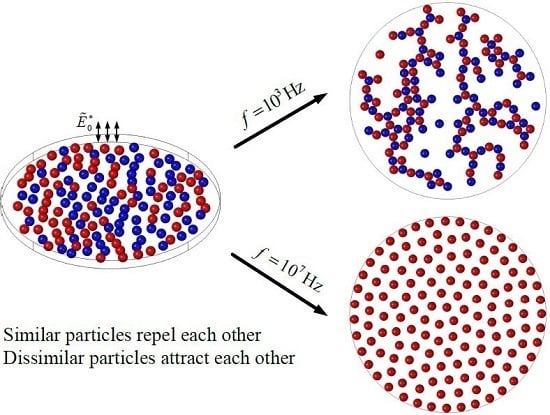
Three-Dimensional Interaction of a Large Number of Dense DEP Particles on a Plane Perpendicular to an AC Electrical Field †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Mathematical Model
2.1. Physical Description
2.2. The Iterative Dipole Moment Method (IDM)
2.3. The Modified Stokes Formula of a Large Number of Dense Particles
2.4. The Governing Equation of the Particles and the Dimensionless Method
2.5. The Validation of the Accuracy of the Modified Stokes Formula
3. Numerical Examples and Discussions
3.1. The Interaction of Five Particles with Different Conductivities
3.2. The Interaction of a Large Number of Particles with the Same Size
3.3. The DEP Interaction of Large Numbers of Particles on a Bounded Circular Plate Chip
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jones, T.B. Electromechanics of Particles; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, H.; Green, N.G. AC Electrokinetics: Colloids and Nanoparticles; Research Studies Press: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Li, D. Electrokinetic motion of particles and cells in microchannels. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 6, 431–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piacentini, N.; Mernier, G.; Tornay, R.; Renaud, P. Separation of platelets from other blood cells in continuous-flow by dielectrophoresis field-flow-fractionation. Biomicrofluidics 2011, 5, 034122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, H.S.; Kwon, K.; Kim, S.I.; Han, H.; Sohn, J.; Lee, S.; Jung, H.I. Continuous separation of breast cancer cells from blood samples using multi-orifice flow fractionation (MOFF) and dielectrophoresis (DEP). Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1118–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshareef, M.; Metrakos, N.; Perez, E.J.; Azer, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, X.; Wang, G. Separation of tumor cells with dielectrophoresis-based microfluidic chip. Biomicrofluidics 2013, 7, 011803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salomon, S.; Leichlé, T.; Nicu, L. A dielectrophoretic continuous flow sorter using integrated microelectrodes coupled to a channel constriction. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Bassat, D.; Boymelgreen, A.; Yossifon, G. The influence of flow intensity and field frequency on continuous-flow dielectrophoretic trapping. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 442, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Shao, J.; Jia, Y.; Tao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ren, Y. Trapping and chaining self-assembly of colloidal polystyrene particles over a floating electrode by using combined induced-charge electroosmosis and attractive dipole–dipole interactions. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 8105–8112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lumsdon, S.O.; Kaler, E.W.; Williams, J.P.; Velev, O.D. Dielectrophoretic assembly of oriented and switchable two-dimensional photonic crystals. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 949–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsdon, S.O.; Kaler, E.W.; Velev, O.D. Two-dimensional crystallization of microspheres by a coplanar AC electric field. Langmuir 2004, 20, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangwal, S.; Pawar, A.; Kretzschmar, I.; Velev, O.D. Programmed assembly of metallodielectric patchy particles in external AC electric fields. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giner, V.; Sancho, M.; Lee, R.S.; Martínez, G.; Pethig, R. Transverse dipolar chaining in binary suspensions induced by RF fields. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1999, 32, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermanson, K.D.; Lumsdon, S.O.; Williams, J.P.; Kaler, E.W.; Velev, O.D. Dielectrophoretic assembly of electrically functional microwires from nanoparticle suspensions. Science 2001, 294, 1082–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Alargova, R.G.; Kilpatrick, P.K.; Velev, O.D. On-chip electric field driven assembly of biocomposites from live cells and functionalized particles. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 726–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chang, H.C.; Protasenko, V.; Kuno, M.; Singh, A.K.; Jena, D.; Xing, H. CdSe nanowires with illumination-enhanced conductivity: Induced dipoles, dielectrophoretic assembly, and field-sensitive emission. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 101, 073704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schütte, J.; Hagmeyer, B.; Holzner, F.; Kubon, M.; Werner, S.; Freudigmann, C.; Benz, K.; Böttger, J.; Gebhardt, R.; Becker, H.; et al. “Artificial micro organs”—A microfluidic device for dielectrophoretic assembly of liver sinusoids. