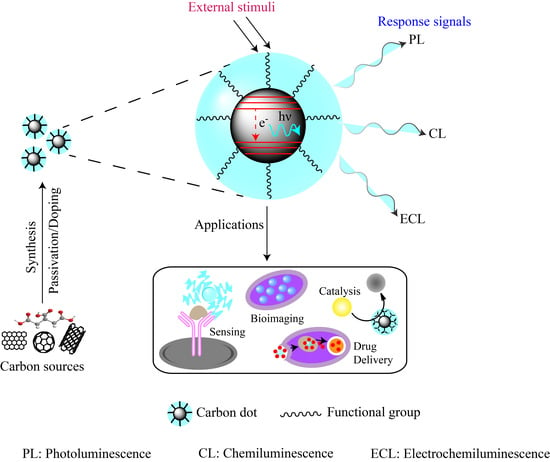
Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Synthesis of CDs
2.1. Heteroatoms Doped-CD Synthesis
2.1.1. Non-Metal Doping
2.1.2. Metal Doping
2.2. Surface Passivation and Functionalization of CDs
2.3. Characterization of CDs
2.3.1. Microscopic and Diffraction Technique
2.3.2. Spectroscopic Technique
3. Properties of CDs
3.1. Physical Property
Chemical Structure
3.2. Chemical and Optical Property
3.2.1. Ultraviolet-Visible Absorption
3.2.2. Photoluminescence
3.2.3. Electron Transfer of CDs
3.2.4. Cytotoxicity and Photostability of CDs
3.2.5. Emerging Property: Chirality of CDs
4. PL Mechanism of CDs
5. CDs as Smart Materials
5.1. pH Sensitive
5.2. Temperature Sensitive
5.3. Light Sensitive
5.4. Pressure Sensitive
5.5. Multi-Sensitive
5.6. Phase Sensitive
5.7. Solvent Sensitive
6. CDs in Optical-Based Analytical
6.1. Photoluminescence
Dual-Mode Detection Systems
6.2. Chemiluminescence
6.3. Electrochemiluminescence
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semeniuk, M.; Yi, Z.; Poursorkhabi, V.; Tjong, J.; Jaffer, S.; Lu, Z.-H.; Sain, M. Future Perspectives and Review on Organic Carbon Dots in Electronic Applications. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 6224–6255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, M.; Qiu, J.; Sun, Y.-P. Design and Fabrication of Carbon Dots for Energy Conversion and Storage. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 2315–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J. Carbon Dots-in-Matrix Boosting Intriguing Luminescence Properties and Applications. Small 2019, 15, 1805504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, P.; Rajput, P.; Thakur, A.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, P. Recent Advances in Carbon Quantum Dot-Based Sensing of Heavy Metals in Water. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 171–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Goswami, P. Nanozymes as Potential Catalysts for Sensing and Analytical Applications. In Advanced Materials and Techniques for Biosensors and Bioanalytical Applications, 1st ed.; Goswami, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 143–162. ISBN 978-1-00-308385-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ngashangva, L.; Chakma, B.; Goswami, P. Smart Materials for Developing Sensor Platforms. In Advanced Materials and Techniques for Biosensors and Bioanalytical Applications, 1st ed.; Goswami, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 47–68. ISBN 978-1-00-308385-6. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, G.; Wu, M.; Han, M.-Y. Stimuli-Responsive Hybridized Nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1903439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanov, A.E.; Zubov, V.P. Smart Polymers as Surface Modifiers for Bioanalytical Devices and Biomaterials: Theory and Practice. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2016, 85, 565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Song, Y.; Zhao, X.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, B. The Photoluminescence Mechanism in Carbon Dots (Graphene Quantum Dots, Carbon Nanodots, and Polymer Dots): Current State and Future Perspective. Nano Res. 2015, 8, 355–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Ding, H.; Xu, M.; Hu, X.; Li, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, C.; et al. Recent Advances in Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Biomedical Applications of Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2019, 2, 2317–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Wang, S.; Xu, Z.; Liu, J.; Huang, Y.; Hu, S.; Ren, X. Synthesis of Novel Cationic Carbon Dots and Application to Quantitative Detection of K+ in Human Serum Samples. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 17937–17940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Yan, H.; Li, X.; Wang, X. In Situ Fabrication of Carbon Dots-Based Lubricants Using a Facile Ultrasonic Approach. Green Chem. 2019, 21, 2279–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.-B.; Liu, K.-K.; Song, S.-Y.; Zhou, R.; Shan, C.-X. Fluorescent Nano-Biomass Dots: Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction and Their Application as Nanoprobe for Fe3+ Detection. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, V.; Zhao, N.; Yan, L.; Zhong, P.; Nguyen, V.C.; Le, P.H. Double-Pulse Femtosecond Laser Ablation for Synthesis of Ultrasmall Carbon Nanodots. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 015606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Chai, S.; Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Yu, Z.; Yang, T.; Feng, C.; Huang, C. 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Detection by a New Portable Sensing Gadget Using Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Probe. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 2291–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roshni, V.; Gujar, V.; Pathan, H.; Islam, S.; Tawre, M.; Pardesi, K.; Santra, M.K.; Ottoor, D. Bioimaging Applications of Carbon Dots (C. Dots) and Its Cystamine Functionalization for the Sensitive Detection of Cr(VI) in Aqueous Samples. J. Fluoresc. 2019, 29, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, H.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X. Carbon Dots Derived from Tobacco for Visually Distinguishing and Detecting Three Kinds of Tetracyclines. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 8139–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Liu, J.; Gan, L.; Yang, X. Employing Cryptococcus-Directed Carbon Dots for Differentiating and Detecting m-Benzenediol and p-Benzenediol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 301, 127077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Ding, H.; Lu, S.; Geng, T.; Xiao, G.; Zou, B.; Bi, H. Photoactivated Fluorescence Enhancement in F,N-Doped Carbon Dots with Piezochromic Behavior. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 9986–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, A.; Singh, N. Cell Microenvironment PH Sensing in 3D Microgels Using Fluorescent Carbon Dots. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 3, 3620–3627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Ding, C.; Lin, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, H.; Zhu, X.; Dai, Y.; Luo, C. Highly Selective and Sensitive Chemiluminescence Biosensor for Adenosine Detection Based on Carbon Quantum Dots Catalyzing Luminescence Released from Aptamers Functionalized Graphene@magnetic β-Cyclodextrin Polymers. Talanta 2018, 186, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Peng, L.; Lv, L.; Cao, Y.; Tu, J.; Huang, W.; Zhang, K. In Situ Growth of Carbon Dots on TiO2 Nanotube Arrays for PEC Enzyme Biosensors with Visible Light Response. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 15084–15091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, F.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, M.; Tan, C.; Tang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W. Metal-Triggered Fluorescence Enhancement of Multicolor Carbon Dots in Sensing and Bioimaging. Opt. Mater. 2019, 94, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, T.; Chen, M.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Chen, W. Facile Synthesis and Photoluminescence Mechanism of Green Emitting Xylose-Derived Carbon Dots for Anti-Counterfeit Printing. Carbon 2019, 146, 636–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Zhang, F.; Xu, L.; Liu, X.; Ma, P.; Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Song, D. A Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Biosensor Based on Carbon Dots and Gold Nanoparticles for the Detection of Trypsin. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadzadeh-Khaneghah, S.; Habibi-Yangjeh, A.; Nakata, K. Decoration of Carbon Dots over Hydrogen Peroxide Treated Graphitic Carbon Nitride: Exceptional Photocatalytic Performance in Removal of Different Contaminants under Visible Light. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 374, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.; Balachandran, M. Green Luminescence and Irradiance Properties of Carbon Dots Cross-Linked with Polydimethylsiloxane. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 19835–19843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, M.; Xu, Z.; Jiang, Q.; Feng, J.; Sun, J.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. Interfacial Engineering of Carbon Dots with Benzenediboronic Acid for Fluorescent Biosensing. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, X.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. Carbon Dots with Red Emission as a Fluorescent and Colorimeteric Dual-Readout Probe for the Detection of Chromium(vi) and Cysteine and Its Logic Gate Operation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 6099–6107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Feng, D.-Q.; Qian, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, J.-J. Construction of FRET Biosensor for Off-on Detection of Lead Ions Based on Carbon Dots and Gold Nanorods. Talanta 2019, 201, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, B.P.; Sigmon, L.R.; Deline, A.R.; Lankone, R.S.; Gallagher, M.J.; Zhi, B.; Haynes, C.L.; Fairbrother, D.H. Photochemical Transformations of Carbon Dots in Aqueous Environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 4160–4170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.; Reckmeier, C.J.; Xiong, Y.; von Seckendorff, M.; Susha, A.S.; Kasák, P.; Rogach, A.L. Molecular Fluorescence in Citric Acid-Based Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 2014–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Zhao, X.; Song, Y.; Lu, S.; Yang, B. Beyond Bottom-up Carbon Nanodots: Citric-Acid Derived Organic Molecules. Nano Today 2016, 11, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Nie, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Guo, X.; Xing, Z.; Li, M.; Zhang, S.X.-A. Inorganic Salt Incorporated Solvothermal Synthesis of Multicolor Carbon Dots, Emission Mechanism, and Antibacterial Study. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandi, R.; Dadigala, R.; Gangapuram, B.R.; Guttena, V. Green Synthesis of Highly Fluorescent Nitrogen—Doped Carbon Dots from Lantana Camara Berries for Effective Detection of Lead(II) and Bioimaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 178, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakoçak, B.B.; Liang, J.; Kavadiya, S.; Berezin, M.Y.; Biswas, P.; Ravi, N. Optimizing the Synthesis of Red-Emissive Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for Use in Bioimaging. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3682–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzimitakos, T.; Kasouni, A.; Sygellou, L.; Leonardos, I.; Troganis, A.; Stalikas, C. Human Fingernails as an Intriguing Precursor for the Synthesis of Nitrogen and Sulfur-Doped Carbon Dots with Strong Fluorescent Properties: Analytical and Bioimaging Applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 267, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Chen, S.; Zuo, W.; Shi, B. Cu-Doped Carbon Dots as Catalysts for the Chemiluminescence Detection of Glucose. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 9911–9917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Su, R.; Chen, Y.; Theruvakkattil Sreenivasan, S.; Li, N.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J.; Pan, H.; Li, W.; Xu, C.; et al. Metal Charge Transfer Doped Carbon Dots with Reversibly Switchable, Ultra-High Quantum Yield Photoluminescence. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 1886–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoa-De León, I.C.; Johny, J.; Vázquez-Rodríguez, S.; García-Gómez, N.; Carranza-Bernal, S.; Mendivil, I.; Shaji, S.; Sepúlveda-Guzmán, S. Tuning the Luminescence of Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots Synthesized by Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid and Their Use as a Selective Photoluminescence on–off–on Probe for Ascorbic Acid Detection. Carbon 2019, 150, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiprop Kipnusu, W.; Doñate-Buendía, C.; Fernández-Alonso, M.; Lancis, J.; Mínguez-Vega, G. Nonlinear Optics to Glucose Sensing: Multifunctional Nitrogen and Boron Doped Carbon Dots with Solid-State Fluorescence in Nanoporous Silica Films. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, H.; Huang, J. Facile Ultrasonic Synthesized NH2-Carbon Quantum Dots for Ultrasensitive Co2+ Ion Detection and Cell Imaging. Talanta 2019, 205, 120121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, X.; Wu, F.; Sun, B.; Zhang, M.; Song, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, N.; Shen, J. Genipin Cross-Linked Carbon Dots for Antimicrobial, Bioimaging and Bacterial Discrimination. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2020, 190, 110930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atchudan, R.; Edison, T.N.J.I.; Perumal, S.; Clament Sagaya Selvam, N.; Lee, Y.R. Green Synthesized Multiple Fluorescent Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as an Efficient Label-Free Optical Nanoprobe for in Vivo Live-Cell Imaging. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2019, 372, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milenkovic, I.; Algarra, M.; Alcoholado, C.; Cifuentes, M.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.M.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; Mutavdžić, D.; Radotić, K.; Bandosz, T.J. Fingerprint Imaging Using N-Doped Carbon Dots. Carbon 2019, 144, 791–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Zhuo, S.; Zhu, C. Fluorescent Sensing Platform for the Detection of P-Nitrophenol Based on Cu-Doped Carbon Dots. Opt. Mater. 2019, 97, 109396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Dong, S.; Zhao, F.; Deng, M.; Fu, Y.; Lü, C. Tricolor Emissive Carbon Dots for Ultra-Wide Range pH Test Papers and Bioimaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, M.; Yu, Y.; Yang, G.; Su, X. Label-Free Fluorescence Assay Based on near-Infrared B,N-Doped Carbon Dots as a Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Sialic Acid. New J. Chem. 2020, 44, 2350–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Qin, Z.; Wang, M.; Liu, W.; Jiang, H.; Wang, X. Manganese Oxide Doped Carbon Dots for Temperature-Responsive Biosensing and Target Bioimaging. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, I.; Misra, S.K.; Bangru, S.; Boateng, K.A.; Soares, J.A.N.T.; Schwartz-Duval, A.S.; Kalsotra, A.; Pan, D. Complementary Oligonucleotide Conjugated Multicolor Carbon Dots for Intracellular Recognition of Biological Events. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 16137–16149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Yucknovsky, A.; Akulov, K.; Ghorai, N.; Schwartz, T.; Ghosh, H.N.; Amdursky, N. Efficient Photosensitizing Capabilities and Ultrafast Carrier Dynamics of Doped Carbon Dots. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 15413–15422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.-Y.; Gong, X.-J.; Liu, Y.; Lu, W.-J.; Gao, Y.-F.; Xian, M.; Shuang, S.-M.; Dong, C. Facile Preparation of Bright Orange Fluorescent Carbon Dots and the Constructed Biosensing Platform for the Detection of PH in Living Cells. Talanta 2018, 189, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.-L.; Zang, J.-H.; Lou, Q.; Su, L.-X.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Dong, L.; Shan, C.-X. In-Situ Embedding of Carbon Dots in a Trisodium Citrate Crystal Matrix for Tunable Solid-State Fluorescence. Carbon 2018, 136, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, Y.; Geng, T.