Plasma microRNA Levels Combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the Follow-Up of Colorectal Cancer Patients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Changes between Preoperative and Postoperative miRNA Plasma Levels
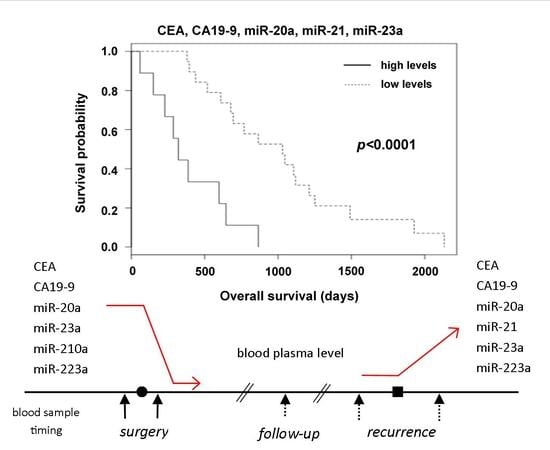
2.2. The Relation of Preoperative Plasma Levels of miRNAs to Prognosis
2.3. Detection of Disease Recurrence
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients
4.2. Blood Samples
4.3. Quantitative Measurement of microRNAs
4.4. Processing of Real-Time PCR Data
4.5. Quantitative Measurement of CEA and CA19-9
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagan, S.; Orr, M.C.M.; Doyle, B. Targeted therapies in colorectal cancer-an integrative view by PPPM. EPMA J. 2013, 4, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalyan, A.; Kircher, S.; Shah, H.; Mulcahy, M.; Benson, A. Updates on immunotherapy for colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2018, 9, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wille-Jørgensen, P.; Syk, I.; Smedh, K.; Laurberg, S.; Nielsen, D.T.; Petersen, S.H.; Renehan, A.G.; Horváth-Puhó, E.; Påhlman, L.; Sørensen, H.T.; et al. Effect of more vs. less frequent follow-up testing on overall and colorectal cancer-specific mortality in patients with stage II or III colorectal cancer: The colofol randomized clinical trial. Jama 2018, 319, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffy, M.J.; van Dalen, A.; Haglund, C.; Hansson, L.; Holinski-Feder, E.; Klapdor, R.; Lamerz, R.; Peltomaki, P.; Sturgeon, C.; Topolcan, O. Tumour markers in colorectal cancer: European Group on Tumour Markers (EGTM) guidelines for clinical use. Eur. J. Cancer 2007, 43, 1348–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, G.Y.; Hamilton, S.; Harris, J.; Jessup, J.M.; Kemeny, N.; Macdonald, J.S.; Somerfield, M.R.; Hayes, D.F.; Bast, R.C. ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, E.; Gouvas, N.; Nicholls, R.J.; Ziprin, P.; Xynos, E.; Tekkis, P.P. Diagnostic precision of carcinoembryonic antigen in the detection of recurrence of colorectal cancer. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 18, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.J.; Choi, G.-S.; Lim, K.H.; Kang, B.M.; Jun, S.H. Serum carcinoembryonic antigen monitoring after curative resection for colorectal cancer: Clinical significance of the preoperative level. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 3087–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, Y.J.; Tokumitsu, A.; Mizokami, K.; Sasaki, J.; Tsujinaka, S.; Konishi, F. First alert for recurrence during follow-up after potentially curative resection for colorectal carcinoma: CA 19-9 should be included in surveillance programs. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2010, 9, 48–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, C.; Yan, X.; Li, H.; Huang, L.; Yin, M.; Yang, Y.; Gao, R.; Hong, L.; Ma, Y.; Shi, C.; et al. Systematic literature review and clinical validation of circulating microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers for colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68317–68328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalanotto, C.; Cogoni, C.; Zardo, G. MicroRNA in control of gene expression: An overview of nuclear functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghdam, S.G.; Ebrazeh, M.; Hemmatzadeh, M.; Seyfizadeh, N.; Shabgah, A.G.; Azizi, G.; Ebrahimi, N.; Babaie, F.; Mohammadi, H. The role of microRNAs in prostate cancer migration, invasion, and metastasis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 9927–9942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smid, D.; Kulda, V.; Srbecka, K.; Kubackova, D.; Dolezal, J.; Daum, O.; Kucera, R.; Topolcan, O.; Treska, V.; Skalicky, T.; et al. Tissue microRNAs as predictive markers for gastric cancer patients undergoing palliative chemotherapy. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 2693–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratap, P.; Raza, S.T.; Abbas, S.; Mahdi, F. MicroRNA-associated carcinogenesis in lung carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Yang, W. Regulatory miRNAs in colorectal carcinogenesis and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulda, V.; Pesta, M.; Topolcan, O.; Liska, V.; Treska, V.; Sutnar, A.; Rupert, K.; Ludvikova, M.; Babuska, V.; Holubec, L.; et al. Relevance of miR-21 and miR-143 expression in tissue samples of colorectal carcinoma and its liver metastases. Cancer Genet. Cytogenet. 