Micro-Hole Drilling on Glass Substrates—A Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
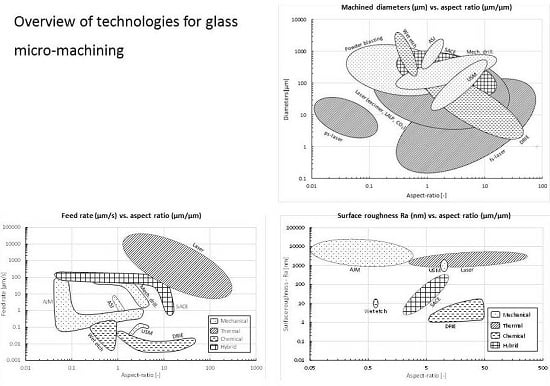
2. Common Glass Micro-Drilling Techniques
2.1. Mechanical Methods
2.1.1. Mechanical Drilling
2.1.2. Powder Blasting
2.1.3. Ultrasonic Drilling
2.2. Thermal Methods
2.2.1. Laser Machining
2.2.2. Focused Electrical Discharge Method
2.3. Chemical Methods
2.3.1. Wet Etching
2.3.2. Deep Reactive Ion Etching (DRIE)
2.4. Hybrid Methods
2.4.1. Assisted Hybrid Micromachining Techniques
2.4.2. Combined Hybrid Micromachining Processes
- -
- Adjusting the tool shape: different tool shapes including tools with side insulation, flat sidewalls, and spherical ends proved to reduce the taper and overcut [102], enhance machining accuracy [103,104,105], and reduce the hole entrance diameter by up to 65% and the machining time by up to 83% for a 500 mm deep hole [106].
- -
- -
- Tool, electrolyte or workpiece vibrations: low frequency vibrations (0–30 Hz) of a cylindrical 400 μm tool increase the material removal rate (MRR) by factor of two [107] where square waveform showed better improved compared to sinusoidal tool vibration [108,109]. Electrolyte ultrasonic vibration (1.7 MHz) shows improvements in machining depth (320 μm to 550 μm), and reduction in taper and overcut when applying ultrasonic vibrations to the electrolyte [110].
- -
- Pulsed voltage: results in better machining and surface finish [111].
- -
- Inducing a local magnetic field: locally stirs the electrolyte which enhances the surface quality and machining depth while reducing machining time (by around 57.4%) and the overcut (by 23.8%) and at low electrolyte concentration [112].
- -
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Mechanical Methods | Material | Diameter (μm) | Aspect Ratio | Taper Angle * (°) | Speed (μm/s) | Depth (μm) | Surface Roughness (nm) | References |
| Grinding-drilling | optical grade glass and quartz | 1011–1323 | 3.96–3.02 | - | 5 | 4000 | - | [24] |
| Micro-drilling | soda-lime glass | 100–400 | 1.3–0.33 | - | 125 | 130 | - | [25] |
| Mechanical drilling | glass | >150 | 4–14 | - | slow | - | - | [113] |
| Powder blasting (30 μm particles) | glass | 150–1000 | 0.07–0.24 | - | 0.083–0.133 | 10–240 | - | [114] |
| Powder blasting | glass | <50 | 2.5 | - | 0.4 | - | 2500 | [28] |
| AJM (abrasive jet micromachining) | borosilicate glass | 800 | <0.06 | - | 32 | 50 | high | [7] |
| ASJ (Abrasive slurry jet) | - | 390 | 0.9 | - | 4.38 | 350 | - | [32] |
| ASJM (Abrasive slurry jet—Al2O3 10 μm particle slurry flowrate:1.67 mL/s) | Borosilicate glass | 800 | 1.13 | - | 1.88 | 900 | frosting | [33] |
| - | 2000 | 1.5 | 34 | 0.56 | 3000 | - | [33] | |
| Micro-ultra-sonic (abrasive grains) | pyrex 7740 | 420 | >10 | 0.6 | - | 5000 | 1000 | [42] |
| Ultrasonic (combined with EDM) | glass | 150 | 3–4 | - | 0.13–0.15 | - | - | [115] |
| Ultrasonic vibration drilling | - | 10 | 2 | - | 0.05 | 20 | no cracks | [40] |
| Ultrasonic vibration drilling (combining ultrasonic and low-frequency/diamond core drill) | glass | 964 | - | - | 16.67 | - | - | [37] |
| Ultrasonic grinding (cemented tungsten carbide micro pins) | crown glass | 10–30 | - | - | 0.25–0.27 | - | - | [41] |
| Chemical Methods | Material | Diameter (μm) | Aspect Ratio | Taper Angle * (°) | Speed (μm/s) | Depth (μm) | Surface Roughness (nm) | References |
| wet etching (HF + mask Cr/Au/Cr/Au + SPR220-7) | glass | - | 0.78 | - | 0.24–0.07 | 300 | - | [116] |
| wet etching (HF 49% + mask Si/Si-carbide/photo-resist) | glass | 3000 | 0.33 | - | 0.13 | 1000 | - | [66] |
| HF etching (mask Cr/Au (50 nm/1 μm) + photoresist AZ7220) | Pyrex 7740 | ±1600 | ±0.3 | 44 | 0.238 | 500 | - | [3] |
| HF etching (49% HF) | Pyrex 7740 | 240 | 0.58 | - | 0.14 | 140 | - | [117] |
| HF etching (HFPR-mask) | fused silica | - | 0.70 | - | 0.01 | 600 | 10 | [118] |
| DRIE etching (Ni/a-Si/SU-8 masks deep plasma etching) | glass | 200 | 1.25 | - | >0.035 | 250 | - | [9] |