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C.; Zhang, X.; Lei, B.; Zhuang, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, D.; Xiao, G.; et al. Near-Ultraviolet to Near-Infrared Fluorescent Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots with Two-Photon and Piezochromic Luminescence. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 27920–27927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Zu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X.; Ma, T.; Chen, L. Yellow-Emissive Carbon Dots with a Large Stokes Shift Are Viable Fluorescent Probes for Detection and Cellular Imaging of Silver Ions and Glutathione. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Wang, Y.-K.; Sharma, G.; Dong, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, P.; Johnston, A.; Bappi, G.; Fan, J.Z.; Kung, H.; et al. Bright High-Colour-Purity Deep-Blue Carbon Dot Light-Emitting Diodes via Efficient Edge Amination. Nat. Photonics 2020, 14, 171–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, M.; Wang, D.; Li, Z.; Primo, F.L.; Tedesco, A.C.; Bi, H. Copper-Doped Carbon Dots for Optical Bioimaging and Photodynamic Therapy. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 13394–13402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xing, M.; Wu, Q. A Universal Facile Synthesis of Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon Dots from Cellulose-Based Biowaste for Fluorescent Detection of Fe3+ Ions and Intracellular Bioimaging. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 99, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Z.; Hua, J.; Feng, S.; Yang, Y. A Ratiometric Fluorescence and Light Scattering Sensing Platform Based on Cu-Doped Carbon Dots for Tryptophan and Fe(III). Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Dong, T. Photoluminescence Tuning in Carbon Dots: Surface Passivation or/and Functionalization, Heteroatom Doping. J. Mater. Chem. C 2018, 6, 7944–7970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, L.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Ge, D.; Shi, W.; Sun, Y. Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Polydopamine Carbon Dots for Photothermal Therapy. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Panneerselvam, P.; Marieeswaran, M. A Green Synthetic Route for the Surface-Passivation of Carbon Dots as an Effective Multifunctional Fluorescent Sensor for the Recognition and Detection of Toxic Metal Ions from Aqueous Solution. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momper, R.; Steinbrecher, J.; Dorn, M.; Rörich, I.; Bretschneider, S.; Tonigold, M.; Ramanan, C.; Ritz, S.; Mailänder, V.; Landfester, K.; et al. Enhanced Photoluminescence Properties of a Carbon Dot System through Surface Interaction with Polymeric Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 518, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Tang, Q.; Meng, Y.; Liu, J.; Feng, T.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, S.; Yu, W.; Yang, B. Reversible “Off–On” Fluorescence of Zn2+ Passivated Carbon Dots: Mechanism and Potential for the Detection of EDTA and Zn2+. Langmuir 2018, 34, 7767–7775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, X.; Yuan, M.; Jiang, H.; Li, L.; Liu, Z. A Universal Strategy to Obtain Chiroptical Carbon Quantum Dots through the Optically Active Surface Passivation Procedure. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 13735–13740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, G.-H.; Song, Z.-M.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Su, Q.; Liang, W.; Cao, A.; Sun, Y.-P.; Wang, H. Effects of Carbon Dots Surface Functionalities on Cellular Behaviors—Mechanistic Exploration for Opportunities in Manipulating Uptake and Translocation. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 181, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Song, W.; Zhao, B.; Yang, B. Spectroscopic Studies of the Optical Properties of Carbon Dots: Recent Advances and Future Prospects. Mater. Chem. Front. 2020, 4, 472–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Li, W.; Ding, L.; Yang, W.; Xiao, H.; Ong, W.-J. Function-Driven Engineering of 1D Carbon Nanotubes and 0D Carbon Dots: Mechanism, Properties and Applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 1475–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinek, R. Characterization and Physical Properties of Carbon-Dots. In Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Properties and Applications; Carbon Nanostructures; Jelinek, R., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 29–46. ISBN 978-3-319-43911-2. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Z.; Lee, S.-T. Carbon Dots: Advances in Nanocarbon Applications. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 19214–19224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Feng, Y.; Dong, P.; Huang, J. A Mini Review on Carbon Quantum Dots: Preparation, Properties, and Electrocatalytic Application. Front. Chem. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajik, S.; Dourandish, Z.; Zhang, K.; Beitollahi, H.; Van Le, Q.; Won Jang, H.; Shokouhimehr, M. Carbon and Graphene Quantum Dots: A Review on Syntheses, Characterization, Biological and Sensing Applications for Neurotransmitter Determination. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 15406–15429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddique, A.B.; Pramanick, A.K.; Chatterjee, S.; Ray, M. Amorphous Carbon Dots and Their Remarkable Ability to Detect 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Verma, N.C.; Chethana; Nandi, C.K. Carbon Dots for Single-Molecule Imaging of the Nucleolus. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Wang, R.; Gong, X.; Dong, C. An Efficient Turn-on Fluorescence Biosensor for the Detection of Glutathione Based on FRET between N,S Dual-Doped Carbon Dots and Gold Nanoparticles. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 6687–6695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Liang, C.; Ushakova, E.V.; Sun, M.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Jing, P.; Yoo, S.J.; Kim, J.-G.; Liu, E.; et al. Thermally Activated Upconversion Near-Infrared Photoluminescence from Carbon Dots Synthesized via Microwave Assisted Exfoliation. Small 2019, 15, 1905050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Feng, X.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Preparation of Multicolor Photoluminescent Carbon Dots by Tuning Surface States. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carbonaro, C.M.; Chiriu, D.; Stagi, L.; Casula, M.F.; Thakkar, S.V.; Malfatti, L.; Suzuki, K.; Ricci, P.C.; Corpino, R. Carbon Dots in Water and Mesoporous Matrix: Chasing the Origin of Their Photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 25638–25650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.-P.; Yu, Y.-X.; Guo, X.-L.; Ding, Z.-Y.; Zhou, B.; Liang, H.; Shen, X.-C. White-Emitting Carbon Dots with Long Alkyl-Chain Structure: Effective Inhibition of Aggregation Caused Quenching Effect for Label-Free Imaging of Latent Fingerprint. Carbon 2018, 128, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mintz, K.J.; Guerrero, B.; Leblanc, R.M. Photoinduced Electron Transfer in Carbon Dots with Long-Wavelength Photoluminescence. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 29507–29515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, H.M.; Neves, S.A.F.; Duarte, A.; de Zea Bermudez, V. Nanofluid Based on Carbon Dots Functionalized with Ionic Liquids for Energy Applications. Energies 2020, 13, 649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Emanuele, A.; Cailotto, S.; Campalani, C.; Branzi, L.; Raviola, C.; Ravelli, D.; Cattaruzza, E.; Trave, E.; Benedetti, A.; Selva, M.; et al. Precursor-Dependent Photocatalytic Activity of Carbon Dots. Molecules 2020, 25, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cailotto, S.; Mazzaro, R.; Enrichi, F.; Vomiero, A.; Selva, M.; Cattaruzza, E.; Cristofori, D.; Amadio, E.; Perosa, A. Design of Carbon Dots for Metal-Free Photoredox Catalysis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 40560–40567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Wei, J.