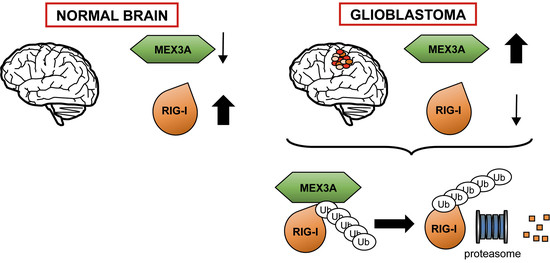
The RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligase MEX3A Affects Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis by Inducing Ubiquitylation and Degradation of RIG-I
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MEX3A Expression is Up-Regulated in GB
2.2. MEX3A Up-Regulation Correlates with Low Protein Levels of RIG-I in GB
2.3. MEX3A Impairs RIG-I Protein Stability
2.4. MEX3A Binds and Ubiquitylates RIG-I
2.5. MEX3A Affects GB Cell Proliferation
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures, Transfections and Lentiviral Infections
4.2. Plasmids, Antibodies and Treatments
4.3. Immunoblot Analysis and Immunoprecipitation
4.4. In Vivo Ubiquitylation Assay
4.5. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.6. mRNA Expression Analysis
- hMEX3A For 5′- ATCGTGGGCAGG CAAGGCT-3′
- hMEX3A Rev 5′- GCTGCTGAGATGATTT CCC-3′
- hRNF122 For 5′- CCAACAAGTCCTGCTCGATG-3′
- hRNF122 Rev 5′- ACTGCGCAGGTCTGCCCATA-3′
- hMEX3C For 5′ –TGAACGGGGAGCAGGCG-3′
- hMEX3C Rev 5′- TGACTTGGACGGTGGTTTGA-3′
- hRIG-I For 5′- TGTGCTCCTACAGGTTGTGGA-3G
- hRIG-I Rev 5I- CACTGGGATCTGATTCGCAAA A-3n
- hGAPDH For 5′- TCCCATCACCATCTTCCAGG-3′
- hGAPDH Rev 5′- ATGAGTCCTTCCACGATACC-3′
- hHPRT For 5′- ATTATGCTGAGGATTTGGAAAGGG-3′
- hHPRT Rev 5′- GCCTCCCATCTCCTTCATCAC-3′
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
4.8. In Vitro Wound Healing Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neurooncology 2017, 19, v1–v88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Polivka, J.; Holubec, L.; Kubikova, T.; Priban, V.; Hes, O.; Pivovarcikova, K.; Treskova, I. Advances in Experimental Targeted Therapy and Immunotherapy for Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Touat, M.; Idbaih, A.; Sanson, M.; Ligon, K.L. Glioblastoma targeted therapy: updated approaches from recent biological insights. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1457–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, C.; Mansouri, S.; Mora, C.; Nassiri, F.; Suppiah, S.; Martino, J.; Zadeh, G.; Fernández-Luna, J.L. Molecular and Clinical Insights into the Invasive Capacity of Glioblastoma Cells. J. Oncol. 2019, 2019, 1740763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Silantyev, A.S.; Falzone, L.; Libra, M.; Gurina, O.I.; Kardashova, K.S.; Nikolouzakis, T.K.; Nosyrev, A.E.; Sutton, C.W.; Mitsias, P.D.; Tsatsakis, A. Current and Future Trends on Diagnosis and Prognosis of Glioblastoma: From Molecular Biology to Proteomics. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zuccarini, M.; Giuliani, P.; Ziberi, S.; Carluccio, M.; Iorio, P.D.; Caciagli, F.; Ciccarelli, R. The Role of Wnt Signal in Glioblastoma Development and Progression: A Possible New Pharmacological Target for the Therapy of This Tumor. Genes 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tompa, M.; Kalovits, F.; Nagy, A.; Kalman, B. Contribution of the Wnt Pathway to Defining Biology of Glioblastoma. Neuromol. Med. 2018, 20, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoni, M.; Burattini, L.; Nabissi, M.; Morelli, M.B.; Berardi, R.; Santoni, G.; Cascinu, S. Essential role of Gli proteins in glioblastoma multiforme. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2013, 14, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, B.K.; Stathias, V.; Maloof, M.E.; Vidovic, D.; Winterbottom, E.F.; Capobianco, A.J.; Clarke, J.; Schurer, S.; Robbins, D.J.; Ayad, N.G. Epigenetic pathways and glioblastoma treatment: insights from signaling cascades. J. Cell Biochem. 2015, 116, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komander, D.; Rape, M. The ubiquitin code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2012, 81, 203–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yau, R.; Rape, M. The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Infante, P.; Lospinoso Severini, L.; Bernardi, F.; Bufalieri, F.; Di Marcotullio, L. Targeting Hedgehog Signalling through the Ubiquitylation Process: The Multiple Roles of the HECT-E3 Ligase Itch. Cells 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Shaik, S.; Dai, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, W. Targeting the ubiquitin pathway for cancer treatment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1855, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Staudt, L.M. Protein ubiquitination in lymphoid malignancies. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 263, 240–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Liang, P.; Ji, W.; Yu, Z.; Chen, H.; Jiang, L. Ubiquitin-specific protease 4 promotes glioblastoma multiforme via activating ERK pathway. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Qi, S.; Yu, S.; Weng, Z.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Xin, Z.; Shi, L.; et al. HERC3-Mediated SMAD7 Ubiquitination Degradation Promotes Autophagy-Induced EMT and Chemoresistance in Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3602–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.; Muzumdar, D.; Shiras, A. Attenuation of Tumor Suppressive Function of FBXO16 Ubiquitin Ligase Activates Wnt Signaling In Glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2019, 21, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvar, B.; Raghuram, V.; Pisitkun, T.; Sarkar, A.; Knepper, M.A. Comprehensive database of human E3 ubiquitin ligases: application to aquaporin-2 regulation. Physiol. Genom. 