| DRIE (SF6 plasma) | Pyrex glass | 40–80 | >10 | 10 | 0.01 | 200 | - | [75] |
| DRIE (C4F8/O2—Ni mask 8 μm) | glass | 3 | 40 | 4–14 | 0.017 | 120 | 2–10 | [76] |
| DRIE (SF6/Ar—Ni 5 μm) | glass | - | - | - | 0.0089 | 20 | 1.97 | [119] |
| DRIE (SF6—Cr) | glass | - | - | 4 | 0.02 | <20 | very high | [120] |
| DRIE (C4F8/He/O2—Si wafer 400 μm) | glass | 83.33 | 3 | 8–20 | 0.0083 | 250 | - | [121] |
| DRIE (C4F8/He/O2—Si wafer 400 μm) | glass | 100 | 3 | - | 0.0058 | 300 | - | [121] |
| DRIE (C4F8/O2—Ni mask 5 μm) | glass | 22.86 | 3.5 | 8–20 | 0.012 | 80 | - | [9] |
| DRIE (SF6—Ni mask) | glass | 20 | 10 | 4 | 0.01 | 200 | 4 | [75] |
| DRIE (SF6—Ni mask) | glass | - | - | >4 | 0.0125 | 40 | - | [71] |
| DRIE (SF6/Ar—Ni mask) | glass | - | - | 4 | 0.009 | 27 | - | [71] |
| DRIE (C4F8/O2—Ni mask 6 μm) | glass | 20 | 6 | 4–14 | 0.013 | 120 | 2 | [122] |
| DRIE | glass | >1 | 30 | - | 0.0055 | - | - | [123] |
| Deep anisotropic dry etching | - | 50 | - | 0.4 | 0.0001 | - | - | [124] |
| Thermal Methods | Material | Diameter (μm) | Aspect Ratio | Taper Angle * (°) | Speed (μm/s) | Depth (μm) | Surface Roughness (nm) | References |
| Femtosecond laser (liquid assisted) | - | 5–70 | 40–50 | - | 30 | - | - | [48] |
| Laser drilling (femtosecond pulses) | fused silica | 7–10 | 3 | - | - | 30 | <HAZ, no cracks, smooth | [52] |
| Laser drilling (femtosecond pulses) | Foturan glass | 56 | 7.05 | - | 100–1000 | 395 | - | [55] |
| Laser drilling femtosecond fiber laser | soda-lime glass | 400 | 2.5 | 10 | - | 1000 | no cracks, HAZ, rough | [57] |
| TiSa laser (fs pulse width) | D263T glass foil | 208 99 | 2.4 5.1 | 15 10 | - | 500 505 | <HAZ, no debris | [53] |
| Laser (absorbent powder) | glass | 200 | >12 | - | 100 | 2500 | - | [58] |
| Laser drilling (short pulse solid state laser) | Nippon sheet glass | 15 | 0,017 | - | - | 0.25 | no cracks, smooth | [50] |
| CO2 laser | D263T glass foil | <100 | >5 | 3 | 2000 | 500 | smooth | [13] |
| CO2 laser | glass | 71 | 7,04 | 3 | <2000 | 500 | - | [63] |
| CO2 laser | glass | 122 | 4,10 | 10 | <2000 | 500 | - | [63] |
| CO2 laser (pulsed) | alkali free glass | 25 | 4 | - | 20,000 | 100 | - | [64] |
| Laser (CO2 infrared laser/Ni grid mask) | - | 9.2 | 0.00043 | - | - | 0.004 | irregular | [43] |
| LALP (CO2 laser, 6W—workpiece immersed in water) | Pyrex 7740 | 280 | 1.79 | 24 | 11,400 | 500 | no cracks | [62] |
| Laser (selective etching) | glass | 25 | 40 | - | 10 | - | - | [125] |
| Focused EDM | Alkali-free EN-A1 | 20 | 5 | - | 500–200 | 100 | - | [4] |
| - | 65.5 | 7.6 | 2 | - | 500 | smooth | [4] | |
| Hybrid Methods | Material | Diameter (μm) | Aspect Ratio | Taper Angle * (°) | Speed (μm/s) | Depth (μm) | Surface Roughness (nm) | References |
| ECDM | glass | 180–40 | 11 | - | 1 | 1200 | 250–350 | [93] |
| ECDM (pulsed voltage + offset) | glass | 455 | 0.99 | - | 7.5 | 450 | - | [96] |
| ECDM (EPDG polishing) | - | 210 | 2.38 | 0.4° | - | 500 | 5 | [88] |
| SACE (gravity feed) | glass | 540 | 0.37 | - | - | 200 | smooth | [126] |
| SACE (gravity feed) | glass | 600 | 0.55 | - | - | 330 | HAZ | [126] |
References
- Voldman, J.; Gray, M.L.; Schmidt, M.A. Microfabrication in biology and medicine. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 1, 401–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvela, D. Overview of Glass Micromachining Processes for MEMS Applications. MEMS J. 2010. Available online: http://www.memsjournal.com/2010/11/overview-of-glass-micro-machining-processes-for-mems-applications.html (accessed on 7 February 2017). [Google Scholar]
- Iliescu, C.; Tay, F.E.H.; Miao, J. Strategies in deep wet etching of Pyrex glass. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 133, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Horiuchi, K.; Tatsukoshi, K.; Ono, M.; Imajo, N.; Mobely, T. Development of through glass via (TGV) formation technology using electrical discharging for 2.5/3D integrated packaging. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE 63rd Electronic Components and Technology Conference (ECTC), 28–31 May 2013; pp. 348–352.
