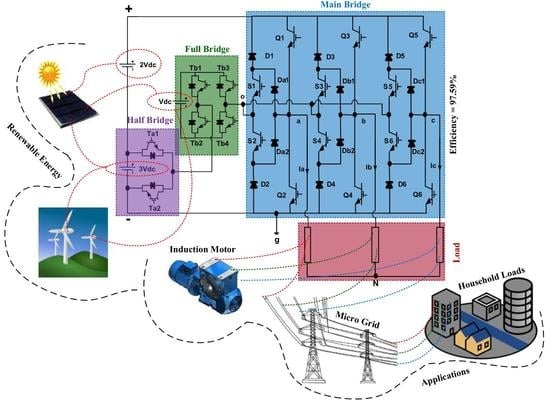
Three-Phase Six-Level Multilevel Voltage Source Inverter: Modeling and Experimental Validation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- The advantages of both multilevel DC-links and H-bridge circuits have been inherited by the suggested topology. The proposed MLI has been able to lower total voltage stress and generate greater voltage levels with fewer components because of this smart design.
- Since it does not contain switched capacitors, the proposed MLI does not require a complex control approach or additional circuits to deal with voltage balancing or excessive power losses.
- Depending on the application needs, the proposed topology can be modified to achieve higher voltage levels.
- The suggested MLI’s modularity and smart switching arrangements have allowed it to perform in four different ways depending on the modulation indices. This has provided the MLI with more flexibility and reliability.
2. Operating Principle of Three-Phase MLI
2.1. Proposed Topology
2.2. Extended Structure
2.3. Efficiency Calculation
2.4. Switching Pulses Generation Using Nearest Vector Modulation
3. Simulation Results
4. Comparative Analysis
5. Experimental Validation and Results
5.1. Experimental Setup
5.2. Experimental Results
6. Conclusions
- The proposed MLI utilized a reduced number of power electric components compared to classical and other recently developed MLIs.
- The modularity of the MLI makes it a suitable candidate for high voltage operations.
- The operating efficiency of the MLI is 97.59% and effectively follows the IEEE 1547 standard, making it suitable to be applied as an interconnected device in grid systems.
- The low current THD of 5.8% would allow this inverter to be utilized in the grid’s current and voltage compensation systems, including shunt active power filters (SAPFs), voltage restorers and unified power quality conditioners (UPQCs).
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shayestegan, M.; Shakeri, M.; Abunima, H.; Reza, S.S.; Akhtaruzzaman, M.; Bais, B.; Mat, S.; Sopian, K.; Amin, N. An overview on prospects of new generation single-phase transformerless inverters for grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 82, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X. A set of multilevel modular medium-voltage high power converters for 10-MW wind turbines. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Energy 2014, 5, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, S.T.; Hasan, M.K.; Islam, J.; El-Ebiary, Y.A.B.; Nebhen, J.; Hossain, M.; Alam, K.; Vo, N. A diamond shaped multilevel inverter with dual mode of operation. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 59873–59887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.N.; Ishak, D.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Ooi, C.A. An asymmetrical multilevel inverter with optimum number of components based on new basic structure for photovoltaic renewable energy system. Sol. Energy 2020, 204, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannan, M.A.; Ali, J.A.; Mohamed, A.; Uddin, M.N. A random forest regression based space vector PWM inverter controller for the induction motor drive. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 64, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, K.H. An effective voltage controller for quasi-Z-source inverter-based STATCOM with constant DC-link voltage. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 8137–8150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jibhakate, C.; Chaudhari, M.; Renge, M. A reduced switch AC–AC converter with the application of D-STATCOM and induction motor drive. Electronics 2018, 7, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.; Kang, D.; Lee, J. A study on the improved capacitor voltage balancing method for modular multilevel converter based on hardware-in-the-loop simulation. Electronics 2019, 8, 1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katebi, R.; He, J.; Weise, N. An advanced three-level active neutral-point-clamped converter with improved fault-tolerant capabilities. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 6897–6909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nair, V.; Rahul, A.; Kaarthik, S.; Kshirsagar, A.; Gopakumar, K. Generation of higher number of voltage levels by stacking inverters of lower multilevel structures with low voltage devices for drives. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadaei, E.; Kaviani, M.; Iranian, M.; Pouresmaeil, E. The P-type module with virtual DC links to increase levels in multilevel inverters. Electronics 2019, 8, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meraj, S.T.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Hasan, K.; Masaoud, A. A hybrid T-type (HT-type) multilevel inverter with reduced components. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2021, 12, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahato, B.; Mittal, S.; Majumdar, S.; Jana, K.; Nayak, P.K. Multilevel inverter with optimal reduction of power semi-conductor switches. In Renewable Energy and Its Innovative Technologies; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Lin, W.; Cen, D.; Liu, J. Novel K-type multilevel inverter with reduced components and self-balance. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2020, 8, 4343–4354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.P.; Kumar, L.; Gupta, S. Hybrid topology of symmetrical multilevel inverter using less number of devices. IET Power Electron. 2015, 8, 2125–2135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayarajan, P.; Shunmugalatha, A.; Sathik, J. A new hybrid multilevel inverter topology for medium and high voltage applications. Appl. Math. Inf. Sci. 2017, 11, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaei, E.; Laali, S.; Alilu, S. Cascaded multilevel inverter with series connection of novel h-bridge basic units. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2014, 61, 6664–6671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaoud, A.; Mekhilef, S.; Ping, H.W.; Wong, K.I. A simplified structure for three-phase 4-level inverter employing fundamental frequency switching technique. IET Power Electron. 2017, 10, 1870–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raushan, R.; Mahato, B.; Jana, K.C. Comprehensive analysis of a novel three-phase multilevel inverter with minimum number of switches. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 1600–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hota, A.; Jain, S.; Agarwal, V. An optimized three-phase multilevel inverter topology with separate level and phase sequence generation part. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 7414–7418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena, M.; Kouro, S.; Dieckerhoff, S.; Rodriguez, J. Reduced multilevel converter: A novel multilevel converter with a reduced number of active switches. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajan, V.; Somasundaram, P.; Kumar, K.R. Simulation and analysis of novel extendable multilevel inverter topology. J. Circuits Syst. Comput. 2019, 28, 1950089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, M.N.; Ishak, D.; Zainuri, M.A.A.M.; Ooi, C.A. Multilevel inverter with improved basic unit structure for symmetric and asymmetric source configuration. IET Power Electron. 2020, 13, 1445–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meraj, S.T.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Hasan, K.; Masaoud, A. Single phase 21 level hybrid multilevel inverter with reduced power components employing low frequency modulation technique. Int. J. Power Electron. Drive Syst. 2020, 11, 810–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Lai, J.-S.; Peng, F.Z. Multilevel inverters: A survey of topologies, controls, and applications. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 724–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmadi, D.; Wang, J. Online selective harmonic compensation and power generation with distributed energy resources. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 3738–3747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, J.; Meraj, S.T.; Masaoud, A.; Mahmud, A.; Nazir, A.; Kabir, M.A.; Hossain, M.; Mumtaz, F. Opposition-based quantum bat algorithm to eliminate lower-order harmonics of multilevel inverters. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 103610–103626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oskouei, A.B.; Dehghanzadeh, A.R. Generalized space vector controls for MLZSI. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2015, 6, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayago, J.A.; Bruckner, T.; Bernet, S. How to select the system voltage of mv drives—A comparison of semiconductor expenses. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3381–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Lin, K.; Li, J.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, X.-P. Cost analysis and comparison between modular multilevel converter (MMC) and modular multilevel matrix converter (M3C) for offshore wind power transmission. In Proceedings of the 15th IET International Conference on AC and DC Power Transmission (ACDC 2019), Coventry, UK, 5–7 February 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Tseng, M.-L.; Wong, W.-P.; Liu, B. Distributed systematic grid-connected inverter using IGBT junction temperature predictive control method: An optimization approach. Symmetry 2020, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sa | Q1 | S1 | S2 | Q2 | Ta1 | Ta2 | Tb1 | Tb2 | Tb3 | Tb4 | Vag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +5Vdc |
| 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +4Vdc |
| 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | +3Vdc |
| 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | +2Vdc |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | +Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Sa | Q1 | S1 | S2 | Q2 | Ta1 | Ta2 | Tb1 | Tb2 | Tb3 | Tb4 | Vag |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | +5Vdc |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Components | NPC | FC | CHB | [9] | [15] | Proposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Switches | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 2 log2 (N − 1) + 12 | 12 [log3 (N/2) − 1] + 18 | 4 log3 [2/3 (N) − 1] + 14 |
| Diodes | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 2 log2 (N − 1) + 12 | 12 [log3 (N/2) − 1] + 18 | 4 log3 [2/3 (N) − 1] + 14 |
| Clamping diodes | 6 (N − 2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gate drivers | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 2 log2 (N − 1) + 9 | 12 [log3 (N/2) − 1] + 18 | 4 log3 [2/3 (N) − 1] + 11 |
| DC supplies | N − 1 | N – 1 | 3 (N − 1)/2 | 1 + log2(N − 1) | 3 [log3 (N/2) − 1] + 4 | log3 [2/3 (N) − 1] + 2 |
| Capacitors | 0 | 3 (N − 2) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Control signals | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 6 (N − 1) | 2 log2 (N − 1) + 9 | 12 [log3 (N/2) − 1] + 18 | 4 log3 [2/3 (N) − 1]+11 |
| Switches | Main Bridge | Bidirectional | Half-Bridge | Full-Bridge |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage rating | (N − 1) Vdc | (N − 2) Vdc | 3n (Vdc) | 3(n − 1) (Vdc) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Meraj, S.T.; Yahaya, N.Z.; Hasan, K.; Hossain Lipu, M.S.; Masaoud, A.; Ali, S.H.M.; Hussain, A.; Othman, M.M.; Mumtaz, F. Three-Phase Six-Level Multilevel Voltage Source Inverter: Modeling and Experimental Validation. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091133
Meraj ST, Yahaya NZ, Hasan K, Hossain Lipu MS, Masaoud A, Ali SHM, Hussain A, Othman MM, Mumtaz F. Three-Phase Six-Level Multilevel Voltage Source Inverter: Modeling and Experimental Validation. Micromachines. 2021; 12(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091133
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeraj, Sheikh Tanzim, Nor Zaihar Yahaya, Kamrul Hasan, Molla Shahadat Hossain Lipu, Ammar Masaoud, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Aini Hussain, Muhammad Murtadha Othman, and Farhan Mumtaz. 2021. "Three-Phase Six-Level Multilevel Voltage Source Inverter: Modeling and Experimental Validation" Micromachines 12, no. 9: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091133
APA StyleMeraj, S. T., Yahaya, N. Z., Hasan, K., Hossain Lipu, M. S., Masaoud, A., Ali, S. H. M., Hussain, A., Othman, M. M., & Mumtaz, F. (2021). Three-Phase Six-Level Multilevel Voltage Source Inverter: Modeling and Experimental Validation. Micromachines, 12(9), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi12091133