2010, 200, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Wu, D.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Shi, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, W. The expression and significance of microRNA in different stages of colorectal cancer. Medicine 2018, 97, e9635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vychytilova-Faltejskova, P.; Radova, L.; Sachlova, M.; Kosarova, Z.; Slaba, K.; Fabian, P.; Grolich, T.; Prochazka, V.; Kala, Z.; Svoboda, M.; et al. Serum-based microRNA signatures in early diagnosis and prognosis prediction of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis 2016, 37, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fang, Z.; Tang, J.; Bai, Y.; Lin, H.; You, H.; Jin, H.; Lin, L.; You, P.; Li, J.; Dai, Z.; et al. Plasma levels of microRNA-24, microRNA-320a, and microRNA-423-5p are potential biomarkers for colorectal carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maierthaler, M.; Benner, A.; Hoffmeister, M.; Surowy, H.; Jansen, L.; Knebel, P.; Chang-Claude, J.; Brenner, H.; Burwinkel, B. Plasma miR-122 and miR-200 family are prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, P.; Canale, M.; Passardi, A.; Marisi, G.; Valgiusti, M.; Frassineti, G.L.; Calistri, D.; Amadori, D.; Scarpi, E. Circulating plasma levels of miR-20b, miR-29b and miR-155 as predictors of bevacizumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaou, S.; Qiu, S.; Fiorentino, F.; Rasheed, S.; Tekkis, P.; Kontovounisios, C. Systematic review of blood diagnostic markers in colorectal cancer. Tech. Coloproctol. 2018, 22, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saito, G.; Sadahiro, S.; Kamata, H.; Miyakita, H.; Okada, K.; Tanaka, A.; Suzuki, T. Monitoring of serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels after curative resection of colon cancer: Cutoff values determined according to preoperative levels enhance the diagnostic accuracy for recurrence. Oncology 2017, 92, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, F.; Chen, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Tang, H.; Peng, Z. Combined detection of preoperative serum CEA, CA19-9 and CA242 improve prognostic prediction of surgically treated colorectal cancer patients. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 14853–14863. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-H.; Jiang, J.-K.; Chang, S.-C.; Juang, C.-J.; Lin, J.-K. Clinical significance of CA19-9 in the follow-up of colorectal cancer patients with elevated preoperative serum CA19-9. Hepatogastroenterology 2013, 60, 1021–1027. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yong, F.L.; Law, C.W.; Wang, C.W. Potentiality of a triple microRNA classifier: miR-193a-3p, miR-23a and miR-338-5p for early detection of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.H.; Deng, Z.H.; Hao, H.; Wu, X.L.; Gao, H.; Tang, S.H.; Tang, H. MicroRNA-23a promotes colorectal cancer cell survival by targeting PDK4. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 373, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.; Yang, R.; Wei, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zen, K.; Li, L. HIF-1α-induced miR-23a∼27a∼24 cluster promotes colorectal cancer progression via reprogramming metabolism. Cancer Lett. 2019, 440–441, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tan, H.-Y.; Feng, Y.-G.; Zhang, C.; Chen, F.; Feng, Y. microRNA-23a in human cancer: Its roles, mechanisms and therapeutic relevance. Cancers 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, J.S.L.; Luthra, R.; Romans, A.; Abraham, R.; Ensor, J.; Yao, H.; Hamilton, S.R. Association of microRNA expression with microsatellite instability status in colorectal adenocarcinoma. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zekri, A.-R.N.; Youssef, A.S.E.-D.; Lotfy, M.M.; Gabr, R.; Ahmed, O.S.; Nassar, A.; Hussein, N.; Omran, D.; Medhat, E.; Eid, S.; et al. Circulating serum miRNAs as diagnostic markers for colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, H.; Tan, J.-Y.; Cao, B.; Song, M.-Q.; Tian, Z.