-S.; Chen, X.-B.; Xiong, H.-M. Heteroatom-Doped Carbon Dots Based Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 716–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Yue, L.; Yang, L.; Wang, K.; Liu, G.; Luo, X.; Zhu, X. Ln(III) Chelates-Functionalized Carbon Quantum Dots: Synthesis, Optical Studies and Multimodal Bioimaging Applications. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 175, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, L.; Li, H.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Luo, X.; Wu, F.; Zhu, X. Red-Emissive Ruthenium-Containing Carbon Dots for Bioimaging and Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ru, Y.; Ai, L.; Jia, T.; Liu, X.; Lu, S.; Tang, Z.; Yang, B. Recent Advances in Chiral Carbonized Polymer Dots: From Synthesis and Properties to Applications. Nano Today 2020, 34, 100953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekini, M.; Prince, E.; Zhao, L.; Mundoor, H.; Smalyukh, I.I.; Kumacheva, E. Chiral Carbon Dots Synthesized on Cellulose Nanocrystals. Adv. Opt. Mater. 2020, 8, 1901911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ðorđević, L.; Arcudi, F.; D’Urso, A.; Cacioppo, M.; Micali, N.; Bürgi, T.; Purrello, R.; Prato, M. Design Principles of Chiral Carbon Nanodots Help Convey Chirality from Molecular to Nanoscale Level. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zheng, D.; Wu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, L. Gel Systems Doped with Chiral Carbon Dots for Optical Combination. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2020, 3, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Xie, Z.; Zheng, M. Chiral Carbon Dots-Based Nanosensors for Sn(II) Detection and Lysine Enantiomers Recognition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 319, 128265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Guan, S.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zeng, H.; Xie, Z.; Chen, P.; Zhou, S. Highly Efficient Carbon Dots with Reversibly Switchable Green–Red Emissions for Trichromatic White Light-Emitting Diodes. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 16005–16014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Preeyanka, N.; Majhi, D.; Seth, S.; Sarkar, M. Striking Similarities in the Fluorescence Behavior between Carbon Dots and Ionic Liquids: Toward Understanding the Fluorescence Behavior of Carbon Dots. J. Phys. Chem. C 2018, 122, 12384–12394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Lu, S.; Yang, H.; Yang, L.; Ding, C.; Yu, S. Cross-Linked Polyamide Chains Enhanced the Fluorescence of Polymer Carbon Dots. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8219–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, J.; Weber, F.; Weigert, F.; Wang, Y.; Choudhury, S.; Xiao, J.; Lauermann, I.; Resch-Genger, U.; Bande, A.; Petit, T. Influence of Surface Chemistry on Optical, Chemical and Electronic Properties of Blue Luminescent Carbon Dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 2056–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, J.; Yin, T.; Shen, W. Effect of Surface Modification on the Peroxidase-like Behaviors of Carbon Dots. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2019, 178, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behera, R.K.; Sau, A.; Mishra, L.; Bera, K.; Mallik, S.; Nayak, A.; Basu, S.; Sarangi, M.K. Redox Modifications of Carbon Dots Shape Their Optoelectronics. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 27937–27944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paulo-Mirasol, S.; Gené-Marimon, S.; Martínez-Ferrero, E.; Palomares, E. Inverted Hybrid Light-Emitting Diodes Using Carbon Dots as Selective Contacts: The Effect of Surface Ligands. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2020, 2, 1388–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Schneider, J.; Ushakova, E.V.; Rogach, A.L. Influence of Molecular Fluorophores on the Research Field of Chemically Synthesized Carbon Dots. Nano Today 2018, 23, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrat, F.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Schneider, J.; Löf, A.; Wyrwich, R.; Rogach, A.L.; Stolarczyk, J.K.; Urban, A.S.; Feldmann, J. Tracking the Source of Carbon Dot Photoluminescence: Aromatic Domains versus Molecular Fluorophores. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 7710–7716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, M.; Paloncýová, M.; Medved’, M.; Otyepka, M. Molecular Fluorophores Self-Organize into C-Dot Seeds and Incorporate into C-Dot Structures. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 8252–8258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprzyk, W.; Świergosz, T.; Bednarz, S.; Walas, K.; Bashmakova, N.V.; Bogdał, D. Luminescence Phenomena of Carbon Dots Derived from Citric Acid and Urea—A Molecular Insight. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 13889–13894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sendão, R.M.S.; Crista, D.M.A.; Afonso, A.C.P.; de Yuso, M.D.V.M.; Algarra, M.; da Silva, J.C.G.E.; da Silva, L.P. Insight into the Hybrid Luminescence Showed by Carbon Dots and Molecular Fluorophores in Solution. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2019, 21, 20919–20926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wei, W.; Qu, X. Colorimetric Biosensing Using Smart Materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4215–4236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledin, P.A.; Jeon, J.-W.; Geldmeier, J.A.; Ponder, J.F.; Mahmoud, M.A.; El-Sayed, M.; Reynolds, J.R.; Tsukruk, V.V. Design of Hybrid Electrochromic Materials with Large Electrical Modulation of Plasmonic Resonances. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13064–13075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cobo, I.; Li, M.; Sumerlin, B.S.; Perrier, S. Smart Hybrid Materials by Conjugation of Responsive Polymers to Biomacromolecules. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Cheng, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, Y.; Qu, L.; Shi, G. Graphene-Based Smart Materials. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angione, M.D.; Pilolli, R.; Cotrone, S.; Magliulo, M.; Mallardi, A.; Palazzo, G.; Sabbatini, L.; Fine, D.; Dodabalapur, A.; Cioffi, N.; et al. Carbon Based Materials for Electronic Bio-Sensing. Mater. Today 2011, 14, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Spinks, G.M.; Kim, S.J. Carbon Nanotube Yarn for Fiber-Shaped Electrical Sensors, Actuators, and Energy Storage for Smart Systems. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1902670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scidà, A.; Haque, S.; Treossi, E.; Robinson, A.; Smerzi, S.; Ravesi, S.; Borini, S.; Palermo, V. Application of Graphene-Based Flexible Antennas in Consumer Electronic Devices. Mater. Today 2018, 21, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, F.; Liu, L.; Leng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H. A Humidity-Driven Flexible Carbon Nitride Film with Multiple Deformations. Smart Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 105007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Nie, M.; Wang, Q. Facile Fabrication of Electrically Conductive Low-Density Polyethylene/Carbon Fiber Tubes for Novel Smart Materials via Multiaxial Orientation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghdi, T.; Golmohammadi, H.; Yousefi, H.; Hosseinifard, M.; Kostiv, U.; Horák, D.; Merkoçi, A. Chitin Nanofiber Paper toward Optical (Bio)Sensing Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 15538–15552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, R.; Zhong, J.; Fei, L.; Cai, W.; Guan, Q.; Li, W.; Li, N.; Chen, Y.; Cai, L.; et al. Red/Orange Dual-Emissive Carbon Dots for pH Sensing and Cell Imaging. Nano Res. 2019, 12, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyne, A.; Layek, S.; Patra, A.; Sarkar, N. An Easy and Smart Way to Explore the Light-Emitting Responses of Carbon Dot and Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Assembly: White Light Generation and pH-Dependent Reversible Photoswitching. J. Mater. Chem. C 2019, 7, 6414–6425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Tang, Y.; Gao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Q. Green Anhydrous Assembly of Carbon Dots via Solar Light Irradiation and Its Multi-Modal Sensing Performance. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 165, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.; Zhou, L. One-Step Sonochemical Synthesis of Versatile Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots for Sensitive Detection of Fe2+ Ions and Temperature in Vitro. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 101, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, K.; Gao, X.; Feng, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, H. Carbon Dots with Dual-Emissive, Robust, and Aggregation-Induced Room-Temperature Phosphorescence Characteristics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Fu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.; Wang, A.; Li, C.; Shan, G.; Liu, Y. Bidirectional Photochromism via Anchoring of Carbon Dots to TiO2 Porous Films. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 6262–6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Yang, X.; Zou, B.; Yang, B.; Lu, S. Pressure-Triggered Aggregation-Induced Emission Enhancement in Red Emissive Amorphous Carbon Dots. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Xiao, X.; Zhou, C.; Lyu, F.; Fu, L.; Wang, C.; Ruan, S. Large-Scale Synthesis of Carbon Dots/ TiO2 Nanocomposites for the Photocatalytic Color Switching System. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 1819–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, S.; Xiao, G.; Sui, L.; Feng, T.; Yong, X.; Zhu, S.; Li, B.; Liu, Z.; Zou, B.; Jin, M.; et al. Piezochromic Carbon Dots with Two-Photon Fluorescence. Angew. Chem. 2017, 129, 6283–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, T.; Feng, T.; Ma, Z.; Cao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tao, S.; Xiao, G.; Lu, S.; Yang, B.; Zou, B. Insights into Supramolecular-Interaction-Regulated Piezochromic Carbonized Polymer Dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5072–5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, P.; Han, D.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Shen, D.; Xiao, G.; Zou, B.; Qu, S. Surface Related Intrinsic Luminescence from Carbon Nanodots: Solvent Dependent Piezochromism. Nanoscale Horiz. 2019, 4, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhang, L.; Van Vliet, K.; Miserez, A.; Holten-Andersen, N. White Light-Emitting Multistimuli-Responsive Hydrogels with Lanthanides and Carbon Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10409–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, D. Lanthanide Based White-Light-Emitting Hydrogel Mediated by Fluorescein and Carbon Dots with High Quantum Yield and Multi-Stimuli Responsiveness. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3380–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Ni, H.; Yang, Y.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Cao, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, W.; Tang, Y. Smart Nanoprobe Based on Two-Photon Sensitized Terbium-Carbon Dots for Dual-Mode Fluorescence Thermometer and Antibacterial. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1792–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Mao, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, S. Multi-Stimuli Responsive Nanosystem Modified by Tumor-Targeted Carbon Dots for Chemophototherapy Synergistic Therapy. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 552, 639–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Z.; Lei, B.; Zhuang, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Z.; Hu, C. Hydrophobic Carbon Dots with Blue Dispersed Emission and Red Aggregation-Induced Emission. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, H.; Yang, M.; Xing, L.; Dong, W.; Li, A.; Zheng, H.; Wang, G. Smart Integration of Carbon Quantum Dots in Metal-Organic Frameworks for Fluorescence-Functionalized Phase Change Materials. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 18, 349–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, R.; Chen, M.; Cui, X.; Wang, Q.; Liu, X.; Geng, B. Simultaneous and Reversible Triggering of the Phase Transfer and Luminescence Change of Amidine-Modified Carbon Dots by CO2. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 22851–22857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, S.; Azad, F.; Zhao, L.; Su, S. A Simple Method for the Preparation of Multi-Color Carbon Quantum Dots by Using Reversible Regulatory Color Transformation. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthamizhan, A.; Fragouli, D.; Balusamy, B.; Patil, B.; Palei, M.; Sabella, S.; Uyar, T.; Athanassiou, A. Hydrochromic Carbon Dots as Smart Sensors for Water Sensing in Organic Solvents. Nanoscale Adv. 2019, 1, 4258–4267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, D.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Liao, L.; Xiao, X.; Cheng, H. Synthesis of Multicolor Carbon Dots Based on Solvent Control and Its Application in the Detection of Crystal Violet. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, M.-J.; Park, S.-Y. Carbon-Dot-Based Ratiometric Fluorescence Glucose Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lu, W.; Liu, Y.; Han, H.; Gong, X.; Li, L.; Shuang, S.; Dong, C. One-Step Synthesis of a Dual-Emitting Carbon Dot-Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for the Visual Assay of Pb2+ and PPi and Development of a Paper Sensor. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 5502–5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Q.; Su, R.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, R.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Xu, M.; Fei, L.; Xu, Q. Highly Fluorescent Dual-Emission Red Carbon Dots and Their Applications in Optoelectronic Devices and Water Detection. New J. Chem. 2019, 43, 3050–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xu, D.; Yuan, H.; Luo, Q.; Tang, S.; Liu, L.; Wu, Y. A Novel Fluorescent Nanocellulosic Hydrogel Based on Carbon Dots for Efficient Adsorption and Sensitive Sensing in Heavy Metals. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 27081–27088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chekini, M.; Krivoshapkina, E.; Shkodenko, L.; Koshel, E.; Shestovskaya, M.; Dukhinova, M.; Kheiri, S.; Khuu, N.; Kumacheva, E. Nanocolloidal Hydrogel with Sensing and Antibacterial Activities Governed by Iron Ion Sequestration. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 10066–10075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, L.J.; Omer, K.M. Dual Functional Highly Luminescence B, N Co-Doped Carbon Nanodots as Nanothermometer and Fe 3+ /Fe 2+ Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Ding, L.; Lin, H.; Wu, W.; Huang, J. A Novel Optical Fiber Glucose Biosensor Based on Carbon Quantum Dots-Glucose Oxidase/Cellulose Acetate Complex Sensitive Film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 146, 111760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Yang, H.-F.; Shao, G.; Gan, F. Highly Selective Fluorescent Carbon Dots Probe for Mercury(II) Based on Thymine–Mercury(Ii)–Thymine Structure. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 3982–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, F.; Bai, Z.; Ma, T.; Sun, X.; Zu, F.