Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CD47 Expression in MM Patients
2.2. The Effect of Tumor Microenvironment on CD47 Expression in Cell Lines
2.3. Effect of Vx1000R on MM Killing in 2D and 3DTEBM
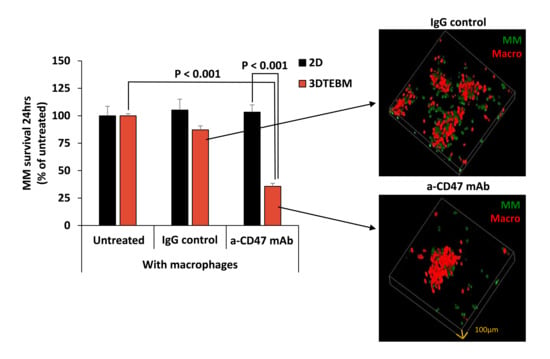
2.4. Effect of Vx1000R on Phagocytosis of MM by Macrophages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.1.1. MM Cell Lines
4.1.2. Mice BM Macrophages (BMMs)
4.2. Gene Expression
4.3. Protein Expression by Flow Cytometry
4.3.1. Protein Expression in MM Primary Patient Cells
4.3.2. Cell Lines
4.4. 3DTEBM Culture
4.5. Cell Survival and Phagocytosis by Flow Cytometry
4.6. Cell Survival and Phagocytosis by Confocal Microscopy
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ludwig, H. Advances in biology and treatment of multiple myeloma. Ann. Oncol. 2005, 16 (Suppl. 2), ii106-112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Puente, P.; Muz, B.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; Azab, A.K. Molecularly targeted therapies in multiple myeloma. Leuk. Res. Treat. 2014, 2014, 976567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Donk, N.W.; Lokhorst, H.M.; Dimopoulos, M.; Cavo, M.; Morgan, G.; Einsele, H.; Kropff, M.; Schey, S.; Avet-Loiseau, H.; Ludwig, H.; et al. Treatment of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma in the era of novel agents. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 266–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Li, Q.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Z.; Liu, S.; Chen, L.; Li, H.; Gao, S.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y.; et al. Immunotherapy Strategies Against Multiple Myeloma. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 16, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pardoll, D.M. The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 252–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, S.P.; Kurzrock, R. PD-L1 Expression as a Predictive Biomarker in Cancer Immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.G.; Xu, N. Immunohistochemical localization of programmed death-1 ligand-1 (PD-L1) in gastric carcinoma and its clinical significance. Acta Histochem. 2006, 108, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, J.; Yamazaki, K.; Azuma, M.; Kinoshita, I.; Dosaka-Akita, H.; Nishimura, M. B7-H1 expression on non-small cell lung cancer cells and its relationship with tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and their PD-1 expression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5094–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leach, D.R.; Krummel, M.F.; Allison, J.P. Enhancement of antitumor immunity by CTLA-4 blockade. Science 1996, 271, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parish, C.R. Cancer immunotherapy: The past, the present and the future. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2003, 81, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesokhin, A.M.; Ansell, S.M.; Armand, P.; Scott, E.C.; Halwani, A.; Gutierrez, M.; Millenson, M.M.; Cohen, A.D.; Schuster, S.J.; Lebovic, D.; et al. Nivolumab in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancy: Preliminary Results of a Phase Ib Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2698–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mateos, M.V.; Blacklock, H.; Schjesvold, F.; Oriol, A.; Simpson, D.; George, A.; Goldschmidt, H.; Larocca, A.; Chanan-Khan, A.; Sherbenou, D.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone for patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (KEYNOTE-183): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2019, 6, e459–e469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, T.A.; Chawla, A.; Pollard, J.W. Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature 2013, 496, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, D.; Iida, T.; Nakase, H. The Phagocytic Function of Macrophage-Enforcing Innate Immunity and Tissue Homeostasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pozzi, L.A.; Maciaszek, J.W.; Rock, K.L. Both dendritic cells and macrophages can stimulate naive CD8 T cells in vivo to proliferate, develop effector function, and differentiate into memory cells. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 2071–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiskopf, K. Cancer immunotherapy targeting the CD47/SIRPalpha axis. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 76, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majeti, R.; Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Pang, W.W.; Jaiswal, S.; Gibbs, K.D., Jr.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is an adverse prognostic factor and therapeutic antibody target on human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Cell 2009, 138, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jaiswal, S.; Jamieson, C.H.; Pang, W.W.; Park, C.Y.; Chao, M.P.; Majeti, R.; Traver, D.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 is upregulated on circulating hematopoietic stem cells and leukemia cells to avoid phagocytosis. Cell 2009, 138, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folkes, A.S.; Feng, M.; Zain, J.M.; Abdulla, F.; Rosen, S.T.; Querfeld, C. Targeting CD47 as a cancer therapeutic strategy: The cutaneous T-cell lymphoma experience. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2018, 30, 332–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willingham, S.B.; Volkmer, J.P.; Gentles, A.J.; Sahoo, D.; Dalerba, P.; Mitra, S.S.; Wang, J.; Contreras-Trujillo, H.; Martin, R.; Cohen, J.D.; et al. The CD47-signal regulatory protein alpha (SIRPa) interaction is a therapeutic target for human solid tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6662–6667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, H.; Shao, R.; Huang, H.; Wang, X.; Rong, Z.; Lin, Y. Engineering macrophages to phagocytose cancer cells by blocking the CD47/SIRPa axis. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4245–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Tang, C.; Myklebust, J.H.; Varghese, B.; Gill, S.; Jan, M.; Cha, A.C.; Chan, C.K.; Tan, B.T.; et al. Anti-CD47 antibody synergizes with rituximab to promote phagocytosis and eradicate non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell 2010, 142, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.; Wang, J.; Willingham, S.B.; Martin, R.; Wernig, G.; Weissman, I.L. Anti-CD47 antibodies promote phagocytosis and inhibit the growth of human myeloma cells. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2538–2545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhan, F.; Huang, Y.; Colla, S.; Stewart, J.P.; Hanamura, I.; Gupta, S.; Epstein, J.; Yaccoby, S.; Sawyer, J.; Burington, B.; et al. The molecular classification of multiple myeloma. Blood 2006, 108, 2020–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Azab, A.K.; Hu, J.; Quang, P.; Azab, F.; Pitsillides, C.; Awwad, R.; Thompson, B.; Maiso, P.; Sun, J.D.; Hart, C.P.; et al. Hypoxia promotes dissemination of multiple myeloma through acquisition of epithelial to mesenchymal transition-like features. Blood 2012, 119, 5782–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; Azab, A.K. Hypoxia promotes stem cell-like phenotype in multiple myeloma cells. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De la Puente, P.; Muz, B.; Gilson, R.C.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.; King, J.; Achilefu, S.; Vij, R.; Azab, A.K. 3D tissue-engineered bone marrow as a novel model to study pathophysiology and drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de la Puente, P.; Quan, N.; Hoo, R.S.; Muz, B.; Gilson, R.C.; Luderer, M.; King, J.; Achilefu, S.; Salama, N.N.; Vij, R.; et al. Newly established myeloma-derived stromal cell line MSP-1 supports multiple myeloma proliferation, migration, and adhesion and induces drug resistance more than normal-derived stroma. Haematologica 2016, 101, e307–e311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodi, F.S.; O’Day, S.J.; McDermott, D.F.; Weber, R.W.; Sosman, J.A.; Haanen, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Hassel, J.C.; et al. Improved survival with ipilimumab in patients with metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 711–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon, E.B.; Rizvi, N.A.; Hui, R.; Leighl, N.; Balmanoukian, A.S.; Eder, J.P.; Patnaik, A.; Aggarwal, C.; Gubens, M.; Horn, L.; et al. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motzer, R.J.; Escudier, B.; McDermott, D.F.; George, S.; Hammers, H.J.; Srinivas, S.; Tykodi, S.S.; Sosman, J.A.; Procopio, G.; Plimack, E.R.; et al. Nivolumab versus Everolimus in Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1803–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.; Retz, M.; Siefker-Radtke, A.; Baron, A.; Necchi, A.; Bedke, J.; Plimack, E.R.; Vaena, D.; Grimm, M.O.; Bracarda, S.; et al. Nivolumab in metastatic urothelial carcinoma after platinum therapy (CheckMate 275): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelle-Rieser, C.; Thangavadivel, S.; Biedermann, R.; Brunner, A.; Stoitzner, P.; Willenbacher, E.; Greil, R.; Johrer, K. T cells in multiple myeloma display features of exhaustion and senescence at the tumor site. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sponaas, A.M.; Moen, S.H.; Liabakk, N.B.; Feyzi, E.; Holien, T.; Kvam, S.; Groseth, L.A.; Stordal, B.; Buene, G.; Espevik, T.; et al. The proportion of CD16(+)CD14(dim) monocytes increases with tumor cell load in bone marrow of patients with multiple myeloma. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2015, 3, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manier, S.; Sacco, A.; Leleu, X.; Ghobrial, I.M.; Roccaro, A.M. Bone marrow microenvironment in multiple myeloma progression. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 157496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muz, B.; de la Puente, P.; Azab, F.; Luderer, M.J.; King, J.; Vij, R.; Azab, A.K. A CD138-independent strategy to detect minimal residual disease and circulating tumour cells in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 173, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rendtlew Danielsen, J.M.; Knudsen, L.M.; Dahl, I.M.; Lodahl, M.; Rasmussen, T. Dysregulation of CD47 and the ligands thrombospondin 1 and 2 in multiple myeloma. Br. J. Haematol. 2007, 138, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusakari, S.; Ohnishi, H.; Jin, F.J.; Kaneko, Y.; Murata, T.; Murata, Y.; Okazawa, H.; Matozaki, T. Trans-endocytosis of CD47 and SHPS-1 and its role in regulation of the CD47-SHPS-1 system. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1213–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hakkinen, K.M.; Harunaga, J.S.; Doyle, A.D.; Yamada, K.M. Direct comparisons of the morphology, migration, cell adhesions, and actin cytoskeleton of fibroblasts in four different three-dimensional extracellular matrices. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 713–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenblatt, J.; Glotzbecker, B.; Mills, H.; Vasir, B.; Tzachanis, D.; Levine, J.D.; Joyce, R.M.; Wellenstein, K.; Keefe, W.; Schickler, M.; et al. PD-1 blockade by CT-011, anti-PD-1 antibody, enhances ex vivo T-cell responses to autologous dendritic cell/myeloma fusion vaccine. J. Immunother. 2011, 34, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorgun, G.; Samur, M.K.; Cowens, K.B.; Paula, S.; Bianchi, G.; Anderson, J.E.; White, R.E.; Singh, A.; Ohguchi, H.; Suzuki, R.; et al. Lenalidomide Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade-Induced Immune Response in Multiple Myeloma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4607–4618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, J.; Muz, B.; Alhallak, K.; Markovic, M.; Gurley, S.; Wang, Z.; Guenthner, N.; Wasden, K.; Fiala, M.; King, J.; et al. Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020305
Sun J, Muz B, Alhallak K, Markovic M, Gurley S, Wang Z, Guenthner N, Wasden K, Fiala M, King J, et al. Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Jennifer, Barbara Muz, Kinan Alhallak, Matea Markovic, Shannon Gurley, Zhe Wang, Nicole Guenthner, Katherine Wasden, Mark Fiala, Justin King, and et al. 2020. "Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma" Cancers 12, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020305
APA StyleSun, J., Muz, B., Alhallak, K., Markovic, M., Gurley, S., Wang, Z., Guenthner, N., Wasden, K., Fiala, M., King, J., Kohnen, D., Salama, N. N., Vij, R., & Azab, A. K. (2020). Targeting CD47 as a Novel Immunotherapy for Multiple Myeloma. Cancers, 12(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020305