Reconstruction of Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics Reveals Characteristics of EWSR1-FLI1 Permissibility
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
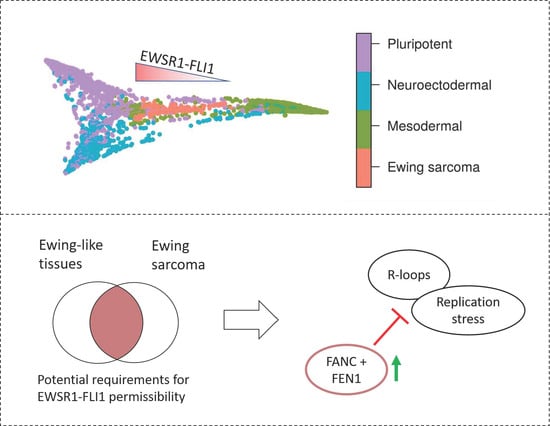
2.1. Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context Reconstructed from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics
2.2. EWSR1-FLI1 Expression Levels Determine Ewing Sarcoma’s PHATE within a Developmental Context
2.3. PHATE_1 Gene Scores Identify Mesenchymal-Like Cellular Subpopulation in Ewing Sarcoma Single Cell Transcriptomes
2.4. Permissible PHATE_1-Low Tissues Show Important Transcriptional Similarities with EWSR1-FLI1 Transcriptome
2.5. The Capability to Resolve R-Loops and Replication Stress are Probable Requirements for Stable EWSR1-FLI1 Expression
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines
4.2. Single Cell RNA-Sequencing (scRNA-Seq) of Ewing Sarcoma Cell Lines
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. RNA:DNA Hybrid Intensity Analysis
4.6. Gene Set Collections Generated and Utilized
4.7. Pre-Processing of Publicly Available Bulk RNA-Seq Data
4.8. PHATE Analysis of Top EWS-Like Clusters
4.9. Processing of Ewing Sarcoma Cell Line and Publicly Available scRNA-Seq Data
4.10. Processing of ssDRIP-Seq Data from Developmental Context Cell Types
4.11. Data and Software Availability
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Delattre, O.; Zucman, J.; Plougastel, B.; Desmaze, C.; Melot, T.; Peter, M.; Kovar, H.; Joubert, I.; De Jong, P.; Rouleau, G.; et al. Gene fusion with an ETS DNA-binding domain caused by chromosome translocation in human tumours. Nature 1992, 359, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, B.I.; Alonso, J.; Carrillo, J.; Acquadro, F.; Largo, C.; Suela, J.; Teixeira, M.R.; Cerveira, N.; Molares, A.; Goméz-López, G.; et al. Array CGH and gene-expression profiling reveals distinct genomic instability patterns associated with DNA repair and cell-cycle checkpoint pathways in Ewing’s sarcoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 2084–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brohl, A.S.; Solomon, D.A.; Chang, W.; Wang, J.; Song, Y.; Sindiri, S.; Patidar, R.; Hurd, L.; Chen, L.; Shern, J.F.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of the Ewing Sarcoma Family of Tumors Reveals Recurrent STAG2 Mutation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lessnick, S.L.; Dacwag, C.S.; Golub, T.R. The Ewing’s sarcoma oncoprotein EWS/FLI induces a p53-dependent growth arrest in primary human fibroblasts. Cancer Cell 2002, 1, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohn, E.J.; Li, H.; Reidy, K.; Beers, L.F.; Christensen, B.L.; Lee, S.B. EWS/FLI1 oncogene activates caspase 3 transcription and triggers apoptosis in vivo. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torres-Ruiz, R.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Martin, M.C.; Garcia, A.; Bueno, C.; Castaño, J.; Ramirez, J.C.; Menendez, P.; Cigudosa, J.C.; Rodriguez-Perales, S. Efficient Recreation of t(11;22) EWSR1-FLI1+ in Human Stem Cells Using CRISPR/Cas9. Stem Cell Reports 2017, 8, 1408–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minas, T.Z.; Surdez, D.; Javaheri, T.; Tanaka, M.; Howarth, M.; Kang, H.J.; Han, J.; Han, Z.Y.; Sax, B.; Kream, B.E.; et al. Combined experience of six independent laboratories attempting to create an Ewing sarcoma mouse model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 34141–34163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lachmann, A.; Torre, D.; Keenan, A.B.; Jagodnik, K.M.; Lee, H.J.; Wang, L.; Silverstein, M.C.; Ma’ayan, A. Massive mining of publicly available RNA-seq data from human and mouse. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, K.R.; Stanley, J.S.; Burkhardt, D.; van Dijk, D.v.; Wolf, G.; Krishnaswamy, S. Manifold learning-based methods for analyzing single-cell RNA-sequencing data. Curr. Opin. Syst. Biol. 2018, 7, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, L.; Healy, J.; Saul, N.; Großberger, L. UMAP: Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondel, V.D.; Guillaume, J.L.; Lambiotte, R.; Lefebvre, E. Fast unfolding of communities in large networks. J. Stat. Mech. Theory Exp. 2008, 2008, P10008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moon, K.R.; van Dijk, D.; Wang, Z.; Gigante, S.; Burkhardt, D.B.; Chen, W.S.; Yim, K.; van den Elzen, A.; Hirn, M.J.; Coifman, R.R.; et al. Visualizing structure and transitions in high-dimensional biological data. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1482–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; Suvà, D.; Cironi, L.; Provero, P.; Tercier, S.; Joseph, J.M.; Stehle, J.C.; Baumer, K.; Kindler, V.; et al. EWS-FLI-1 expression triggers a ewing’s sarcoma initiation program in primary human mesenchymal stem cells. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2176–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aynaud, M.M.; Mirabeau, O.; Gruel, N.; Grossetête, S.; Boeva, V.; Durand, S.; Surdez, D.; Saulnier, O.; Zaïdi, S.; Gribkova, S.; et al. Transcriptional Programs Define Intratumoral Heterogeneity of Ewing Sarcoma at Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Howarth, M.M.; Simpson, D.; Ngok, S.P.; Nieves, B.; Chen, R.; Siprashvili, Z.; Vaka, D.; Breese, M.R.; Crompton, B.D.; Alexe, G.; et al. Long noncoding RNA EWSAT1-mediated gene repression facilitates Ewing sarcoma oncogenesis. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 5275–5290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liberzon, A.; Subramanian, A.; Pinchback, R.; Thorvaldsdóttir, H.; Tamayo, P.; Mesirov, J.P. Molecular signatures database (MSigDB) 3.0. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1739–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, S.; Theisen, E.R.; Bearss, J.; Mulvihill, T.; Hoffman, L.M.; Sorna, V.; Beckerle, M.C.; Sharma, S.; Lessnick, S.L. Reversible LSD1 inhibition interferes with global EWS/ETS transcriptional activity and impedes Ewing sarcoma tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 4584–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katschnig, A.M.; Kauer, M.O.; Schwentner, R.; Tomazou, E.M.; Mutz, C.N.; Linder, M.; Sibilia, M.; Alonso, J.; Aryee, D.N.T.; Kovar, H. EWS-FLI1 perturbs MRTFB/YAP-1/TEAD target gene regulation inhibiting cytoskeletal autoregulatory feedback in Ewing sarcoma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5995–6005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franzetti, G.A.; Laud-Duval, K.; Van Der Ent, W.; Brisac, A.; Irondelle, M.; Aubert, S.; Dirksen, U.; Bouvier, C.; De Pinieux, G.; Snaar-Jagalska, E.; et al. Cell-to-cell heterogeneity of EWSR1-FLI1 activity determines proliferation/migration choices in Ewing sarcoma cells. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3505–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- von Levetzow, C.; Jiang, X.; Gwye, Y.; von Levetzow, G.; Hung, L.; Cooper, A.; Hsu, J.H.R.; Lawlor, E.R. Modeling initiation of ewing sarcoma in human neural crest cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gordon, D.J.; Motwani, M.; Pellman, D. Modeling the initiation of Ewing sarcoma tumorigenesis in differentiating human embryonic stem cells. Oncogene 2016, 35, 3092–30102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovar, H.; Amatruda, J.; Brunet, E.; Burdach, S.; Cidre-Aranaz, F.; De Alava, E.; Dirksen, U.; Van Der Ent, W.; Grohar, P.; Grünewald, T.G.P.; et al. The second European interdisciplinary Ewing sarcoma research summit—A joint effort to deconstructing the multiple layers of a complex disease. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8613–8624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gorthi, A.; Romero, J.C.; Loranc, E.; Cao, L.; Lawrence, L.A.; Goodale, E.; Iniguez, A.B.; Bernard, X.; Masamsetti, V.P.; Roston, S.; et al. EWS-FLI1 increases transcription to cause R-Loops and block BRCA1 repair in Ewing sarcoma. Nature 2018, 555, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percharde, M.; Bulut-Karslioglu, A.; Ramalho-Santos, M. Hypertranscription in Development, Stem Cells, and Regeneration. Dev. Cell 2017, 40, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, X.; Eastman, A.E.; Guo, S. Cell cycle dynamics in the reprogramming of cellular identity. FEBS Lett. 2019, 593, 2840–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babos, K.N.; Galloway, K.E.; Kisler, K.; Zitting, M.; Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Quintino, B.; Chow, R.H.; Zlokovic, B.V.; Ichida, J.K. Mitigating Antagonism between Transcription and Proliferation Allows Near-Deterministic Cellular Reprogramming. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zatreanu, D.; Han, Z.; Mitter, R.; Tumini, E.; Williams, H.; Gregersen, L.; Dirac-Svejstrup, A.B.; Roma, S.; Stewart, A.; Aguilera, A.; et al. Elongation Factor TFIIS Prevents Transcription Stress and R-Loop Accumulation to Maintain Genome Stability. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nieto-Soler, M.; Morgado-Palacin, I.; Lafarga, V.; Lecona, E.; Murga, M.; Callen, E.; Azorin, D.; Alonso, J.; Lopez-Contreras, A.J.; Nussenzweig, A.; et al. Efficacy of ATR inhibitors as single agents in Ewing sarcoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 58759–58767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- García-Rubio, M.L.; Pérez-Calero, C.; Barroso, S.I.; Tumini, E.; Herrera-Moyano, E.; Rosado, I.V.; Aguilera, A. The Fanconi Anemia Pathway Protects Genome Integrity from R-loops. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teasley, D.C.; Parajuli, S.; Nguyen, M.; Moore, H.R.; Alspach, E.; Lock, Y.J.; Honaker, Y.; Saharia, A.; Piwnica-Worms, H.; Stewart, S.A. Flap endonuclease 1 limits telomere fragility on the leading strand. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 15133–15145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kazak, L.; Reyes, A.; He, J.; Wood, S.R.; Brea-Calvo, G.; Holen, T.T.; Holt, I.J. A Cryptic Targeting Signal Creates a Mitochondrial FEN1 Isoform with Tailed R-Loop Binding Properties. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tantyo, N.A.; Karyadi, A.S.; Rasman, S.Z.; Salim, M.R.G.; Devina, A.; Sumarpo, A. The prognostic value of S100A10 expression in cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, S.A.; Brekken, R.A. SPARC: A matricellular regulator of tumorigenesis. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 3, 255–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- González-Cruz, R.D.; Dahl, K.N.; Darling, E.M. The emerging role of Lamin C as an important LMNA isoform in mechanophenotype. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riggi, N.; Suvà, M.L.; De Vito, C.; Provero, P.; Stehle, J.C.; Baumer, K.; Cironi, L.; Janiszewska, M.; Petricevic, T.; Suvà, D.; et al. EWS-FLI-1 modulates miRNA145 and SOX2 expression to initiate mesenchymal stem cell reprogramming toward Ewing sarcoma cancer stem cells. Genes Dev. 2010, 24, 916–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crossley, M.P.; Bocek, M.; Cimprich, K.A. R-Loops as Cellular Regulators and Genomic Threats. Mol. Cell 2019, 73, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gadaleta, M.C.; Noguchi, E. Regulation of DNA replication through natural impediments in the eukaryotic genome. Genes (Basel). 2017, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parajuli, S.; Teasley, D.C.; Murali, B.; Jackson, J.; Vindigni, A.; Stewart, S.A. Human ribonuclease H1 resolves R-loops and thereby enables progression of the DNA replication fork. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 15216–15224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DepMap. The Cancer Dependency Map Consortium. Available online: https://depmap.org/portal/depmap/ (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Riggi, N.; Knoechel, B.; Gillespie, S.M.; Rheinbay, E.; Boulay, G.; Suvà, M.L.; Rossetti, N.E.; Boonseng, W.E.; Oksuz, O.; Cook, E.B.; et al. EWS-FLI1Utilizes Divergent Chromatin Remodeling Mechanisms to Directly Activate or Repress Enhancer Elements in Ewing Sarcoma. Cancer Cell 2014, 26, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rorie, C.J.; Thomas, V.D.; Chen, P.; Pierce, H.H.; O’Bryan, J.P.; Weissman, B.E. The Ews/Fli-1 Fusion Gene Switches the Differentiation Program of Neuroblastomas to Ewing Sarcoma/Peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumors. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 1266–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torchia, E.C.; Boyd, K.; Rehg, J.E.; Qu, C.; Baker, S.J. EWS/FLI-1 Induces Rapid Onset of Myeloid/Erythroid Leukemia in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 7918–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stuart, T.; Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Hafemeister, C.; Papalexi, E.; Mauck, W.M.; Hao, Y.; Stoeckius, M.; Smibert, P.; Satija, R. Comprehensive Integration of Single-Cell Data. Cell 2019, 177, 1888–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R, 3.6.2; R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Core Team. Available online: https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 8 April 2020).








© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miller, H.E.; Gorthi, A.; Bassani, N.; Lawrence, L.A.; Iskra, B.S.; Bishop, A.J.R. Reconstruction of Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics Reveals Characteristics of EWSR1-FLI1 Permissibility. Cancers 2020, 12, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040948
Miller HE, Gorthi A, Bassani N, Lawrence LA, Iskra BS, Bishop AJR. Reconstruction of Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics Reveals Characteristics of EWSR1-FLI1 Permissibility. Cancers. 2020; 12(4):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040948
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiller, Henry E., Aparna Gorthi, Nicklas Bassani, Liesl A. Lawrence, Brian S. Iskra, and Alexander J. R. Bishop. 2020. "Reconstruction of Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics Reveals Characteristics of EWSR1-FLI1 Permissibility" Cancers 12, no. 4: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040948
APA StyleMiller, H. E., Gorthi, A., Bassani, N., Lawrence, L. A., Iskra, B. S., & Bishop, A. J. R. (2020). Reconstruction of Ewing Sarcoma Developmental Context from Mass-Scale Transcriptomics Reveals Characteristics of EWSR1-FLI1 Permissibility. Cancers, 12(4), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040948