A Rapid Micromixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Operational Principle and Design
- (1)
- Pre-load the samples. At the initial state, the sample liquids are introduced to the loading chambers.
- (2)
- Deliver the sample liquids to the mixing chamber by increasing the spinning rate of the disc. The vent hole in the figure is needed to release the air as the fluid sample flow into the mixing chamber and pushes air out.
- (3)
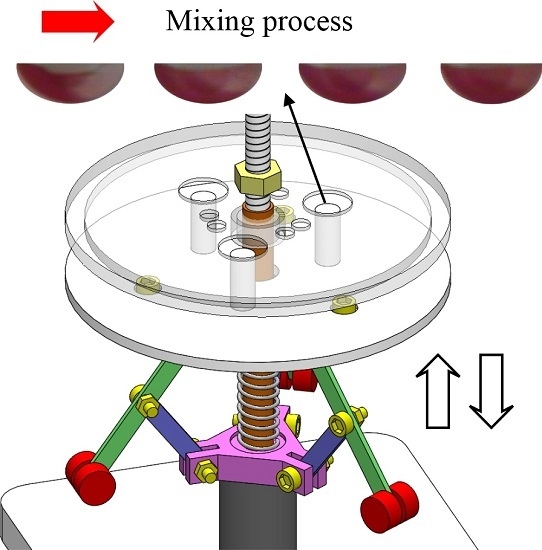
- Chaotic mixing. After samples are introduced into the mixing chamber, the rotational speed of the system is oscillated to drive the actuation disc to move up and down. The pin on in the actuation disc is therefore pressed against the covering membrane of the mixing chamber and then released repeatedly. The fluids in the mixing chamber are therefore agitated to cause chaotic mixing.
3. Experimental Results and Discussions
3.1. Fabrication of the Microfluidic Disc
3.2. Test of the Prototype Micromixer
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, R.H.; Stremler, M.A.; Sharp, K.V.; Olsen, M.G.; Santiago, J.G.; Adrian, R.J.; Aref, H.; Beebe, D.J. Passive mixing in a three-dimensional serpentine microchannel. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengeaud, V.; Josserand, J.; Girault, H.H. Mixing processes in a zigzag microchannel: Finite element simulations and optical study. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 4279–4286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroock, A.D.; Dertinger, S.K.; Ajdari, A.; Mezić, I.; Stone, H.A.; Whitesides, G.M. Chaotic mixer for microchannels. Science 2002, 295, 647–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bottausci, F.; Mezic, I.; Meinhart, C.D.; Cardonne, C. Mixing in the shear superposition micromixer: Three-dimensional analysis. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 1001–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Goto, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Maeda, R. Active micromixer for microfluidic systems using lead-zirconate-titanate (PZT)-generated ultrasonic vibration. Electrophoresis 2000, 21, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensing, G.A.; Pearce, T.M.; Graham, M.D.; Beebe, D.J. An externally driven magnetic microstirrer. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2004, 362, 1059–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Moctar, A.O.; Aubry, N.; Batton, J. Electro-hydrodynamic micro-fluidic mixer. Lab Chip 2003, 3, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biddiss, E.; Erickson, D.; Li, D. Heterogeneous surface charge enhanced micromixing for electrokinetic flows. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grumann, M.; Geipel, A.; Riegger, L.; Zengerle, R.; Ducree, J. Batch-mode mixing on centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Lab Chip 2005, 5, 560–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noroozi, Z.; Kido, H.; Micic, M.; Pan, H.; Bartolome, C.; Princevac, M.; Zoval, J.; Madou, M. Reciprocating flow-based centrifugal microfluidics mixer. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2009, 80, 075102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.C.R.; Salin, E.D. Micromixing by pneumatic agitation on continually rotating centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2012, 13, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiang, J.; Wang, W. A pinch-valve for centrifugal microfluidic platforms and its application in sequential valving operation and plasma extraction. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W. A magnetically actuated valve for centrifugal microfluidic applications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Xiang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, W. Membrane-based valves and inward-pumping system for centrifugal microfluidic platforms. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 228, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Z.; Xiang, J.; Chen, H.; Wang, W. A Rapid Micromixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines 2016, 7, 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7050089
Cai Z, Xiang J, Chen H, Wang W. A Rapid Micromixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines. 2016; 7(5):89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7050089
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ziliang, Jiwen Xiang, Hualing Chen, and Wanjun Wang. 2016. "A Rapid Micromixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms" Micromachines 7, no. 5: 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7050089
APA StyleCai, Z., Xiang, J., Chen, H., & Wang, W. (2016). A Rapid Micromixer for Centrifugal Microfluidic Platforms. Micromachines, 7(5), 89. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi7050089