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L. Surface Modification of Carbon Quantum Dots by Fluorescein Derivative for Dual-Emission Ratiometric Fluorescent Hypochlorite Biosensing and in Vivo Bioimaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 296, 126638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaraki, R.; Sadeghinejad, N. Microwave Assisted Synthesis of Doped Carbon Dots and Their Application as Green and Simple Turn off–on Fluorescent Sensor for Mercury (II) and Iodide in Environmental Samples. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 153, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathumsuwan, T.; Jamnongsong, S.; Sampattavanich, S.; Paoprasert, P. Preparation of Carbon Dots from Succinic Acid and Glycerol as Ferrous Ion and Hydrogen Peroxide Dual-Mode Sensors and for Cell Imaging. Opt. Mater. 2018, 86, 517–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Chakma, B.; Jain, P.; Goswami, P. Protein-Induced Fluorescence Enhancement Based Detection of Plasmodium Falciparum Glutamate Dehydrogenase Using Carbon Dot Coupled Specific Aptamer. ACS Comb. Sci. 2018, 20, 350–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Bai, Y.; Wang, H.; Qin, J.; Liu, H.; Feng, F. Development of a Novel Fluorescence Ratiometric Glucose Sensor Based on Carbon Dots and a Potential Fluorophore m -Dihydroxybenzene. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5380–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Liu, X.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, H.; Fan, H.; Zhang, X. Exploring of Multicolor Emissive Carbon Dots with Novel Double Emission Mechanism. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 277, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Meng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, M.; Zhu, B.; Chai, F.; Wang, C.; Su, Z. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots for the Detection of Mercury Ions in Living Cells and Visualization of Latent Fingerprints. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 6824–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Lv, R.; Su, J.; Li, H.; Yang, B.; Gu, W.; Liu, X. A Dual-Emission Nano-Rod MOF Equipped with Carbon Dots for Visual Detection of Doxycycline and Sensitive Sensing of– MnO4-. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 4766–4772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhati, A.; Raj Anand, S.; Saini, D.; Khare, P.; Dubey, P.; Kumar Sonkar, S. Self-Doped Nontoxic Red-Emitting Mg–N-Embedded Carbon Dots for Imaging, Cu(II) Sensing and Fluorescent Ink. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 19548–19556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishnan, K.; Panneerselvam, P. Green Synthesis of Surface-Passivated Carbon Dots from the Prickly Pear Cactus as a Fluorescent Probe for the Dual Detection of Arsenic(III) and Hypochlorite Ions from Drinking Water. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 30455–30467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Liu, S.; Xie, Y.; Bi, J.; Li, Y.; Song, Y.; Cheng, S.; Li, D.; Tan, M. Facile One-Step Synthesis of Highly Luminescent N-Doped Carbon Dots as an Efficient Fluorescent Probe for Chromium(vi) Detection Based on the Inner Filter Effect. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 3729–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, C.; Tong, D.; Wu, Q.; Jiang, K.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. Red Emitting and Highly Stable Carbon Dots with Dual Response to pH Values and Ferric Ions. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L.; Zhou, T.; Liu, M.; Huang, N.; Li, Y.; Ding, L.; et al. Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Carbon Dots for “Turn-on” Fluorometric Determination of Hg(II) via Aggregation-Induced Emission. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Tan, D.; Xu, Z.; Mei, T.; Li, J.; Xue, L.; Wang, X. Green Emitting N,S-Co-Doped Carbon Dots for Sensitive Fluorometric Determination of Fe(III) and Ag(I) Ions, and as a Solvatochromic Probe. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Ren, D.; Chai, Y.; Cheng, X.; Mei, J.; Bao, J.; Wei, F.; Xu, G.; Hu, Q.; Cen, Y. Dual-Emission Carbon Dots-Based Fluorescent Probe for Ratiometric Sensing of Fe(III) and Pyrophosphate in Biological Samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yuan, X.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Jiang, Z. A Novel Fluorescence Aptamer Biosensor for Trace Pb(II) Based on Gold-Doped Carbon Dots and DNAzyme Synergetic Catalytic Amplification. J. Lumin. 2020, 221, 117056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, L.; Jia, J.; Eltayeb, O.; Lu, W.; Tang, Y.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Dual Photoluminescence Emission Carbon Dots for Ratiometric Fluorescent GSH Sensing and Cancer Cell Recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18250–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuang, E.; Mao, Q.-X.; Wang, J.-H.; Chen, X.-W. Carbon Dots with Tunable Dual Emissions: From the Mechanism to the Specific Imaging of Endoplasmic Reticulum Polarity. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 6852–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Lu, W.; Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Han, H.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Orange-Emitting N-Doped Carbon Dots as Fluorescent and Colorimetric Dual-Mode Probes for Nitrite Detection and Cellular Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2123–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.; Ren, G.; Yu, L.; Zhu, B.; Chai, F.; Chen, L. The Carbon Dots as Colorimetric and Fluorescent Dual-Readout Probe for 2-Nitrophenol and 4-Nitrophenol Detection. J. Lumin. 2019, 207, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ma, Q.; Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Feng, F.; Shuang, S. Novel Single Excitation Dual-Emission Carbon Dots for Colorimetric and Ratiometric Fluorescent Dual Mode Detection of Cu2+ and Al3+ Ions. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 38568–38575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yi, C. Facile Synthesis of pH-Responsive Gadolinium(III)-Doped Carbon Nanodots with Red Fluorescence and Magnetic Resonance Properties for Dual-Readout Logic Gate Operations. Carbon 2020, 166, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Duan, W.; Ren, C.; Wu, J.; Liu, D.; Chen, H. A Dual-Mode Sensor for Colorimetric and “Turn-on” Fluorescent Detection of Ascorbic Acid. Dyes Pigment. 2018, 149, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yan, X.; Lu, G.; Su, X. Carbon Dot-Based Bioplatform for Dual Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensing of Organophosphate Pesticides. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 260, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, X.; Pan, W.; Yu, G.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J. A Carbon Dots/Rutin System for Colorimetric and Fluorimetric Dual Mode Detection of Al3+ in Aqueous Solution. Analyst 2018, 143, 5467–5473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, G.; Lu, D.; Tang, Y.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q. Smart Choice of Carbon Dots as a Dual-Mode Onsite Nanoplatform for the Trace Level Detection of Cr2O72-. Dyes Pigment. 2019, 163, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, H.; Bai, Y.; Qin, J.; Feng, F. Colorimetric and Ratiometric Fluorescence Dual-Mode Sensing of Glucose Based on Carbon Quantum Dots and Potential UV/Fluorescence of o-Diaminobenzene. Sensors 2019, 19, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qu, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xie, Y.; Cai, J.; Zha, G.; Jing, S. N, P-Co-Doped Carbon Dots as a Dual-Mode Colorimetric/Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor for Formaldehyde and Cell Imaging via an Aminal Reaction-Induced Aggregation Process. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, F.; Yao, W.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, S.; Zheng, L.; Lin, X. Carbon Nitride Quantum Dot-Enhanced Chemiluminescence of Hydrogen Peroxide and Hydrosulfite and Its Application in Ascorbic Acid Sensing. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, S. Carbon Dots-Enhanced Chemiluminescence Method for the Sensitive Determination of Iodide. Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Hallaj, T.; Manzoori, J.L.; Shahbazsaghir, T. An Amplified Chemiluminescence System Based on Si-Doped Carbon Dots for Detection of Catecholamines. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 201, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallaj, T.; Amjadi, M.; Song, Z.; Bagheri, R. Strong Enhancement of the Chemiluminescence of the Cu(II)- H2O2 System on Addition of Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots, and Its Application to the Detection of H2O2 and Glucose. Microchim. Acta 2017, 185, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.N.A.; Dou, X.; Khan, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Lin, J.-M. N-Doped Carbon Dots/H2O2 Chemiluminescence System for Selective Detection of Fe2+ Ion in Environmental Samples. Talanta 2019, 196, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, S.; Liu, H.; Du, Y. A Carbon Quantum Dots-Enhanced Chemiluminescence Method for the Determination of Gallic Acid in Food Samples. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2018, 65, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Jia, Y.; Cao, J.; Li, G.; Ren, H.; Li, H.; Yao, H. Carbon Dots-Enhanced Luminol Chemiluminescence and Its Application to 2-Methoxyestradiol Determination. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-T.; Zhang, W.-S.; Wang, H.; Ma, S.-H.; Liu, Y.-M. A Novel Nitrogen and Sulfur Co-Doped Carbon Dots- H2O2 Chemiluminescence System for Carcinoembryonic Antigen Detection Using Functional HRP-Au@Ag for Signal Amplification. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 219, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, B.; Su, Y.; Duan, Y.; Chen, S.; Zuo, W. A Nanocomposite Prepared from Copper(II) and Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots with Peroxidase Mimicking Properties for Chemiluminescent Determination of Uric Acid. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Liu, G.; Yan, M.; Ye, J.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; Yang, X. Cu2+ Enhanced Chemiluminescence of Carbon Dots- H2O2 System in Alkaline Solution. Talanta 2020, 208, 120380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amjadi, M.; Hallaj, T.; Mirbirang, F. A Chemiluminescence Reaction Consisting of Manganese(IV), Sodium Sulfite, and Sulfur- and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots, and Its Application for the Determination of Oxytetracycline. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachu, V.; Goswami, P. Bioelectrochemiluminescence as an Analytical Signal of Extreme Sensitivity. In Advanced Materials and Techniques for Biosensors and Bioanalytical applications, 1st ed.; Goswami, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020; pp. 233–250. ISBN 978-1-00-308385-6. [Google Scholar]
- Venkateswara Raju, C.; Kalaiyarasan, G.; Paramasivam, S.; Joseph, J.; Senthil Kumar, S. Phosphorous Doped Carbon Quantum Dots as an Efficient Solid State Electrochemiluminescence Platform for Highly Sensitive Turn-on Detection of Cu2+ Ions. Electrochim. Acta 2020, 331, 135391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Shang, L.; Ma, R.; Jia, L.; Jia, W.; Wang, H.; Niu, L. Perylenetetracarboxylic Acid and Carbon Quantum Dots Assembled Synergistic Electrochemiluminescence Nanomaterial for Ultra-Sensitive Carcinoembryonic Antigen Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 103, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, Q.; Nie, G. An Ultrasensitive Electrochemiluminescence Assay for Hg2+ through Graphene Quantum Dots and Poly(5-Formylindole) Nanocomposite. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 282, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Q. Wavelength-Dependent Surface Plasmon Coupling Electrochemiluminescence Biosensor Based on Sulfur-Doped Carbon Nitride Quantum Dots for K-RAS Gene Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 13780–13786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Liang, W.; Wang, H.; Zhuo, Y.; Chai, Y.; Yuan, R. Anodic Electrochemiluminescence of Carbon Dots Promoted by Nitrogen Doping and Application to Rapid Cancer Cell Detection. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 1379–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, A.; Yu, Y.; Chai, Y.; Zhuo, Y.; Yuan, R. Electrochemiluminescent Carbon Dot-Based Determination of MicroRNA-21 by Using a Hemin/G-Wire Supramolecular Nanostructure as Co-Reaction Accelerator. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Gong, J. Bifunctional S, N-Codoped Carbon Dots-Based Novel Electrochemiluminescent Bioassay for Ultrasensitive Detection of Atrazine Using Activated Mesoporous Biocarbon as Enzyme Nanocarriers. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1073, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaiyarasan, G.; Raju, C.V.; Veerapandian, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Joseph, J. Impact of Aminated Carbon Quantum Dots as a Novel Co-Reactant for Ru(Bpy)32+: Resolving Specific Electrochemiluminescence for Butein Detection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 539–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Precursors | Synthesis Route/Temp/Time | Types of CDs | Size(nm)/QY (%) | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QR, NaOH | Ultrasonic | CDs | 2.99/27.7 | [11] | |
| RT/6 h | |||||
| CA, PEG | Ultrasonic | CDs | 2.38/NA | [12] | |
| RT/1 h | |||||
| Soybean | Ultrasonic | NBDs | 24/16.7 | [13] | |
| 2 h | |||||
| Graphite, ethanol | Laser ablation | CDs | Fs | 1.4/NA | [14] |
| 800 nm, 150 fs | 2Fs | 2/NA | |||
| Fd-2 | 1.1/NA | ||||
| Fd-10 | 1.5/NA | ||||
| DEASA, H3PO4 | Hydrothermal | CDs | 4.69/19.4 | [15] | |
| 200 °C/2 h | |||||
| Jeera | Hydrothermal | CDs | 6–9/5.33 | [16] | |
| 250 °C/6 h | |||||
| Tobacco | Hydrothermal | CDs | 2.14 ± 0.3/27.9 | [17] | |
| 300 °C/3 h | |||||
| Cryptococcus | Hydrothermal | CDs | 4–9/14.13 | [18] | |
| 160 °C/1 h | |||||
| TMA | Hydrothermal | CDs | 4.3/13.4 | [19] | |
| 260 °C/12 h | |||||
| Agaricus bisporus | Hydrothermal | CDs | NA/4.2 | [20] | |
| 160 °C/12 h | |||||
| Chitosan, AA | Hydrothermal | CQDs | 5/NA | [21] | |
| 180 °C/12 h | |||||
| CA, EA | Hydrothermal | CDs | 4/NA | [22] | |
| 180 °C/8 h | |||||
| Folic acid, Glucose | Hydrothermal210 °C/12 h | CDs1 | 1.6/23.5 | [23] | |
| CDs2 | 2.6/42.8 | ||||
| Xylose, H3PO4, | Microwave | CDs1 | 6.80/73.6 | [24] | |
| m-PD | 220 °C/10 min | ||||
| Xylose, H3PO4, | Microwave | CDs2 | 7.23/56.1 | ||
| m-PD | 200 °C/10 min | ||||
| Xylose, H3PO4, | Microwave | CDs3 | 6.80/40.9 | ||
| m-PD | 180 °C/10 min | ||||
| Xylose, m-PD | Microwave | CDs4 | 9.88/65.3 | ||
| HNO3 | 220 °C/10 min | ||||
| Xylose, m-PD | Microwave | CDs5 | 8.83/49.5 | ||
| CH3COOH | 220 °C/10 min | ||||
| Xylose, m-PD | Microwave | CDs6 | 6.87/42.8 | ||
| 220 °C/10 min | |||||
| Xylose, m-PD, Na3PO4 | Microwave | CDs7 | 16.37/8 | ||
| 220 °C/10 min | |||||
| Xylose, m-PD, NaOH | Microwave | CDs8 | 10.70/6.8 | ||
| 220 °C/10 min | |||||
| CA, EDA | Microwave | CDs | 4/24 | [25] | |
| 720 W/2 min | |||||
| CA, urea | Microwave | CDs | NA/NA | [26] | |
| 750 W/5 min | |||||
| Anthracite coal, H2SO4, HNO3 | Pyrolysis in oil bath | CDs | 3.5/NA | [27] | |
| 120 °C/24 h | |||||
| CA, Glu, Asp, lysine | Thermal pyrolysis | CDs | 4/8.8 | [28] | |
| 200 °C/30 min | |||||
| CA, acrylamide | Solvothermal | CDs | 9.5/NA | [29] | |
| 200 °C/4 h | |||||
| CA | Oven | CDs | 3/NA | [30] | |
| 200 °C/1h | |||||
| Precursors | Synthesis Route/Temp/Time | Types of CDs | Size (nm)/QY(%) | Ref | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cryomilled graphite, DMF | Laser ablation | N-CDs | 3/4.05 | [40] | ||
| 800 °C/3 h | ||||||