-B. Effects of miR-223 on colorectal cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis through regulating FoxO3a/BIM. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 3771–3778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Y.; Du, L.; Dong, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, G.; Qu, A.; Wang, C. Overexpression of miR-223 correlates with tumor metastasis and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Ju, H.; Pesta, M.; Kulda, V.; Jin, W.; Cai, M.; Liu, C.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of microRNA-21 in colorectal cancer: An original study and individual participant data meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2783–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guraya, S. Prognostic significance of circulating microRNA-21 expression in esophageal, pancreatic and colorectal cancers; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2018, 60, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Xia, C.; Jin, H.; Fan, Y. Serum miR-20a and miR-486 are potential biomarkers for discriminating colorectal neoplasia: A pilot study. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 1572–1577. [Google Scholar]
- Yamada, A.; Horimatsu, T.; Okugawa, Y.; Nishida, N.; Honjo, H.; Ida, H.; Kou, T.; Kusaka, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Yagi, M.; et al. Serum miR-21, miR-29a, and miR-125b are promising biomarkers for the early detection of colorectal neoplasia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4234–4242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wei, Y.; Wang, Z. microRNA-21 and hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2018, 41, 649–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sobin, L.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Wittekind, C. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, L.H.; Litière, S.; de Vries, E.; Ford, R.; Gwyther, S.; Mandrekar, S.; Shankar, L.; Bogaerts, J.; Chen, A.; Dancey, J.; et al. RECIST 1.1-Update and clarification: From the RECIST committee. Eur. J. Cancer 2016, 62, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faltejskova, P.; Bocanek, O.; Sachlova, M.; Svoboda, M.; Kiss, I.; Vyzula, R.; Slaby, O. Circulating miR-17-3p, miR-29a, miR-92a and miR-135b in serum: Evidence against their usage as biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biomark. Sect. Dis. Markers 2012, 12, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, T.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, D.; Fan, Q.; Wang, X.; Ning, T.; et al. Serum miRNA expression profile as a prognostic biomarker of stage II/III colorectal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunet Vega, A.; Pericay, C.; Moya, I.; Ferrer, A.; Dotor, E.; Pisa, A.; Casalots, À.; Serra-Aracil, X.; Oliva, J.-C.; Ruiz, A.; et al. microRNA expression profile in stage III colorectal cancer: Circulating miR-18a and miR-29a as promising biomarkers. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ristau, J.; Staffa, J.; Schrotz-King, P.; Gigic, B.; Makar, K.W.; Hoffmeister, M.; Brenner, H.; Ulrich, A.; Schneider, M.; Ulrich, C.M.; et al. Suitability of circulating miRNAs as potential prognostic markers in colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2014, 23, 2632–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellatt, D.F.; Stevens, J.R.; Wolff, R.K.; Mullany, L.E.; Herrick, J.S.; Samowitz, W.; Slattery, M.L. Expression profiles of miRNA subsets distinguish human colorectal carcinoma and normal colonic mucosa. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Bai, Z.; Song, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, W.; Zhang, J.; Meng, H.; Ma, X.; Yang, Y.; et al. Differential expression of serum miR-126, miR-141 and miR-21 as novel biomarkers for early detection of liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 26, 95–103. [Google Scholar]