- Yoshida, S. AGC Succeeds in Developing Micro Hole Drilling Processing Technology for Ultra-Thin Glass with a Thickness in the Order of Microns. Available online: http://www.agc.com/english/news/2012/0305e.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Tseng, A.; Chen, Y.T.; Chao, C.L.; Ma, K.J.; Chen, T.P. Recent developments on microablation of glass materials using excimer lasers. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2007, 45, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobeity, A.; Getu, H.; Papini, M.; Spelt, J.K. Surface evolution models for abrasive jet micromachining of holes in glass and polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA). J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 2175–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, R.; Fascio, V. Machining of non-conducting materials using electrochemical discharge phenomenon—An overview. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolari, K.; Saarela, V.; Franssila, S. Deep plasma etching of glass for fluidic devices with different mask materials. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 64010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinton, D. Energy: The microfluidic frontier. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fredrickson, C.K.; Fan, Z.H. Macro-to-micro interfaces for microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2004, 4, 526–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Temiz, Y.; Lovchik, R.D.; Kaigala, G.V.; Delamarche, E. Lab-on-a-chip devices: How to close and plug the lab? Microelectron. Eng. 2015, 132, 156–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusberg, L.; Queisser, M.; Gentsch, C.; Schröder, H.; Lang, K.-D. Advances in CO2-laser drilling of glass substrates. Phys. Procedia 2012, 39, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delmdahl, R.; Paetzel, R. Laser drilling of high-density through glass vias (TGVs) for 2.5D and 3D packaging. J. Microelectron. Packag. Soc. 2014, 21, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimelahi, S.; Abolghasemi, L.; Herman, P.R. Rapid micromachining of high aspect ratio holes in fused silica glass by high repetition rate picosecond laser. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2014, 114, 91–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavoshi, S.Z.; Luo, X. Hybrid micromachining processes: A review. Precis. Eng. 2015, 41, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cardoso, P.; Davim, J.P. A brief review on micromachining of materials. Rew. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2012, 30, 98–102. [Google Scholar]
- Brehl, D.E.; Dow, T.A. Review of vibration-assisted machining. Precis. Eng. 2008, 32, 153–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwers, B.; Klocke, F.; Klink, A.; Tekkaya, A.E.; Neugebauer, R.; Mcintosh, D. Hybrid processes in manufacturing. CIRP Ann.-Manuf. Technol. 2014, 63, 561–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo Kumar, S.P.; Jerald, J.; Kumanan, S.; Prabakaran, R. A review on current research aspects in tool-based micromachining processes. Mater. Manuf. Process. 2014, 29, 1291–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Taylor, H.; Avram, M.; Miao, J.; Franssila, S. A practical guide for the fabrication of microfluidic devices using glass and silicon. Biomicrofluidics 2012, 6, 016505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, A.K.; Pandey, P.M. Study of Peck drilling of borosilicate glass with μrUM process for MEMS. J. Manuf. Process. 2016, 22, 134–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-H.; Chung, S.; Kim, S.-C.; Jee, W.-H.; Chung, S.-C. Condition monitoring of micro-drilling processes on glass by using machine vision. In Proceedings of the ASPE Challenges at the Intersection of Precision Engineering and Vacuum Technology, Pittsburgh, PA, USA, 1–2 May 2006; pp. 535–538.