| 2-aminopyrimidine-5-boronic acid | Laser ablation | N, B-CD | 3/58 | [41] | ||
| 170 mW/1014 Wcm−1 | ||||||
| Graphite rods and ammonia hydroxide | Electrochemical and ultrasonic | N-CDs | 3–5/NA | [42] | ||
| 80 °C/3 h | ||||||
| L-tryptophan, chlorhexidine acetate | Hydrothermal | N-CDs | ~4.0/NA | [43] | ||
| 200 °C/12 h | ||||||
| P. acidus, aq. ammonia | Hydrothermal | N-CDs | 5/12.5 | [44] | ||
| 200 °C/12 h | ||||||
| PVP | Hydrothermal | N-CDs | 6.5/6 | [45] | ||
| 200 °C/6 h | ||||||
| EDA, CuCl2.2H2O | Hydrothermal | Cu-CDs | 1.8/7.8 | [46] | ||
| 180 °C/10 h | ||||||
| Aphen, CA | Hydrothermal | AC-CDs | 25/52 | [47] | ||
| 200 °C/7 h | ||||||
| OPD, ABPA | Hydrothermal | B,N-CDs | 4.09/8.56 | [48] | ||
| 160 °C/6 h | ||||||
| Mn(III)(C5H7O2)3 | Hydrothermal | MnOx-CDs | 5.65 ± 0.30/11.3 | [49] | ||
| 200 °C/12 h | ||||||
| Sucrose, nitrobenzene, nitrosobenzene | Hydrothermal | CD-NO, and CD-NO2 | gCD | 11/21 | [50] | |
| 180°C/12 h | rCD | 13/18 | ||||
| CA, EDA | Microwave | N-CDs | ~5/95, 11 | [51] | ||
| CA, EDA, sodium borate | 300 W/10 min | B-CDs | ~5/63, 9 | |||
| CA, EDA, K2PO4 | P-CDs | ~5/63, 6 | ||||
| p-PDA, EDA | Microwave | N-CDs | 4.8/14 | [52] | ||
| 500 W/20 min | ||||||
| TSCDH, Urea, DMF | Solvothermal | N-CD11 | 4.5/21.6 | [53] | ||
| TSCDH, Urea, DMAC | 160 °C/4 h | N-CD12 | 4.5/18.7 | |||
| TSCDH, Urea, DEF | N-CD21 | 4.5/17.6 | ||||
| H2O2, ethanol, NH3 | Solvothermal | N-CDs | 2.15/56.1 | [54] | ||
| 180 °C/NA | ||||||
| CA, PD | Solvothermal | Y-CDs | 7.2/24 | [55] | ||
| 170 °C/4 h | ||||||
| CA and DAN | Solvothermal | HCP-DB-CDs | 2.4/70 ± 10 | [56] | ||
| 160 °C/6 h | ||||||
| PAA, CuN, HH, (NH4)2S2O8 | Carbonization/polymerization and pyrolyzation | Cu-CDs | 2.8/36 | [57] | ||
| Stirring/24 h and 400 °C/90 min | ||||||
| Willow Catkin, Urea and H2SO4 | Combustion | N,S-CDs | 7.3/14.3 | [58] | ||
| Na2[Cu(EDTA)] and Ascorbic acid | Thermolysis | Cu-CDs | 3.48/9.8 | [59] | ||
| 250 °C/2 h | ||||||
| Precursor and Synthesis Route | Size (QY) | Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Citric acid, urea, and thiourea | 10 nm (19.2%) | Mercury (II) and iodide detection | [144] |
| Microwave-assisted | |||
| Succinic acid and glycerol | 2.3 nm (11%) (Blue-CD) | Fe2+, H2O2 detection and bioimaging | [145] |
| Hydrothermal | 4.6 nm (7%) (Green-CD) | ||
| L-glutamate | 2 nm–4 nm (34%) | Plasmodium falciparum glutamate dehydrogenase detection | [146] |
| Pyrolysis | |||
| Citric acid and ethylenediamine | 3.6 nm (NA) | Detection of glucose | [147] |
| Microwave-assisted hydrothermal | |||
| Citric acid, formamide, and ethanol (E-CD) | 4.5 nm (15.81%—water, 22.43%—DMSO, 25.80%—DMF, 19.42%—methanol) (E-CD) | Fluorescent pH sensor | [148] |
| Citric acid, formamide (N-CD) | |||
| Solvothermal | 5.5 nm (NA) (N-CD) | ||
| Sodium citrate and urea | 3.52 nm (67%) | Mercury ion detection in living cells and visualization of latent fingerprints | [149] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| Citric acid and ethylenediamine | 2 nm (NA) | Doxycycline and MnO4- detection | [150] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| Leaf extract of Bougainvillea | 10.7 nm (~41%) | Bioimaging, detection of Cu (II), and as red-emitting fluorescent ink | [151] |
| Microwave-assisted | |||
| Pricky pear cactus | 5.6 nm (12.7%) | Arsenic (III) and hypochlorite ion detection in drinking water | [152] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| Citric acid and glycine | 2.8 nm (78%) | Detection of chromium (VI) | [153] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| p-phenylenediamine | 3.8 nm (15%) | Detection of pH and Fe3+ | [154] |
| Microwave-assisted | |||
| Glycerol and cysteine | 1–6 nm (3.5%) | Detection of Hg(II) | [155] |
| Microwave-assisted | |||
| Sodium lignosulphonate and p-phenylenediamine | 2.02 nm (11.25%—ethanol, 13.77%—n-propanol, 11.66%—isopropanol, 15.07%—DMF, 14.29%—DMA), 5.12% (water), 5.58% (acetic acid), 5.77% (propionic acid) | Detection of Fe(III), Ag(I) and as a solvatochromic probe | [156] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| Glutathione, sodium citrate, (blue-CDs) and 1,2,4-triaminobenzene (yellow-CDs) | 4.0 nm (Blue-CD) | Detection of Fe3+ and PPi | [157] |
| 2.4 nm (Yellow-CD) | |||
| (N A) | |||
| Hydrothermal (blue-CDs), Solvothermal (yellow CDs) | |||
| Cellulose-based willow catkin biowaste | 7.3 nm (13.3%) | Detection of Fe3+ and bioimaging | [58] |
| Combustion treatment | |||
| Melamine and dithiosalicylic sacid | 6.5 nm (5.96%) | Two-switch-mode luminescence ink | [129] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| Glucose and HAuCl4 | 10 nm (0.15%) | Detection of Pb2+ | [158] |
| Microwave-assisted | |||
| Alizarine carmine | 2.37 ± 0.23 nm (6.3%) | Detection of glutathione and cancer cells. | [159] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| o-phenylenediamine and lysine | CDs-0-2.51 nm | Endoplasmic reticulum polarity | [160] |
| CDs-1-2.55 nm | |||
| CDs-2-3.35 nm | |||
| CDs-3-2.95 nm | |||
| (NA) | |||
| Hydrothermal |
| Precursor and Synthesis Route | Size (QY) | Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2,5-diaminobenzene sulphonic acid, 4-aminophenylboronic acid hydrochloride and Fe3+ | NA (0.7%—in the absence of ascorbic acid, 2.3%—in the presence of ascorbic acid) | Detection of ascorbic acid | [165] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| Folic acid and p-phenylenediamine | 2 nm (8.4%) | Detection of organophosphate pesticide | [166] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| Methylene-bis-acrylamide, p-phenylenediamine, and trifluoroacetic acid | 3.9 ± 0.2 nm (7.5%) | Detection of Al3+ | [167] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| m-phenylenediamine and citric acid | 3–4 nm (65%) | Detection of Cr (VI) | [168] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| Citric acid and ethylenediamine | NA | Detection of glucose | [169] |
| Microwave-assisted hydrothermal | |||
| N-(phosphonomethyl)iminodiacetic acid (PMIDA) and branched PEI | 6.71 nm (15.91%) | Detection of formaldehyde and bioimaging | [170] |
| Hydrothermal |
| Precursor and Synthesis Route | Size (QY) | Target of Detection | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glucose | 4 nm (NA) | Gallic acid | [176] |
| Ultrasonic | |||
| Ethylene glycol | 5 ± 1 nm (NA) | Methoxyestradiol | [177] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| L-cysteine and citric acid | 3.1 nm (NA) | Carcinoembryonic antigen | [178] |
| Pyrolysis | |||
| Citric acid and 1-3-(3,4-Dihyroxyphenyl) alanine (L-DOPA) | 4.5 nm (NA) | Uric acid | [179] |
| Solid phase thermal | |||
| Phloroglucinol | 5.4 nm (NA) | Ascorbic acid | [180] |
| Solvothermal | |||
| Citric acid, L-cysteine, and heteroatoms | 10 nm (80%) | Oxytetracycline | [181] |
| Hydrothermal |
| Precursor and Synthesis Route | Size (QY) | Application | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fullerene (C60) | 3.5 ± 1 nm (NA) | Determination of microRNA-21 | [188] |
| Hydrothermal | |||
| Citric acid and L-cysteine | NA | Detection of atrazine | [189] |
| Pyrolysis | |||
| Melamine | 2 nm (NA) | Detection of butein | [190] |
| Hydrothermal |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Das, S.; Ngashangva, L.; Goswami, P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines 2021, 12, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010084
Das S, Ngashangva L, Goswami P. Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines. 2021; 12(1):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010084
Chicago/Turabian StyleDas, Smita, Lightson Ngashangva, and Pranab Goswami. 2021. "Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications" Micromachines 12, no. 1: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010084
APA StyleDas, S., Ngashangva, L., & Goswami, P. (2021). Carbon Dots: An Emerging Smart Material for Analytical Applications. Micromachines, 12(1), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12010084