2016, 48, 502–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buchet-Poyau, K.; Courchet, J.; Le Hir, H.; Séraphin, B.; Scoazec, J.Y.; Duret, L.; Domon-Dell, C.; Freund, J.N.; Billaud, M. Identification and characterization of human Mex-3 proteins, a novel family of evolutionarily conserved RNA-binding proteins differentially localized to processing bodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pereira, B.; Le Borgne, M.; Chartier, N.T.; Billaud, M.; Almeida, R. MEX-3 proteins: recent insights on novel post-transcriptional regulators. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Dong, C.; Xue, J.; Wei, W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Yang, C. Knockdown of hMex-3A by small RNA interference suppresses cell proliferation and migration in human gastric cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pereira, B.; Sousa, S.; Barros, R.; Carreto, L.; Oliveira, P.; Oliveira, C.; Chartier, N.T.; Plateroti, M.; Rouault, J.P.; Freund, J.N.; et al. CDX2 regulation by the RNA-binding protein MEX3A: impact on intestinal differentiation and stemness. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 3986–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Fang, C.; Shi, J.W.; Wen, Y.; Liu, D. Identification of hMex-3A and its effect on human bladder cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61215–61225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chatterji, P.; Rustgi, A.K. RNA Binding Proteins in Intestinal Epithelial Biology and Colorectal Cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 490–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, H.; Deng, L.; Xu, F.; Yu, Z.; Xu, X.; Huang, J.; Zeng, T. MEX3C regulates lipid metabolism to promote bladder tumorigenesis through JNK pathway. Onco. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 3285–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, M.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, W.J.; Su, T.T.; Shi, L.H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Si, J.M.; Wang, L.J.; Chen, S.J. HOTAIR induces the ubiquitination of Runx3 by interacting with Mex3b and enhances the invasion of gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2018, 21, 756–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moududee, S.A.; Jiang, Y.; Gilbert, N.; Xie, G.; Xu, Z.; Wu, J.; Gong, Q.; Tang, Y.; Shi, Y. Structural and functional characterization of hMEX-3C Ring finger domain as an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuniyoshi, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Pandey, S.; Satoh, T.; Iwasaki, H.; Akira, S.; Kawai, T. Pivotal role of RNA-binding E3 ubiquitin ligase MEX3C in RIG-I-mediated antiviral innate immunity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5646–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.X.; Wan, H.; Nie, L.; Shao, T.; Xiang, L.X.; Shao, J.Z. RIG-I: A multifunctional protein beyond a pattern recognition receptor. Protein Cell 2018, 9, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsen, T.A.; Brinchmann, J.E. Liposome delivery of microRNA-145 to mesenchymal stem cells leads to immunological off-target effects mediated by RIG-I. Mol. Ther. 2013, 21, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boelens, M.C.; Wu, T.J.; Nabet, B.Y.; Xu, B.; Qiu, Y.; Yoon, T.; Azzam, D.J.; Twyman-Saint Victor, C.; Wiemann, B.Z.; Ishwaran, H.; et al. Exosome transfer from stromal to breast cancer cells regulates therapy resistance pathways. Cell 2014, 159, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Glas, M.; Coch, C.; Trageser, D.; Dassler, J.; Simon, M.; Koch, P.; Mertens, J.; Quandel, T.; Gorris, R.; Reinartz, R.; et al. Targeting the cytosolic innate immune receptors RIG-I and MDA5 effectively counteracts cancer cell heterogeneity in glioblastoma. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, L.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. The anticancer functions of RIG-I-like receptors, RIG-I and MDA5, and their applications in cancer therapy. Transl. Res. 2017, 190, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, M.; Liu, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, W.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, X. RNF122 suppresses antiviral type I interferon production by targeting RIG-I CARDs to mediate RIG-I degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9581–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anjum, K.; Shagufta, B.I.; Abbas, S.Q.; Patel, S.; Khan, I.; Shah, S.A.A.; Akhter, N.; Hassan, S.S.U. Current status and future therapeutic perspectives of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) therapy: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 92, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messaoudi, K.; Clavreul, A.; Lagarce, F. Toward an effective strategy in glioblastoma treatment. Part I: resistance mechanisms and strategies to overcome resistance of glioblastoma to temozolomide. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blackinton, J.G.; Keene, J.D. Post-transcriptional RNA regulons affecting cell cycle and proliferation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 34, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morris, A.R.; Mukherjee, N.; Keene, J.D. Systematic analysis of posttranscriptional gene expression. Wiley Interdiscip Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2010, 2, 162–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisenberg-Lerner, A.; Ciechanover, A.; Merbl, Y. Post-translational modification profiling - A novel tool for mapping the protein modification landscape in cancer. Exp. Biol Med. (Maywood) 2016, 241, 1475–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lecker, S.H.; Goldberg, A.L.; Mitch, W.E. Protein degradation by the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in normal and disease states. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1807–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, F.M.; Shyu, R.Y.; Jiang, S.Y. RIG1 inhibits the Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by suppressing the activation of Ras. Cell Signal. 2006, 18, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulois, D.; Loo Yau, H.; Singhania, R.; Wang, Y.; Danesh, A.; Shen, S.Y.; Han, H.; Liang, G.; Jones, P.A.; Pugh, T.J.; et al. DNA-Demethylating Agents Target Colorectal Cancer Cells by Inducing Viral Mimicry by Endogenous Transcripts. Cell 2015, 162, 961–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chiappinelli, K.B.; Strissel, P.L.; Desrichard, A.; Li, H.; Henke, C.; Akman, B.; Hein, A.; Rote, N.S.; Cope, L.M.; Snyder, A.; et al. Inhibiting DNA Methylation Causes an Interferon Response in Cancer via dsRNA Including Endogenous Retroviruses. Cell 2015, 162, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oshiumi, H.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T. Ubiquitin-mediated modulation of the cytoplasmic viral RNA sensor RIG-I. J. Biochem. 2012, 151, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Kouwaki, T.; Fukushima, Y.; Oshiumi, H. Regulation of RIG-I Activation by K63-Linked Polyubiquitination. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Xian, H.; Tian, S.; Sun, T.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, S.; Cui, J. A Hierarchical Mechanism of RIG-I Ubiquitination Provides Sensitivity, Robustness and Synergy in Antiviral Immune Responses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Lai, L.; Chong, Z.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Xie, Y.; Chen, S.; Dong, P.; Chen, L.; et al. E3 ligase FBXW7 is critical for RIG-I stabilization during antiviral responses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lipkowitz, S.; Weissman, A.M. RINGs of good and evil: RING finger ubiquitin ligases at the crossroads of tumour suppression and oncogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 629–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, L.; Sun, Y. SCF E3 ubiquitin ligases as anticancer targets. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2011, 11, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Characteristics | Number of Patients (27) |
|---|---|
| Age years | (%) |
| <60 | 44.45 |
| ≥60 | 55.55 |
| Sex | |
| Male | 51.85 |
| Female | 48.15 |
| IDH1 status | |
| Wild Type | 77.77 |
| Mutant | 7.4 |
| n.d. | 14.83 |
| EGFR expression | |
| Not expressed | 22.22 |
| Expressed | 22.22 |
| Highly expressed | 25.92 |
| n.d. | 39.63 |
| p53 expression | |
| Not expressed | 37.03 |
| Very Low Expressed | 7.4 |
| Expressed | 40.74 |
| n.d. * | 14.83 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bufalieri, F.; Caimano, M.; Lospinoso Severini, L.; Basili, I.; Paglia, F.; Sampirisi, L.; Loricchio, E.; Petroni, M.; Canettieri, G.; Santoro, A.; et al. The RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligase MEX3A Affects Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis by Inducing Ubiquitylation and Degradation of RIG-I. Cancers 2020, 12, 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020321
Bufalieri F, Caimano M, Lospinoso Severini L, Basili I, Paglia F, Sampirisi L, Loricchio E, Petroni M, Canettieri G, Santoro A, et al. The RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligase MEX3A Affects Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis by Inducing Ubiquitylation and Degradation of RIG-I. Cancers. 2020; 12(2):321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020321
Chicago/Turabian StyleBufalieri, Francesca, Miriam Caimano, Ludovica Lospinoso Severini, Irene Basili, Francesco Paglia, Luigi Sampirisi, Elena Loricchio, Marialaura Petroni, Gianluca Canettieri, Antonio Santoro, and et al. 2020. "The RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligase MEX3A Affects Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis by Inducing Ubiquitylation and Degradation of RIG-I" Cancers 12, no. 2: 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020321
APA StyleBufalieri, F., Caimano, M., Lospinoso Severini, L., Basili, I., Paglia, F., Sampirisi, L., Loricchio, E., Petroni, M., Canettieri, G., Santoro, A., D’Angelo, L., Infante, P., & Di Marcotullio, L. (2020). The RNA-Binding Ubiquitin Ligase MEX3A Affects Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis by Inducing Ubiquitylation and Degradation of RIG-I. Cancers, 12(2), 321. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020321