- Chen, S.T.; Jiang, Z.H.; Wu, Y.Y.; Yang, H.Y. Development of a grindingdrilling technique for holing optical grade glass. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2011, 51, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Chu, C.N. Prevention of exit crack in micro drilling of soda-lime glass. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 51, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solignac, D.; Sayah, A.; Constantin, S.; Freitag, R.; Gijs, M.M. Powder blasting for the realisation of microchips for bio-analytic applications. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 92, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belloy, E.; Sayah, A.; Gijs, M.A.M. Oblique powder blasting for three-dimensional micromachining of brittle materials. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 92, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wensink, H.; Berenschot, J.W.; Jansen, H.V.; Elwenspoek, M.C. High resolution powder blast micromachining. In Proceedings of the Thirteenth Annual International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Miyazaki, Japan, 22–27 January 2000; pp. 769–774.
- Wensink, H. Fabrication of Microstructures by Powder Blasting; University of Twente: Enshede, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schlautmann, S.; Wensink, H.; Schasfoort, R.; Elwenspoek, M.; van den Berg, A. Powder-blasting technology as an alternative tool for microfabrication of capillary electrophoresis chips with integrated conductivity sensors. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2001, 11, 386–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Kuriyagawa, T.; Yasutomi, Y.; Zhao, J. Investigation into micro abrasive intermittent jet machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 873–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouraei, H.; Kowsari, K.; Spelt, J.K.; Papini, M. Surface evolution models for abrasive slurry jet micromachining of channels and holes in glass. Wear 2014, 309, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowsari, K.; Nouraei, H.; James, D.F.; Spelt, J.K.; Papini, M. Abrasive slurry jet micromachining of holes in brittle and ductile materials. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2014, 214, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schorderet, A.; Deghilage, E.; Agbeviade, K. Tool type and hole diameter influence in deep ultrasonic drilling of micro-holes in glass. Procedia CIRP 2013, 6, 565–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Rentsch, R.; Brinksmeier, E. Advances in micro ultrasonic assisted lapping of microstructures in hard–brittle materials: A brief review and outlook. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2005, 45, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.H.; Wang, A.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Huang, F.Y. Study of precision micro-holes in borosilicate glass using micro EDM combined with micro ultrasonic vibration machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2002, 42, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, K.I.; Suwabe, H.; Nishide, T.; Uneda, M. Study on combined vibration drilling by ultrasonic and low-frequency vibrations for hard and brittle materials. Precis. Eng. 1998, 22, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, K.; Masuzawa, T. Microultrasonic Machining by the Application of Workpiece Vibration. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1999, 48, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzzo, A.A.; Shinohara, P.L.; Raslan, A.H. A comparative study on ultrasonic machining of hard and brittle materials. In Proceedings of the COBEF 2003—II Brazilian Manufacturing Congress, Uberlandia, Brazil, 18–21 May 2003.
- Egashira, K.; Mizutani, K.; Nagao, T. Ultrasonic vibration drilling of microholes in glass. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2002, 51, 339–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egashira, K.; Kumagai, R.; Okina, R.; Yamaguchi, K.; Ota, M. Drilling of microholes down to 10 μm in diameter using ultrasonic grinding. Precis. Eng. 2014, 38, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan Malek, C.; Robert, L.; Boy, J.J.; Blind, P. Deep microstructuring in glass for microfluidic applications. Microsyst. Technol. 2007, 13, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Torii, S.; Makimura, T.; Niino, H.; Murakami, K.; Nakamura, D.; Takahashi, A.; Okada, T. Sub-wavelength micromachining of silica glass by irradiation of CO2 laser with Fresnel diffraction. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2011, 104, 593–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.K.; Yadava, V. Laser beam machining—A review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovatsek, J.; Patel, R.S. DPSS Lasers Overcome Glass Process Challenges. Available online: http://www.photonics.com/Article.aspx?AID=51733&PID=5&VID=100&IID=631 (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Femtoprint SA. 3D printing for glass microdevices. Available online: http://www.femtoprint.ch (accessed on 10 January 2017).
