The Progress of PVDF as a Functional Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Background of Energy Harvesting Based on the Triboelectric Effect
1.2. The Four Fundamental Modes of the Triboelectric Nanogenerator
1.3. The Importance of Dielectrics in the Triboelectric Nanogenerator
2. Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) as an Effective Dielectric in Triboelectric Nanogenerators
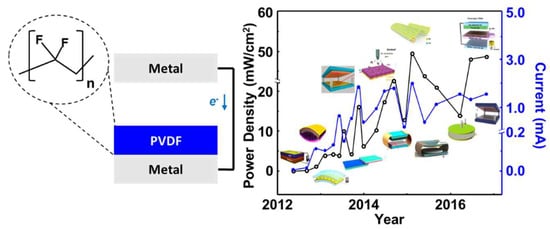
2.1. PVDF-Based Polymers as an Effective Dielectric
2.2. PVDF-Based Polymers Hybridized with Inorganic Materials
3. PVDF Based Applications
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible triboelectric generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Lin, L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.L. Transparent Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Pressure Sensors Based on Micropatterned Plastic Films. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Reviving Vibration Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Sensing by a Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Joule 2017, 1, 480–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4283–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.-R.; Luo, J.; Tang, W.; Li, C.; Zhang, C.; Tian, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Highly transparent and flexible triboelectric nanogenerators: Performance improvements and fundamental mechanisms. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 13219–13225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Cylindrical Rotating Triboelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 6361–6366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zou, H.; Liu, R.; Tao, C.; Fan, X.; Wang, Z.L. Micro-cable structured textile for simultaneously harvesting solar and mechanical energy. Nat. Energy 2016, 1, 16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Deng, W.; Jin, L.; Chun, F.; Pan, H.; Gu, B.; Zhang, H.; Lv, Z.; Yang, W.; et al. Self-Powered Acceleration Sensor Based on Liquid Metal Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Vibration Monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 7440–7446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, L.; Cui, X.; Gao, M.; Su, Y.; Yang, W.; et al. Smart network node based on hybrid nanogenerator for self-powered multifunctional sensing. Nano Energy 2017, 33, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Lin, L. Progress in triboelectric nanogenerators as a new energy technology and self-powered sensors. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 2250–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Chen, J.; Zhang, T.; Jing, Q.; Wang, Z.L. Radial-arrayed rotary electrification for high performance triboelectric generator. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Bai, P.; Meng, X.S.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Shape-Adaptive Thin-Film-Based Approach for 50% High-Efficiency Energy Generation through Micro-Grating Sliding Electrification. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 3788–3796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. Power-generating shoe insole based on triboelectric nanogenerators for self-powered consumer electronics. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Yang, W.; Qi, X.; Su, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Personalized Keystroke Dynamics for Self-Powered Human–Machine Interfacing. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Cheng, G.; Chen, J.; Lin, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Z.L. A Hybridized Power Panel to Simultaneously Generate Electricity from Sunlight, Raindrops, and Wind around the Clock. Adv. Energy Mater. 2015, 5, 1501152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Chen, J.; Li, X.; Zhou, Z.; Meng, K.; Wei, W.; Yang, J.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator Enabled Body Sensor Network for Self-Powered Human Heart-Rate Monitoring. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 8830–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.L.; Lin, L.; Chen, J.; Niu, S.; Zi, Y. Triboelectric Nanogenerators, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, J.; Lee, J.; Kim, S.; Ha, J.; Lee, B.-S.; Park, Y.; Choong, C.; Kim, J.-B.; Wang, Z.L.; Kim, H.-Y.; et al. Flutter-driven triboelectrification for harvesting wind energy. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4929–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, G.; Su, Y.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Jing, Q.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Harvesting Water Wave Energy by Asymmetric Screening of Electrostatic Charges on a Nanostructured Hydrophobic Thin-Film Surface. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6031–6037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.N.; Lee, J.P.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.C.; Baik, J.M. Ergonomically designed replaceable and multifunctional triboelectric nanogenerator for a uniform contact. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 88526–88530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoscale Triboelectric-Effect-Enabled Energy Conversion for Sustainably Powering Portable Electronics. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 6339–6346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Pan, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Toward Large-Scale Energy Harvesting by a Nanoparticle-Enhanced Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Wang, Z.L. Sliding-Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on In-Plane Charge-Separation Mechanism. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, Z.L. Maximum Surface Charge Density for Triboelectric Nanogenerators Achieved by Ionized-Air Injection: Methodology and Theoretical Understanding. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6720–6728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liu, M.; Huang, B.; Liu, H.; Hu, W.; Shao, L.-H.; Wang, Z.L. Nanoporous-Gold-Based Hybrid Cantilevered Actuator Dealloyed and Driven by A Modified Rotary Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chun, J.; Ye, B.U.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, D.; Kang, C.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Boosted output performance of triboelectric nanogenerator via electric double layer effect. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Lin, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Theoretical study of contact-mode triboelectric nanogenerators as an effective power source. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3576–3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seung, W.; Yoon, H.-J.; Kim, T.Y.; Ryu, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.J.; et al. Nanogenerators: Boosting Power-Generating Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerators via Artificial Control of Ferroelectric Polarization and Dielectric Properties. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1600988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, B.U.; Kim, B.-Y.; Ryu, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Baik, J.M.; Hong, K. Electrospun ion gel nanofibers for flexible triboelectric nanogenerator: Electrochemical effect on output power. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 16189–16194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.Y.; Yoon, H.-J.; Jiang, T.; Wen, X.; Seung, W.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.L. Fully Packaged Self-Powered Triboelectric Pressure Sensor Using Hemispheres-Array. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3109–3114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, L.; Gudla, S.; Shan, X.; Wang, Z.; Tay, F.E.H.; Heng, C.H.; Lee, C. Large Scale Triboelectric Nanogenerator and Self-Powered Pressure Sensor Array Using Low Cost Roll-to-Roll UV Embossing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Jing, Q.; Li, Z.; Yi, F.; Wen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Eardrum-Inspired Active Sensors for Self-Powered Cardiovascular System Characterization and Throat-Attached Anti-Interference Voice Recognition. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Yang, J.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Wei, W.; Liu, J.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Large-Scale and Washable Smart Textiles Based on Triboelectric Nanogenerator Arrays for Self-Powered Sleeping Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018, 28, 1704112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Chen, J.; Wen, X.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification Based Motion Sensor for Human-Machine Interfacing. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 7479–7484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, J.; Jin, L.; Deng, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, M.; Yang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Rotating-Disk-Based Hybridized Electromagnetic–Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Sustainably Powering Wireless Traffic Volume Sensors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 6241–6247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, G.; Yang, W.; Jing, Q.; Bai, P.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.; Wang, Z.L. Harmonic-Resonator-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator as a Sustainable Power Source and a Self-Powered Active Vibration Sensor. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 6094–6099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Chun, J.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, W.J.; Baik, J.M. Self-powered Room Temperature Electronic Nose based on Triboelectrification and Heterogeneous Catalytic Reaction. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2015, 25, 7049–7055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Wu, W.; Pradel, K.C.; Wang, Z.L. Dual-Mode Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Water Energy and as a Self-Powered Ethanol Nanosensor. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6440–6448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Su, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, C.; Wu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wong, C.P.; Bando, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator as self-powered active sensors for detecting liquid/gaseous water/ethanol. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Z.; Chen, J.; Yeh, M.-H.; Guo, H.; Li, Z.; Fan, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, L.; Wang, Z.L. Blow-driven triboelectric nanogenerator as an active alcohol breath analyzer. Nano Energy 2015, 16, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Yang, Y.; Bai, P.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.L. A Self-Powered Triboelectric Nanosensor for Mercury Ion Detection. Angew. Chem. 2013, 52, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Hou, T.-C.; Su, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric nanogenerator built inside clothes for self-powered glucose biosensors. Nano Energy 2013, 2, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Yang, J.; Su, Y.; Fan, X.; Wu, Y.; Yu, C.; Wang, Z.L. β-cyclodextrin enhanced triboelectrification for self-powered phenol detection and electrochemical degradation. Energy Environ Sci. 2015, 8, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Guo, H.; Fan, X.; Wen, Z.; Yeh, M.-H.; Yu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectrification-Enabled Self-Powered Detection and Removal of Heavy Metal Ions in Wastewater. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 2983–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.W.; Ye, B.U.; Baik, J.M. Research Update: Recent progress in the development of effective dielectrics for high-output triboelectric nanogenerator. APL Mater. 2017, 5, 073802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, Y.S.; Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Dipole-moment-induced effect on contact electrification for triboelectric nanogenerators. Nano Res. 2014, 7, 990–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soin, N.; Zhao, P.; Prashanthi, K.; Chen, J.; Ding, P.; Zhou, E.; Shah, T.; Ray, S.C.; Tsonos, C.; Thundat, T.; et al. High performance triboelectric nanogenerators based on phase-inversionpiezoelectric membranes of poly(vinylidenefluoride)-zinc stannate (PVDF-ZnSnO3) and polyamide-6 (PA6). Nano Energy 2016, 30, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.W.; Cho, H.J.; Chun, J.; Kim, K.N.; Kim, S.; Ahn, C.W.; Kim, I.W.; Kim, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Yang, C.; et al. Robust nanogenerators based on graft copolymers via control of dielectrics for remarkable output power enhancement. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, 1602902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Kim, J.W.; Jung, W.; Kang, C.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Wang, Z.L.; Baik, J.M. Mesoporous pores impregnated with Au nanoparticles as effective dielectrics for enhancing triboelectric nanogenerator performance in harsh environments. Energy Environ. Sci. 2015, 8, 3006–3012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.; Ye, B.Y.; Kim, K.N.; Lee, J.W.; Choi, W.J.; Baik, J.M. 3D printed noise-cancelling triboelectric nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2017, 38, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jing, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhang, G.; Ma, J.; Wang, Z.L. Integrated Multilayered Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Biomechanical Energy from Human Motions. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3713–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Wen, X.; Zhu, G.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Bai, P.; Wu, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Hybrid triboelectric nanogenerator for harvesting water wave energy and as a self-powered distress signal emitter. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.; Liu, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, C.; Pang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Shao, L.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Efficient Charging of Li-Ion Batteries with Pulsed Output Current of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Sci. 2015, 26, 1500255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, P.; Zhu, G.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Chen, J.; Su, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.L. Membrane-Based Self-Powered Triboelectric Sensors for Pressure Change Detection and Its Uses in Security Surveillance and Healthcare Monitoring. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 5807–5813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Wang, S.; Niu, S.; Lin, L.; Jing, Q.; Yang, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.L. Grating-Structured Freestanding Triboelectric-Layer Nanogenerator for Harvesting Mechanical Energy at 85% Total Conversion Efficiency. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 6599–6607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Xie, Y.; Niu, S.; Wang, S.; Yang, P.-K.; Wang, Z.L. Robust Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Rolling Electrification and Electrostatic Induction at an Instantaneous Energy Conversion Efficiency of ∼55%. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 922–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Wang, S.; Xie, Y.; Jing, Q.; Niu, S.; Hu, Y.; Wang, Z.L. Segmentally Structured Disk Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting Rotational Mechanical Energy. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 2916–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Z.; Pu, X.; Du, C.; Li, L.; Jiang, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, Z.L. Freestanding Flag-Type Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Harvesting High-Altitude Wind Energy from Arbitrary Directions. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 1780–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.H.; Ryu, H.; Lee, J.-H.; Khan, U.; Kim, H.; Kwak, S.S.; Kim, S.-W. High-Performance Piezoelectric, Pyroelectric, and Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on P(VDF-TrFE) with Controlled Crystallinity and Dipole Alignment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2017, 27, 1700702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Lu, M.; Yu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Zhu, M. Enhanced Power Output of a Triboelectric Nanogenerator Composed of Electrospun Nanofiber Mats Doped with Graphene Oxide. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Yang, C. A flexible and biocompatible triboelectric nanogenerator with tunable internal resistance for powering wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.-H.; Cheng, G.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.S.; Lee, S.; Wang, Z.L. Triboelectric Nanogenerator as an Active UV Photodetector. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 2810–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.H.; Shin, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Lee, M.H.; Nah, J. Triboelectric contact surface charge modulation and piezoelectric charge inducement using polarized composite thin film for performance enhancement of triboelectric generators. Nano Energy 2016, 25, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Guo, H.; He, X.; Liu, G.; Xi, Y.; Shi, H.; Hu, C. Enhancing Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator by Filling High Dielectric Nanoparticles into Sponge PDMS Film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 736–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, L.; Yuan, M.; Wang, Z.; Qin, Y.; Wang, T. An electrospun nanowire-based triboelectric nanogenerator and its application in a fully self-powered UV detector. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7842–7846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, C.; He, Q. A flexible triboelectric-piezoelectric hybrid nanogenerator based on P(VDF-TrFE) nanofibers and PDMS/MWCNT for wearable devices. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.; Kim, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, H.S.; Ko, H. Fingertip skin–inspired microstructured ferroelectric skins discriminate static/dynamic pressure and temperature stimuli. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, 1500661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, K.-Y.; Cheong, O.J.; Kim, J.H.; Jang, J. Highly sensitive and multifunctional tactile sensor using free-standing ZnO/PVDF thin film with graphene electrodes for pressure and temperature monitoring. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.-F.; Xiong, J.; Wang, J.; Parida, K.; Lee, P.S. Core-shell nanofiber mats for tactile pressure sensor and nanogenerator applications. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Positively Charged Materials | Negatively Charged Materials | Working Mode | Output Power (mW/cm2) | Charge Density (μC/m2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 [1] | PET | Kapton | Vertical-contact | 0.00036 | - |
| #2 [2] | PET | PDMS | Vertical-contact | 0.00234 | - |
| #3 [21] | Al | PDMS | Vertical-contact | 3.56 | - |
| #4 [22] | Au | PDMS | Vertical-contact | 31.3 | 594.2 (calculated) |
| #5 [23] | Nylon | PTFE | Lateral-sliding | 0.53 | 59 |
| #6 [24] | Al | FEP | Vertical-contact | 31.5 | 240 |
| #7 [46] | Al | PVDF | Vertical-contact | 0.26 | 360.2 |
| #8 [12] | Cu | PTFE | Freestanding | 50 | 323 |
| #9 [47] | Al | ZnSnO3-PVDF (composites) | Vertical-contact | 3 | 101.3 |
| #10 [25] | Cu | Kapton | Lateral-sliding | 13.2 | - |
| #11 [26] | Al | PDMS | Vertical-contact | 46.8 | 270 |
| #12 [48] | Al | PVDF-Gn | Vertical-contact | 2.6 | 23 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.P.; Lee, J.W.; Baik, J.M. The Progress of PVDF as a Functional Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors. Micromachines 2018, 9, 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100532
Lee JP, Lee JW, Baik JM. The Progress of PVDF as a Functional Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors. Micromachines. 2018; 9(10):532. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100532
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jin Pyo, Jae Won Lee, and Jeong Min Baik. 2018. "The Progress of PVDF as a Functional Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors" Micromachines 9, no. 10: 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100532
APA StyleLee, J. P., Lee, J. W., & Baik, J. M. (2018). The Progress of PVDF as a Functional Material for Triboelectric Nanogenerators and Self-Powered Sensors. Micromachines, 9(10), 532. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi9100532