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aubry, N.; Singh, P. Control of electrostatic particle-particle interactions in dielectrophoresis. Europhys. Lett. 2006, 74, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubry, N.; Singh, P. Influence of particle-particle interactions and particles rotational motion in traveling wave dielectrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2006, 27, 703–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Qian, S. DC dielectrophoretic particle–particle interactions and their relative motions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2010, 346, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Qian, S. Direct numerical simulation of AC dielectrophoretic particle–particle interactive motions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 417, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Ng, C.O.; Zhou, X.; Wu, J. Numerical study of interactive motion of dielectrophoretic particles. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2015, 49, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, B.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Zhou, X. Frequency effects on interactive motion of dielectrophoretic particles in an AC electrical field. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2015, 53, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Maniyeri, R. Dielectrophoretic motions of multiple particles and their analogy with the magnetophoretic counterparts. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2012, 26, 3503–3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S. Two-dimensional dipolophoretic motion of a pair of ideally polarizable particles under a uniform electric field. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2013, 41, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S. Dielectrophoretic motion of two particles with diverse sets of the electric conductivity under a uniform electric field. Comput. Fluids 2014, 105, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S. Dielectrophoretic motions of multiple particles under an alternating-current electric field. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2015, 54, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossan, M.R.; Dillon, R.; Roy, A.K.; Dutta, P. Modeling and simulation of dielectrophoretic particle–particle interactions and assembly. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 394, 619–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kretschmer, R.; Fritzsche, W. Pearl chain formation of nanoparticles in microelectrode gaps by dielectrophoresis. Langmuir 2004, 20, 11797–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho, M.; Martínez, G.; Muñoz, S.; Sebastián, J.L.; Pethig, R. Interaction between cells in dielectrophoresis and electrorotation experiments. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 022802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.H.; Yu, C.; Papazoglou, E.; Farouk, B.; Noh, H.M. Dielectrophoretic particle–particle interaction under AC electrohydrodynamic flow conditions. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hodge, J.; Brcka, J.; Faguet, J.; Lee, E.; Zhang, G. Effect of electric field distortion on particle-particle interaction under DEP. In Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2013, Boston, MA, USA, 9–11 October 2013.
- Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Wu, J. Iterative dipole moment method for calculating dielectrophoretic forces of particle-particle electric field interactions. Appl. Math. Mech. 2015, 36, 1499–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Chiu-On, N.; Wu, J. A new method for the interaction between multiple DEP particles: Iterative dipole moment method. Microsyst. Technol. 2015, 22, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Wu, J. Numerical study of particle chains of a large number of randomly distributed DEP particles using iterative dipole moment method. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 91, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Wu, J. Iterative dipole moment method for the interaction of multiple dielectrophoretic particles in an AC electrical field. Eur. J. Mech. B Fluids 2016, 58, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, F.M.; Corfield, I. Viscous Fluid Flow; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]











| Coordinate | Particle 1 | Particle 2 | Particle 3 | Particle 4 | Particle 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2 | −2 | −2 | 2 | |
| 0 | 3 | 3 | −3 | −3 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xie, C.; Chen, B.; Wu, J. Three-Dimensional Interaction of a Large Number of Dense DEP Particles on a Plane Perpendicular to an AC Electrical Field. Micromachines 2017, 8, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010026
Xie C, Chen B, Wu J. Three-Dimensional Interaction of a Large Number of Dense DEP Particles on a Plane Perpendicular to an AC Electrical Field. Micromachines. 2017; 8(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleXie, Chuanchuan, Bo Chen, and Jiankang Wu. 2017. "Three-Dimensional Interaction of a Large Number of Dense DEP Particles on a Plane Perpendicular to an AC Electrical Field" Micromachines 8, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010026
APA StyleXie, C., Chen, B., & Wu, J. (2017). Three-Dimensional Interaction of a Large Number of Dense DEP Particles on a Plane Perpendicular to an AC Electrical Field. Micromachines, 8(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8010026