- Fraunhofer ILT, Selective Laser Etching of Glass and Sapphire. Available online: http://www.ilt.fraunhofer.de/en/media-center/brochures/brochure-Selective-Laser-Etching-of-Glass-and-Sapphire.html (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Hwang, D.J.; Choi, T.Y.; Grigoropoulos, C.P. Liquid-assisted femtosecond laser drilling of straight and three-dimensional microchannels in glass. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2004, 79, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.K.; Lin, S.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Tan, T.K.; Tu, K.Z.; Lung, H.F. Fabrication and simulation of glass micromachining using CO2 laser processing with PDMS protection. Appl. Phys. A 2013, 113, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikumb, S.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Reshef, H.; Zheng, H.Y.; Qiu, H.; Low, D. Precision glass machining, drilling and profile cutting by short pulse lasers. Thin Solid Films 2005, 477, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, A.; Yan, L.; Yan-Ping, D.; Ying, F.; Hong, Y.; Qi-Huang, G. Laser micro-hole drilling of soda-lime glass with femtosecond pulses. Chin. Phys. Lett. 2004, 21, 2465–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillejo, M.; Ossi, P.M.; Zhigilei, L. Lasers in Materials Science; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Brusberg, L.; Schroder, H.; Topper, M.; Reichl, H. Photonic system-in-package technologies using thin glass substrates. In Proceedings of the 2009 11th Electronics Packaging Technology Conference (EPTC ’09), Singapore, 9–11 December 2009.
- Herman, P.R.; Oettl, A.; Chen, K.P.; Marjoribanks, R.S. Laser micromachining of “transparent” fused silica with 1-ps pulses and pulse trains. In Proceendings of the SPIE 3616, Commercial and Biomedical Applications of Ultrafast Lasers, San Jose, CA, USA, 23 January 1999; pp. 148–155.
- Wu, Y.; Jia, W.; Wang, C.Y.; Hu, M.; Ni, X.; Chai, L. Micro-hole fabricated inside FOTURAN glass using femtosecond laser writing and chemical etching. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2007, 39, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Hong, M.H.; Fuh, J.Y.H.; Lu, L.; Lukyanchuk, B.S.; Wang, Z.B. Near-field enhanced femtosecond laser nano-drilling of glass substrate. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 449, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, L.; Liu, J. Micro-hole drilling and cutting using femtosecond fiber laser. Opt. Eng. 2014, 53, 51513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kono, I.; Nakanishi, A.; Warisawa, S.; Mitsuishi, M. Study on non-crack laser machining of glass by using absorbent powder. In Proceedings of the American Society for Precision Engineering, Norfolk, VA, USA, 9–14 October 2005; pp. 1793–1997.
- Basting, D.; Marowsky, G. Excimer Laser Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rivzi, N. Micro Manufacturing with Lasers; Med-Tech Innovation: St. Asaph, UK, 2012; pp. 16–21. [Google Scholar]
- Corning, Corning Gorilla Glass. Available online: https://www.corning.com/gorillaglass/worldwide/en.html (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Chung, C.K.; Lin, S.L. CO2 laser micromachined crackless through holes of Pyrex 7740 glass. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraunhofer Institute for Reliability and Micro-Integration IZM, CO2-Laser Drilling of through Glass Vias (TGVs). Available online: http://www.izm.fraunhofer.de/en/abteilungen/system_integrationinterconnectiontechnologies/leistungsangebot/prozessdienstleistungenprototypen/co2-laserbohren-von-loechern-in-glas-tgv-.html (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Mitsubishi Electric Corporation. Mitsubishi Electric Develops Micro Glass-Processing Technology Incorporating Pulsed CO2 Laser. 2014. Available online: http://www.mitsubishielectric.com/news/2014/pdf/0213-c.pdf (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Keiper, B.; Exner, H.; Loschner, U.; Kuntze, T. Drilling of glass by excimer laser mask projection technique. J. Laser Appl. 2000, 12, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Chen, B.; Miao, J. On the wet etching of Pyrex glass. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 143, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iliescu, C.; Chen, B.; Miao, J. Deep wet etching-through 1mm Pyrex glass wafer for microfluidic applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 20th International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Hyogo, Japan, 21–25 January 2007; pp. 393–396.