- Toiyama, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Hur, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M.; Boland, C.R.; Goel, A. Serum miR-21 as a diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 849–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogata-Kawata, H.; Izumiya, M.; Kurioka, D.; Honma, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Furuta, K.; Gunji, T.; Ohta, H.; Okamoto, H.; Sonoda, H.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Du, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, C. Serum microRNA panel as biomarkers for early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1985–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cogdell, D.; Calin, G.A.; Sun, B.; Kopetz, S.; Hamilton, S.R.; Zhang, W. Examining plasma microRNA markers for colorectal cancer at different stages. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 11434–11449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, I.-P.; Tsai, H.-L.; Miao, Z.-F.; Huang, C.-W.; Kuo, C.-H.; Wu, J.-Y.; Wang, W.-M.; Juo, S.-H.H.; Wang, J.-Y. Development of a deregulating microRNA panel for the detection of early relapse in postoperative colorectal cancer patients. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hongliang, C.; Shaojun, H.; Aihua, L.; Hua, J. Correlation between expression of miR-155 in colon cancer and serum carcinoembryonic antigen level and its contribution to recurrence and metastasis forecast. Saudi Med. J. 2014, 35, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, T. Predicting distant metastasis and chemoresistance using plasma miRNAs. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.; Li, K.; Zhu, K.; Yan, R.; Dang, C. Plasma miR-183 predicts recurrence and prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, R.; Nishimura, J.; Kagawa, Y.; Osawa, H.; Hasegawa, J.; Murata, K.; Okamura, S.; Ota, H.; Uemura, M.; Hata, T.; et al. Circulating miR-199a-3p as a novel serum biomarker for colorectal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 32, 2354–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Zhi, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, T.; Ma, Q. Up-regulation of miR-592 correlates with tumor progression and poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2015, 69, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroh, E.M.; Parkin, R.K.; Mitchell, P.S.; Tewari, M. Analysis of circulating microRNA biomarkers in plasma and serum using quantitative reverse transcription-PCR (qRT-PCR). Methods 2010, 50, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hellemans, J.; Mortier, G.; De Paepe, A.; Speleman, F.; Vandesompele, J. qBase relative quantification framework and software for management and automated analysis of real-time quantitative PCR data. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzenbach, H.; da Silva, A.M.; Calin, G.; Pantel, K. Data normalization strategies for MicroRNA quantification. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Treatment | All (n = 85) | Radical (n = 57) | Palliative (n = 28) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marker | 1Preoperative | 1Postoperative | p-Value | 1Preoperative | 1Postoperative | p-Value | 1Preoperative | 1Postoperative | p-Value |
| miR-20a | 0.247 | 0.200 | 0.0093 | 0.261 | 0.155 | 0.0004 | 0.246 | 0.266 | n.s. |
| miR-21 | 1.050 | 1.007 | n.s. | 1.050 | 0.973 | 0.0336 | 1.094 | 1.097 | n.s. |
| miR-23a | 0.705 | 0.379 | 0.0013 | 0.964 | 0.559 | 0.0044 | 0.367 | 0.297 | n.s. |
| miR-29 | 0.005 | 0.005 | n.s. | 0.006 | 0.003 | n.s. | 0.005 | 0.009 | n.s. |
| miR-92a | 23.264 | 19.698 | n.s. | 17.630 | 19.160 | n.s. | 38.288 | 26.715 | n.s. |
| miR-155 | 0.016 | 0.012 | n.s. | 0.017 | 0.011 | 0.0375 | 0.013 | 0.014 | n.s. |
| miR-199a | 0.321 | 0.490 | n.s. | 0.334 | 0.495 | 0.0537 | 0.262 | 0.349 | n.s. |
| miR-210 | 0.024 | 0.021 | 0.0392 | 0.021 | 0.013 | 0.0228 | 0.032 | 0.050 | n.s. |
| miR-223 | 1.275 | 0.555 | 0.0214 | 1.283 | 0.540 | n.s. | 0.747 | 0.600 | n.s. |
| CEA | 3.1 ng/mL | 2.4 ng/mL | <0.0001 | 2.0 ng/mL | 1.1 ng/mL | <0.0001 | 18.5 ng/mL | 6.8 ng/mL | 0.0002 |
| CA19-9 | 11 U/mL | 9 U/mL | 0.0007 | 8 U/mL | 7 U/mL | 0.0117 | 39 U/mL | 34 U/mL | 0.0278 |
| Marker | Recurrence n = 9 | Remission n = 22 | Sensitivity | Specificity | Positive Predictive Value | Negative Predictive Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| True Positive | False Negative | True Negative | False Positive | |||||
| miR-20a | 6 | 3 | 12 | 10 | 66.7% | 54.6% | 37.50% | 80.0% |
| miR-21 | 7 | 2 | 12 | 10 | 77.8% | 54.6% | 41.18% | 85.7% |
| miR-23a | 6 | 3 | 13 | 9 | 66.67% | 59.1% | 40.00% | 81.3% |
| miR-223 | 3 | 6 | 12 | 10 | 33.3% | 54.6% | 23.1% | 66.7% |
