble removal in microfluidic channels: physical mechanisms and design criteria. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2010, 9, 765–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Lintel, H.; Mernier, G.; Renaud, P. High-Throughput Micro-Debubblers for bubble removal with Sub-Microliter dead volume. Micromachines 2012, 3, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Thompson, J.A.; Bau, H.H. A membrane-based, high-efficiency, microfluidic debubbler. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Meer, A.D.; Poot, A.A.; Feijen, J.; Vermes, I. Analyzing shear stress-induced alignment of actin filaments in endothelial cells with a microfluidic assay. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 011103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.Z.; Yuan, W.M.; Xiang, C.; Zeng, D.P.; Liu, B.; Qin, K.R. A microfluidic device with spatiotemporal wall shear stress and ATP signals to investigate the intracellular calcium dynamics in vascular endothelial cells. Biomech. Model. Mechanobiol. 2019, 18, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santaguida, S.; Janigro, D.; Hossain, M.; Oby, E.; Rapp, E.; Cucullo, L. Side by side comparison between dynamic versus static models of blood–brain barrier in vitro: A permeability study. Brain Res. 2006, 1109, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, C.F.; Verbridge, S.S.; Vlachos, P.P.; Rylander, M.N. Flow shear stress regulates endothelial barrier function and expression of angiogenic factors in a 3D microfluidic tumor vascular model. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 517–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meng, D.D.; Kim, J.; Kim, C.J. A degassing plate with hydrophobic bubble capture and distributed venting for microfluidic devices. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 419–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsao, C.-W.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Cheng, J.-H.; Fan, S.-K.; Yao, D.-J.; Tung, Y.-C. Fluid Flow Shear Stress Stimulation on a Multiplex Microfluidic Device for Rat Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Differentiation Enhancement. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1996–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhyankar, V.V.; Wu, M.; Koh, C.Y.; Hatch, A.V. A reversibly sealed, easy access, modular (SEAM) microfluidic architecture to establish in vitro tissue interfaces. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.R.; Peri, S.S.S.; Sabane, V.P.; Mansur, N.; Gao, J.X.; Nguyen, K.T.; Weidanz, J.A.; Iqbal, S.M.; Abhyankar, V. V One-step fabrication of flexible nanotextured PDMS as a substrate for selective cell capture. Biomed. Phys. Eng. Express 2018, 4, 025015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, K.M.; Stroka, K.M. Vascular endothelial cell mechanosensing: New insights gained from biomimetic microfluidic models. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 71, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suo, J.; Ferrara, D.E.; Sorescu, D.; Guldberg, R.E.; Taylor, W.R.; Giddens, D.P. Hemodynamic shear stresses in mouse aortas: Implications for atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bretherton, F.P. The motion of long bubbles in tubes. J. Fluid Mech. 1961, 10, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaseboer, E.; Gupta, R.; Manica, R. An extended Bretherton model for long Taylor bubbles at moderate capillary numbers. Phys. Fluids 2014, 26, 32107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Williams, M.J.; Lee, N.K.; Mylott, J.A.; Mazzola, N.; Ahmed, A.; Abhyankar, V.V. A Low-Cost, Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Module for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications. Micromachines 2019, 10, 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060360
Williams MJ, Lee NK, Mylott JA, Mazzola N, Ahmed A, Abhyankar VV. A Low-Cost, Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Module for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications. Micromachines. 2019; 10(6):360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060360
Chicago/Turabian StyleWilliams, Matthew J., Nicholas K. Lee, Joseph A. Mylott, Nicole Mazzola, Adeel Ahmed, and Vinay V. Abhyankar. 2019. "A Low-Cost, Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Module for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications" Micromachines 10, no. 6: 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060360
APA StyleWilliams, M. J., Lee, N. K., Mylott, J. A., Mazzola, N., Ahmed, A., & Abhyankar, V. V. (2019). A Low-Cost, Rapidly Integrated Debubbler (RID) Module for Microfluidic Cell Culture Applications. Micromachines, 10(6), 360. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060360