- Fertig, N.; Meyer, C.; Blick, R.H.; Trautmann, C.; Behrends, J.C. Microstructured glass chip for ion-channel electrophysiology. Phys. Rev. E. Stat. Nonlinear Soft Matter Phys. 2001, 64, 40901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliescu, C.; Jing, J.; Tay, F.E.H.; Miao, J.; Sun, T. Characterization of masking layers for deep wet etching of glass in an improved HF/HCl solution. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 198, 314–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, T.; Tsujino, K.; Matsumura, M. Making microholes in glass by electrochemical local acidification of fluoride-containing solution. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2012, 1, P1–P4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Abe, T.; Liu, Y.; Esashi, M. Fabrication of high-density electrical feed-throughs by deep-reactive-ion etching of Pyrex glass. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2002, 11, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Lee, N.-E.; Lee, J.; Park, J.S.; Park, H.D. Deep dry etching of borosilicate glass using SF6 and SF6/Ar inductively coupled plasmas. Microelectron. Eng. 2005, 82, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akashi, T.; Yoshimura, Y. Deep reactive ion etching of borosilicate glass using an anodically bonded silicon wafer as an etching mask. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leech, P.W. Reactive ion etching of quartz and silica-based glasses in CF4/CHF3 plasmas. Vacuum 1999, 55, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolari, K. Deep plasma etching of glass with a silicon shadow mask. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 141, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Abe, T.; Esashi, M. Deep reactive ion etching of Pyrex glass using SF6 plasma. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2001, 87, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Queste, S.; Salut, R.; Clatot, S.; Rauch, J.Y.; Khan Malek, C.G. Manufacture of microfluidic glass chips by deep plasma etching, femtosecond laser ablation, and anodic bonding. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 1485–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauwers, B. Surface integrity in hybrid machining processes. Procedia Eng. 2011, 19, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisel, U.; Eisseler, R.; Eber, R.; Wallaschek, J.; Twiefel, J.; Huang, M. Ultrasonic-assisted machining of stone. Prod. Eng. 2011, 5, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, J.; Wang, X.; Zhou, M.; Ngoi, B.; Zhong, Z. Ultraprecision diamond turning of glass with ultrasonic vibration. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2003, 21, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klocke, F.; Rubenach, O. Ultrasonic-assisted diamond turning of glass and steel. Ind. Diam. Rev. 2000, 60, 229–239. [Google Scholar]
- Moriwaki, T.; Shamoto, E.; Inoue, K. Ultraprecision ductile cutting of glass by applying ultrasonic vibration. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1992, 41, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, R.; Saxena, I.; Ehmann, K.; Cao, J. Laser-induced plasma micromachining (LIPMM) for enhanced productivity and flexibility in laser-based micromachining processes. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2013, 62, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, K.L.; Ogawa, Y.; Kanbargi, G.; Otra, V.; Raff, L.M.; Komanduri, R. Micromachining of silicon by short-pulse laser ablation in air and under water. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 372, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jeon, B.; Kim, B. Chemical-assisted ultrasonic machining of glass. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2007, 191, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, T.; Yoshihara, N.; Yan, J.; Kuriyagawa, T. Study on electrorheological fluid-assisted microultrasonic machining. Int. J. Abras. Technol. 2009, 2, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, T.; Yoshihara, N.; Yan, J.W.; Kuriyagawa, T. Fabrication of high-aspect ratio micro holes on hard brittle materials—Study on electrorheological fluid-assisted micro ultrasonic machining. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 389–390, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tateishi, T.; Shimada, K.; Yoshihara, N.; Yan, J.W.; Kuriyagawa, T. Effect of electrorheological fluid assistance on micro ultrasonic machining. Adv. Mater. Res. 2009, 69–70, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, A.; Zeidler, H.; Oschätzchen, M.H.; Schneider, J.; Hahn, M. Enhancing micro-EDM using ultrasonic vibration and approaches for machining of nonconducting ceramics. Strojniški Vestnik 2013, 59, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohri, N.; Fukuzawa, Y.; Tani, T.; Saito, N.; Furutani, K. Assisting electrode method for machining insulating ceramics. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 1996, 45, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edelmann, J.; Worsch, C.; Schubert, A.; Rüssel, C. Micro structuring of inorganic glass by hot embossing of coated glass wafers. Microsyst. Technol. 2010, 16, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; Huang, F.-Y.; Lu, Z.-H. Electrophoretic deposition grinding (EPDG) for improving the precision of microholes drilled via ECDM. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, B.R.; Doloi, B.; Bhattacharyya, B. Parametric analysis on electrochemical discharge machining of silicon nitride ceramics. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2006, 28, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razfar, M.R.; Ni, J.; Behroozfar, A.; Lan, S. An investigation on electrochemical discharge micro-drilling of glass. In Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Manufacturing Science and Engineering Conference collocated with the 41st North American Manufacturing Research Conference, Madison, WI, USA, 10–14 June 2013.
