High-Q MEMS Resonators for Laser Beam Scanning Displays
Abstract
:1. Introduction

| WVGA | HD720 | XGA | HD1080 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pixel resolution | 852 × 480 | 1,280 × 720 | 1,024 × 768 | 1,920 × 1,080 |
| corresponding line scan frequency @ 60 Hz image refresh [lines/second] | 28,800 | 43,200 | 46,080 | 64,800 |
| required MEMS oscillation frequency raster scan mode @ 80% duty cycle [kHz] | 18 | 27 | 28.8 | 40.5 |
| required MEMS oscillation frequency raster scan mode @ 60% duty cycle [kHz] | 24 | 36 | 38.4 | 54 |
| required MEMS oscillation frequency Lissajous scan mode [kHz] | 22.6 | 33.9 | 36.2 | 50.9 |
 (1)
(1) | WVGA | HD720 | XGA | HD1080 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pixel resolution | 852 × 480 | 1,280 × 720 | 1,024 × 768 | 1,920 × 1,080 |
| required theta-D-product [degrees*mm] | +/−10 | +/−15 | +/−12 | +/−22.5 |
2. MEMS Mirror Concept

3. MEMS Mirror Fabrication Process


4. Fabrication of Glass Cap Wafers

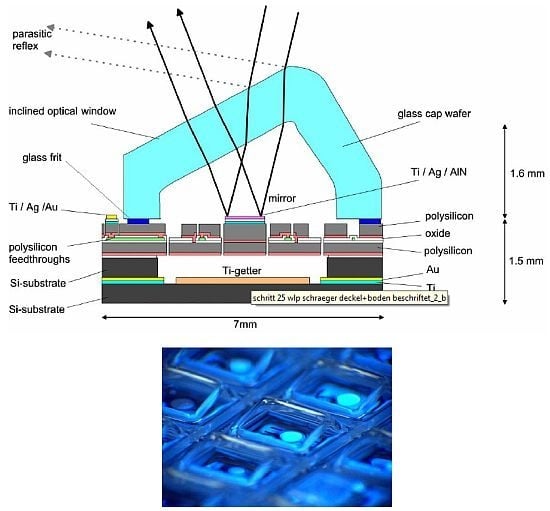
5. Wafer Level Vacuum Packaging Process

6. Characterization of Vacuum Packaged Resonant MEMS Scanning Mirrors
6.1. Qualitative Result

6.2. Measurement Setup for Wafer Level Testing of Vacuum Packaged MEMS Mirrors

6.3. Characterization of 1D-Fast Axis Scanners

| Design #1 | Design #2 | Design #3 | Design #4 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mirror aperture size | 0.8 mm | 1.0 mm | 1.0 mm | 1.0 mm |
| Mirror thickness | 60 µm | 60 µm | 60 µm | 60 µm |
| Width of beams | 47 µm | 44 µm | 65 µm | 65 µm |
| Length of beams | 1,440 µm | 1,450 µm | 1,450 µm | 600 µm |
| Thickness of beams | 60 µm | 60 µm | 60 µm | 60 µm |
| Resonant frequency | 30.8 kHz | 16.5 kHz | 25.1 kHz | 38.5 kHz |
| Q-factor | 26,800 | 75,500 | 70,000 | 49,300 |
| Theta-D-product | 17,3 mm × deg | 13.8 mm × deg | 13.8 mm × deg | 10.8 mm × deg |




| (A) = [11] | (B) = [12] | (C) = [13] | (D) = [14] | (E) = [15] | (F) = [16] | (G) = [17] | (H) = [18] |
| (I) = [19] | (J) = this work design #3 | (K) = [20] | (L) = [20] | (M) = this work design #1 | (N) = [21] | (O) = [22] | (P) = this work design #4 |
 is:
is: (2)
(2)  (3)
(3) 
6.4. Characterization of a 2D-Gimbal Mounted Scanner
- Mirror aperture size: 1 mm
- Fast axis resonant frequency: 17.8 kHz
- Slow axis resonant frequency: 0.5 kHz