| CEA | 3 | 6 | 20 | 2 | 33.3% | 90.9% | 60.0% | 76.9% |
| CA19-9 | 3 | 6 | 21 | 1 | 33.3% | 95.5% | 75.0% | 77.8% |
| Variables | Number of Patients | % |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Patients | 85 | 100 |
| Gender | ||
| Male | 56 | 65.9 |
| Female | 29 | 34.1 |
| Type of Surgery | ||
| Radical | 57 | 67.1 |
| Palliative | 28 | 32.9 |
| Histology | ||
| Adenocarcinoma | 85 | 100 |
| T Stage | ||
| T2 | 10 | 11.8 |
| T3 | 62 | 72.9 |
| T4 | 13 | 15.3 |
| N Stage | ||
| N0 | 28 | 32.9 |
| N1 | 40 | 47.1 |
| N2 | 17 | 20.0 |
| M Stage | ||
| M0 | 56 | 65.9 |
| M1 | 29 | 34.1 |
| Grade | ||
| 1 | 14 | 16.5 |
| 2 | 60 | 70.6 |
| 3 | 11 | 12.9 |
| Clinical Stage | ||
| I | 4 | 4.7 |
| II | 17 | 20.0 |
| III | 35 | 41.2 |
| IV | 29 | 34.1 |
| Symbol | miRBase 22 Accession Number | 5′-3′ sequence | Thermo Fisher Scientific Cat. # A25576 | References 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| hsa-miR-17-3p | MIMAT0000071 | acugcagugaaggcacuuguag | 477932_mir | [43,44] |
| hsa-miR-18a-5p | MIMAT0000072 | uaaggugcaucuagugcagauag | 478551_mir | [45,46] |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | MIMAT0000075 | uaaagugcuuauagugcagguag | 478586_mir | [47] |
| hsa-miR-21-5p | MIMAT0000076 | uagcuuaucagacugauguuga | 477975_mir | [19,47,48,49] |
| hsa-miR-23a-3p | MIMAT0000078 | aucacauugccagggauuucc | 478532_mir | [19,50] |
| hsa-miR-27a-3p | MIMAT0000084 | uucacaguggcuaaguuccgc | 478384_mir | [19] |
| hsa-miR-29a-3p | MIMAT0000086 | uagcaccaucugaaaucgguua | 478587_mir | [43,45] |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | MIMAT0000092 | uauugcacuugucccggccugu | 477827_mir | [46,47,51] |
| hsa-miR-93-5p | MIMAT0000093 | caaagugcuguucgugcagguag | 478210_mir | [47] |
| hsa-miR-96-5p | MIMAT0000095 | uuuggcacuagcacauuuuugcu | 478215_mir | [52] |
| hsa-miR-106a-5p | MIMAT0000103 | aaaagugcuuacagugcagguag | 478225_mir | [44,46] |
| hsa-miR-141-3p | MIMAT0000432 | uaacacugucugguaaagaugg | 478501_mir | [48,52,53] |
| hsa-miR-142-5p | MIMAT0000433 | cauaaaguagaaagcacuacu | 477911_mir | [19] |
| hsa-miR-143-3p | MIMAT0000435 | ugagaugaagcacuguagcuc | 477912_mir | [44,46] |
| hsa-miR-155-5p | MIMAT0000646 | uuaaugcuaaucgugauagggguu | 477927_mir | [54,55] |
| hsa-miR-183-5p | MIMAT0000261 | uauggcacugguagaauucacu | 477937_mir | [56] |
| hsa-miR-199a-3p | MIMAT0000232 | acaguagucugcacauugguua | 477961_mir | [57] |
| hsa-miR-200b-3p | MIMAT0000318 | uaauacugccugguaaugauga | 477963_mir | [52] |
| hsa-miR-200c-3p | MIMAT0000617 | uaauacugccggguaaugaugga | 478351_mir | [52,55] |
| hsa-miR-210-3p | MIMAT0000267 | cugugcgugugacagcggcuga | 477970_mir | [55] |
| hsa-miR-223-3p | MIMAT0000280 | ugucaguuugucaaauacccca | 477983_mir | [19,46,50,51] |
| hsa-miR-592 | MIMAT0003260 | uugugucaauaugcgaugaugu | 479075_mir | [58] |
| cel-miR-39-3p 2 | MIMAT0000010 | ucaccggguguaaaucagcuug | 478293_mir | [21,59] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pesta, M.; Kucera, R.; Topolcan, O.; Karlikova, M.; Houfkova, K.; Polivka, J.; Macanova, T.; Machova, I.; Slouka, D.; Kulda, V. Plasma microRNA Levels Combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the Follow-Up of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2019, 11, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060864
Pesta M, Kucera R, Topolcan O, Karlikova M, Houfkova K, Polivka J, Macanova T, Machova I, Slouka D, Kulda V. Plasma microRNA Levels Combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the Follow-Up of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers. 2019; 11(6):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060864
Chicago/Turabian StylePesta, Martin, Radek Kucera, Ondrej Topolcan, Marie Karlikova, Katerina Houfkova, Jiri Polivka, Tereza Macanova, Iva Machova, David Slouka, and Vlastimil Kulda. 2019. "Plasma microRNA Levels Combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the Follow-Up of Colorectal Cancer Patients" Cancers 11, no. 6: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060864
APA StylePesta, M., Kucera, R., Topolcan, O., Karlikova, M., Houfkova, K., Polivka, J., Macanova, T., Machova, I., Slouka, D., & Kulda, V. (2019). Plasma microRNA Levels Combined with CEA and CA19-9 in the Follow-Up of Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancers, 11(6), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11060864