- Kim, D.J.; Ahn, Y.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.K. Voltage pulse frequency and duty ratio effects in an electrochemical discharge microdrilling process of Pyrex glass. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 1064–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.S.; Howard, D.; Liang, E.; Collins, S.D.; Smith, R.L. Removable tubing interconnects for glass-based micro-fluidic systems made using ECDM. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2004, 14, 535–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jui, S.K.; Kamaraj, A.B.; Sundaram, M.M. High aspect ratio micromachining of glass by electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM). J. Manuf. Process. 2013, 15, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, R.; Hof, L.A. The gas film in spark assisted chemical engraving (SACE)—A key element for micromachining applications. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2006, 46, 828–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hof, L.A. 3D Microstructuring of Glass; Delft University of Technology: Delft, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Z.-P.; Lin, J.-K.; Huang, F.-Y.; Yan, B.-H. Improving the machining efficiency in electrochemical discharge machining (ECDM) microhole drilling by offset pulse voltage. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 25014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-P.; Cheng, W.-H.; Yan, B.-H. 3D microstructuring of Pyrex glass using the electrochemical discharge machining process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-S.; Min, B.-K.; Lee, S.J. Modeling gas film formation in electrochemical discharge machining processes using a side-insulated electrode. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2008, 18, 45019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-P.; Wu, K.-L.; Mai, C.-C.; Yang, C.-K.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Yan, B.-H. Study of gas film quality in electrochemical discharge machining. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2010, 50, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-P.; Su, H.-C.; Huang, F.-Y.; Yan, B.-H. The tool geometrical shape and pulse-off time of pulse voltage effects in a Pyrex glass electrochemical discharge microdrilling process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Ni, J.; Hu, D. Electrochemical discharge machining using micro-drilling tools. Trans. N. Am. Manuf. Res. Inst. SME 2010, 38, 105–111. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, C.K.; Wu, K.L.; Hung, J.C.; Lee, S.M.; Lin, J.C.; Yan, B.H. Enhancement of ECDM efficiency and accuracy by spherical tool electrode. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2011, 51, 528–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, R.; Despont, B.; Maillard, P.; Bleuler, H. Improving the material removal rate in spark-assisted chemical engraving (SACE) gravity-feed micro-hole drilling by tool vibration. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2006, 16, N28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusli, M.; Furutani, K. Performance of micro-hole drilling by ultrasonic-assisted electro-chemical discharge machining. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 445, 865–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razfar, M.R.; Behroozfar, A.; Ni, J. Study of the effects of tool longitudinal oscillation on the machining speed of electrochemical discharge drilling of glass. Precis. Eng. 2014, 38, 885–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.-S.; Min, B.-K.; Lee, S.J. Geometric improvement of electrochemical discharge micro-drilling using an ultrasonic-vibrated electrolyte. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 65004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.D.; Kim, B.H.; Chu, C.N. Micro-structuring of glass with features less than 100 μm by electrochemical discharge machining. Precis. Eng. 2009, 33, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-P.; Wu, K.-L.; Mai, C.-C.; Hsu, Y.-S.; Yan, B.-H. Magnetic field-assisted electrochemical discharge machining. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2010, 20, 75019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wüthrich, R.; Abou Ziki, J.D. Micromachining Using Electrochemical Discharge Phenomenon; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Abou Ziki, J.D.; Wüthrich, R. Forces exerted on the tool-electrode during constant-feed glass micro-drilling by spark assisted chemical engraving. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 73, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Ziki, J.D.; Wüthrich, R. Nature of drilling forces during spark assisted chemical engraving. Manuf. Lett. 2015, 4, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Ziki, J.D. Spark Assisted Chemical Engraving: A Novel Approach for Quantifying the Machining Zone Parameters Using Drilling Forces; Concordia University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- UKAM. UKAM Industrial Superhard Tools, Micro Diamond Drills Product Catalogue. Available online: http://www.ukam.com/micro_core_drills.htm (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Sayah, A.; Thivolle, P.