Hydrodynamic Microparticle Separation Mechanism Using Three-Dimensional Flow Profiles in Dual-Depth and Asymmetric Lattice-Shaped Microchannel Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
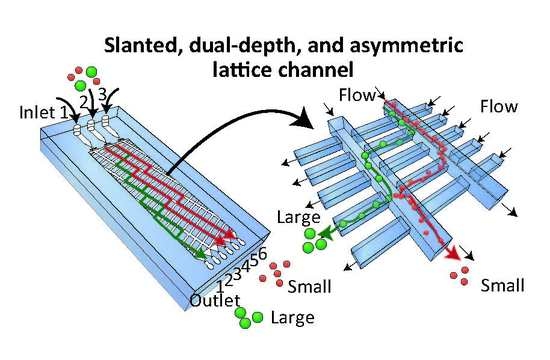
2.1. Separation Mechanism
2.2. Fabrication and Design of Microfluidic Devices
2.3. Particle Separation Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Separation Using Microdevice A
3.2. Observation of 3D Particle Behavior Using High-Speed Confocal Microscopy
3.3. Effect of the Main Channel Depth on Particle Separation
3.4. Tuning of Separation Size
3.5. Control of the Vertical Position of Particles
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Ali, J.; Sorger, P.K.; Jensen, K.F. Cells on chips. Nature 2006, 442, 403–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Naranjo, J.C.; Wu, H.J.; Ugaz, V.M. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: Enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3558–3577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulasinghe, A.; Wu, H.; Punyadeera, C.; Warkiani, M.E. The use of microfluidic technology for cancer applications and liquid biopsy. Micromachines 2018, 9, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gossett, D.R.; Weaver, W.M.; Mach, A.J.; Hur, S.C.; Tse, H.T.; Lee, W.; Amini, H.; Di Carlo, D. Label-free cell separation and sorting in microfluidic systems. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 397, 3249–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shields, C.W., IV; Reyes, C.D.; Lopez, G.P. Microfluidic cell sorting: A review of the advances in the separation of cells from debulking to rare cell isolation. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1230–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalili, A.; Samiei, E.; Hoorfar, M. A review of sorting, separation and isolation of cells and microbeads for biomedical applications: Microfluidic approaches. Analyst 2018, 144, 87–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.R.; Cox, E.C.; Austin, R.H.; Sturm, J.C. Continuous particle separation through deterministic lateral displacement. Science 2004, 304, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, S.; Zeming, K.K.; Jureen, R.; Fisher, D.; Zhang, Y. DLD pillar shape design for efficient separation of spherical and non-spherical bioparticles. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 4250–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tottori, N.; Nisisako, T.; Park, J.; Yanagida, Y.; Hatsuzawa, T. Separation of viable and nonviable mammalian cells using a deterministic lateral displacement microfluidic device. Biomicrofluidics 2016, 10, 014125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Nakashima, M.; Seki, M. Pinched flow fractionation: Continuous size separation of particles utilizing a laminar flow profile in a pinched microchannel. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 5465–5471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Xuan, X. Elasto-inertial pinched flow fractionation for continuous shape-based particle separation. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 11523–11530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, M.; Seki, M. Hydrodynamic filtration for on-chip particle concentration and classification utilizing microfluidics. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Yamada, M.; Mitamura, R.; Ike, K.; Toyama, K.; Seki, M. Magnetophoresis-integrated hydrodynamic filtration system for size- and surface marker-based two-dimensional cell sorting. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7666–7673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Chun, M.S.; Chang, M.S. Sorting of human mesenchymal stem cells by applying optimally designed microfluidic chip filtration. Analyst 2015, 140, 1265–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhagat, A.A.; Kuntaegowdanahalli, S.S.; Papautsky, I. Continuous particle separation in spiral microchannels using Dean flows and differential migration. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 1906–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warkiani, M.E.; Khoo, B.L.; Wu, L.; Tay, A.K.; Bhagat, A.A.; Han, J.; Lim, C.T. Ultra-fast, label-free isolation of circulating tumor cells from blood using spiral microfluidics. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 134–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petchakup, C.; Tay, H.M.; Li, K.H.H.; Hou, H.W. Integrated inertial-impedance cytometry for rapid label-free leukocyte isolation and profiling of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1736–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Song, S.; Choi, C.; Park, J.K. Hydrophoretic sorting of micrometer and submicrometer particles using anisotropic microfluidic obstacles. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Choi, S. Design rules for size-based cell sorting and sheathless cell focusing by hydrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2013, 1302, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Lee, J.K.; Choi, S. Continuous sorting and washing of cancer cells from blood cells by hydrophoresis. Biochip. J. 2015, 10, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.; Edd, J.F.; Irimia, D.; Tompkins, R.G.; Toner, M. Equilibrium separation and filtration of particles using differential inertial focusing. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 2204–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ma, Z.; Tayebi, M.; Ai, Y. Submicron particle focusing and exosome sorting by wavy microchannel structures within viscoelastic fluids. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4577–4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.S.; Song, S.H.; Jung, H.I. Continuous focusing of microparticles using inertial lift force and vorticity via multi-orifice microfluidic channels. Lab Chip 2009, 9, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.L.; He, X.K.; Han, Y.; Du, L.; Zhao, L.; Zhe, J. Continuous size-based separation of microparticles in a microchannel with symmetric sharp corner structures. Biomicrofluidics 2014, 8, 024108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, Y.J.; Wu, Y.C.; Chen, Y.; Kung, Y.C.; Wu, T.H.; Huang, K.W.; Sheen, H.J.; Chiou, P.Y. Three dimensional microfluidics with embedded microball lenses for parallel and high throughput multicolor fluorescence detection. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 044212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wu, T.H.; Kung, Y.C.; Teitell, M.A.; Chiou, P.Y. 3D pulsed laser-triggered high-speed microfluidic fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Analyst 2013, 138, 7308–7315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Munoz, H.E.; Schmidt, A.; Guo, B.; Lei, C.; Goda, K.; Di Carlo, D. Inertial focusing of ellipsoidal Euglena gracilis cells in a stepped microchannel. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4458–4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Thomas, A.; Lee, E.; Yang, S.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Y. Highly efficient and selective isolation of rare tumor cells using a microfluidic chip with wavy-herringbone micro-patterned surfaces. Analyst 2016, 141, 2228–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rafeie, M.; Zhang, J.; Asadnia, M.; Li, W.H.; Warkiani, M.E. Multiplexing slanted spiral microchannels for ultra-fast blood plasma separation. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 2791–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.; Wang, X.; Zhou, J.; Papautsky, I. Single stream inertial focusing in low aspect-ratio triangular microchannels. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Seko, W.; Yanai, T.; Ninomiya, K.; Seki, M. Slanted, asymmetric microfluidic lattices as size-selective sieves for continuous particle/cell sorting. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, J.C.; Whitesides, G.M. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) as a material for fabricating microfluidic devices. Acc. Chem. Res. 2002, 35, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.Q.; Liu, G.Y.; Lu, W.; Fu, J.P. Continuous-flow microfluidic blood cell sorting for unprocessed whole blood using surfacemicromachined microfiltration membranes. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, R.; Iwadate, H.; Toyoda, H.; Yamada, M.; Seki, M. A numbering-up strategy of hydrodynamic microfluidic filters for continuous-flow high-throughput cell sorting. Lab Chip 2019, 19, 1828–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Microdevice | wmain (μm) | wsep (μm) | dmain (μm) | dsep (μm) | Dmain (μm) | Dsep (μm) | Lattice Size (mm × mm) | Size Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 35 | 15 | 40 | 15 | 93 | 25 | 32 × 12 | 1 |
| B | 35 | 15 | 25 | 15 | 93 | 25 | 32 × 12 | - |
| C | 35 | 15 | 70 | 15 | 93 | 25 | 32 × 12 | - |
| D | 52 | 23 | 60 | 23 | 139 | 38 | 48 × 18 | 1.5 |
| E | 23 | 10 | 27 | 10 | 62 | 17 | 21.3 × 8 | 0.67 |
| F | 17 | 7 | 20 | 7 | 46 | 13 | 16 × 6 | 0.5 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanai, T.; Ouchi, T.; Yamada, M.; Seki, M. Hydrodynamic Microparticle Separation Mechanism Using Three-Dimensional Flow Profiles in Dual-Depth and Asymmetric Lattice-Shaped Microchannel Networks. Micromachines 2019, 10, 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060425
Yanai T, Ouchi T, Yamada M, Seki M. Hydrodynamic Microparticle Separation Mechanism Using Three-Dimensional Flow Profiles in Dual-Depth and Asymmetric Lattice-Shaped Microchannel Networks. Micromachines. 2019; 10(6):425. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060425
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanai, Takuma, Takatomo Ouchi, Masumi Yamada, and Minoru Seki. 2019. "Hydrodynamic Microparticle Separation Mechanism Using Three-Dimensional Flow Profiles in Dual-Depth and Asymmetric Lattice-Shaped Microchannel Networks" Micromachines 10, no. 6: 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060425
APA StyleYanai, T., Ouchi, T., Yamada, M., & Seki, M. (2019). Hydrodynamic Microparticle Separation Mechanism Using Three-Dimensional Flow Profiles in Dual-Depth and Asymmetric Lattice-Shaped Microchannel Networks. Micromachines, 10(6), 425. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi10060425