6.5. Capacitive Phase Feedback and Closed Loop Control


6.6. Lissajous Laser Projection Based on High-Q Scanning Mirrors


6.7. Ongoing Improvements




7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Hofmann, U.; Muehlmann, S.; Witt, M.; Doerschel, K.; Schuetz, R.; Wagner, B. Electrostatically driven micromirrors for a miniaturized confocal laser scanning microscope. Proc. SPIE 1999, 3878, 29–38. [Google Scholar]
- Conant, R.A.; Hagelin, P.M.; Krishnamoorthy, U.; Solgaard, O.; Lau, K.Y.; Muller, R.S. A raster-scanning full-motion video display using polysilicon micromachined mirrors. In Proceedings of IEEE Transducers Conference, Sendai, Japan, 7–10 June 1999.
- Urey, H.; Wine, D.; Lewis, J. Scanner design and resolution tradeoffs for miniature scanning displays. In Proceedings of SPIE Conference on Flat Panel Display Technology and Display Metrology, San Jose, CA, USA, 27–29 January 1999; pp. 60–68.
- Yalcinkaya, A.D.; Urey, H.; Brown, D.; Montague, T.; Sprague, R. Two-axis electromagnetic Microscanner for high resolution displays. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 15, 786–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urey, H.; Wine, D.W.; Osborn, T.D. Optical performance requirements for mems-scanner based microdisplays. Proc. SPIE 2000, 4178, 176–185. [Google Scholar]
- Kurth, S.; Kaufmann, C.; Hahn, R.; Mehner, J.; Doetzel, W.; Gessner, T. A novel 24 kHz resonant scanner for high resolution laser display. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5721, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Gokce, S.K.; Holstrom, S.; Brown, D.; Davis, W.O.; Urey, H. A high-frequency comb-actutated resonant mems scanner for microdisplays. In Proceedings of International Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics (OMN), Istanbul, Turkey, 8–11 August 2011.
- Kirsten, M.; Wenk, B.; Ericson, F.; Schweitz, J.A.; Riethmüller, W.; Lange, P. Deposition of thick doped polysilicon films with low stress in an epitaxial reactor for surface micromachining applications. Thin Solid Films 1995, 259, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, P.; Quenzer, H.J.; Bernt, H.; Wagner, B.; Zoberbier, M. A novel micromachining technology for structuring borosilicate glass substrates. In Proceedings of IEEE Transducers Conference, Boston, MA, USA, 8–12 June 2003; pp. 258–261.
- Oldsen, M.; Hofmann, U.; Quenzer, H.J.; Wagner, B. A novel fabrication technology for waferlevel vacuum packaged microscanning mirrors. In Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Electronics Packaging Technology (EPTC), Singapore, 10–12 December 2007; pp. 303–307.
- Wine, D.W.; Helsel, M.P.; Jenkins, L.; Urey, H.; Osborn, T.D. Performance of a biaxial MEMS-based scanner for microdisplay applications. SPIE Vol. 2000, 4178, 186–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.-H.; Choi, M.; Kim, S.-C.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.-H.; Yee, Y.; Bu, J.-U. An electrostatic scanning micromirror with diaphragm mirror plate and diamond-shaped reinforcement frame. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalcinkaya, A.D.; Urey, H.; Brown, D.; Montague, T.; Sprague, R. Two-axis electromagnetic microscanner for high resolution displays. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2006, 1, 968–971. [Google Scholar]
- Arslan, A.; Brown, D.; Davis, W.O.; Holmström, S.; Gokce, S.K.; Urey, H. Comb-actuated resonant torsional microscanner with mechanical amplification. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010, 19, 936–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoda, M.; Isamoto, K.; Chong, C.; Ito, H.; Murata, A.; Kamisuki, S.; Atobe, M.; Toshiyoshi, H. A MEMS 1-D optical scanner for laser projection display using self-assembled vertical combs and scan-angle magnifying mechanism. In Proceedings of Conference on Solid-state Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Seoul, Korea, 5–9 June 2005.
- Kurth, S.; Kaufmann, C.; Hahn, R.; Mehner, J.; Doetzel, W.; Gessner, T. A novel 24-kHz resonant scanner for high-resolution laser display. Proc. SPIE 2005, 5721, 23–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.C.; Chob, J.W.; Muna, Y.K.; Jeong, H.G.; Choi, W.K.; Kima, J.W.; Park, Y.H.; Yoo, J.B.; Lee, J.H. Eye-type scanning mirror with dual vertical combs for laser display. Sens. Actuat. A 2006, 126, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.W.; Park, Y.H.; Ko, Y.C.; Lee, B.L.; Kang, S.J.; Chung, S.W.; Choi, W.K.; Cho, Y.C.; Chang, S.M.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Electrostatic 1D microscanner with vertical combs for HD resolution display. Proc. SPIE 2007, 6466, 64660B:1–64660B:12. [Google Scholar]
- Tachibana, H.; Kawano, K.; Ueda, H.; Noge, H. Vacuum wafer level packaged two-dimensional optical scanner by anodic bonding. In Proceedings of IEEE Conference on MEMS, Sorrento, Italy, 25–29 January 2009.
- Gokce, S.K.; Holmstrom, S.; Brown, D.; Davis, W.O.; Urey, H. A high-frequency comb-actuated resonant MEMS scanner for microdisplays. In Proceedings of Conference on Optical MEMS and Nanophotonics, Istanbul, Turkey, 8–11 August 2011.
- Hsu, S.; Klose, T.; Drabe, C.; Schenk, H. Fabrication and characterization of a dynamically flat high resolution micro-scanner. J. Opt. A: Pure Appl. Opt. 2008, 10, 44005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iseki, T.; Okumura, M.; Sugawara, T. High-speed and wide-angle deflection optical mems scanner using piezoelectric actuation. IEEJ Trans. Elec. Electron. Eng. 2010, 5, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conant, R.A.; Nee, J.T.; Lau, K.Y.; Muller, R.S. A flat high-frequency scanning micromirror. In Proceedings of Hilton Head Solid-State Sensor and Actuator Workshop, Hilton Head Island, SC, USA, June 2000; pp. 6–9.
- Hofmann, U.; Oldsen, M.; Quenzer, H.; Janes, J.; Heller, M.; Weiss, M.; Fakas, G.; Ratzmann, L.; Marchetti, E.; D’Ascoli, F.; et al. Wafer-level vacuum packaged resonant micro-scanning mirrors for compact laser projection displays. In Proceedings of Conference on MOEMS and Miniaturized Systems VII, San Jose, CA, USA, 22–23 January 2008.
© 2012 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Hofmann, U.; Janes, J.; Quenzer, H.-J. High-Q MEMS Resonators for Laser Beam Scanning Displays. Micromachines 2012, 3, 509-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi3020509
Hofmann U, Janes J, Quenzer H-J. High-Q MEMS Resonators for Laser Beam Scanning Displays. Micromachines. 2012; 3(2):509-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi3020509
Chicago/Turabian StyleHofmann, Ulrich, Joachim Janes, and Hans-Joachim Quenzer. 2012. "High-Q MEMS Resonators for Laser Beam Scanning Displays" Micromachines 3, no. 2: 509-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi3020509
APA StyleHofmann, U., Janes, J., & Quenzer, H.-J. (2012). High-Q MEMS Resonators for Laser Beam Scanning Displays. Micromachines, 3(2), 509-528. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi3020509