-A.; Parashar, V.K.; Gijs, M.AM. Fabrication of microfluidic mixers with varying topography in glass using the powder-blasting process. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2009, 19, 85024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.H.; Tan, L.K. Effects of ultrasonic vibrations in micro electro-discharge machining of microholes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 1999, 19, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bu, M.; Melvin, T.; Ensell, G.J.; Wilkinson, J.S.; Evans, A.G.R. A new masking technology for deep glass etching and its microfluidic application. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2004, 115, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, J.; Giachino, J.M.; Najafi, K. Fabrication and characterization of a wafer-level MEMS vacuum package with vertical feedthroughs. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2008, 17, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarah, J.M.; Wagenaar, D.A. Ultradeep fused silica glass etching with an HF-resistant photosensitive resist for optical imaging applications. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2012, 22, 35011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, A.; Hood, V.; Tadigadapa, S. High speed anisotropic etching of Pyrex® for microsystems applications. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2006, 352, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichiki, T.; Sugiyama, Y.; Taura, R.; Koidesawa, T.; Horiike, Y. Plasma applications for biochip technology. Thin Solid Films 2003, 435, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolari, K. Plasma etching of high aspect ratio structures on glass. In Proceedings of the 19th Micromechanics Europe Workshop, Aachen, Germany, 28–30 September 2008; pp. 81–84.
- Queste, C.; Ulliac, S.; Jeannot, G.; Malek, J.C. DRIE of nonconventional materials: First results. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Multi-Material Micro Manufacture, Cardiff, UK, 9–11 September 2008; pp. 171–174.
- Salleo, A.; Génin, F.Y.; Feit, M.D.; Rubenchik, M.; Sands, T.; Mao, S.S.; Russo, R.E. Energy deposition at front and rear surfaces during picosecond laser interaction with fused silica. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 2840–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavius, M.; Hibert, C.; Fluckiger, P.; Renaud, P.; Rolland, L.; Puech, M. Profile angle control in SiO2 deep anisotropic dry etching for MEMS fabrication. In Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Maastricht, The Netherlands, 25–29 January 2004; pp. 669–672.
- Schott, Foturan Glass. Available online: http://www.design.caltech.edu/micropropulsion/foturane.html (accessed on 7 February 2017).
- Maillard, P.; Despont, B.; Bleuler, H.; Wüthrich, R. Geometrical characterization of micro-holes drilled in glass by gravity-feed with spark assisted chemical engraving (SACE). J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desbiens, J.P.; Masson, P. ArF excimer laser micromachining of Pyrex, SiC and PZT for rapid prototyping of MEMS components. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2007, 136, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Process | Mechanical | Thermal | Chemical | Hybrid | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Drilling | Powder Blasting | ASJ | USM | Laser Drilling | FEDM | Wet Etching | DRIE | SACE | |
| Aspect Ratio 1 | − | −− | −− | − | ++ | − | −− | ++ | + |
| Machining Speed (Serial) 1 | + | − | −− | −− | ++ | + | −− | −− | + |
| Surface Roughness 2 (Ra) | − | −− | − | − | + | + | ++ | + | |
| Minimum Dimensions (μm) | 150 | 50 | 300 | 200 (10) | 5 | 20 | 1 | 0.5 | 100 |
| Rapid Prototyping (Serial Mode) 3 | ++ | −− | + | + | ++ | − | −− | −− | ++ |
| Mass Fabrication (Parallel Mode) 3 | −− | ++ | − | − | − | + | ++ | ++ | −− |
| Tooling Complexity/Costs 4 | −− | −− | − | − | ++ | + | −− | −− | ++ |
| Applicable to Wide Range of Glass Types 3 | ++ | ++ | ++ | ++ | + | −− | − | −− | ++ |
| Equipment Costs/Complexity 5 | ++ | + | +/− | − | − | − | − | −− | + |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hof, L.A.; Abou Ziki, J. Micro-Hole Drilling on Glass Substrates—A Review. Micromachines 2017, 8, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020053
Hof LA, Abou Ziki J. Micro-Hole Drilling on Glass Substrates—A Review. Micromachines. 2017; 8(2):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020053
Chicago/Turabian StyleHof, Lucas A., and Jana Abou Ziki. 2017. "Micro-Hole Drilling on Glass Substrates—A Review" Micromachines 8, no. 2: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020053
APA StyleHof, L. A., & Abou Ziki, J. (2017). Micro-Hole Drilling on Glass Substrates—A Review. Micromachines, 8(2), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi8020053